当前位置:网站首页>Hands on data analysis unit 3 model building and evaluation
Hands on data analysis unit 3 model building and evaluation
2022-06-26 13:50:00 【Cangye 2021】
hands-on-data-analysis Unit three Model building and evaluation
List of articles
1. Model structures,
1.1. Import related libraries
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
# matplotlib.pyplot and seaborn It's a drawing library
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
from IPython.display import Image
# Embedded display picture
%matplotlib inline
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei'] # Used to display Chinese labels normally
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False # Used to display negative sign normally
plt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = (10, 6) # Set output picture size
1.2. Loading of data sets
# Read the original data set
train = pd.read_csv('train.csv')
train.shape
Output is :
(891, 12)
1.3. Dataset analysis
train.head()
Output is :
| PassengerId | Survived | Pclass | Name | Sex | Age | SibSp | Parch | Ticket | Fare | Cabin | Embarked | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 3 | Braund, Mr. Owen Harris | male | 22.0 | 1 | 0 | A/5 21171 | 7.2500 | NaN | S |
| 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | Cumings, Mrs. John Bradley (Florence Briggs Th… | female | 38.0 | 1 | 0 | PC 17599 | 71.2833 | C85 | C |
| 2 | 3 | 1 | 3 | Heikkinen, Miss. Laina | female | 26.0 | 0 | 0 | STON/O2. 3101282 | 7.9250 | NaN | S |
| 3 | 4 | 1 | 1 | Futrelle, Mrs. Jacques Heath (Lily May Peel) | female | 35.0 | 1 | 0 | 113803 | 53.1000 | C123 | S |
| 4 | 5 | 0 | 3 | Allen, Mr. William Henry | male | 35.0 | 0 | 0 | 373450 | 8.0500 | NaN | S |
train.info()
<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
RangeIndex: 891 entries, 0 to 890
Data columns (total 12 columns):
# Column Non-Null Count Dtype
--- ------ -------------- -----
0 PassengerId 891 non-null int64
1 Survived 891 non-null int64
2 Pclass 891 non-null int64
3 Name 891 non-null object
4 Sex 891 non-null object
5 Age 714 non-null float64
6 SibSp 891 non-null int64
7 Parch 891 non-null int64
8 Ticket 891 non-null object
9 Fare 891 non-null float64
10 Cabin 204 non-null object
11 Embarked 889 non-null object
dtypes: float64(2), int64(5), object(5)
memory usage: 83.7+ KB
You can see that these data still need to be cleaned , The cleaned data sets are as follows :
# Read the cleaned data set
data = pd.read_csv('clear_data.csv')
data.head()
| PassengerId | Pclass | Age | SibSp | Parch | Fare | Sex_female | Sex_male | Embarked_C | Embarked_Q | Embarked_S | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 3 | 22.0 | 1 | 0 | 7.2500 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 38.0 | 1 | 0 | 71.2833 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 2 | 2 | 3 | 26.0 | 0 | 0 | 7.9250 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 3 | 3 | 1 | 35.0 | 1 | 0 | 53.1000 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 4 | 4 | 3 | 35.0 | 0 | 0 | 8.0500 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
data.info()
Output is :
<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
RangeIndex: 891 entries, 0 to 890
Data columns (total 11 columns):
# Column Non-Null Count Dtype
--- ------ -------------- -----
0 PassengerId 891 non-null int64
1 Pclass 891 non-null int64
2 Age 891 non-null float64
3 SibSp 891 non-null int64
4 Parch 891 non-null int64
5 Fare 891 non-null float64
6 Sex_female 891 non-null int64
7 Sex_male 891 non-null int64
8 Embarked_C 891 non-null int64
9 Embarked_Q 891 non-null int64
10 Embarked_S 891 non-null int64
dtypes: float64(2), int64(9)
memory usage: 76.7 KB
1.4. Model structures,
sklearn The algorithm chooses the path
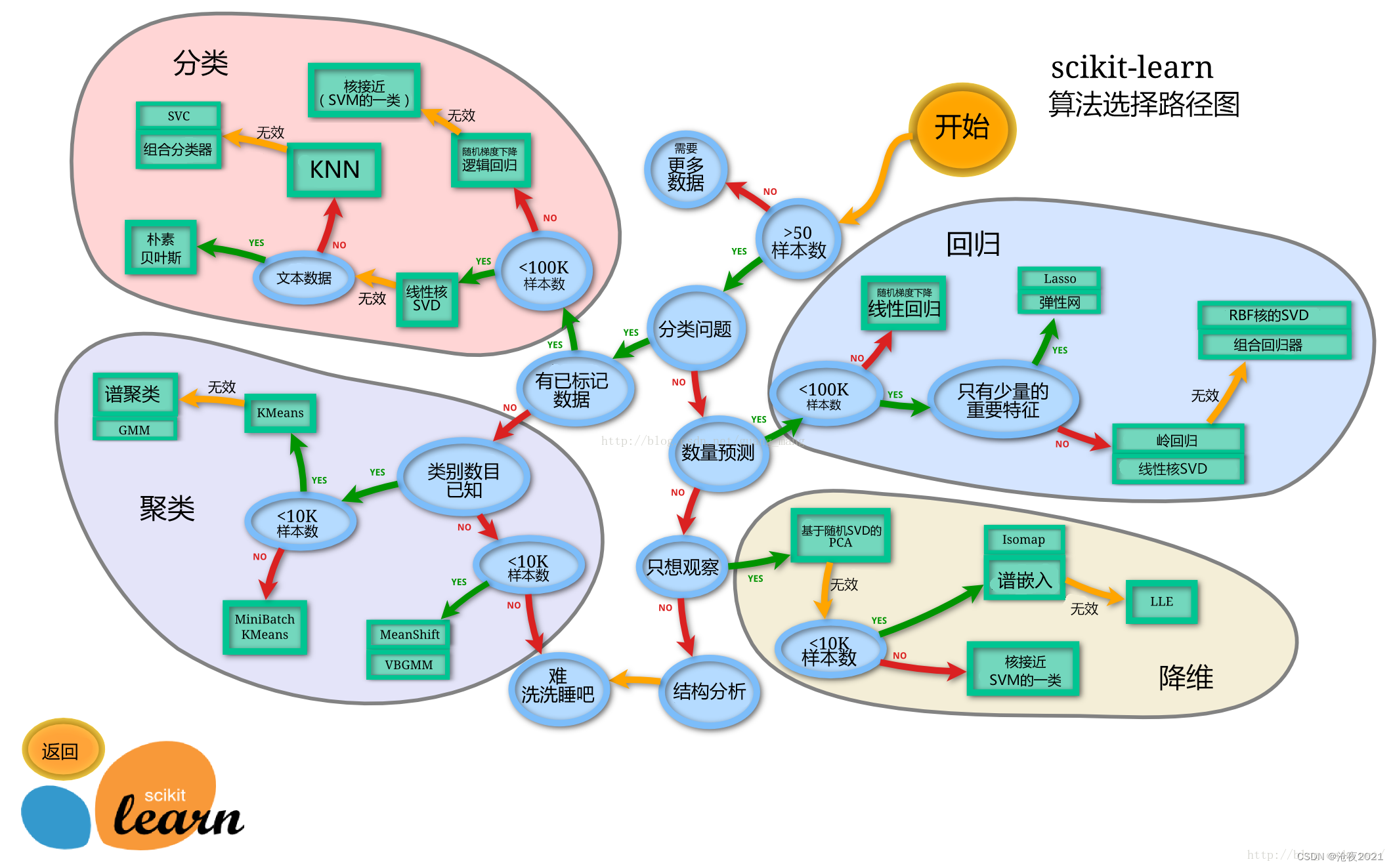
Split the dataset
# train_test_split Is a function used to cut data sets
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
# Usually take it out first X and y Then cut , In some cases, uncut... Will be used , Now X and y You can use it ,x It's cleaned data ,y Is the survival data we want to predict 'Survived'
X = data
y = train['Survived']
# Cut the dataset
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, stratify=y, random_state=0)
# View data shapes
X_train.shape, X_test.shape
Output is :
((668, 11), (223, 11))
X_train.info()
Output is :
<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
Int64Index: 668 entries, 671 to 80
Data columns (total 11 columns):
# Column Non-Null Count Dtype
--- ------ -------------- -----
0 PassengerId 668 non-null int64
1 Pclass 668 non-null int64
2 Age 668 non-null float64
3 SibSp 668 non-null int64
4 Parch 668 non-null int64
5 Fare 668 non-null float64
6 Sex_female 668 non-null int64
7 Sex_male 668 non-null int64
8 Embarked_C 668 non-null int64
9 Embarked_Q 668 non-null int64
10 Embarked_S 668 non-null int64
dtypes: float64(2), int64(9)
memory usage: 82.6 KB
X_test.info()
Output is :
<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
Int64Index: 223 entries, 288 to 633
Data columns (total 11 columns):
# Column Non-Null Count Dtype
--- ------ -------------- -----
0 PassengerId 223 non-null int64
1 Pclass 223 non-null int64
2 Age 223 non-null float64
3 SibSp 223 non-null int64
4 Parch 223 non-null int64
5 Fare 223 non-null float64
6 Sex_female 223 non-null int64
7 Sex_male 223 non-null int64
8 Embarked_C 223 non-null int64
9 Embarked_Q 223 non-null int64
10 Embarked_S 223 non-null int64
dtypes: float64(2), int64(9)
memory usage: 30.9 KB
1.5. Import model
1.5.1. Logistic regression model with default parameters
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
lr = LogisticRegression()
lr.fit(X_train, y_train)
Output is :
LogisticRegression(C=1.0, class_weight=None, dual=False, fit_intercept=True,
intercept_scaling=1, l1_ratio=None, max_iter=100,
multi_class='auto', n_jobs=None, penalty='l2',
random_state=None, solver='lbfgs', tol=0.0001, verbose=0,
warm_start=False)
# View training sets and test sets score value
print("Training set score: {:.2f}".format(lr.score(X_train, y_train)))
print("Testing set score: {:.2f}".format(lr.score(X_test, y_test)))
Training set score: 0.80
Testing set score: 0.79
1.5.2. A logistic regression model for adjusting parameters
lr2 = LogisticRegression(C=100)
lr2.fit(X_train, y_train)
Output is :
LogisticRegression(C=100, class_weight=None, dual=False, fit_intercept=True,
intercept_scaling=1, l1_ratio=None, max_iter=100,
multi_class='auto', n_jobs=None, penalty='l2',
random_state=None, solver='lbfgs', tol=0.0001, verbose=0,
warm_start=False)
print("Training set score: {:.2f}".format(lr2.score(X_train, y_train)))
print("Testing set score: {:.2f}".format(lr2.score(X_test, y_test)))
Output is :
Training set score: 0.79
Testing set score: 0.78
1.5.3. Random forest classification model with default parameters
rfc = RandomForestClassifier()
rfc.fit(X_train, y_train)
Output is :
RandomForestClassifier(bootstrap=True, ccp_alpha=0.0, class_weight=None,
criterion='gini', max_depth=None, max_features='auto',
max_leaf_nodes=None, max_samples=None,
min_impurity_decrease=0.0, min_impurity_split=None,
min_samples_leaf=1, min_samples_split=2,
min_weight_fraction_leaf=0.0, n_estimators=100,
n_jobs=None, oob_score=False, random_state=None,
verbose=0, warm_start=False)
print("Training set score: {:.2f}".format(rfc.score(X_train, y_train)))
print("Testing set score: {:.2f}".format(rfc.score(X_test, y_test)))
Output is :
Training set score: 1.00
Testing set score: 0.82
1.5.4. A stochastic forest classification model with adjusted parameters
rfc2 = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=100, max_depth=5)
rfc2.fit(X_train, y_train)
Output is :
RandomForestClassifier(bootstrap=True, ccp_alpha=0.0, class_weight=None,
criterion='gini', max_depth=5, max_features='auto',
max_leaf_nodes=None, max_samples=None,
min_impurity_decrease=0.0, min_impurity_split=None,
min_samples_leaf=1, min_samples_split=2,
min_weight_fraction_leaf=0.0, n_estimators=100,
n_jobs=None, oob_score=False, random_state=None,
verbose=0, warm_start=False)
print("Training set score: {:.2f}".format(rfc2.score(X_train, y_train)))
print("Testing set score: {:.2f}".format(rfc2.score(X_test, y_test)))
Output is :
Training set score: 0.87
Testing set score: 0.81
1.6. prediction model
General supervisory model in sklearn There's a predict Can output prediction labels ,predict_proba Label probability can be output
# Forecast tags
pred = lr.predict(X_train)
# Now we can see 0 and 1 Array of
pred[:10]
Output is :
array([0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1])
# Predicted tag probability
pred_proba = lr.predict_proba(X_train)
pred_proba[:10]
Output is :
array([[0.60884602, 0.39115398],
[0.17563455, 0.82436545],
[0.40454114, 0.59545886],
[0.1884778 , 0.8115222 ],
[0.88013064, 0.11986936],
[0.91411123, 0.08588877],
[0.13260197, 0.86739803],
[0.90571178, 0.09428822],
[0.05273217, 0.94726783],
[0.10924951, 0.89075049]])
2. Model to evaluate
2.1. Cross validation
There are many kinds of cross validation , The first is the simplest , It's easy to think of : Divide the data set into two parts , Is a training set (training set), One is the test set (test set).
however , There are two drawbacks to this simple approach .
1. The final model and parameter selection will largely depend on how you divide the training set and test set .
2. This method only uses part of the data to train the model , Failure to take full advantage of the data in the dataset .
To solve this problem , The following technicians have carried out a variety of optimizations , The next step is K Crossover verification :
We will no longer have only one data per test set , It's more than one. , The specific number will be based on K The choice of . such as , If K=5, So the steps we take to cross verify with a 30% discount are :
1. Divide all data sets into 7 Share
2. Do not repeatedly take one of them at a time as a test set , Use other 6 Make a training set training model , And then calculate the MSE
3. take 7 Take the average of times to get the final MSE

from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score
lr = LogisticRegression(C=100)
scores = cross_val_score(lr, X_train, y_train, cv=10)
# k Fold cross validation score
scores
Output :
array([0.82089552, 0.74626866, 0.74626866, 0.7761194 , 0.88059701,
0.8358209 , 0.76119403, 0.8358209 , 0.74242424, 0.75757576])
# Average cross validation score
print("Average cross-validation score: {:.2f}".format(scores.mean()))
Output :
Average cross-validation score: 0.79
2.2. Confusion matrix
Confusion matrix is used to summarize the results of a classifier . about k Metaclassification , In fact, it is a k x k Table for , Used to record the prediction results of the classifier .

The method of confusion matrix is sklearn Medium sklearn.metrics modular
The confusion matrix needs to input the real label and prediction label
Accuracy 、 Recall rate and f- Scores can be used classification_report modular
In fact, the quality of the model , Just look at the main diagonal of the confusion matrix .
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix
# Training models
lr = LogisticRegression(C=100)
lr.fit(X_train, y_train)
LogisticRegression(C=100, class_weight=None, dual=False, fit_intercept=True,
intercept_scaling=1, l1_ratio=None, max_iter=100,
multi_class='auto', n_jobs=None, penalty='l2',
random_state=None, solver='lbfgs', tol=0.0001, verbose=0,
warm_start=False)
# Model predictions
pred = lr.predict(X_train)
# Confusion matrix
confusion_matrix(y_train, pred)
array([[354, 58],
[ 83, 173]])
# Classified reports
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report
# Accuracy 、 Recall rate and f1-score
print(classification_report(y_train, pred))
precision recall f1-score support
0 0.81 0.86 0.83 412
1 0.75 0.68 0.71 256
accuracy 0.79 668
macro avg 0.78 0.77 0.77 668
weighted avg 0.79 0.79 0.79 668
2.3.ROC curve
ROC The curve originated from the judgment of radar signal by radar soldiers during World War II . At that time, the task of every radar soldier was to analyze the radar signal , But the radar technology was not so advanced at that time , There is a lot of noise , So whenever a signal appears on the radar screen , Radar soldiers need to decipher it . Some radar soldiers are more cautious , Whenever there is a signal , He tends to interpret it as an enemy bomber , Some radar soldiers are more nervous , It tends to be interpreted as a bird . In this case, a set of evaluation indicators is urgently needed to help him summarize the prediction information of each radar soldier and evaluate the reliability of this radar . therefore , One of the earliest ROC The curve analysis method was born . After that ,ROC Curve is widely used in medicine and machine learning .
ROC The full name is Receiver Operating Characteristic Curve, The Chinese name is 【 The working characteristic curve of subjects 】
ROC The curve is in sklearn The module in is sklearn.metrics
ROC The larger the area surrounded by the curve, the better
from sklearn.metrics import roc_curve
fpr, tpr, thresholds = roc_curve(y_test, lr.decision_function(X_test))
plt.plot(fpr, tpr, label="ROC Curve")
plt.xlabel("FPR")
plt.ylabel("TPR (recall)")
# Find the closest to 0 The threshold of
close_zero = np.argmin(np.abs(thresholds))
plt.plot(fpr[close_zero], tpr[close_zero], 'o', markersize=10, label="threshold zero", fillstyle="none", c='k', mew=2)
plt.legend(loc=4)

3. Reference material
【 machine learning 】Cross-Validation( Cross validation ) Detailed explanation - You know (zhihu.com)
边栏推荐
- MySQL explanation (II)
- Sed editor
- Wechat applet - bind and prevent event bubble catch
- hands-on-data-analysis 第三单元 模型搭建和评估
- [MySQL from introduction to mastery] [advanced part] (II) representation of MySQL directory structure and tables in the file system
- Bigint: handles large numbers (integers of any length)
- 虫子 类和对象 上
- PHP非对称加密算法(RSA)加密机制设计
- Included angle of 3D vector
- [path of system analyst] Chapter 15 double disk database system (database case analysis)
猜你喜欢

shell脚本详细介绍(四)

计算两点之间的距离(二维、三维)

There are many contents in the widget, so it is a good scheme to support scrolling

李航老师新作《机器学习方法》上市了!附购买链接

33、使用RGBD相机进行目标检测和深度信息输出

Ring queue PHP

LAMP编译安装

【Spark】. Explanation of several icons of scala file in idea

Es sauvegarde et restauration des données par instantané

Use performance to see what the browser is doing
随机推荐
虫子 运算符重载的一个好玩的
微信小程序注册指引
[how to connect the network] Chapter 2 (Part 1): establish a connection, transmit data, and disconnect
sed编辑器
KITTI Detection dataset whose format is letf_ top_ right_ bottom to JDE normalied xc_ yc_ w_ h
虫子 STL string 下 练习题
Mediapipe gestures (hands)
Go language - pipeline channel
Nlp-d60-nlp competition D29
Detailed sorting of HW blue team traceability process
CVPR 2022文档图像分析与识别相关论文26篇汇集简介
d检查类型是指针
输入文本自动生成图像,太好玩了!
虫子 内存管理 下 内存注意点
7-2 picking peanuts
Use of wangeditor rich text editor
Generate JDE dot train
7-3 minimum toll
d的is表达式
使用 Performance 看看浏览器在做什么