当前位置:网站首页>Develop scalable contracts based on hardhat and openzeppelin (II)
Develop scalable contracts based on hardhat and openzeppelin (II)
2022-07-02 11:35:00 【Ni xiansen_】
be based on Hardhat and Openzeppelin Develop scalable contracts ( Two )
In this chapter, I will begin to introduce and demonstrate be based on Openzeppelin Scalable contract solution
brief introduction
According to design , Smart contracts are immutable . But with the new customer requirements and the upgrading and iteration of product design , The contract also needs to be upgraded .
Openzeppelin The basic scalable contract solution is to separate contract data from logic .
- Agency contract (Proxy) Responsible for forwarding transactions to logical contracts , And save Contract data
- Logical contract (Logic) Responsible for implementing functional logic
Upgrade time , Just redeploy the new version of the logical contract , And the agency contract Logical contract instance Point to New version of logical contract instance that will do
The principle of scalable contracts -DelegateCall
Third party Library
- Hardhat About Hardhat Installation and introduction of , Refer to another article of mine << Introduce the smart contract development framework -Hardhat>>
- Upgrades Plugins
install openzeppelin library
# Install scaffolding tools
* npm install --save-dev @openzeppelin/hardhat-upgrades
# install openzepplein Scalable contract Library , We will quote the contract documents here when developing the contract
* npm install @openzeppelin/contracts-upgradeable
code
Modify the contract documents
be based on Last chapter Modify the items in , So here is the modification MyContract.sol Contract documents
Initialization function transformation
Here we need to quote Openzeppelin Scalable contract Library @openzeppelin/contracts-upgradeable
// SPDX-License-Identifier: UNLICENSED
pragma solidity ^0.8.0;
// quote @openzeppelin/contracts-upgradeable Scalable contract Library
import "@openzeppelin/contracts-upgradeable/proxy/utils/Initializable.sol";
// Our contract needs to be inherited Initializable
contract MyContract is Initializable {
int storageValue;
// modifier( Decorators ) initializer To ensure that initialize Will only be called once
function initialize(int initValue) public initializer {
storageValue = initValue;
}
function setValue(int newValue) public {
storageValue = newValue + 1;
}
function getValue() public view returns (int) {
return storageValue;
}
}
Here we have done two things :
- Introduce scalable contract Library
- Transform initialization function
What needs to be highlighted is , In scalable contracts , The constructor of the contract cannot be used constructor()
《 be based on Openzeppelin Considerations for scalable contract solutions 》
compile
If you just follow the first chapter , Please press twice Ctrl + C Exit the console and enter the compile command to compile
# compile
* npx hardhat compile
Compiled 3 Solidity files successfully
# Prompt successful compilation 3 individual solidity file , because MyContract The inherited parent contract should also be compiled
# Because we inherited Initializable, as well as Initializable Inherited from AddressUpgradeable
Here the compiler passes , Let's move on to the next step Deployment and interaction testing
Deployment and debugging
Modify and register the upgradeable plug-in
modify hardhat.config.js file , add to @openzeppelin/hardhat-upgrades References to
require("@nomiclabs/hardhat-waffle");
require('@openzeppelin/hardhat-upgrades');
Modify deployment script file
Or modify deploy.js Script files
// quote Upgradeable plug-ins
const {
ethers, upgrades } = require("hardhat");
async function main() {
// obtain MyContract contract
const MyContract = await ethers.getContractFactory("MyContract");
// Deploy , Incoming initialization storageValue Value
const myContract = await upgrades.deployProxy(
MyContract, // Contracts to deploy
[666], // Initialize parameters
{
initializer: 'initialize' } // Specify the initialization function name
);
// wait for MyContract Contract deployment completed
await myContract.deployed();
// Output MyContract Contract address
console.log("MyContract deployed to:", myContract.address);
}
// We recommend this pattern to be able to use async/await everywhere
// and properly handle errors.
main()
.then(() => process.exit(0))
.catch((error) => {
console.error(error);
process.exit(1);
});
Deploy
We still deploy to the local node , Make sure that the local node is started , If there is no input npx hardhat node Command to start , And open a new console program to operate and deploy
Here are the deployment commands
* npx hardhat run --network localhost scripts/deploy.js
MyContract deployed to: 0xDc64a140Aa3E981100a9becA4E685f962f0cF6C9
Contract deployment succeeded !
But here we only got an address 0xDc64a140Aa3E981100a9becA4E685f962f0cF6C9, But as we said before, scalable contracts include logical contracts and agency contracts , Why is there only one contract address here ?
Now let's decrypt
Real contract address
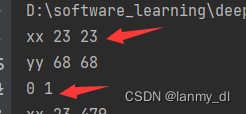
Open the project directory and find .openzeppelin In the catalog unknown-31337.json file 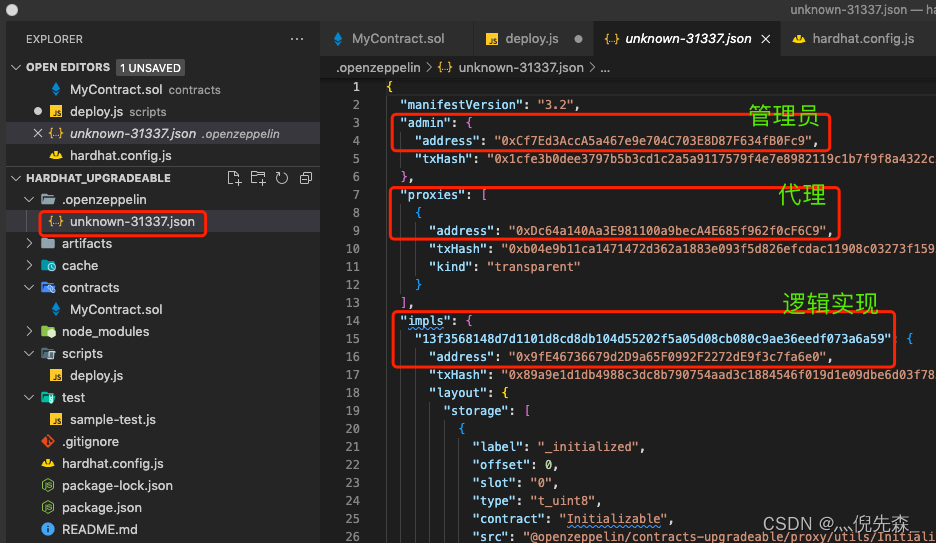
Here I am right unknown-31337.json The data in is marked , You can open the picture to see the details
Here you can see three addresses , But I only mentioned two before , Because before we practice the operation, the administrator (admin) The contract will be more abstract , So it's more appropriate to talk about it now
- Administrators (admin) contract , The administrator here mainly refers to management Agency contract And Logical contract The relationship between , When we operate the contract upgrade, we are actually modifying Agency contract in Logical contract The instance of points to the new version Logical contract
Now we can see three addresses :
- Administrator contract :
0xCf7Ed3AccA5a467e9e704C703E8D87F634fB0Fc9 - Agency contract :
0xDc64a140Aa3E981100a9becA4E685f962f0cF6C9 - Logical contract :
0x9fE46736679d2D9a65F0992F2272dE9f3c7fa6e0MyContract The real address of the contract
Next, we test the contract just deployed through the console
Contract interactions on local nodes
The steps in the previous chapter are the same
* npx hardhat console --network localhost
Welcome to Node.js v16.15.1.
Type ".help" for more information.
> const MyContract = await ethers.getContractFactory("MyContract")
undefined
> const myContract = await MyContract.attach("0xDc64a140Aa3E981100a9becA4E685f962f0cF6C9")
undefined
> await myContract.getValue()
BigNumber {
value: "666" }
> await myContract.setValue(111)
{
hash: '0x806e46660e1eacf6c967fa1d6a75414bae230b34a208ae4f855e420d47961319',
type: 2,
accessList: [],
blockHash: '0x731b09b68c08232cc9bc2ed0d18a336ec1c6bf6f9c964c9ad97717000d94418e',
blockNumber: 6,
transactionIndex: 0,
confirmations: 1,
from: '0xf39Fd6e51aad88F6F4ce6aB8827279cffFb92266',
gasPrice: BigNumber {
value: "455945547" },
maxPriorityFeePerGas: BigNumber {
value: "0" },
maxFeePerGas: BigNumber {
value: "577056082" },
gasLimit: BigNumber {
value: "34472" },
to: '0xDc64a140Aa3E981100a9becA4E685f962f0cF6C9',
value: BigNumber {
value: "0" },
nonce: 5,
data: '0x5093dc7d000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000006f',
r: '0xf31ab81921058ccb193d6c39165c185febdf0c4437117bc6cad4f33f5c27ab1d',
s: '0x1c53f8eea9967c097e2f9fa4aa02d8ab94107350a7bfb0751c11c981bdf0f123',
v: 0,
creates: null,
chainId: 31337,
wait: [Function (anonymous)]
}
> await myContract.getValue()
BigNumber {
value: "112" }
Here you can see , We are instantiating MyContract At the time of the contract , The specified address is the agency contract address 0xDc64a140Aa3E981100a9becA4E685f962f0cF6C9, Not a logical contract ( real MyContract contract ) Address 0x9fE46736679d2D9a65F0992F2272dE9f3c7fa6e0 , And the transactions were successfully executed .
This is because the agency contract will forward our transaction to MyContract contract , Finally, return the results to us .
problem
I mentioned in the last chapter , I want to pass. setValue Method to set a new storageValue value , But we wrote one more code in the contract +1( Although it was intended to demonstrate ). So I want to fix the contract code bug, Delete this part of the code 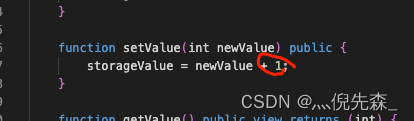
Then let's start writing the new version of the contract code , And complete the contract upgrade
Upgrade the new version
New version of contract code
We are contracts New under the directory MyContractV2.sol Contract documents , hold MyContract.sol Copy the code of , Modify the contract name , Fix the error code , And add a new string Type state variables and operation methods
like this
// SPDX-License-Identifier: UNLICENSED
pragma solidity ^0.8.0;
import "@openzeppelin/contracts-upgradeable/proxy/utils/Initializable.sol";
// Our contract needs to be inherited Initializable
contract MyContractV2 is Initializable {
int storageValue;
// New state variables
string storageStr;
function initialize(int initValue) public initializer {
storageValue = initValue;
}
function setValue(int newValue) public {
storageValue = newValue;
}
function getValue() public view returns (int) {
return storageValue;
}
// Set up storageStr
function setStr(string memory newStr) public {
storageStr = newStr;
}
// Inquire about storageStr
function getStr() public view returns (string memory) {
return storageStr;
}
}
compile
* npx hardhat compile
Compiled 1 Solidity file successfully
# Because the contract written above has been compiled in the last compilation file , So this time only compile the new MyContractV2
Deploy
Modify deployment script file
Before deployment , We still need to scripts New under the directory upgrade-MyContract.js Upgrade script file , And add the following code
const {
ethers, upgrades } = require("hardhat");
// Agency contract address
const myContractProxyAddr = "0xDc64a140Aa3E981100a9becA4E685f962f0cF6C9"
async function main() {
const MyContractV2 = await ethers.getContractFactory("MyContractV2");
// upgrade
const myContractV2 = await upgrades.upgradeProxy(myContractProxyAddr, MyContractV2);
console.log("myContractV2 upgraded");
}
main()
.then(() => process.exit(0))
.catch((error) => {
console.error(error);
process.exit(1);
});
Deploy
# function pgrade-MyContract.js
* npx hardhat run --network localhost scripts/upgrade-MyContract.js
myContractV2 upgraded
Deployment completed
Contract address
Open the project directory again and find .openzeppelin In the catalog unknown-31337.json file , We can see impls There is an additional contract address in 
there 0x0165878A594ca255338adfa4d48449f69242Eb8F It is the logical contract that has just been successfully deployed (MyContractV2)
Contract interaction
The operation is the same as before , But this time we have a few points :
- After the contract is upgraded , Whether the previous data is normal ?
- After upgrading ,bug Has it been repaired
- Newly added
stringWhether type state variables and related operation methods can be called normally
Then start
* npx hardhat console --network localhost
Welcome to Node.js v16.15.1.
Type ".help" for more information.
> const MyContractV2 = await ethers.getContractFactory("MyContractV2")
undefined
#
# Here, the instantiation contract , We still want the same agency contract address
> const myContractV2 = await MyContractV2.attach("0xDc64a140Aa3E981100a9becA4E685f962f0cF6C9")
undefined
#
# Here we verify the 1 spot , The data will remain after upgrading
> await myContractV2.getValue()
BigNumber {
value: "112" }
#
# Call again setValue Method
> await myContractV2.setValue(111)
{
hash: '0x3e40f270713a705e403e89d4436b9a058a0463290ce0d903367f37efcc103b5c',
type: 2,
accessList: [],
blockHash: '0xccb9f43f973204a8ebf96e563269bc89a2d9f37131653a1ad5f22bfc78d649f1',
blockNumber: 9,
transactionIndex: 0,
confirmations: 1,
from: '0xf39Fd6e51aad88F6F4ce6aB8827279cffFb92266',
gasPrice: BigNumber {
value: "307113676" },
maxPriorityFeePerGas: BigNumber {
value: "0" },
maxFeePerGas: BigNumber {
value: "388690746" },
gasLimit: BigNumber {
value: "34239" },
to: '0xDc64a140Aa3E981100a9becA4E685f962f0cF6C9',
value: BigNumber {
value: "0" },
nonce: 8,
data: '0x5093dc7d000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000006f',
r: '0xd074afac4ae37c931d2c270e9123e02e9291e0cf514d1640e67ce13d077628a1',
s: '0x3c47a9528e95e67a325ffb79c6a52da3523b2268bc3dbff0e3589a0f843b293f',
v: 1,
creates: null,
chainId: 31337,
wait: [Function (anonymous)]
}
#
# Verified the 2 spot , Previous bug Fixed
> await myContractV2.getValue()
BigNumber {
value: "111" }
> await myContractV2.getStr()
''
#
# Call the method added in the new version setStr
> await myContractV2.setStr("i am lyon")
{
hash: '0x017db24bdc29a1b56bc02a197f7347ae2186508aed8eeec206c810c52f2d358c',
type: 2,
accessList: [],
blockHash: '0x5d66d6259200a092eea01a448fbbbf43b000773433aa6f75658cf75210960a09',
blockNumber: 10,
transactionIndex: 0,
confirmations: 1,
from: '0xf39Fd6e51aad88F6F4ce6aB8827279cffFb92266',
gasPrice: BigNumber {
value: "268811416" },
maxPriorityFeePerGas: BigNumber {
value: "0" },
maxFeePerGas: BigNumber {
value: "340214448" },
gasLimit: BigNumber {
value: "52779" },
to: '0xDc64a140Aa3E981100a9becA4E685f962f0cF6C9',
value: BigNumber {
value: "0" },
nonce: 9,
data: '0x191347df000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000002000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000096920616d206c796f6e0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000',
r: '0x2519d536c6a0fb26e2fca71738247aedb9f9e14cf6b66f9cea67b3fe999f9837',
s: '0x2aad3b415db1d9078d8766bb79f6f0fc98eb8ce5d8d4c9688c5e63016183d899',
v: 0,
creates: null,
chainId: 31337,
wait: [Function (anonymous)]
}
#
# Here we verify the 3 spot , The newly added methods and state variables are accessed normally
> await myContractV2.getStr()
'i am lyon'
So far, we have successfully completed the contract upgrade , And through console verification, it is verified that the upgraded contract meets the expectations .
summary
I believe that readers who have just come into contact with contract upgrading will certainly have a lot of questions , I will continue to introduce the relevant knowledge of contract upgrading in the following article .
The principle of scalable contracts -DelegateCall
There is a problem , Or suggest leaving a message , thank you .
边栏推荐
- [play with FPGA learning 5 in simple terms ----- reset design]
- spritejs
- [cloud native] 2.5 kubernetes core practice (Part 2)
- 【云原生】2.5 Kubernetes 核心实战(下)
- Webauthn - official development document
- TIPC Getting Started6
- ros缺少xacro的包
- 二.Stm32f407芯片GPIO编程,寄存器操作,库函数操作和位段操作
- Is the Ren domain name valuable? Is it worth investing? What is the application scope of Ren domain name?
- I STM32 development environment, keil5/mdk5.14 installation tutorial (with download link)
猜你喜欢
TIPC Service and Topology Tracking4
Is the Ren domain name valuable? Is it worth investing? What is the application scope of Ren domain name?

How does the whole network display IP ownership?

RPA advanced (II) uipath application practice

Solve the problem of data blank in the quick sliding page of the uniapp list
enumrate的start属性的坑

Attribute acquisition method and operation notes of C # multidimensional array
Tidb DM alarm DM_ sync_ process_ exists_ with_ Error troubleshooting
QT learning diary 7 - qmainwindow

TIPC Service and Topology Tracking4
随机推荐
函数式接口和方法引用
Is bond fund safe? Does the bond buying foundation lose principal?
Homer预测motif
[in simple terms, play with FPGA learning 3 ----- basic grammar]
spritejs
TIPC Service and Topology Tracking4
tidb-dm报警DM_sync_process_exists_with_error排查
Win11 arm system configuration Net core environment variable
mysql 基本语句
由粒子加速器产生的反中子形成的白洞
TIPC messaging3
Liftover for genome coordinate conversion
ImportError: cannot import name ‘Digraph‘ from ‘graphviz‘
MTK full dump grab
MySQL比较运算符IN问题求解
2022 love analysis · panoramic report of digital manufacturers of state-owned enterprises
Programmer growth Chapter 6: how to choose a company?
【云原生】2.5 Kubernetes 核心实战(下)
Iii. Système de démarrage et d'horloge à puce
flutter 问题总结