当前位置:网站首页>[advanced ROS] lesson 5 TF coordinate transformation in ROS
[advanced ROS] lesson 5 TF coordinate transformation in ROS
2022-07-01 14:59:00 【Life is like Zhaoxu】
【ROS Advanced 】 The first five lectures ROS Medium TF Coordinate transformation
List of articles
Preface
In the introductory chapter ROS tutorial , We have simply studied about TF Content of coordinate transformation , The purpose of advanced chapter is to understand more deeply from the perspective of programming TF How to use coordinate transformation , And give static state 、 Dynamic and multi coordinate transformation And so on , Better grasp TF Function pack .
One 、TF Introduction to function package
1. Concept
- TF: namely TransForm Frame, Refers to coordinate transformation ;
- Coordinate system : That is, the position calibration system of the object , With Right hand coordinate system As the standard ;

- effect : Realize the transformation of points or vectors between different coordinate systems
2. TF2 And TF
- TF2: In the present ROS In the system ,TF2 The replacement has been 了 TF Use , It also includes the original functions ;
- difference :
- TF2 The function package corresponds to tf2、tf2_ros;TF The function package corresponds to tf package ,TF2 The feature pack of enhances cohesion , And internal differences API Completed subcontracting ;
- TF2 More efficient , Here is a demonstration of static coordinate transformation ;
- Static coordinate transformation demonstration : Because the information is fixed , so TF2 More efficient
- TF2:
Transform instruction :rosrun tf2_ros static_transform_publisher 0 0 0 0 0 0 /base_link /laser
Check the topic messages (rostopic):rostopic echo /tf( Cyclic output )- TF:
Transform instruction :rosrun tf static_transform_publisher 0 0 0 0 0 0 /base_link /laser 100
TF More startup parameters , There is a release frequency
Check the topic messages (rostopic):rostopic echo /tf_static( Single output )
- Common function packs :
- tf2_geometry_msgs: Can be ROS The message is converted to tf2 news .
- tf2: Encapsulates common messages of coordinate transformation .
- tf2_ros: by tf2 Provides roscpp and rospy binding , Encapsulates the commonly used coordinate transformation API.
- Refer to website address :ROS WIki TF2
3. Coordinate system viewing method
- Corresponding function package :tf2_tools, The installation instructions are as follows
sudo apt install ros-noetic-tf2-tools
- Tool use : Generate corresponding pdf file , Atlas presentation A tree structure
- Start the broadcast coordinate system program
- Run the toolkit instructions :
rosrun tf2_tools view_frames.py- The generated log is as follows :
[INFO] [1592920556.827549]: Listening to tf data during 5 seconds... [INFO] [1592920561.841536]: Generating graph in frames.pdf file...
- Open the pdf file :
evince frames.pdf
4. Coordinate information
- Commonly used msg Information :
- geometry_msgs/TransformStamped: It is used to transmit the position information related to the coordinate system
std_msgs/Header header # Header information uint32 seq #|-- Serial number time stamp #|-- Time stamp string frame_id #|-- coordinate ID string child_frame_id # Of the sub coordinate system id geometry_msgs/Transform transform # Coordinate information geometry_msgs/Vector3 translation # Offset float64 x #|-- X Offset of direction float64 y #|-- Y Offset of direction float64 z #|-- Z The offset in the direction geometry_msgs/Quaternion rotation # Four yuan number float64 x float64 y float64 z float64 w
- geometry_msgs/PointStamped: It is used to transmit the information of coordinate points in a coordinate system
std_msgs/Header header # head uint32 seq #|-- Serial number time stamp #|-- Time stamp string frame_id #|-- Of the coordinate system id geometry_msgs/Point point # Point coordinates float64 x #|-- x y z coordinate float64 y float64 z
- see msg Information command :
rosmsg info
Two 、 Static coordinate transformation
1. Scenario hypothesis
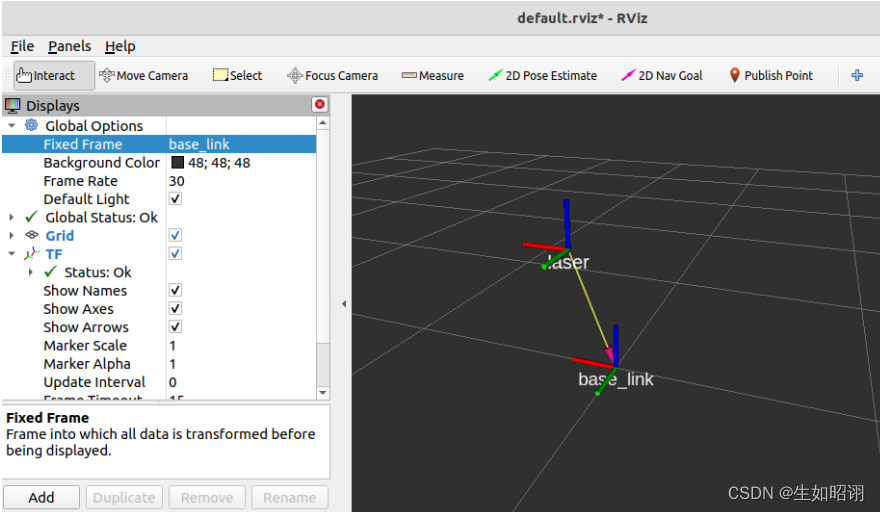
Question presentation : Suppose a robot model , The trunk body and the radar are respectively fixedly connected to two coordinate systems , The origin of the two coordinate system is located at the corresponding physical center , The displacement relationship between the radar origin and the torso origin is :x:0.2 y:0.0 z:0.5, In the radar coordinate system, the coordinate of an object is (2.0 3.0 5.0), Find the coordinates of this object in the torso coordinate system ?
3d Presentation under : The figure uses rviz Components , See the follow-up blog for specific usage
2. Programming to realize
- The basic idea :
- Create Feature Pack : Need to include tf2、tf2_ros、tf2_geometry_msgs、roscpp rospy std_msgs geometry_msgs etc.
- Create publisher : Release the relative relationship between torso coordinate system and radar coordinate
- Create subscribers : Subscribe to published information , According to the object information , With the help of TF The function package realizes coordinate transformation and output ;
notes :ROS The system also provides nodes for static coordinate conversion :
rosrun tf2_ros static_transform_publisher x Offset y Offset z Offset z angle of yaw y Pitch angle x Roll angle Parent coordinate system Sub coordinate system
- Publisher code :
/* Static coordinate transformation publisher : Release about laser Location information of coordinate system Implementation process : 1. Include header file 2. initialization ROS node 3. Create a static coordinate conversion broadcaster 4. Create coordinate system information 5. The broadcaster publishes coordinate system information 6.spin() */
// 1. Include header file
#include "ros/ros.h"
#include "tf2_ros/static_transform_broadcaster.h"
#include "geometry_msgs/TransformStamped.h"
#include "tf2/LinearMath/Quaternion.h"
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
setlocale(LC_ALL,"");
// 2. initialization ROS node
ros::init(argc,argv,"static_brocast");
// 3. Create a static coordinate conversion broadcaster
tf2_ros::StaticTransformBroadcaster broadcaster;
// 4. Create coordinate system information
geometry_msgs::TransformStamped ts;
//---- Set header information
ts.header.seq = 100;
ts.header.stamp = ros::Time::now();
ts.header.frame_id = "base_link";
//---- Set the child coordinate system
ts.child_frame_id = "laser";
//---- Set the offset of the child relative to the parent
ts.transform.translation.x = 0.2;
ts.transform.translation.y = 0.0;
ts.transform.translation.z = 0.5;
//---- Set quaternion : take Convert Euler angle data into quaternions
tf2::Quaternion qtn;
qtn.setRPY(0,0,0);
ts.transform.rotation.x = qtn.getX();
ts.transform.rotation.y = qtn.getY();
ts.transform.rotation.z = qtn.getZ();
ts.transform.rotation.w = qtn.getW();
// 5. The broadcaster publishes coordinate system information
broadcaster.sendTransform(ts);
ros::spin();
return 0;
}
- Subscriber code :
/* Subscribe to coordinate system information , Generate a relative to Coordinate point data of sub coordinate system , Convert to coordinate points in the parent coordinate system Implementation process : 1. Include header file 2. initialization ROS node 3. establish TF Subscription node 4. Generate a coordinate point ( Relative to the child coordinate system ) 5. Convert coordinate points ( Relative to the parent coordinate system ) 6.spin() */
//1. Include header file
#include "ros/ros.h"
#include "tf2_ros/transform_listener.h"
#include "tf2_ros/buffer.h"
#include "geometry_msgs/PointStamped.h"
#include "tf2_geometry_msgs/tf2_geometry_msgs.h" // Be careful : call transform Must contain the header file
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
setlocale(LC_ALL,"");
// 2. initialization ROS node
ros::init(argc,argv,"tf_sub");
ros::NodeHandle nh;
// 3. establish TF Subscription node
tf2_ros::Buffer buffer;
tf2_ros::TransformListener listener(buffer);
ros::Rate r(1);
while (ros::ok())
{
// 4. Generate a coordinate point ( Relative to the child coordinate system )
geometry_msgs::PointStamped point_laser;
point_laser.header.frame_id = "laser";
point_laser.header.stamp = ros::Time::now();
point_laser.point.x = 1;
point_laser.point.y = 2;
point_laser.point.z = 7.3;
// 5. Convert coordinate points ( Relative to the parent coordinate system )
// Create a new coordinate point , Used to receive conversion results
//-------------- Use try Statement or sleep , Otherwise, coordinate conversion may fail due to cache reception delay ------------------------
try
{
geometry_msgs::PointStamped point_base;
point_base = buffer.transform(point_laser,"base_link");
ROS_INFO(" Converted data :(%.2f,%.2f,%.2f), The reference coordinate system is :",point_base.point.x,point_base.point.y,point_base.point.z,point_base.header.frame_id.c_str());
}
catch(const std::exception& e)
{
// std::cerr << e.what() << '\n';
ROS_INFO(" Abnormal program .....");
}
r.sleep();
ros::spinOnce();
}
return 0;
}
3、 ... and 、 Dynamic coordinate transformation
1. Scenario hypothesis
Question presentation : Keyboard controls turtle movement , Dynamically release the relationship between the turtle coordinate system and the world coordinate system ;
3d demonstration (rviz):

2. Programming to realize
- The basic idea :
- Create Feature Pack : Dependencies contain tf2、tf2_ros、tf2_geometry_msgs、roscpp rospy std_msgs geometry_msgs、turtlesim;
- Create publisher : subscribe turtle1/pose, Get the tortoise in the world coordinate system x coordinate 、y coordinate 、 Offset, linear velocity and angular velocity , take pose Information is converted into relative information of coordinate system and released
- Create subscribers : Subscribe to relative information and output ;
- Publisher code :
/* Dynamic coordinate system relative attitude release ( The relative posture of one coordinate system relative to another coordinate system is constantly changing ) Implementation process : 1. Include header file 2. initialization ROS node 3. establish ROS Handle 4. Create subscription object 5. The callback function processes the subscribed data ( Realization TF radio broadcast ) 5-1. establish TF Broadcaster 5-2. establish Broadcast data ( adopt pose Set up ) 5-3. The broadcaster publishes data 6.spin */
// 1. Include header file
#include "ros/ros.h"
#include "turtlesim/Pose.h"
#include "tf2_ros/transform_broadcaster.h"
#include "geometry_msgs/TransformStamped.h"
#include "tf2/LinearMath/Quaternion.h"
void doPose(const turtlesim::Pose::ConstPtr& pose){
// 5-1. establish TF Broadcaster
static tf2_ros::TransformBroadcaster broadcaster;
// 5-2. establish Broadcast data ( adopt pose Set up )
geometry_msgs::TransformStamped tfs;
// |---- Head set
tfs.header.frame_id = "world";
tfs.header.stamp = ros::Time::now();
// |---- Coordinate system ID
tfs.child_frame_id = "turtle1";
// |---- Coordinate system relative information setting
tfs.transform.translation.x = pose->x;
tfs.transform.translation.y = pose->y;
tfs.transform.translation.z = 0.0; // Two dimensional implementation ,pose There is no z,z yes 0
// |--------- Quaternion settings
tf2::Quaternion qtn;
qtn.setRPY(0,0,pose->theta);
tfs.transform.rotation.x = qtn.getX();
tfs.transform.rotation.y = qtn.getY();
tfs.transform.rotation.z = qtn.getZ();
tfs.transform.rotation.w = qtn.getW();
// 5-3. The broadcaster publishes data
broadcaster.sendTransform(tfs);
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
setlocale(LC_ALL,"");
// 2. initialization ROS node
ros::init(argc,argv,"dynamic_tf_pub");
// 3. establish ROS Handle
ros::NodeHandle nh;
// 4. Create subscription object
ros::Subscriber sub = nh.subscribe<turtlesim::Pose>("/turtle1/pose",1000,doPose);
// 5. The callback function processes the subscribed data ( Realization TF radio broadcast )
//
// 6.spin
ros::spin();
return 0;
}
- Subscriber code :
//1. Include header file
#include "ros/ros.h"
#include "tf2_ros/transform_listener.h"
#include "tf2_ros/buffer.h"
#include "geometry_msgs/PointStamped.h"
#include "tf2_geometry_msgs/tf2_geometry_msgs.h" // Be careful : call transform Must contain the header file
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
setlocale(LC_ALL,"");
// 2. initialization ROS node
ros::init(argc,argv,"dynamic_tf_sub");
ros::NodeHandle nh;
// 3. establish TF Subscription node
tf2_ros::Buffer buffer;
tf2_ros::TransformListener listener(buffer);
ros::Rate r(1);
while (ros::ok())
{
// 4. Generate a coordinate point ( Relative to the child coordinate system )
geometry_msgs::PointStamped point_laser;
point_laser.header.frame_id = "turtle1";
point_laser.header.stamp = ros::Time();
point_laser.point.x = 1;
point_laser.point.y = 1;
point_laser.point.z = 0;
// 5. Convert coordinate points ( Relative to the parent coordinate system )
// Create a new coordinate point , Used to receive conversion results
//-------------- Use try Statement or sleep , Otherwise, coordinate conversion may fail due to cache reception delay ------------------------
try
{
geometry_msgs::PointStamped point_base;
point_base = buffer.transform(point_laser,"world");
ROS_INFO(" The coordinate point is relative to world The coordinates of the for :(%.2f,%.2f,%.2f)",point_base.point.x,point_base.point.y,point_base.point.z);
}
catch(const std::exception& e)
{
// std::cerr << e.what() << '\n';
ROS_INFO(" Abnormal program :%s",e.what());
}
r.sleep();
ros::spinOnce();
}
return 0;
}
notes : As for the advanced programming between dynamic coordinate transformations, in fact, the introduction of the introductory chapter shows the programming implementation of turtle tracking, that is, demonstration , Please read the introductory tutorial
Four 、 Multi coordinate transformation
1. Scenario hypothesis
- Question presentation : Suppose there are three coordinate systems , One of the coordinate systems is the parent coordinate system world, The other two are sub coordinate systems , The relative relationship between father and son is known , Find the relationship between two sub coordinate systems ;

2. Programming to realize
- The basic idea :
- Create Feature Pack : Dependencies contain tf2、tf2_ros、tf2_geometry_msgs、roscpp rospy std_msgs geometry_msgs、turtlesim
- Create publisher : Publish coordinate messages between parent and child coordinate systems
- Create subscribers : Subscription relativity , adopt TF Complete the conversion of two coordinate systems
- Publisher code : Use static coordinate transformation to publish
<launch>
<node pkg="tf2_ros" type="static_transform_publisher" name="son1" args="0.2 0.8 0.3 0 0 0 /world /son1" output="screen" />
<node pkg="tf2_ros" type="static_transform_publisher" name="son2" args="0.5 0 0 0 0 0 /world /son2" output="screen" />
</launch>
- Subscriber code :
/* Implementation process : 1. Include header file 2. initialization ros node 3. establish ros Handle 4. establish TF Subscription object 5. Parse the subscription information to get son1 The origin of the coordinate system is son2 The coordinates of analysis son1 The point in is relative to son2 Coordinates of 6.spin */
//1. Include header file
#include "ros/ros.h"
#include "tf2_ros/transform_listener.h"
#include "tf2/LinearMath/Quaternion.h"
#include "tf2_geometry_msgs/tf2_geometry_msgs.h"
#include "geometry_msgs/TransformStamped.h"
#include "geometry_msgs/PointStamped.h"
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
setlocale(LC_ALL,"");
// 2. initialization ros node
ros::init(argc,argv,"sub_frames");
// 3. establish ros Handle
ros::NodeHandle nh;
// 4. establish TF Subscription object
tf2_ros::Buffer buffer;
tf2_ros::TransformListener listener(buffer);
// 5. Parse the subscription information to get son1 The origin of the coordinate system is son2 The coordinates of
ros::Rate r(1);
while (ros::ok())
{
try
{
// analysis son1 The point in is relative to son2 Coordinates of
geometry_msgs::TransformStamped tfs = buffer.lookupTransform("son2","son1",ros::Time(0));
ROS_INFO("Son1 be relative to Son2 Coordinate relationship of : The parent coordinate system ID=%s",tfs.header.frame_id.c_str());
ROS_INFO("Son1 be relative to Son2 Coordinate relationship of : Sub coordinate system ID=%s",tfs.child_frame_id.c_str());
ROS_INFO("Son1 be relative to Son2 Coordinate relationship of :x=%.2f,y=%.2f,z=%.2f",
tfs.transform.translation.x,
tfs.transform.translation.y,
tfs.transform.translation.z
);
// Coordinate point analysis
geometry_msgs::PointStamped ps;
ps.header.frame_id = "son1";
ps.header.stamp = ros::Time::now();
ps.point.x = 1.0;
ps.point.y = 2.0;
ps.point.z = 3.0;
geometry_msgs::PointStamped psAtSon2;
psAtSon2 = buffer.transform(ps,"son2");
ROS_INFO(" stay Son2 The coordinates of :x=%.2f,y=%.2f,z=%.2f",
psAtSon2.point.x,
psAtSon2.point.y,
psAtSon2.point.z
);
}
catch(const std::exception& e)
{
// std::cerr << e.what() << '\n';
ROS_INFO(" Abnormal information :%s",e.what());
}
r.sleep();
// 6.spin
ros::spinOnce();
}
return 0;
}
summary
- Statement : The blog section of this section refers to CSDN User zhaoxuzuo ROS course , From the next blog ROS The advanced tutorial will step into ROSBAG On the basis of learning , Master this powerful ROS Record how the tool is used , Coming soon .
边栏推荐
- Build MySQL master-slave server under Ubuntu 14.04
- Some thoughts on software testing
- [零基础学IoT Pwn] 复现Netgear WNAP320 RCE
- TS报错 Don‘t use `object` as a type. The `object` type is currently hard to use
- Yyds dry goods inventory hcie security day13: firewall dual machine hot standby experiment (I) firewall direct deployment, uplink and downlink connection switches
- Flink 系例 之 TableAPI & SQL 与 MYSQL 分组统计
- Word2vec yyds dry goods inventory
- 【阶段人生总结】放弃考研,参与到工作中,已经顺利毕业了,昨天刚领毕业证
- [leetcode 324] swing sorting II thinking + sorting
- ArrayList 扩容详解,扩容原理[通俗易懂]
猜你喜欢

竣达技术丨多台精密空调微信云监控方案

JVM第二话 -- JVM内存模型以及垃圾回收

MIT团队使用图神经网络,加速无定形聚合物电解质筛选,促进下一代锂电池技术开发

Cannot link redis when redis is enabled

leetcode:329. Longest increasing path in matrix
![Opencv Learning Notes 6 -- image feature [harris+sift]+ feature matching](/img/50/5c8adacea78e470c255070c8621ddd.png)
Opencv Learning Notes 6 -- image feature [harris+sift]+ feature matching
![[leetcode] 16. The sum of the nearest three numbers](/img/60/6a68333d6e543c601e6ed586b830d0.png)
[leetcode] 16. The sum of the nearest three numbers

opencv学习笔记四--银行卡号识别

The State Administration of Chia Tai market supervision, the national development and Reform Commission and the China Securities Regulatory Commission jointly reminded and warned some iron ores

Microservice development steps (Nacos)
随机推荐
生成随机数(4位、6位)
The State Administration of Chia Tai market supervision, the national development and Reform Commission and the China Securities Regulatory Commission jointly reminded and warned some iron ores
241. Design priorities for operational expressions
Quelle valeur le pdnp peut - il apporter aux gestionnaires de produits? Vous savez tout?
一波三折,终于找到src漏洞挖掘的方法了【建议收藏】
tensorflow2-savedmodel convert to pb(frozen_graph)
TypeScript:var
使用net core 6 c# 的 NPOI 包,讀取excel..xlsx單元格內的圖片,並存儲到指定服務器
Flink 系例 之 TableAPI & SQL 与 Kafka 消息插入
Solid basic structure and array, private / public function, return value and modifier of function, event
Written on the first day after Doris graduated
opencv学习笔记五--文件扫描+OCR文字识别
Detailed explanation of ArrayList expansion, expansion principle [easy to understand]
Opencv Learning Notes 6 -- image mosaic
Build MySQL master-slave server under Ubuntu 14.04
常见健身器材EN ISO 20957认证标准有哪些
What if you are always bullied because you are too honest in the workplace?
TS报错 Don‘t use `object` as a type. The `object` type is currently hard to use
Microservice development steps (Nacos)
solidty-基础篇-基础语法和定义函数
