当前位置:网站首页>Go language foundation ----- 02 ----- basic data types and operators
Go language foundation ----- 02 ----- basic data types and operators
2022-07-03 07:36:00 【Mango sauce】
One Basic data types and operators
- file name & keyword & identifier .
- Go The basic structure of the program .
- Constants and variables .
- Data types and operators .
- String type .
1 file name & keyword & identifier
- all go Source code to .go ending .
- Identifiers start with letters or underscores , Cannot start with a number , Case sensitive .
- _ Is a special identifier called anonymous variable , Used to ignore results , Indicates that the value is discarded , Generally, the return value of the matching function has the advantage .
- Reserved keyword .
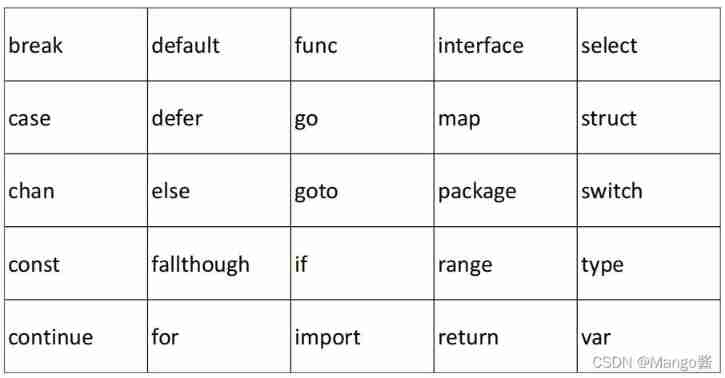
Some commonly used keywords are explained below :
1) var and const : Declaration of variables and constants . For example, the definition of variables ,var varName type perhaps varName : = value.
2) package and import: Package and import .
3) func: Used to define functions and methods .
4) return : Used to return... From a function .
5) defer someCode : Execute before the function exits .
6) go : For parallel .
7) select Used to select different types of communication .
8) interface Used to define interfaces .
9) struct Used to define abstract data types .
10) break、case、continue、for、fallthrough、else、if、switch、goto、default Process control .
11) fallthrough Usage of note summary [ Recommended reading https://blog.csdn.net/ajdfhajdkfakr/article/details/79086125].
1. added fallthrough after , Will run directly 【 The next one 】case or default sentence , Whether the conditions are met or not will be carried out .
2. added fallthrough After the statement ,【 The next one 】case Conditions cannot define constants and variables .
3. After execution fallthrough Then jump directly to the next conditional statement , The statement after this conditional execution statement does not execute .
4.fallthrough The statement should be case The last statement of the clause , Otherwise, an error will be reported fallthrough statement out of place.12) chan be used for channel Communications .
13) type Used to declare custom types .
14) map For declaration map Type data .
15) range For reading slice、map、channel data .
2 Go The basic structure of the program 1
package main
import “fmt”
func main() {
fmt.Println(“hello, world”)
}
- Any code file belongs to a package
- import keyword , Reference other packages :
import(“fmt”)
import(“os”)
It's usually written as :
import (
“fmt”
“os”
)
- golang Executable program ,package main, And there's only one main Entry function .
- Function calls in the package :
a. Functions in the same package , Call directly .
b. Functions in different packages , By package name + spot + Function name , for example fmt.xxx(). - Package access control rules :
a. Capital means this function / Variables are exportable .
b. Lowercase means this function / Variables are private , The package is not accessible from outside .
for example :calc The catalog has 3 individual go file , this 3 Every file is calc package .main The catalog has main.go file , yes main package , then main.go introduce calc A function of the package , For example, quote add.go Of Add function , When will name Add Change to add, that main.go Will fail to visit .
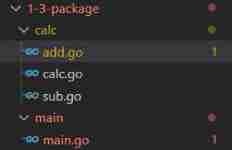
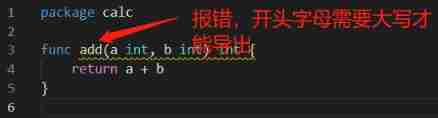
The compiler will report an error like this :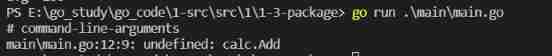
3 Function declarations and comments
1. Function declaration : func Function name ( parameter list ) ( Return value list ){
}
give an example :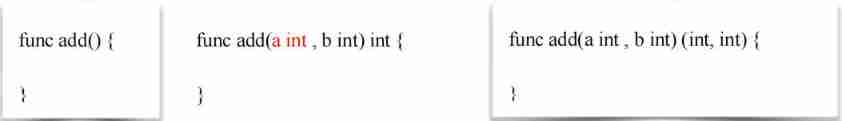
- notes , Two kinds of notes , Single-line comments : // And multiline comments /* */.
4 Constant
- go Variable declaration uses var, Constants use const modification , Represents always read-only , Do not modify .
for example :
var a int = 10
const b int = 20
- const It can only be modified boolean,number(int Related to the type 、 Floating point type 、complex) and string.
- grammar :const identifier [type] = value, among type It can be omitted .
for example :
const b = 20
5 The following is a comprehensive summary go The variable of 、 Constant definition method :
- 1) Single variable 、 Declaration of constants 、 initialization .
- 2) Multiple variables of the same type 、 Declaration of constants 、 initialization .
- 3) Multiple variables of different types 、 Declaration of constants 、 initialization .
package main
import "fmt"
func main(){
// 1. Single variable 、 Declaration of constants 、 initialization .
// 1) Variable
var a int // Statement , Then initialize
a = 10
var b int = 20 // Initialize while declaring
//var b = 20 // int It can be omitted
c := 30 // Use auto derived types for declaration and initialization , When using automatic derivation types , Assignment must be made.
// 2) Constant . Variable usage var keyword , Constant usage const.
//const x int
//x = 10 // error, Constants must be initialized when declared .
const y int = 20
//const z := 30 // error, When the automatic derivation type of constant , Out of commission := The way , direct = that will do .
const z = 30
fmt.Printf("a=%d,b=%d,c=%d\n", a, b, c)
fmt.Printf("y=%d,z=%d\n", y, z)
// 2. Multiple variables of the same type 、 Declaration of constants 、 initialization .
// 1) Variable
var aa, bb int
aa, bb = 10, 20
var cc, dd = 30, 40
ee, ff := 50, 60
// 2) Constant
const xx, yy int = 20, 30
const zz, vv = 20, 30
fmt.Printf("aa=%d,bb=%d,cc=%d,dd=%d,ee=%d,ff=%d\n", aa, bb, cc, dd, ee, ff)
fmt.Printf("aa=%d,bb=%d,cc=%d,dd=%d\n", xx, yy, zz, vv)
// 3. Multiple variables of different types 、 Declaration of constants 、 initialization .
// 1) Variable
// Define different types of methods normally
var A int = 10
var B float64 = 10.1
// Then it can be written as :
var(
AA int
BB float64
)
AA = 2
BB = 10.2
// You can also assign values
var(
AAA int = 3
BBB float64 = 10.3
)
// Constant
// Define different types of methods normally
const O int = 1
const P float64 = 1.1
// Then the statement can be written as ( Because constants must be assigned at the time of declaration , Therefore, assignment cannot be missing ):
const(
OO int = 2
PP float64 = 2.2
)
// Constants can omit types type
const(
OOO = 3
PPP float64 = 3.3
)
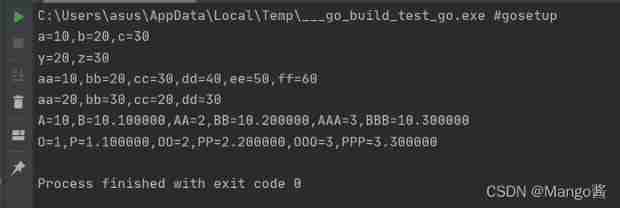
fmt.Printf("A=%d,B=%f,AA=%d,BB=%f,AAA=%d,BBB=%f\n", A, B, AA, BB, AAA, BBB)
fmt.Printf("O=%d,P=%f,OO=%d,PP=%f,OOO=%d,PPP=%f\n", O, P, OO, PP, OOO, PPP)
// So it can be concluded that go The variable of 、 Constant definition method :
// 1) The variables are 3 Kind of :1) At first, just declare , Post assignment ;2) Declare and assign values at the same time ;3) Use automatic derivation type , But you must have a value to deduce .
// 2) The constant is 2 Kind of :1)const varName varType = value;2) Omit the type of data and let it deduce automatically ,const varName = value.
}
6 Value type and reference type
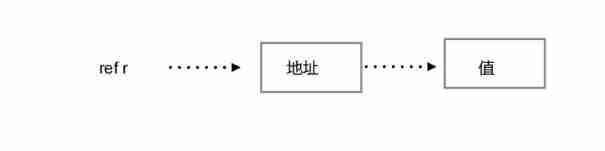
Value type : Variables store values directly , Memory is usually allocated in the stack .

Reference type : Variable stores an address , This address stores the final value . Memory is usually allocated on the heap . adopt GC Recycling .
Value type : Basic data type int、float、bool、string And arrays and struct.
Reference type : The pointer 、slice、map、chan And so on are reference types .
The code for ( contrast C/C++ The value and reference of are still much simpler ):
package main
import (
"fmt"
)
func modify(a int) {
a = 10
return
}
func modify1(a *int) {
*a = 10
}
func main() {
// 1. Print and observe whether different types are value types or reference types
a := 5
b := make(chan int, 1)
fmt.Println("a=", a) // output: 5. The basic type is the value type , Print out the value
fmt.Println("b=", b) // output: 0xc00001a0e0. The channel is a reference type , Print out the address
// 2. Value passing does not modify source variables , The address will .
modify(a)
fmt.Println("a=", a) // output: 5.
modify1(&a)
fmt.Println("a=", a) // output: 10.
}
7 Scope of variable
- Variables declared inside a function are called local variables , The lifecycle is limited to functions .
- Variables declared outside a function are called global variables , The lifecycle acts on the entire package , If it's capital ,
Then it acts on the whole program .
for example :
package main
import "fmt"
// Global variables , Because the name is lowercase, the scope is the whole main package ; If it is capitalized, it is the whole program .
var a = "G"
func main() {
n()
m()
n()
// {
// var aa int
// }
//fmt.Println(aa) // error, and C equally ,aa This is undefined
}
func n() {
fmt.Println(a)
}
func m() {
a := "O" // Write it like this , Represents a new variable defined in this function a, It's a local variable . So what is modified here is the local variable .main Output... In sequence :G O G
//a = "O" // Write it like this , Represents the global variable to be modified .main Output... In sequence :G O O
fmt.Println(a)
}
8 Data types and operators
- bool type , Can only save true and false.
- Numeric type , There are mainly int、int8、int16、int32、int64、uint8、uint16、uint32、uint64、
float32、float64. - Type conversion ,go The type conversion of is strict , Implicit conversion is not supported , Conversion must be displayed . and C/C++ equally , Turning big to small will cause data loss , Small to large will not .
for example :
var a int
var b int32
a = 15
//b = a + a // compiler error. Should be written as b = int32(a + a)
b = b + 5 // ok
fmt.Println(a, b) // 15 5
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
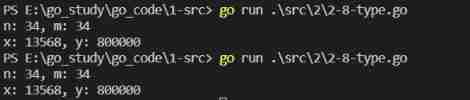
var n int16 = 34
var m int32
m = int32(n) // Small to big , No data loss
var x int16
var y int32 = 800000
x = int16(y) // Big to small , Data loss
fmt.Printf("n: %d, m: %d\n", n, m) // 34 34
fmt.Printf("x: %d, y: %d\n", x, y) // The two values must be different , That is, the data is lost
}
Character type :var a byte. for example var a byte = ‘c’. similar C/C++ Of char.
String type : var str string. for example var str = “hello world”,string It can be omitted . similar C Of char*,C++ Of string object .
Two representations of strings : 1) Double quotes “”.2) The quotation marks ``.
9 Data types and operators
- Logical operators : == 、!=、<、<=、> and >=.
- Mathematical operators :+、-、*、/ wait .C Language is called arithmetic operator .
边栏推荐
- 技术干货|昇思MindSpore NLP模型迁移之Bert模型—文本匹配任务(二):训练和评估
- TypeScript let与var的区别
- Understanding of class
- 哪一刻你才发现青春结束了
- An overview of IfM Engage
- Inverted chain disk storage in Lucene (pfordelta)
- [set theory] Stirling subset number (Stirling subset number concept | ball model | Stirling subset number recurrence formula | binary relationship refinement relationship of division)
- 带你全流程,全方位的了解属于测试的软件事故
- Read config configuration file of vertx
- 圖像識別與檢測--筆記
猜你喜欢
【LeetCode】2. Valid Parentheses·有效的括号

Analysis of the problems of the 7th Blue Bridge Cup single chip microcomputer provincial competition
【LeetCode】3. Merge Two Sorted Lists·合并两个有序链表
【LeetCode】4. Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock·股票买卖最佳时机
UA camouflage, get and post in requests carry parameters to obtain JSON format content
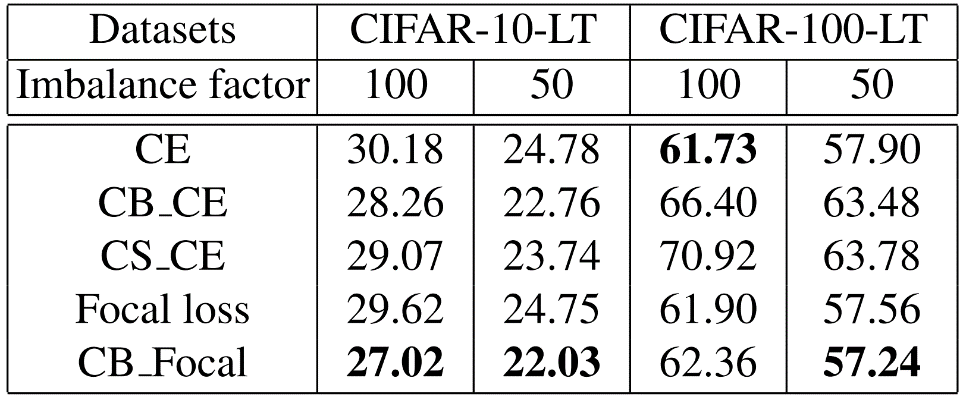
【MindSpore论文精讲】AAAI长尾问题中训练技巧的总结

PAT甲级 1032 Sharing

Common methods of file class

Inverted chain disk storage in Lucene (pfordelta)
【开发笔记】基于机智云4G转接板GC211的设备上云APP控制
随机推荐
What did the DFS phase do
Spa single page application
How long is the fastest time you can develop data API? One minute is enough for me
技术干货|百行代码写BERT,昇思MindSpore能力大赏
Partage de l'expérience du projet: mise en œuvre d'un pass optimisé pour la fusion IR de la couche mindstore
技术干货|昇思MindSpore NLP模型迁移之Bert模型—文本匹配任务(二):训练和评估
IPv4 address
Use of other streams
Lucene hnsw merge optimization
The difference between typescript let and VaR
Common operations of JSP
TreeMap
PgSQL converts string to double type (to_number())
Epoll related references
【MySQL 11】怎么解决MySQL 8.0.18 大小写敏感问题
2021-07-18
Technical dry goods Shengsi mindspire elementary course online: from basic concepts to practical operation, 1 hour to start!
Introduction of transformation flow
Analysis of the ninth Blue Bridge Cup single chip microcomputer provincial competition
Leetcode 213: looting II