当前位置:网站首页>Opencv_ 100 questions_ Chapter II (6-10)
Opencv_ 100 questions_ Chapter II (6-10)
2022-06-10 22:43:00 【Fioman_ Hammer】
List of articles
6. Subtractive treatment
Subtraction is the process of subtracting a picture 256 ^ 3 A hue becomes 4 ^ 3 A hue , That is to say, every original channel 256 The color levels are divided into four sections and compressed to 4 Color levels , These four gray levels are given . Namely 32, 96, 160,224.
pix = 32 (0 <= pix < 64)
pix = 96 (64 <= pix < 128)
pix = 160 (128 <= pix < 192)
pix = 224 (192 <= pix < 256)
You can get a formula that is
pix = (int)(pix/64)*64 + 32
Code section :
# @Time : 2022/6/9 13:46
# @Author : Fioman
# @Phone : 13149920693
# @Tips : Talk is Cheap,Show me the code! ^_^^_^
from settings import *
# Dicrease color
def dicrease_color(image):
""" The image is subtracted :param image: :return: """
out = image.copy()
out = out // 64 * 64 + 32
return out
if __name__ == '__main__':
imagePath = os.path.join(OPENCV_100_Q_PATH,"gray_01.bmp")
imageOriginal = cv.imread(imagePath,cv.IMREAD_COLOR)
imageDicrease = dicrease_color(imageOriginal)
cv.imshow("ImageOriginal",imageOriginal)
cv.imshow("ImageDicrease",imageDicrease)
cv.waitKey(0)
7. The average pooling (Average Pool)
Divide the image into fixed size grids , The pixel value in the grid is the average value of all pixels in the grid .
We will use the same size grid to divide the image , The operation of finding the representative values in the grid is called pooling (Pooling).
Pool operation isConvolutional neural networks (Convolutional Neural Network)The important image processing method in . Average pooling is defined as follows :

Please put the size 128 * 128 Use the picture of 8 * 8 The grid is pooled evenly , Average pooling is to change all pixel values in the region to draw values
# @Time : 2022/6/9 14:10
# @Author : Fioman
# @Phone : 13149920693
# @Tips : Talk is Cheap,Show me the code! ^_^^_^
from settings import *
def average_pooling(image, G=8):
out = image.copy()
if len(image.shape) == 3:
H, W, C = image.shape
else:
H, W = image.shape[:2]
C = []
newW = int(W / G)
newH = int(H / G)
for y in range(newH):
for x in range(newW):
if C != []:
for c in range(C):
out[G * y:G * (y + 1), G * x:G * (x + 1), c] =
np.mean(out[G * y, G * (y + 1), G * x:G * (x + 1), c]).astype(np.uint8)
else:
out[G * y:G * (y + 1), G * x:G * (x + 1)] =
np.mean(out[G * y:G * (y + 1), G * x:G * (x + 1)]).astype(np.uint8)
return out
if __name__ == '__main__':
imagePath = os.path.join(OPENCV_100_Q_PATH, "gray_01.bmp")
imageOriginal = cv.imread(imagePath, cv.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE)
averPoolImage = average_pooling(imageOriginal, 8)
cv.imshow("Original", imageOriginal)
cv.imshow("AverPoolImage", averPoolImage)
cv.waitKey(0)
8. Maximum pooling (Max Pooling)
The values in the grid are not averaged , Instead, the maximum value in the grid is taken for pooling
# @Time : 2022/6/9 15:56
# @Author : Fioman
# @Phone : 13149920693
# @Tips : Talk is Cheap,Show me the code! ^_^^_^
from settings import *
def max_pooling(image, G=8):
# Max Pooling
out = image.copy()
if len(image.shape) == 3:
H, W, C = image.shape
else:
H, W = image.shape[:2]
C = None
hNums = int(H / G)
wNums = int(W / G)
for y in range(hNums):
for x in range(wNums):
if C is not None:
for c in range(C):
out[G * y:G * (y + 1), G * x:G * (x + 1), c] =
np.max(out[G * y:G * (y + 1), G * x:G * (x + 1)], c)
else:
out[G * y:G * (y + 1), G * x:G * (x + 1)] =
np.max(out[G * y:G * (y + 1), G * x:G * (x + 1)])
return out
if __name__ == '__main__':
imagePath = os.path.join(OPENCV_100_Q_PATH, "gray_01.bmp")
imageOrginal = cv.imread(imagePath, cv.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE)
maxPool = max_pooling(imageOrginal, 8)
cv.imshow("Orginal", imageOrginal)
cv.imshow("MaxPool", maxPool)
cv.waitKey(0)
9. Gauss filtering (Gaussian Filter)
Gauss filtering (Gaussian Filter) It is a kind of linear filtering . Gaussian filtering is mainly used for smoothing ( Fuzzy ) Images , Gaussian filter is also a low-pass filter .
The idea of Gaussian filter :
The value of each pixel on the image , It is obtained by weighted averaging the values of itself and other pixels in the neighborhood . Just this weighted kernel , It's based on the Gaussian distribution . The center point is the pixel itself , The whole kernel obeys Gaussian distribution .
Gauss function :
One dimensional Gaussian function :
G(x)FollowsigmaThe value of has a great relationship ,sigmaThe larger the value , The smoother the image ,sigmaThe smaller the value , The sharper the image .


To understand Gaussian Blur , First of all, understand a little , Gauss formula is used to calculate the value of kernel weight , And the convex part of the center point is the pixel to be calculated . Now assume a set of pixels , another sigma=1.5:

Bring the pixel coordinates into the Gaussian formula , The weight of the occupation is :
The result calculated here is the weight of the relative position , This weight has nothing to do with the value of the pixel value , It is calculated by applying Gauss formula according to relative position . After calculating this value , According to normalization , Is to make the sum of weights 1, The method is to divide the above values by their sum , Finally, their sum is 1.
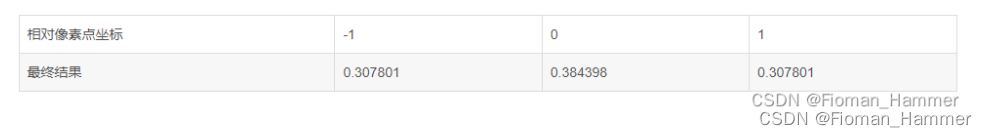
Here we get the Gaussian convolution kernel , Then convolute with the pixel value :
Expand to 2D

Generation of Gaussian filter template :
It is calculated by two-dimensional Gaussian function , Let's say that the length and width of a Gaussian template are 5, The variance of 0.5, So first of all , We are building a coordinate system on the convolution kernel template , Its origin is the center point of Gaussian template , Here's the picture :


Gaussian filter template : Two forms , One is in decimal form , One is in integer form
Template in decimal form :Is the value calculated directly , Then divide the values by their sum .Template in integer form :It needs to be normalized , Normalize the value of the upper left corner of the template to 1. The integer template needs to add a coefficient , The coefficient is the reciprocal of the sum of the template coefficients .
sigma The significance and selection of :
In Gaussian distribution sigma Represents the standard deviation . The standard deviation represents the degree of dispersion , It also represents the width of the pendulum image with Gaussian distribution . sigma The smaller it is , Indicates that the greater the degree of dispersion , The distribution is relatively concentrated , The proportion of the middle part is much higher than that of the other parts . and sigma The bigger it is , Indicates the smaller the degree of dispersion , The distribution is quite scattered , The proportion of the middle part is about the same as that of the other parts .
Gaussian filter code implementation :
# @Time : 2022/6/10 10:35
# @Author : Fioman
# @Phone : 13149920693
# @Tips : Talk is Cheap,Show me the code! ^_^^_^
from settings import *
def gaussian_filter(image, kSize=3, sigma=1.3):
""" Gaussian filter implementation :param image: :param kSize: :param sigma: :return: """
if len(image.shape) == 3:
H, W, C = image.shape
else:
image = np.expand_dims(image, axis=-1)
H, W, C = image.shape
## Zero Padding
pad = kSize // 2
out = np.zeros((H + pad * 2, W + pad * 2, C), dtype=np.float32)
out[pad:pad + H, pad:pad + W] = image.copy().astype(np.float32)
## preprare Kernel
K = np.zeros((kSize, kSize), dtype=np.float32)
for x in range(-pad, -pad + kSize):
for y in range(-pad, -pad + kSize):
K[y + pad, x + pad] = np.exp(-(x ** 2 + y ** 2) / (2 * (sigma ** 2)))
K /= (2 * np.pi * sigma * sigma)
K /= K.sum()
temp = out.copy()
# filter
for y in range(H):
for x in range(W):
for c in range(C):
out[pad + y, pad + x, c] = np.sum(K * temp[y:y + kSize, x:x + kSize, c])
out = np.clip(out, 0, 255)
out = out[pad:pad + H, pad:pad + W].astype(np.uint8)
return out
if __name__ == '__main__':
imagePath = os.path.join(OPENCV_100_Q_PATH, "gray_01.bmp")
imageOriginal = cv.imread(imagePath, cv.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE)
gaussianFilter = gaussian_filter(imageOriginal, 3, 1.2)
cv.imshow("Original", imageOriginal)
cv.imshow("GaussianFilter",gaussianFilter)
cv.waitKey(0)
10. median filtering
Median filter is also a kind of filter that can make the image smooth . The median value of pixels within the filtering core range is used for filtering . Edge fill uses Zero Padding
Code implementation :
# @Time : 2022/6/10 10:54
# @Author : Fioman
# @Phone : 13149920693
# @Tips : Talk is Cheap,Show me the code! ^_^^_^
from settings import *
def median_filter(image, kSize=3):
""" median filtering :param image: Filtered picture :param kSize: Filter core size :return: """
if len(image.shape) == 3:
H, W, C = image.shape
else:
image = np.expand_dims(image, axis=-1)
H, W, C = image.shape
pad = kSize // 2
imagePadding = np.zeros((H + 2 * pad, W + 2 * pad, C), dtype=np.float32)
imagePadding[pad:pad + H, pad:pad + W] = image.copy().astype(np.float32)
temp = imagePadding.copy()
for y in range(H):
for x in range(W):
for c in range(C):
imagePadding[pad + y, pad + x, c] = np.median(temp[y:y + kSize, x:x + kSize, c])
imagePadding = imagePadding[pad:pad + H, pad:pad + W].astype(np.uint8)
return imagePadding
if __name__ == '__main__':
imagePath = os.path.join(OPENCV_100_Q_PATH,"gray_01.bmp")
imageOriginal = cv.imread(imagePath,cv.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE)
medianBlured = median_filter(imageOriginal,3)
cv.imshow("Original",imageOriginal)
cv.imshow("MedianBlured",medianBlured)
cv.waitKey(0)
边栏推荐
- 【Debug】could not find ref wiht poc XXX解决
- Tcapulusdb Jun · industry news collection (VI)
- 【Xpath】使用following-sibling获取后面的同级节点
- Several Apache related security vulnerability fixes
- TcaplusDB君 · 行业新闻汇编(三)
- 罗永浩:我要是负责人 能让苹果产品上去三个台阶不止
- torch_geometric
- mathtype7.x的基本使用
- 笔记(四)- 多线程
- Tcapulusdb Jun · industry news collection (III)
猜你喜欢

很流行的状态管理库 MobX 是怎么回事?

Model construction of mmdetection

Web3生态去中心化金融平台——Sealem Finance

1. Introduction to tornado & introduction to tornado project in this column
![[tcapulusdb knowledge base] Introduction to tcapulusdb process startup](/img/df/08a5e9b939ab158a86c75c92697864.png)
[tcapulusdb knowledge base] Introduction to tcapulusdb process startup

【TcaplusDB知识库】TcaplusDB TcapDB扩缩容介绍
【TcaplusDB知识库】TcaplusDB查看进程所在机器介绍

TcaplusDB君 · 行业新闻汇编(四)

【TcaplusDB知识库】TcaplusDB事务管理介绍

Web3生态去中心化金融平台——Sealem Finance
随机推荐
Whale conference sharing: what should we do if the conference is difficult?
Modify frontsortinglayer variable of spritemask
TcaplusDB君 · 行业新闻汇编(五)
Notes (V) - JVM
Digital twin: third person mouse operation
Pytorch 安装超简单
Opencv_100问_第三章 (11-15)
Implementation of simply untyped lambda calculus
Matlab - 演化博弈论实现
鲸会务会议分享:大会难办怎么办?
1.Tornado简介&&本专栏搭建tornado项目简介
[tcapulusdb knowledge base] tcapulusdb tcapdb capacity expansion and contraction introduction
GMPNN:Drug-drug interaction prediction with learnable size-adaptive molecular substructures.
Shell基础概念
Error parsing mapper XML
Different ways to create four indexes in MySQL
【phpstorm】 No data sources are configured to run this SQL and provide advanced c
鲸会务智慧景区管理解决方案
torch_ geometric
datagrip 报错 “The specified database user/password combination is rejected...”的解决方法