当前位置:网站首页>xxl-job惊艳的设计,怎能叫人不爱
xxl-job惊艳的设计,怎能叫人不爱
2022-07-04 09:32:00 【二哥学Java】
目录
- 通信底层介绍
- 通信整体流程
- 惊艳的设计
通信底层介绍
xxl-job 使用 netty http 的方式进行通信,虽然也支持 Mina,jetty,netty tcp 等方式,但是代码里面固定写死的是 netty http。
通信整体流程
我以调度器通知执行器执行任务为例,绘制的活动图:
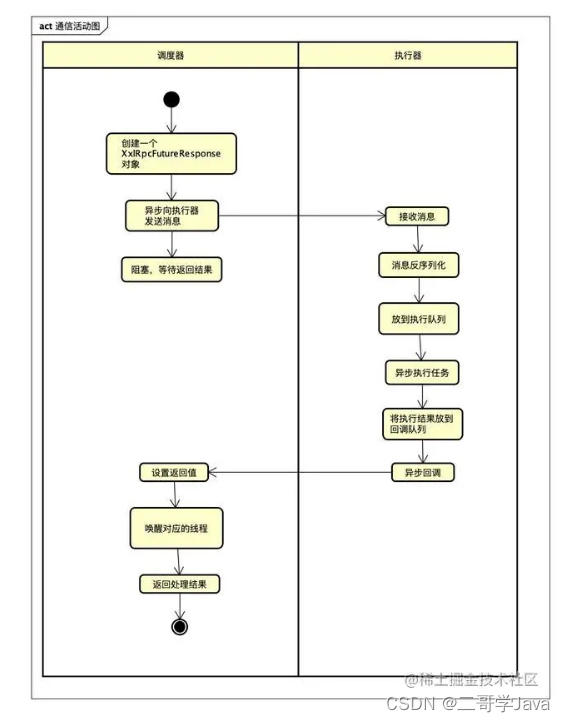
活动图
惊艳的设计
看完了整个处理流程代码,设计上可以说独具匠心,将 netty,多线程的知识运用得行云流水。
我现在就将这些设计上出彩的点总结如下:
| 使用动态代理模式,隐藏通信细节
xxl-job 定义了两个接口 ExecutorBiz,AdminBiz,ExecutorBiz 接口中封装了向心跳,暂停,触发执行等操作,AdminBiz 封装了回调,注册,取消注册操作,接口的实现类中,并没有通信相关的处理。
XxlRpcReferenceBean 类的 getObject() 方法会生成一个代理类,这个代理类会进行远程通信。
| 全异步处理
执行器收到消息进行反序列化,并没有同步执行任务代码,而是将任务信息存储在 LinkedBlockingQueue 中,异步线程从这个队列中获取任务信息,然后执行。
而任务的处理结果,也不是说处理完之后,同步返回的,也是放到回调线程的阻塞队列中,异步的将处理结果返回回去。
这样处理的好处就是减少了 netty 工作线程的处理时间,提升了吞吐量。
| 对异步处理的包装
对异步处理进行了包装,代码看起来是同步调用的。
我们看下调度器,XxlJobTrigger 类触发任务执行的代码:
public static ReturnT<String> runExecutor(TriggerParam triggerParam, String address){
ReturnT<String> runResult = null;
try {
ExecutorBiz executorBiz =
XxlJobScheduler.getExecutorBiz(address);
//这里面做了很多异步处理,最终同步得到处理结果
runResult = executorBiz.run(triggerParam);
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error(">>>>>>>>>>> xxl-job trigger error, please check if the executor[{}] is running.", address, e);
runResult = new ReturnT<String>(ReturnT.FAIL_CODE, ThrowableUtil.toString(e));
}
StringBuffer runResultSB = new StringBuffer(I18nUtil.getString("jobconf_trigger_run") + ":");
runResultSB.append("<br>address:").append(address);
runResultSB.append("<br>code:").append(runResult.getCode());
runResultSB.append("<br>msg:").append(runResult.getMsg());
runResult.setMsg(runResultSB.toString());
return runResult;
}
ExecutorBiz.run 方法我们说过了,是走的动态代理,和执行器进行通信,执行器执行结果也是异步处理完,才返回的,而这里看到的 run 方法是同步等待处理结果返回。
我们看下xxl-job是如何同步获取处理结果的:调度器向执行器发出消息后,该线程阻塞。等到执行器处理完毕后,将处理结果返回,唤醒被阻塞的线程,调用处拿到返回值。
动态代理代码如下:
//代理类中的触发调用
if (CallType.SYNC == callType) {
// future-response set
XxlRpcFutureResponse futureResponse = new XxlRpcFutureResponse(invokerFactory, xxlRpcRequest, null);
try {
// do invoke
client.asyncSend(finalAddress, xxlRpcRequest);
// future get
XxlRpcResponse xxlRpcResponse = futureResponse.get(timeout, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
if (
xxlRpcResponse.getErrorMsg() != null) {
throw new XxlRpcException(
xxlRpcResponse.getErrorMsg());
}
return xxlRpcResponse.getResult();
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.info(">>>>>>>>>>> xxl-rpc, invoke error, address:{}, XxlRpcRequest{}", finalAddress, xxlRpcRequest);
throw (e instanceof XxlRpcException)?e:new XxlRpcException(e);
} finally{
// future-response remove
futureResponse.removeInvokerFuture();
}
}
XxlRpcFutureResponse 类中实现了线程的等待,和线程唤醒的处理:
//返回结果,唤醒线程
public void setResponse(XxlRpcResponse response) {
this.response = response;
synchronized (lock) {
done = true;
lock.notifyAll();
}
}
@Override
public XxlRpcResponse get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException {
if (!done) {
synchronized (lock) {
try {
if (timeout < 0) {
//线程阻塞
lock.wait();
} else {
long timeoutMillis = (TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS==unit)?
timeout:TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.convert(timeout , unit);
lock.wait(timeoutMillis);
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw e;
}
}
}
if (!done) {
throw new XxlRpcException("xxl-rpc, request timeout at:"+ System.currentTimeMillis() +", request:" + request.toString());
}
return response;
}
有的同学可能会问了,调度器接收到返回结果,怎么确定唤醒哪个线程呢?
每一次远程调用,都会生成 uuid 的请求 id,这个 id 是在整个调用过程中一直传递的,就像一把钥匙,在你回家的的时候,拿着它就带开门。
这里拿着请求 id 这把钥匙,就能找到对应的 XxlRpcFutureResponse,然后调用 setResponse 方法,设置返回值,唤醒线程。
public void notifyInvokerFuture(String requestId, final XxlRpcResponse xxlRpcResponse){
// 通过requestId找到XxlRpcFutureResponse,
final XxlRpcFutureResponse futureResponse = futureResponsePool.get(requestId);
if (futureResponse == null) {
return;
}
if (
futureResponse.getInvokeCallback()!=null) {
// callback type
try {
executeResponseCallback(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
if (
xxlRpcResponse.getErrorMsg() != null) {
futureResponse.getInvokeCallback().onFailure(new XxlRpcException(
xxlRpcResponse.getErrorMsg()));
} else {
futureResponse.getInvokeCallback().onSuccess(xxlRpcResponse.getResult());
}
}
});
}catch (Exception e) {
logger.error(e.getMessage(), e);
}
} else {
// 里面调用lock的notify方法
futureResponse.setResponse(xxlRpcResponse);
}
// do remove
futureResponsePool.remove(requestId);
}
边栏推荐
- "How to connect the network" reading notes - Web server request and response (4)
- Les différents modèles imbriqués de listview et Pageview avec les conseils de flutter
- 2022-2028 global probiotics industry research and trend analysis report
- Jianzhi offer 09 realizes queue with two stacks
- Reading notes on how to connect the network - tcp/ip connection (II)
- 2022-2028 global seeder industry research and trend analysis report
- Global and Chinese market of bipolar generators 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
- 26. Delete duplicates in the ordered array (fast and slow pointer de duplication)
- UML 时序图[通俗易懂]
- UML sequence diagram [easy to understand]
猜你喜欢

26. Delete duplicates in the ordered array (fast and slow pointer de duplication)
Clion console output Chinese garbled code
el-table单选并隐藏全选框
回复评论的sql

2022-2028 global edible probiotic raw material industry research and trend analysis report
Web端自动化测试失败原因汇总
Nurse level JDEC addition, deletion, modification and inspection exercise

2022-2028 global small batch batch batch furnace industry research and trend analysis report
Mac platform forgets the root password of MySQL

HMS core helps baby bus show high-quality children's digital content to global developers
随机推荐
HMS core helps baby bus show high-quality children's digital content to global developers
Get the source code in the mask with the help of shims
165 webmaster online toolbox website source code / hare online tool system v2.2.7 Chinese version
Summary of the most comprehensive CTF web question ideas (updating)
The 14th five year plan and investment risk analysis report of China's hydrogen fluoride industry 2022 ~ 2028
Global and Chinese markets of water heaters in Saudi Arabia 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
"How to connect the network" reading notes - Web server request and response (4)
【leetcode】29. Divide two numbers
Report on investment analysis and prospect trend prediction of China's MOCVD industry Ⓤ 2022 ~ 2028
How do microservices aggregate API documents? This wave of show~
2022-2028 global industrial gasket plate heat exchanger industry research and trend analysis report
Tkinter Huarong Road 4x4 tutorial II
Ultimate bug finding method - two points
什么是权限?什么是角色?什么是用户?
Trees and graphs (traversal)
`Example of mask ` tool use
Four common methods of copying object attributes (summarize the highest efficiency)
LeetCode 74. Search 2D matrix
Global and Chinese trisodium bicarbonate operation mode and future development forecast report Ⓢ 2022 ~ 2027
C # use ffmpeg for audio transcoding
