当前位置:网站首页>Redis knowledge points & summary of interview questions
Redis knowledge points & summary of interview questions
2022-06-09 17:45:00 【Floating across the sea】
Redis Knowledge point & Interview question summary
Redis Basics
A brief introduction Redis!
Simply speaking Redis It's a use C Language development database , But unlike traditional databases Redis The data of is stored in memory , That is, it's a memory database , So the speed of reading and writing is very fast , therefore Redis Widely used in cache direction .
in addition ,Redis Besides caching , It is also often used for distributed locks , Even message queuing .
Redis A variety of data types are provided to support different business scenarios .Redis It also supports transactions 、 Persistence 、Lua Script 、 Multiple clustering schemes .
What are the common technology selection schemes of distributed cache ?
For distributed caching , The most commonly used ones are Memcached and Redis. however , I haven't seen it now. There are still projects to use Memcached To do caching , It's all direct use Redis.
Memcached It's the first thing that distributed caching came into being , More commonly used . later , With Redis The development of , People are slowly turning to more powerful Redis 了 .
Distributed cache mainly solves the problem that the capacity of stand-alone cache is limited by the server and can not save general information . because , Local caching is only valid in the current service , For example, if you deploy two identical services , There's no common cache data between them .
The way Redis and Memcached The difference and common ground of
Now companies generally use Redis To implement caching , and Redis I'm getting stronger and stronger ! however , understand Redis and Memcached The difference and common ground of , It helps us to choose the appropriate technology , To be able to do it with good reason !
Common ground :
- They're all memory based databases , It is generally used as a cache .
- There are expiration strategies .
- Both have very high performance .
difference :
- Redis Support for richer data types ( Support more complex application scenarios ).Redis It's not just about supporting simple k/v Data of type , It also provides list,set,zset,hash Such as data structure storage .Memcached Only the simplest k/v data type .
- Redis Support data persistence , Data in memory can be kept on disk , When you restart, you can load it again for use , and Memcached Store all the data in memory .
- Redis There are disaster recovery mechanisms . Because you can persist the data in the cache to the disk .
- Redis After the server memory is used up , You can put unused data on disk . however ,Memcached After the server memory is used up , It will report an exception directly .
- Memcached No native cluster mode , Need to rely on the client to write data to the cluster in pieces ; however Redis Now it's native support cluster Mode .
- Memcached Is a multithreaded , Non blocking IO Multiplexing network model ;Redis Use single threaded multiplexing IO Reuse model . (Redis 6.0 Introduced multithreading IO )
- Redis Support publish subscribe model 、Lua Script 、 Functions such as transaction , and Memcached I won't support it . also ,Redis Support more programming languages .
- Memcached The deletion strategy of expired data only uses lazy deletion , and Redis At the same time, inert deletion and periodic deletion are used .
I believe after I look at the comparison above , There is no reason why we can choose to use it Memcached As a distributed cache for your project .
What is the processing flow of cached data ?
As warm man number one , I made a sketch for you .
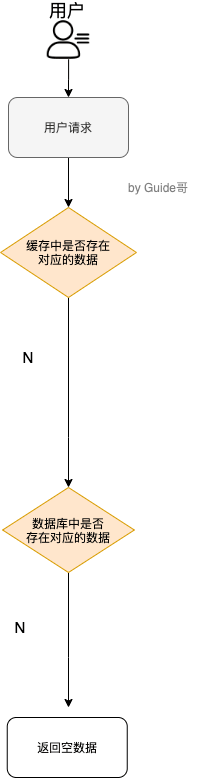
In a nutshell :
- If the data requested by the user is in the cache, it is returned directly .
- If it doesn't exist in the cache, it depends on whether it exists in the database .
- Update the data in the cache if it exists in the database .
- If it doesn't exist in the database, it will return null data .
Why use Redis/ Why cache ?
Simple , The main purpose of using cache is to improve the user experience and deal with more users .
Let's start with “ High performance ” and “ High concurrency ” Let's look at these two points .
[ Failed to transfer the external chain picture , The origin station may have anti-theft chain mechanism , It is suggested to save the pictures and upload them directly (img-BpqrsE6W-1654738289278)(https://javaguide.cn/assets/%E4%BD%BF%E7%94%A8%E7%BC%93%E5%AD%98%E4%B9%8B%E5%90%8E.05f09010.png)]
High performance :
Contrast to the above The picture I drew . Let's imagine this scenario :
If a user accesses some data in the database for the first time , This process is relatively slow , After all, it was read from the hard disk . however , if , If the data accessed by users belongs to high frequency data and will not change frequently , Then we can safely store the data accessed by the user in the cache .
What good is that ? That is to ensure that the next time users access the data, they can directly get it from the cache . Operation cache is direct operation memory , So it's pretty fast .
however , To keep the data in the database and cache consistent . If the corresponding data in the database changes after , Change the corresponding data in the cache synchronously !
High concurrency :
Generally like MySQL This kind of database QPS Probably all in 1w about (4 nucleus 8g) , But use Redis After caching, it's easy to reach 10w+, Even up to 30w+( Just stand alone redis The situation of ,redis The cluster will be higher ).
QPS(Query Per Second): The number of queries the server can execute per second ;
thus it can be seen , The number of database requests that the direct operation cache can bear is far greater than that of the direct access database , So we can consider transferring part of the data in the database to the cache , In this way, some of the user's requests will go directly to the cache without going through the database . , in turn, , We also improve the concurrency of the whole system .
Redis Except for caching , What else can be done ?
- Distributed lock : adopt Redis Distributed locking is a common way . Usually , We are all based on Redisson To implement distributed locking . Related reading :《 The king scheme in distributed lock - Redisson》open in new window.
- Current limiting : Usually by Redis + Lua Script to achieve current limiting . Related reading :《 I used it 6 Year of Redis Distributed current limiter , It can be said to be very powerful !》open in new window.
- Message queue :Redis Self contained list The data structure can be used as a simple queue .Redis 5.0 The addition of Stream Type of data structure is more suitable for message queuing . It is more similar to Kafka, There is the concept of theme and consumption group , Support message persistence and ACK Mechanism .
- Complex business scenarios : adopt Redis as well as Redis Expand ( such as Redisson) The data structure provided , We can easily complete many complex business scenarios, such as through bitmap Count active users 、 adopt sorted set Maintain leaderboards .
- …
Redis Can I do a message queue ?
Redis 5.0 A new data structure is added Stream It can be used as a message queue ,Stream Support :
- Release / A subscription model
- Consume by consumer group
- Message persistence ( RDB and AOF)
however , Compared with professional message queuing , There are still many deficiencies, such as the problem of message loss and accumulation . therefore , We usually recommend not to use Redis To do the message queue , You can choose some mature message queues in the market, such as RocketMQ、Kafka.
Recommended articles :Redis Three schemes of message queue (List、Streams、Pub/Sub)open in new window.
Redis Common data structures
You can install it on your own redis Or by redis Provided by the official website On-line redis Environmental Science open in new window.
[ Failed to transfer the external chain picture , The origin station may have anti-theft chain mechanism , It is suggested to save the pictures and upload them directly (img-uZvHtkh9-1654738289283)(https://javaguide.cn/assets/try-redis.7ac61820.png)]
string
- Introduce :string The data structure is simple key-value type . although Redis Yes, it is C Written language , however Redis Not used C String representation of , It's about building a kind of Simple dynamic string (simple dynamic string,SDS). Compared with C The native string of ,Redis Of SDS You can save not only text data, but also binary data , And the complexity of getting the length of the string is O(1)(C String is O(N)), besides ,Redis Of SDS API Is safe , No buffer overflow .
- Common commands :
set,get,strlen,exists,decr,incr,setexwait . - Application scenarios : It is commonly used in scenes where counting is required , For example, the number of user visits 、 Hot articles like the number of forwarding and so on .
Let's take a look at its use !
Basic operation of ordinary string :
127.0.0.1:6379> set key value # Set up key-value Type value
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> get key # according to key Get the corresponding value
"value"
127.0.0.1:6379> exists key # Judge a certain key Whether there is
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> strlen key # return key The length of the stored string value .
(integer) 5
127.0.0.1:6379> del key # Delete some key Corresponding value
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> get key
(nil)
Batch settings :
127.0.0.1:6379> mset key1 value1 key2 value2 # Batch settings key-value Type value
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> mget key1 key2 # Get more than one in batch key Corresponding value
1) "value1"
2) "value2"
Counter ( When the content of the string is an integer, you can use ):
127.0.0.1:6379> set number 1
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> incr number # take key The value of the number stored in is increased by one
(integer) 2
127.0.0.1:6379> get number
"2"
127.0.0.1:6379> decr number # take key Subtract one from the number stored in
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> get number
"1"
Be overdue ( The default is never expire ):
127.0.0.1:6379> expire key 60 # The data is in 60s After expired
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> setex key 60 value # The data is in 60s After expired (setex:[set] + [ex]pire)
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> ttl key # Check how long the data is overdue
(integer) 56
list
- Introduce :list That is Linked list . Linked list is a very common data structure , It is easy to insert and delete data elements, and can flexibly adjust the length of the linked list , But random access to the list is difficult . Many high-level programming languages have built-in implementation of linked lists, such as Java Medium LinkedList, however C The language doesn't implement the linked list , therefore Redis It realizes its own linked list data structure .Redis Of list The implementation of is a Double linked list , That is, it can support reverse lookup and traversal , Easier to operate , But it brings some extra memory overhead .
- Common commands :
rpush,lpop,lpush,rpop,lrange,llenetc. . - Application scenarios : Publish and subscribe to or message queuing 、 The slow query .
Let's take a look at its use !
adopt rpush/lpop Implementation queue :
127.0.0.1:6379> rpush myList value1 # towards list The head of ( On the right ) Additive elements
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> rpush myList value2 value3 # towards list The head of ( Far right ) Add multiple elements
(integer) 3
127.0.0.1:6379> lpop myList # take list Tail of ( Leftmost ) Take out the elements
"value1"
127.0.0.1:6379> lrange myList 0 1 # Check the corresponding subscript list list , 0 by start,1 by end
1) "value2"
2) "value3"
127.0.0.1:6379> lrange myList 0 -1 # Look at all the elements in the list ,-1 Represents the last one
1) "value2"
2) "value3"
adopt rpush/rpop Implementation stack :
127.0.0.1:6379> rpush myList2 value1 value2 value3
(integer) 3
127.0.0.1:6379> rpop myList2 # take list The head of ( Far right ) Take out the elements
"value3"
I specially drew a picture for my friends to understand :

adopt lrange View the list elements corresponding to the subscript range :
127.0.0.1:6379> rpush myList value1 value2 value3
(integer) 3
127.0.0.1:6379> lrange myList 0 1 # Check the corresponding subscript list list , 0 by start,1 by end
1) "value1"
2) "value2"
127.0.0.1:6379> lrange myList 0 -1 # Look at all the elements in the list ,-1 Represents the last one
1) "value1"
2) "value2"
3) "value3"
adopt lrange command , You can be based on list Realize paging query , Very high performance !
adopt llen Check the list length :
127.0.0.1:6379> llen myList
(integer) 3
hash
- Introduce :hash Be similar to JDK1.8 Before HashMap, The internal implementation is similar ( Array + Linked list ). however ,Redis Of hash More optimizations . in addition ,hash It's a string Type of field and value Mapping table , Ideal for storing objects , When following up , You can simply change the value of a field in this object . For example, we can hash Data structure to store user information , Product information, etc .
- Common commands :
hset,hmset,hexists,hget,hgetall,hkeys,hvalsetc. . - Application scenarios : The storage of object data in the system .
Let's take a look at its use !
127.0.0.1:6379> hmset userInfoKey name "guide" description "dev" age "24"
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> hexists userInfoKey name # see key Corresponding value Whether the field specified in the .
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> hget userInfoKey name # Gets the value of the specified field stored in the hash table .
"guide"
127.0.0.1:6379> hget userInfoKey age
"24"
127.0.0.1:6379> hgetall userInfoKey # Gets the specified in the hash table key All fields and values of
1) "name"
2) "guide"
3) "description"
4) "dev"
5) "age"
6) "24"
127.0.0.1:6379> hkeys userInfoKey # obtain key list
1) "name"
2) "description"
3) "age"
127.0.0.1:6379> hvals userInfoKey # obtain value list
1) "guide"
2) "dev"
3) "24"
127.0.0.1:6379> hset userInfoKey name "GuideGeGe" # Modify the value of a field
127.0.0.1:6379> hget userInfoKey name
"GuideGeGe"
set
- Introduce : set Be similar to Java Medium
HashSet.Redis Medium set A type is an unordered set , There is no sequence of elements in the collection . When you need to store a list of data , You don't want duplicate data ,set Is a good choice , also set Provides a way to determine whether a member is in a set Important interfaces within a collection , This is also list What cannot be provided . Can be based on set Easy intersection 、 Combine 、 Operation of difference set . such as : You can store all the followers of a user in a collection , Put all its fans in a collection .Redis Can be very convenient to achieve such as common concern 、 Common fans 、 Common preferences and other functions . This process is also the process of intersection . - Common commands :
sadd,spop,smembers,sismember,scard,sinterstore,sunionetc. . - Application scenarios : The data that needs to be stored can not be repeated, and the intersection and union of multiple data sources need to be obtained
Let's take a look at its use !
127.0.0.1:6379> sadd mySet value1 value2 # Add elements to it
(integer) 2
127.0.0.1:6379> sadd mySet value1 # Duplicate elements are not allowed
(integer) 0
127.0.0.1:6379> smembers mySet # see set All the elements in
1) "value1"
2) "value2"
127.0.0.1:6379> scard mySet # see set The length of
(integer) 2
127.0.0.1:6379> sismember mySet value1 # Check if an element exists set in , Only single element can be received
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> sadd mySet2 value2 value3
(integer) 2
127.0.0.1:6379> sinterstore mySet3 mySet mySet2 # obtain mySet and mySet2 The intersection of and stored in mySet3 in
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> smembers mySet3
1) "value2"
sorted set
- Introduce : and set comparison ,sorted set Added a weight parameter score, To enable elements in a collection to press score Arrange in order , You can also use score To get a list of elements . It's kind of like Java in HashMap and TreeSet The combination of .
- Common commands :
zadd,zcard,zscore,zrange,zrevrange,zremetc. . - Application scenarios : Scenarios where data needs to be sorted according to a certain weight . For example, in the live system , The real-time ranking information includes the list of online users in the live room , List of gifts , Barrage news ( It can be understood as message ranking by message dimension ) Etc .
127.0.0.1:6379> zadd myZset 3.0 value1 # Add elements to sorted set in 3.0 For weight
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> zadd myZset 2.0 value2 1.0 value3 # Add more than one element at a time
(integer) 2
127.0.0.1:6379> zcard myZset # see sorted set The number of elements in
(integer) 3
127.0.0.1:6379> zscore myZset value1 # View a certain value The weight of
"3"
127.0.0.1:6379> zrange myZset 0 -1 # Output the elements of a range in sequence ,0 -1 Represents the output of all elements
1) "value3"
2) "value2"
3) "value1"
127.0.0.1:6379> zrange myZset 0 1 # Output the elements of a range in sequence ,0 by start 1 by stop
1) "value3"
2) "value2"
127.0.0.1:6379> zrevrange myZset 0 1 # Output the elements of a range in reverse order ,0 by start 1 by stop
1) "value1"
2) "value2"
bitmap
- Introduce : bitmap What is stored is a continuous binary number (0 and 1), adopt bitmap, Just one bit Bit to indicate the value or state of an element ,key It's the corresponding element itself . We know 8 individual bit Can form a byte, therefore bitmap Itself will greatly save storage space .
- Common commands :
setbit、getbit、bitcount、bitop - Application scenarios : Suitable for saving status information ( For example, whether to check in 、 Log in …) And need to further analyze these information . Such as user check-in 、 Active users 、 User behavior statistics ( For example, have you ever liked a video ).
# SETBIT Will return the value of the previous bit ( The default is 0) This will generate 7 bits
127.0.0.1:6379> setbit mykey 7 1
(integer) 0
127.0.0.1:6379> setbit mykey 7 0
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> getbit mykey 7
(integer) 0
127.0.0.1:6379> setbit mykey 6 1
(integer) 0
127.0.0.1:6379> setbit mykey 8 1
(integer) 0
# adopt bitcount Statistics are set to 1 The number of bits .
127.0.0.1:6379> bitcount mykey
(integer) 2
For some of the scenarios mentioned above , Further explanation here .
Use scenario 1 : User behavior analysis Many websites analyze your preferences , You need to study what you like .
# Record your favorite 001 Little sister
127.0.0.1:6379> setbit beauty_girl_001 uid 1
Use scenario 2 : Count active users
Use time as key, And then the user ID by offset, If the day is active, set to 1
So how do I calculate a certain number of days / month / Active users in ( Let's make an appointment for the time being , It is called active as long as one day is online in the statistical time ), Please come next redis The order of
# For one or more strings that hold binary bits key Perform bit operation , And save the result to destkey On .
# BITOP Command support AND 、 OR 、 NOT 、 XOR Any one of these four operations
BITOP operation destkey key [key ...]
Initialization data :
127.0.0.1:6379> setbit 20210308 1 1
(integer) 0
127.0.0.1:6379> setbit 20210308 2 1
(integer) 0
127.0.0.1:6379> setbit 20210309 1 1
(integer) 0
Statistics 20210308~20210309 Total active users : 1
127.0.0.1:6379> bitop and desk1 20210308 20210309
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> bitcount desk1
(integer) 1
Statistics 20210308~20210309 Number of online active users : 2
127.0.0.1:6379> bitop or desk2 20210308 20210309
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> bitcount desk2
(integer) 2
Use scenario three : User online status
For obtaining or counting users' online status , Use bitmap It is a space saving and efficient method .
Just one key, And then the user ID by offset, If online, set to 1, If you are not online, set it to 0.
Redis Threading model
Redis Do you understand the single thread model ?
Redis be based on Reactor Pattern to design and develop their own set of efficient event processing model (Netty The thread model is also based on Reactor Pattern ,Reactor Patterns are high performance IO Cornerstone ), This set of event handling models corresponds to Redis File event handler in (file event handler). Due to the file event handler (file event handler) It runs in a single thread mode , So we generally say Redis It is a single-threaded model .
Since it's a single thread , So how to monitor a large number of client connections ?
Redis adopt IO Multiplexing program To listen for a large number of connections from clients ( Or monitoring multiple socket), It will be interested in the event and type ( read 、 Write ) Register in the kernel and listen for each event .
The benefits are obvious : I/O Multiplexing technology allows Redis There's no need to create extra threads to listen for a large number of connections from clients , Reduce the consumption of resources ( and NIO Medium Selector It's like a component ).
in addition , Redis The server is an event driver , The server needs to handle two types of events :1. Document events ; 2. Time event .
Time events don't take much time to understand , What we contact most is still Document events ( Client to read and write operations , It involves a series of network communications ).
《Redis Design and implementation 》 There is a paragraph about document events , I think it's pretty good .
Redis be based on Reactor Pattern develops its own network event processor : This processor is called the file event handler (file event handler). The file event handler uses I/O Multiplexing (multiplexing) Program to listen to multiple sockets at the same time , And associate different event handlers for the socket according to the tasks currently performed by the socket .
When the listening socket is ready to perform the connection answer (accept)、 Read (read)、 write in (write)、 Turn off close (close) When waiting for operation , The file event corresponding to the operation will generate , At this time, the file event handler will call the event handler associated with the socket to handle these events .
Although the file event handler runs in a single thread , But by using I/O Multiplexer to listen for multiple sockets , The file event processor has realized the high performance network communication model , It can also be very good with Redis Other modules in the server also run in a single thread mode for docking , This keeps Redis The simplicity of internal single thread design .
It can be seen that , File event handler (file event handler) Mainly including 4 Parts of :
- Multiple socket( Client connection )
- IO Multiplexing program ( Key to supporting multiple client connections )
- File event dispatcher ( take socket Associated with the corresponding event processor )
- Event handler ( Connect to answer processor 、 Command request processor 、 Command reply processor )
[ Failed to transfer the external chain picture , The origin station may have anti-theft chain mechanism , It is suggested to save the pictures and upload them directly (img-hhkoFjK1-1654738289289)(https://javaguide.cn/assets/redis%E4%BA%8B%E4%BB%B6%E5%A4%84%E7%90%86%E5%99%A8.66ac2f3d.png)]
《Redis Design and implementation :12 Chapter 》
Redis6.0 Why not use multithreading before ?
Although I say Redis It is a single-threaded model , however , actually ,Redis stay 4.0 Later versions have added multithreading support .
[ Failed to transfer the external chain picture , The origin station may have anti-theft chain mechanism , It is suggested to save the pictures and upload them directly (img-aQVW0A8i-1654738289290)(https://javaguide.cn/assets/redis4.0-more-thread.6f35d9c0.png)]
however ,Redis 4.0 The added multithreading is mainly for the command of deleting large key value pairs , Using these commands will use threads other than the main process “ Asynchronous processing ”.
In general ,Redis 6.0 Before, it was mainly single thread processing .
that ,Redis6.0 Why not use multithreading before ?
I think the main reasons are as follows 3 individual :
- Single threaded programming is easy and easier to maintain ;
- Redis The performance bottleneck is not CPU , Mainly in memory and network ;
- There will be deadlock in multithreading 、 Thread context switch and other issues , It can even affect performance .
Redis6.0 Why did we introduce multithreading ?
Redis6.0 The main purpose of introducing multithreading is to improve the network IO Read and write performance , Because this is Redis A performance bottleneck in (Redis The bottleneck is mainly limited by memory and network ).
although ,Redis6.0 Introduced multithreading , however Redis Multithreading is only used in time-consuming operations such as reading and writing network data , The execution command is still executed in a single thread sequence . therefore , You don't have to worry about thread safety .
Redis6.0 Multithreading is disabled by default , Use only the main thread . To open it, you need to modify redis The configuration file redis.conf :
io-threads-do-reads yes
When multithreading is turned on , You also need to set the number of threads , Otherwise it won't work . It also needs to be modified redis The configuration file redis.conf :
io-threads 4 # Suggestions on the official website 4 The recommended setting for the core machine is 2 or 3 Threads ,8 The recommended setting for kernel is 6 Threads
Recommended reading :
- Redis 6.0 New characteristics - Multithreaded concatenation 13 ask !open in new window
- Why? Redis Choose a single threaded model open in new window
Redis memory management
Redis What's the use of setting an expiration time for cached data ?
In general , When we set the stored cache data, we will set an expiration time . Why? ?
Because memory is limited , If all the data in the cache is kept all the time , Minutes directly Out of memory.
Redis It has the function of setting the expiration time for the cached data , such as :
127.0.0.1:6379> exp key 60 # The data is in 60s After expired
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> setex key 60 value # The data is in 60s After expired (setex:[set] + [ex]pire)
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> ttl key # Check how long the data is overdue
(integer) 56
Be careful :Redis In addition to the string type, it has its own unique command to set the expiration time setex Outside , Other methods depend on expire Command to set the expiration time . in addition , persist The command can remove the expiration time of a key .
Expiration time not only helps to reduce memory consumption , Is there anything else to use ?
A lot of times , Our business scenario is that we need a certain data to exist only in a certain period of time , For example, our SMS verification code may only be in 1 Valid in minutes , User logged in token Maybe only in 1 Within days .
If you use a traditional database to process , Generally, it's self judgment that is overdue , It's more cumbersome and much worse in performance .
Redis How to judge whether the data is out of date ?
Redis Through an out of date dictionary ( It can be seen as hash surface ) To save the expiration time of the data . Key points to expired Dictionaries Redis In the database key( key ), The value of the expired dictionary is a long long Type integer , This integer holds key The expiration time of the database key pointed to ( Millisecond precision UNIX Time stamp ).

Expired dictionaries are stored in redisDb In this structure :
typedef struct redisDb {
...
dict *dict; // Database key space , All key value pairs in the database are saved
dict *expires // Out of date Dictionary , Save the expiration time of the key
...
} redisDb;
Do you know how to delete expired data ?
If you set up a batch of key Only survive 1 minute , that 1 Minutes later ,Redis How to deal with these key What about deleting ?
There are two common deletion strategies for expired data ( important ! What you need to think about when you build your own cache wheel ):
- Lazy deletion : It's just taking it out key When the data is expired . That's right CPU The friendliest , But it can cause too many expiration key Not deleted .
- Delete periodically : Take a batch at regular intervals key Execute delete expired key operation . also ,Redis The underlying layer will reduce the number of deletions by limiting the duration and frequency of the deletion CPU The effect of time .
Regular deletion is more memory friendly , Inert delete on CPU More friendly . Each has its own merits , therefore Redis It's using Delete periodically + inert / Lazy delete .
however , Just by giving key There is still a problem setting expiration time . Because there may still be periodic deletion and lazy deletion, many expiration dates are missed key The situation of . This leads to a large number of expired key Pile up in memory , And then Out of memory 了 .
How to solve this problem ? The answer is :Redis Memory obsolescence mechanism .
Redis Do you understand the memory obsolescence mechanism ?
Related issues :MySQL Are there in 2000w data ,Redis The only known 20w The data of , How to ensure Redis The data in is hot data ?
Redis Provide 6 A data culling strategy :
- volatile-lru(least recently used): From the set of data for which the expiration time has been set (server.db[i].expires) Select the least recently used data in
- volatile-ttl: From the set of data for which the expiration time has been set (server.db[i].expires) To select the data to be expired
- volatile-random: From the set of data for which the expiration time has been set (server.db[i].expires) In the arbitrary selection of data elimination
- allkeys-lru(least recently used): When the memory is not enough to hold the newly written data , In key space , Remove the least recently used key( This is the most commonly used )
- allkeys-random: From the data set (server.db[i].dict) In the arbitrary selection of data elimination
- no-eviction: Exclusion data , That is, when the memory is not enough to hold the newly written data , Error will be reported in new write operation . This should not be used !
4.0 The following two types are added after the version :
- volatile-lfu(least frequently used): From the set of data for which the expiration time has been set (server.db[i].expires) Select the least frequently used data to eliminate
- allkeys-lfu(least frequently used): When the memory is not enough to hold the newly written data , In key space , Remove the least frequently used key
Redis Persistence mechanism
How to guarantee Redis Data can be recovered by restarting after being hung up ?
Many times we need to persist data, that is, write the data in memory to the hard disk , Most of the reason is to reuse the data later ( For example, restart the machine 、 Recover data after machine failure ), Or backup data to a remote location to prevent system failure .
Redis differ Memcached It's very important that ,Redis Support persistence , And it supports two different persistence operations .Redis One of the persistence methods of is snapshot (snapshotting,RDB), Another way is to just append files (append-only file, AOF). These two methods have their own advantages , I'll elaborate on what these two persistence methods are , How to use it? , How to choose your own persistence method .
What is? RDB Persistence ?
Redis You can create a snapshot to get a copy of the data stored in memory at a certain point in time .Redis After creating the snapshot , You can back up the snapshot , You can replicate the snapshot to another server to create a server copy with the same data (Redis Master-slave structure , Mainly used to improve Redis performance ), You can also leave the snapshot in place for use when you restart the server .
Snapshot persistence is Redis The default persistence method , stay redis.conf The configuration file has this configuration by default :
save 900 1 # stay 900 second (15 minute ) after , If at least 1 individual key change ,Redis Will trigger automatically BGSAVE Command create snapshot .
save 300 10 # stay 300 second (5 minute ) after , If at least 10 individual key change ,Redis Will trigger automatically BGSAVE Command create snapshot .
save 60 10000 # stay 60 second (1 minute ) after , If at least 10000 individual key change ,Redis Will trigger automatically BGSAVE Command create snapshot .
What is? AOF Persistence ?
Compared to snapshot persistence ,AOF Persistence is better in real time , So it has become a mainstream persistence solution . By default Redis It's not turned on AOF(append only file) Persistence of the way , Can pass appendonly Parameter on :
appendonly yes
Turn on AOF Every execution will change after persistence Redis Commands for data in ,Redis The command will be written to the memory cache server.aof_buf in , And then based on appendfsync Configuration to determine when to synchronize it to the disk AOF file .
AOF The location and RDB The location of the files is the same , It's all through dir Parameter setting , The default file name is appendonly.aof.
stay Redis There are three different profiles for AOF Persistence mode , They are :
appendfsync always # Write every time a data change occurs AOF file , This will seriously reduce Redis The speed of
appendfsync everysec # Sync every second , Explicitly synchronize multiple write commands to the hard disk
appendfsync no # Let the operating system decide when to synchronize
In order to balance data and write performance , Users can consider appendfsync everysec Options , Give Way Redis Synchronize once per second AOF file ,Redis Performance is almost unaffected . And even if there is a system crash , Users can only lose data generated within one second at most . When the hard disk is busy performing write operations ,Redis It will also gracefully slow down its own speed to adapt to the maximum write speed of the hard disk .
relevant issue :
- Redis Of AOF The way #783open in new window
- Redis AOF Rewrite description is not accurate #1439open in new window
AOF Do you understand ?
AOF Rewriting can produce a new AOF file , This new AOF Documents and original AOF The database state saved by the file is the same , But smaller .
AOF Rewriting is an ambiguous name , This function is realized by reading the key value pairs in the database , The procedure does not need to be for existing AOF File any read in 、 Analyze or write operations .
In execution BGREWRITEAOF On command ,Redis The server will maintain a AOF Rewrite buffer , This buffer creates a new... In the child process AOF During the documentation , Record all write commands executed by the server . When the subprocess is finished creating a new AOF After the work of the document , The server appends everything in the rewrite buffer to the new AOF End of file , Make new AOF The database state saved by the file is consistent with the existing database state . Last , The server uses the new AOF Replace the old file with AOF file , To complete AOF File rewrite operation .
Redis 4.0 What optimizations have been made for the persistence mechanism ?
Redis 4.0 Start supporting RDB and AOF Mixed persistence of ( Off by default , You can use the configuration item aof-use-rdb-preamble Turn on ).
If you turn on blending persistence ,AOF When rewriting, put RDB The content of AOF Beginning of file . The advantage of this is that it can be combined with RDB and AOF The advantages of , Load quickly without losing too much data . Of course, there are shortcomings , AOF Inside RDB Part of it is that the compression format is no longer AOF Format , Poor readability .
Official document address :https://redis.io/topics/persistence

Redis Business
How to use Redis Business ?
Redis Can pass MULTI,EXEC,DISCARD and WATCH Wait for the command to implement the transaction (transaction) function .
> MULTI
OK
> SET USER "Guide Brother "
QUEUED
> GET USER
QUEUED
> EXEC
1) OK
2) "Guide Brother "
Use MULTIopen in new window After the command, you can enter multiple commands .Redis These orders will not be executed immediately , It's about putting them in a queue , When calling the EXECopen in new window The command will execute all commands .
This is the process :
- Start business (
MULTI). - Order to join the team ( The batch operation Redis The order of , fifo (FIFO) Sequential execution ).
- Perform transactions (
EXEC).
You can also pass DISCARDopen in new window Command to cancel a transaction , It will clear all the commands saved in the transaction queue .
> MULTI
OK
> SET USER "Guide Brother "
QUEUED
> GET USER
QUEUED
> DISCARD
OK
WATCHopen in new window Command is used to listen for the specified key , When calling EXEC When a transaction is ordered to execute , If one is WATCH If the key monitored by the command is modified , The whole transaction will not be executed , Direct return failure .
> WATCH USER
OK
> MULTI
> SET USER "Guide Brother "
OK
> GET USER
Guide Brother
> EXEC
ERR EXEC without MULTI
Redis Official website related introduction https://redis.io/topics/transactionsopen in new window as follows :

Redis Support atomicity ?
Redis Transaction is different from the transaction of relational database that we usually understand . We know that transactions have four characteristics : 1. Atomicity ,2. Isolation, ,3. persistence ,4. Uniformity .
- Atomicity (Atomicity): Transactions are the smallest unit of execution , Division is not allowed . The atomicity of the transaction ensures that the action is either complete , Or it doesn't work at all ;
- Isolation, (Isolation): When accessing the database concurrently , One user's transaction is not interfered by other transactions , The database between concurrent transactions is independent ;
- persistence (Durability): After a transaction is committed . Its changes to the data in the database are persistent , Even if the database fails, it should not have any impact .
- Uniformity (Consistency): Before and after the execution of the transaction , Data consistency , Multiple transactions read the same data with the same result ;
Redis The transaction runs incorrectly , Except for the command with error during execution , Other commands can be executed normally . also ,Redis Rollback is not supported (roll back) Operation of the . therefore ,Redis Transactions do not satisfy atomicity ( And it doesn't satisfy persistence ).
Redis The official website also explained why he does not support rollback . In a nutshell Redis Developers don't feel the need to support rollback , It's simpler, more convenient and better performance .Redis Even if the error is found in the development process, the developer should feel that it is not in the process of executing the production command .
[ Failed to transfer the external chain picture , The origin station may have anti-theft chain mechanism , It is suggested to save the pictures and upload them directly (img-xuKfDWbr-1654738289297)(https://javaguide.cn/assets/redis-rollBack.89c51afa.png)]
You can take Redis The transaction in is understood as :Redis Transactions provide the ability to package multiple command requests . then , Then execute all the packaged commands in order , And it won't be interrupted .
Besides not satisfying atomicity , Every command in a transaction is associated with Redis The server performs network interaction , This is a waste of resources . It is clear that multiple commands can be executed in batch at a time , This kind of operation is really incomprehensible .
therefore ,Redis Transactions are not recommended for daily development .
relevant issue :
- issue452: About Redis The problem that a transaction does not satisfy atomicity open in new window .
- Issue491: About redis No transaction rollback ?open in new window
How to solve Redis Defects in transactions ?
Redis from 2.6 The version starts to support execution Lua Script , Its functions are very similar to transactions . We can use Lua Script to batch execute multiple Redis command , these Redis The command will be submitted to Redis The server completes the execution at one time , Greatly reduce network overhead .
a section Lua A script can be executed as a command , a section Lua There will be no other scripts or Redis The order is executed at the same time , It ensures that the operation will not be inserted or disturbed by other instructions .
If Lua An error occurred while the script was running and ended halfway , The command after an error is not executed . also , The command executed before the error cannot be undone . therefore , Strictly speaking , adopt Lua Script to execute in batches Redis Commands are also not atomic .
in addition ,Redis 7.0 Added Redis functionsopen in new window characteristic , You can take Redis functions As a ratio Lua More powerful scripts .
Redis performance optimization
Redis bigkey
What is? bigkey?
Simply speaking , If one key Corresponding value The memory occupied is relatively large , So this one key Can be seen as bigkey. How big is it ? There is a reference standard that is not particularly precise :string Type of value exceed 10 kb, Composite types value Contains more than 5000 individual ( For compound types value Come on , It doesn't necessarily contain more elements , The more memory it takes up ).
bigkey What's the harm ?
In addition to consuming more memory space ,bigkey It will also have a great impact on the performance .
therefore , We should try to avoid writing bigkey!
How to discover bigkey?
1、 Use Redis Self contained --bigkeys Parameter to find .
# redis-cli -p 6379 --bigkeys
# Scanning the entire keyspace to find biggest keys as well as
# average sizes per key type. You can use -i 0.1 to sleep 0.1 sec
# per 100 SCAN commands (not usually needed).
[00.00%] Biggest string found so far '"ballcat:oauth:refresh_auth:f6cdb384-9a9d-4f2f-af01-dc3f28057c20"' with 4437 bytes
[00.00%] Biggest list found so far '"my-list"' with 17 items
-------- summary -------
Sampled 5 keys in the keyspace!
Total key length in bytes is 264 (avg len 52.80)
Biggest list found '"my-list"' has 17 items
Biggest string found '"ballcat:oauth:refresh_auth:f6cdb384-9a9d-4f2f-af01-dc3f28057c20"' has 4437 bytes
1 lists with 17 items (20.00% of keys, avg size 17.00)
0 hashs with 0 fields (00.00% of keys, avg size 0.00)
4 strings with 4831 bytes (80.00% of keys, avg size 1207.75)
0 streams with 0 entries (00.00% of keys, avg size 0.00)
0 sets with 0 members (00.00% of keys, avg size 0.00)
0 zsets with 0 members (00.00% of keys, avg size 0.00
From the result of this command , We can see that : This command will scan (Scan) Redis All in key , Would be right Redis Has a little impact on the performance of . also , This method can only find out every data structure top 1 bigkey( The most memory intensive string data type , Composite data types with the most elements ).
2、 analysis RDB file
Through analysis RDB File to find big key. The premise of this scheme is your Redis It's using RDB Persistence .
There are ready-made codes on the Internet / Tools can be used directly :
- redis-rdb-toolsopen in new window :Python Written in language to analyze Redis Of RDB Tools for snapshot files
- rdb_bigkeysopen in new window : Go Written in language to analyze Redis Of RDB Tools for snapshot files , Better performance .
A lot of key Focus on expiration issues
I mentioned above : For overdue key,Redis It's using Delete periodically + inert / Lazy delete Strategy .
Periodically delete during execution , If you suddenly encounter a large number of expired key Words , Client requests must wait for periodic cleanup to expire key Task thread execution completed , Because the regular task thread is in Redis Executed in the main thread . This leads to the client request can not be processed in time , The response speed will be slow .
How to solve it ? Here are two common methods :
- to key Set random expiration time .
- Turn on lazy-free( Lazy deletion / Delay release ) .lazy-free Characteristic is Redis 4.0 Introduced , It means to let Redis Use asynchronous mode to delay release key Memory used , Leave the operation to a separate child thread , Avoid blocking the main thread .
Personal suggestion whether it is turned on or not lazy-free, We all try to give key Set random expiration time .
Redis Production problems
Cache penetration
What is cache penetration ?
Cache penetration is simply a large number of requests key It doesn't exist in the cache at all , Causes the request to go directly to the database , There's no caching at all . for instance : Some hacker deliberately creates something that doesn't exist in our cache key Make a lot of requests , Causes a large number of requests to fall to the database .
What is the processing flow of cache penetration ?
As shown in the figure below , The user's request must finally run to the database to query again .

What are the solutions ?
The most basic thing is to check the parameters first , Some illegal parameter requests directly throw exception information back to the client . For example, query database id Not less than 0、 When the format of the incoming mailbox is wrong, it will directly return the error message to the client and so on .
1) Invalid cache key
If neither the cache nor the database can find one key I'll write one of the data to Redis Go to and set expiration time , The specific command is as follows : SET key value EX 10086 . This way we can solve the request key An infrequent situation , If hackers attack maliciously , Each time you build a different request key, It can lead to Redis A large number of invalid key . Obviously , This kind of plan can't solve the problem fundamentally . If we have to solve the problem of penetration in this way , Try to invalidate key The expiration time of is set a little shorter, such as 1 minute .
in addition , Say more here , In general, this is how we design key Of : Table name : Name : Primary key name : Primary key value .
If you use Java Code display , It's about the following :
public Object getObjectInclNullById(Integer id) {
// Get the data from the cache
Object cacheValue = cache.get(id);
// The cache is empty
if (cacheValue == null) {
// Get... From the database
Object storageValue = storage.get(key);
// Caching empty objects
cache.set(key, storageValue);
// If the stored data is empty , You need to set an expiration time (300 second )
if (storageValue == null) {
// Expiration time must be set , Otherwise, there is a risk of being attacked
cache.expire(key, 60 * 5);
}
return storageValue;
}
return cacheValue;
}
2) The bloon filter
The bloon filter is a very magical data structure , Through it, we can easily judge whether a given data exists in the mass data . What we need is judgment key Is it legal , Does it feel like the bloon filter is the one we're looking for “ people ”.
This is exactly how it is done : Store the values of all possible requests in the bloom filter , When the user requests to come , First judge whether the value of the request from the user exists in the bloom filter . If it doesn't exist , Directly return the request parameter error information to the client , If there is one, the following process will be followed .
The flow chart of cache processing after adding bloon filter is as follows .

however , It should be noted that there may be misjudgment in the bloom filter . In conclusion, it is : The bloom filter says that an element exists , A small probability will miscalculate . The bloom filter says that an element is not there , Then this element must not be in .
Why is there a misjudgment ? We have to start with the principle of the bloon filter !
So let's see , When an element is added to the bloom filter , What will be done :
- Use hash function in bloom filter to calculate element value , Get hash value ( There are several hash functions that get a few hash values ).
- According to the hash value , Set the value of the corresponding subscript to 1.
Let's take another look , When we need to determine whether an element exists in the bloom filter , What will be done :
- Do the same hash calculation for the given element again ;
- After getting the value, judge whether each element in the digit group is 1, If the value is 1, So this value is in the bloom filter , If there is a value that is not 1, Indicates that the element is not in the bloom filter .
then , There must be such a situation : Different strings may be hashed out in the same place . ( We can increase the size of bit group or adjust our hash function to reduce the probability )
More about the bloon filter can be found in my original :《 Don't know about bloon filter ? I'll make it clear to you !》open in new window , Strongly recommend , I don't think I can find such a clear article on the Internet .
Cache avalanche
What is a cache avalanche ?
I find the name cache avalanche interesting , ha-ha .
actually , Cache avalanche describes such a simple scene : Cache failure in a large area at the same time , The subsequent requests fall directly onto the database , Cause the database to bear a large number of requests in a short time . It's like an avalanche , The trend of destroying the withered and decaying , You can imagine the pressure of the database , It's possible that you've been knocked down by so many requests .
for instance : There is something wrong with the cache module of the system, for example, it is unavailable due to downtime . Cause all access to the system , We have to go to the database .
Another scenario to cache avalanches is : There's a lot of access to data ( Hot cache ) Large area failure at a certain time , As a result, the corresponding request falls directly on the database . In this case , There are several solutions :
for instance : The second kill begins 12 An hour ago , We have a lot of goods in the store Redis in , The cache expiration time set is also 12 Hours , So when the second kill starts , The access to these second kill products is invalid . The resulting situation is , The corresponding request goes directly to the database , It's like an avalanche .
What are the solutions ?
in the light of Redis Service unavailability :
- use Redis colony , To avoid problems on a single machine, the entire cache service cannot be used .
- Current limiting , Avoid processing large amounts of requests at the same time .
In case of hotspot cache failure :
- Set different expiration time, such as randomly setting cache expiration time .
- Cache never fails .
How to ensure the consistency of cache and database data ?
You can talk a lot about it , But I don't think it's really necessary ( Low voice BB: I don't quite understand many solutions ). Personally, I think after introducing the cache , If it's for a short period of inconsistency , Choose to make the system design more complex , No need at all .
The following is a separate answer to Cache Aside Pattern( Bypass caching mode ) To have a chat .
Cache Aside Pattern Write request encountered in is like this : to update DB, And then delete cache .
If the database update is successful , If the cache deletion step fails , In short, there are two solutions :
- Cache expiration time is shorter ( Not recommended , Treat the symptoms, not the root cause ) : We make the expiration time of cached data shorter , In this way, the cache will load data from the database . in addition , This solution is not applicable to the scenario of operating the cache first and then the database .
- increase cache Update retry mechanism ( Commonly used ): If cache If the cache deletion fails due to the current unavailability of the service , We try again sometime , The number of retries can be set by yourself . If you try again or fail again , We can fail to update the current key Put in the queue , After the cache service is available , Then the corresponding... In the cache key Delete it .
Recommended articles : Cache and database consistency issues , Just read this one - Water drops and silver bullets open in new window
Reference resources
- 《Redis Development and operations 》
- 《Redis Design and implementation 》
- Redis Command summary :http://Redisdoc.com/string/set.html
- Easy to understand Redis Basic course of data structure :https://juejin.im/post/5b53ee7e5188251aaa2d2e16open in new window
- WHY Redis choose single thread (vs multi threads): https://medium.com/@jychen7/sharing-redis-single-thread-vs-multi-threads-5870bd44d153
边栏推荐
- Running the code, I want to add a progress bar to see the running progress of the following code in real time. How can I break it?
- 【玩转华为云】华为云零代码开发图片压缩工具
- 运行代码,想加个进度条实时看以下代码运行进度,怎么破?
- DAY6-T1345&T39 -2022-01-21-非自己作答
- The sisters sit in the bow of the boat while the brothers walk ashore
- 【玩转华为云】基于华为云图像识别标签实战
- Gesture interaction across the space, performing "handy" in the real world
- Traversal and cueing of binary tree
- 14届数独-真题标准数独-Day 5-20220120
- iis怎么打开md文件(is无法打开md文件报错怎么解决)
猜你喜欢

MySQL并行复制(MTS)原理(完整版)

go-zero 微服务实战系列(二、服务拆分)

Construction of sheep (rare species) bsgenome reference genome

二叉树遍历与线索化

Word tutorial, how to change line spacing in word?

一些有趣的B+树优化实验

JLINK RTT can be opened but cannot display problems and bin file output considerations on the desktop

Arm instruction set review | basic instruction usage

从2022年的这几篇论文看推荐系统序列建模的趋势

14届数独-真题标准数独-Day 6-20220121(补)
随机推荐
Manjaro kconsole开启半透明
Operating instructions for abbexa AEC chromogen Kit
Differences between gtf/gff documents and their mutual conversion (Reprint)
图片搜索在 Dropbox 中的工作原理
Word tips
sqllite create a database
nlp网络中两种残差结构对网络的影响
刷脸认证如何实现人脸又快又准完成校验?
[embedded Engineer · single chip microcomputer] ① basic concept of single chip microcomputer
Snap announced that the upgraded camera products and AR ecology will continue to penetrate the Chinese market
永远并不远,五种可能注定要衰落的编程语言
Oracle分页
build sqllite from amalgamation version
基于bs_pagination插件的分页查询功能
R installation / update package error: failed to lock directory '/home/anaconda3/envs/r4.1.2/lib/r/library'
DAY6-T1345&T39 -2022-01-21-非自己作答
AUTOCAD——坐标引线标注
Redis知识点&面试题总结
Leetcode 1979. Find the greatest common divisor of the array
Application of slip ring in automatic control system