当前位置:网站首页>Spark Learning Notes (IV) -- spark core programming RDD
Spark Learning Notes (IV) -- spark core programming RDD
2022-07-27 03:24:00 【One's cow】
Catalog
RDD Definition & characteristic
RDD Parallelism and partitioning
RDD Definition & characteristic
RDD(Resilient Distributed Dataset) It's called elastic distributed data sets , yes Spark The most basic data processing model in . It represents a flexible 、 immutable 、 Divisible 、 A set of elements that can be calculated in parallel .
RDD characteristic :
(1) elastic ;
1) Storage flexibility : Automatic switch between memory and disk ;
2) The resilience of fault tolerance : Data loss can be recovered automatically ;
3) Elasticity of calculation : Calculation error retrial mechanism ;
4) The elasticity of slices : It can be re sliced as needed .
RDD Processing flow
Execution principle

Simple RDD Processing flow

wordcount Processing flow
 wordcount Code
wordcount Code
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
// establish spark Run configuration object
val sparkConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[*]").setAppName("WordCount")
// Establish connection object
val sc:SparkContext = new SparkContext(sparkConf)
// Read the file
val fileRDD: RDD[String] = sc.textFile("datas")
// participle
val wordRDD: RDD[String] = fileRDD.flatMap(_.split(" "))
// Data structure transformation
val word2RDD: RDD[(String, Int)] = wordRDD.map((_,1))
// Group aggregation
val word2count: RDD[(String, Int)] = word2RDD.reduceByKey(_+_)
// Collect results to memory
val wordend: Array[(String, Int)] = word2count.collect()
// Print
word2count.foreach(println)
// close spark
sc.stop()
}RDD Core attributes
(1) Partition list
RDD Partition list exists in data structure , Used for parallel computing when executing tasks , It is an important attribute to realize distributed computing .
(2) Partition calculation function
RDD Basic programming
establish RDD
1) From the collection / Create... In memory RDD
Create... From the collection RDD,Spark It mainly provides two methods :parallelize and makeRDD;
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
// Prepare the environment
val sparkConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[*]").setAppName("RDD")
val sc = new SparkContext(sparkConf)
// establish RDD
// Create from memory RDD, The data source is memory data
//Spark It mainly provides two methods :parallelize and makeRDD
val seq1 = Seq[Int](1,2,3,4)
val seq2 = Seq[Int](2,4,6,8)
//parallelize
val rdd1: RDD[Int] = sc.parallelize(seq1)
//makeRDD
val rdd2: RDD[Int] = sc.makeRDD(seq2)
rdd1.collect().foreach(println)
rdd2.collect().foreach(println)
// Shut down the environment
sc.stop()
}
2) Create from external files RDD
Create from a dataset of an external storage system RDD; Including the local file system and all Hadoop Supported datasets , such as HDFS、HBase;
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
// Prepare the environment
val sparkConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[*]").setAppName("RDD")
val sc = new SparkContext(sparkConf)
// establish RDD
// Create from a file , The data source is a file
//path The default path is the root path of the current environment , You can write absolute paths or relative paths
val rdd: RDD[String] = sc.textFile("datas/word1.txt")
//sc.textFile("D:\\spark\\ec\\word.txt") Local file path
//sc.textFile("hdfs://hadoop01:8020/datas/word.txt") Distributed storage path
//sc.textFile("datas") Directory path
//sc.textFile("datas/*.txt") Wildcard path
//sc.wholeTextFiles("datas")
// Read data in file units , The results are expressed as tuples , The first is the file path , The second is content
rdd.collect().foreach(println)
// Shut down the environment
sc.stop()
}
3) From the other RDD establish RDD
Through one RDD After the calculation , Generate new RDD;
example :wordcount Program
4) Create directly RDD
Use new It's a way to construct RDD, Generally by Spark The framework itself uses .
RDD Parallelism and partitioning
Spark Divide a job into multiple tasks , Send to Executor Node parallel computing , The number of tasks that can be processed in parallel is called parallelism .
This number can be built in RDD When you specify . The number of tasks executed in parallel here does not refer to the number of segmentation tasks .
example : Cut the task into 100 individual , The number of tasks is 100, The degree of parallelism is 20, The number of tasks executed in parallel is 20.
Memory
When reading memory data , Data can be partitioned according to the setting of parallelism .
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
// Environmental preparation
val sparkConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[*]").setAppName("RDD")
//sparkConf.set("spark.default.parallelism","4") To configure 4 Zones ( Mode one )
val sc = new SparkContext(sparkConf)
// establish RDD
// Parallelism & Partition
//sc.makeRDD(List(1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8),4) To configure 4 Zones ( Mode two )
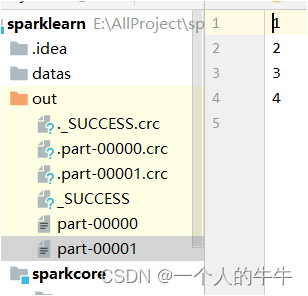
val rdd = sc.makeRDD(List(1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8),2)
rdd.saveAsTextFile("out")
// Shut down the environment
sc.stop()
}

file
When reading file data , The data is based on Hadoop File read rules slice partition .

def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
// Create an environment
val sparkConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[*]").setAppName("RDD")
val sc = new SparkContext(sparkConf)
// establish RDD
//textFile Use files as data sources , It can be partitioned by default
//minPartitions: Minimum number of partitions
//math.min(defaultParallelism, 2) The default partition is 2
//val rdd = sc.textFile("datas/word1.txt") Default partition
//val rdd = sc.textFile("datas/word1.txt",3) Set the minimum number of partitions to 3
val rdd = sc.textFile("datas/word1.txt",3)
// Partition calculation method :totalSize=7,goalSize = 7/3=2...1 3 Partition notes :7 Is the number of bytes
//val rdd = sc.textFile("datas/word1.txt",3)
//totalSize=9,goalSize = 7/4 =1....3 2+1=3 Partition
rdd.saveAsTextFile("output1")
// Shut down the environment
sc.stop()
} 
RDD Conversion operator
RDD Action operator
边栏推荐
- 索引最佳实践
- Submodule cache cache failure
- Worthington过氧化物酶活性的6种测定方法
- [learning notes, dog learning C] string + memory function
- Best practices of opentelemetry in service grid architecture
- Bulk copy baby upload prompt garbled, how to solve?
- Abbkine AbFluor 488 细胞凋亡检测试剂盒特点及实验建议
- Role of thread.sleep (0)
- Database usage security policy
- spark学习笔记(五)——sparkcore核心编程-RDD转换算子
猜你喜欢

Single case mode (double check lock)

Worthington过氧化物酶活性的6种测定方法

Worthington果胶酶的特性及测定方案

深度学习——词汇embedded、Beam Search

安全员及环保员岗位职责

Explain详解

Portraiture5 new and upgraded leather filter plug-in artifact

The diagram of user login verification process is well written!

spark:计算不同分区中相同key的平均值(入门级-简单实现)
How many implementation postures of delay queue? Daily essential skills!
随机推荐
【树链剖分】2022杭电多校2 1001 Static Query on Tree
自己梳理的LocalDateTime的工具类
flask_restful中reqparse解析器继承
【学习笔记之菜Dog学C】字符串+内存函数
如何进行 360 评估
day6
Leetcode 207. curriculum (July 26, 2022)
unity游戏,隐私协议最简单解决方案!仅3行代码就搞定!(转载)
周全的照护 解析LYRIQ锐歌电池安全设计
Role of thread.sleep (0)
深度学习——词汇embedded、Beam Search
数据库使用安全策略
Code practice when the queue reaches the maximum length
Detailed explanation of const usage in C language
Safe-arc/warner power supply maintenance xenon lamp power supply maintenance analysis
[flask] the server obtains the file requested by the client
pip3 设置阿里云
【flask】服务端获取客户端请求的文件
Does Oracle have a distributed database?
redis秒杀案例,跟着b站尚硅谷老师学习