当前位置:网站首页>spark学习笔记(五)——sparkcore核心编程-RDD转换算子
spark学习笔记(五)——sparkcore核心编程-RDD转换算子
2022-07-27 01:31:00 【一个人的牛牛】
目录
(9、10)leftOuterJoin、rightOuterJoin
reduceByKey、foldByKey、aggregateByKey、combineByKey的区别?
RDD转换:对RDD功能的补充和封装,将旧的RDD包装成为新的RDD;
RDD行动:触发任务的调度和作业的执行。
Value型
(1)map
函数签名:def map[U: ClassTag](f: T => U): RDD[U]
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
//创建环境
val sparkConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[*]").setAppName("Operator")
val sc = new SparkContext(sparkConf)
//RDD算子——map
// val rdd = sc.makeRDD(List(1,2,3,4),1)
val rdd = sc.makeRDD(List(1,2,3,4),2)
//转换函数
// 第一种方法
// def mapFunction(num:Int):Int = {
// num * 2
// }
// val mapRdd: RDD[Int] = rdd.map(mapFunction)
// 第二种方法
// val mapRdd: RDD[Int] = rdd.map((num:Int) => {num * 2})
// val mapRdd: RDD[Int] = rdd.map(num => num * 2)
//值转换
val mapRdd: RDD[Int] = rdd.map(_*2)
//类型转换
val mapRdd2: RDD[String] = mapRdd.map(num => {"" + num})
mapRdd.collect().foreach(println)
mapRdd2.collect().foreach(println)
//关闭环境
sc.stop()
}注:
1)RDD在一个分区内计算,数据是一个一个的执行,分区内数据的执行是有序的;
2)RDD在不同分区内计算,数据的执行是无序的。
(2)mapPartitions
函数签名:def mapPartitions[U: ClassTag]( f: Iterator[T] => Iterator[U], preservesPartitioning: Boolean = false): RDD[U]
函数说明:将待处理的数据以分区为单位发送到计算节点进行处理,这里的处理是指可以进行任意的处理,哪怕是过滤数据。
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
//创建环境
val sparkConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[*]").setAppName("Operator")
val sc = new SparkContext(sparkConf)
//RDD算子——mapPartitions
val rdd = sc.makeRDD(List(1,2,3,4),2)
val mapRDD: RDD[Int] = rdd.mapPartitions(
iter => {
println("出现几次就是执行几次,也就是分区数")
iter.map(_ * 2)
}
)
//取最大
val mapRDD1: RDD[Int] = rdd.mapPartitions(
iter => {
println("每个分区的最大值分别为:")
List(iter.max).iterator
}
)
//打印
mapRDD.collect().foreach(println)
mapRDD1.collect().foreach(println)
//关闭环境
sc.stop()
}注:
处理数据时数据会加载到内存,不会被释放,如果数据过大内存会不够用,会出现内存溢出。

(3)mapPartitionsWithIndex
函数签名:def mapPartitionsWithIndex[U: ClassTag]( f: (Int, Iterator[T]) => Iterator[U], preservesPartitioning: Boolean = false): RDD[U]
函数说明:将待处理的数据以分区为单位发送到计算节点进行处理;在处理时同时可以获取当前分区的索引。
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
//创建环境
val sparkConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[*]").setAppName("Operator")
val sc = new SparkContext(sparkConf)
//RDD算子——mapPartitionsWithIndex
val rdd = sc.makeRDD(List(1,2,3,4),2)
//2个分区,分别为【1,2】【3,4】
//取第二个分区的数据
println("取第二个分区的数据")
val mapRDD = rdd.mapPartitionsWithIndex(
(index, iter) => {
if (index == 1) { //index是分区
iter
} else {
Nil.iterator
}
}
)
mapRDD.collect().foreach(println)
//查找分区和分区相应的数字
println("查找分区和分区相应的数字")
val mapRDD1 = rdd.mapPartitionsWithIndex(
(index ,iter) => {
iter.map(
num => {
(index, num) //index是分区
}
)
}
)
mapRDD1.collect().foreach(println)
//关闭环境
sc.stop()
}
(4)flatMap
函数签名:def flatMap[U: ClassTag](f: T => TraversableOnce[U]): RDD[U]
函数说明:将数据进行扁平化后再进行映射,flatMap算子称为扁平映射。
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
//创建环境
val sparkConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[*]").setAppName("Operator")
val sc = new SparkContext(sparkConf)
//RDD算子——flatMap
//将List(1,2),List(3,4)扁平化处理
val rdd: RDD[List[Int]] = sc.makeRDD(List(List(1,2),List(3,4)))
val flatMapRDD: RDD[Int] = rdd.flatMap(
list => {list}
)
flatMapRDD.collect().foreach(println)
//将"hello world","hello scala"扁平化处理
val rdd2: RDD[String] = sc.makeRDD(List("hello world","hello scala"))
val flatMapRDD2: RDD[String] = rdd2.flatMap(
s => {s.split(" ")}
)
flatMapRDD2.collect().foreach(println)
//将List(1,2),7,List(3,4)扁平化处理
val rdd3 = sc.makeRDD(List(List(1,2),7,List(3,4)))
val flatMapRDD3 = rdd3.flatMap(
data => {
data match { //模式匹配
case list: List[_]=>list
case dat => List(dat)
}
}
)
flatMapRDD3.collect().foreach(println)
//关闭环境
sc.stop()
}
(5)glom
函数签名:def glom(): RDD[Array[T]]
函数说明:将同一个分区的数据直接转换为相同类型的内存数组进行处理,分区不变。
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
//TODO 创建环境
val sparkConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[*]").setAppName("Operator")
val sc = new SparkContext(sparkConf)
//TODO RDD算子——glom
val rdd: RDD[Int] = sc.makeRDD(List(1,2,3,4),2)
val glomRDD: RDD[Array[Int]] = rdd.glom()
glomRDD.collect().foreach(data => println(data.mkString(",")))
//计算分区的最大值求和
println("分区的最大值求和")
val glomRDD2: RDD[Array[Int]] = rdd.glom()
val maxRDD: RDD[Int] = glomRDD2.map(
array => {array.max} //取最大值
)
println(maxRDD.collect().sum)
//TODO 关闭环境
sc.stop()
}
(6)groupBy
函数签名:def groupBy[K](f: T => K)(implicit kt: ClassTag[K]): RDD[(K, Iterable[T])]
函数说明:将数据根据指定的规则进行分组, 分区默认不变,但是数据会被打乱重新组合,我们将这样的操作称之为shuffle。极限情况下,数据可能被分在同一个分区中。
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
//TODO 创建环境
val sparkConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[*]").setAppName("Operator")
val sc = new SparkContext(sparkConf)
//TODO RDD算子——groupBy
//groupBy会将数据源的每一个数据进行分组,根据返回的key进行分组,相同的key的数据会在同一个组中
println("以余数进行分组")
val rdd : RDD[Int] = sc.makeRDD(List(1,2,3,4),2)
def groupPunction(num:Int):Int = {
num % 2
}
val groupRDD: RDD[(Int, Iterable[Int])] = rdd.groupBy(groupPunction)
groupRDD.collect().foreach(println)
println("以首字母分组")
val rdd2: RDD[String] = sc.makeRDD(List("hello","scala","hi","spark"),2)
val groupRDD2 = rdd2.groupBy(_.charAt(0))
groupRDD2.collect()foreach(println)
//TODO 关闭环境
sc.stop()
}
(7)filter
函数签名:def filter(f: T => Boolean): RDD[T]
函数说明:把数据根据指定的规则进行筛选过滤,符合规则的数据保留,不符合规则的数据丢弃。
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
//TODO 创建环境
val sparkConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[*]").setAppName("Operator")
val sc = new SparkContext(sparkConf)
//TODO RDD算子——filter
val rdd = sc.makeRDD(List(1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10))
//过滤偶数
println("打印基数")
val filterRDD = rdd.filter(num => num % 2 != 0)
filterRDD.collect().foreach(println)
//过滤基数
println("打印偶数")
val filterRDD2 = rdd.filter((num => num % 2 != 1))
filterRDD2.collect().foreach(println)
//TODO 关闭环境
sc.stop()
}
(8)sample
函数签名:def sample( withReplacement: Boolean, fraction: Double, seed: Long = Utils.random.nextLong): RDD[T]
函数说明:根据指定的规则从数据集中抽取数据。
withReplacement = false(不放回)
withReplacement = true(放回)
fraction = 0.5(概率为0.5)
seed:随机数的种子
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
//TODO 创建环境
val sparkConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[*]").setAppName("Operator")
val sc = new SparkContext(sparkConf)
//TODO RDD算子——sample
val rdd = sc.makeRDD(List(1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10))
//抽取,概率为0.5,不放回
println("抽取,概率为0.5,不放回")
val sampleRDD = rdd.sample(
withReplacement = false,
fraction = 0.5,
)
sampleRDD.collect().foreach(println)
//抽取,概率为0.4,放回
println("抽取,概率为0.4,放回")
val sampleRDD2 = rdd.sample(
withReplacement = true,
fraction = 0.4,
)
sampleRDD2.collect().foreach(println)
//TODO 关闭环境
sc.stop()
}
(9)distinct
函数签名:def distinct()(implicit ord: Ordering[T] = null): RDD[T]
def distinct(numPartitions: Int)(implicit ord: Ordering[T] = null): RDD[T]
函数说明:将数据集中重复的数据去重。
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
//TODO 创建环境
val sparkConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[*]").setAppName("Operator")
val sc = new SparkContext(sparkConf)
//TODO RDD算子——distinct
//去重
val rdd = sc.makeRDD(List(1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,1,2,3,4,1,2,3,4))
val distinctRDD = rdd.distinct()
distinctRDD.collect().foreach(println)
//TODO 关闭环境
sc.stop()
}
(10)coalesce
函数签名:def coalesce(numPartitions: Int, shuffle: Boolean = false, partitionCoalescer: Option[PartitionCoalescer] = Option.empty) (implicit ord: Ordering[T] = null) : RDD[T]
函数说明:根据数据量缩减分区,用于大数据集过滤后,提高小数据集的执行效率。
当 spark 程序中,存在过多的小任务的时候,可以通过coalesce方法,收缩合并分区,减少分区的个数,减小任务调度成本。
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
//TODO 创建环境
val sparkConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[*]").setAppName("Operator")
val sc = new SparkContext(sparkConf)
//TODO RDD算子——coalesce
val rdd = sc.makeRDD(List(1,2,3,4,5,6),6)
val coalesce = rdd.coalesce(2,true)
coalesce.saveAsTextFile("output")
//TODO 关闭环境
sc.stop()
}
(11)repartition
函数签名:def repartition(numPartitions: Int)(implicit ord: Ordering[T] = null): RDD[T]
函数说明:该操作内部其实执行的是coalesce操作,参数shuffle的默认值为 true。无论是将分区数多的RDD转换为分区数少的RDD,还是将分区数少的RDD转换为分区数多的RDD,repartition操作都可以完成,因为无论如何都会经shuffle过程。
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
//TODO 创建环境
val sparkConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[*]").setAppName("Operator")
val sc = new SparkContext(sparkConf)
//TODO RDD算子——repartition
//coalesce
val rdd = sc.makeRDD(List(1,2,3,4,5,6),2)
val repartitionRDD = rdd.coalesce(3,true)
repartitionRDD.saveAsTextFile("output")
//repartition
val repartitionRDD1 = rdd.repartition(3)
repartitionRDD1.saveAsTextFile("output1")
//TODO 关闭环境
sc.stop()
}

(12)sortBy
函数签名:def sortBy[K]( f: (T) => K,ascending: Boolean = true, numPartitions: Int = this.partitions.length) (implicit ord: Ordering[K], ctag: ClassTag[K]): RDD[T]
函数说明:该操作用于排序数据。在排序之前,可以将数据通过f函数进行处理,之后按照f函数处理的结果进行排序,默认为升序排列。排序后新产生的 RDD 的分区数与原 RDD 的分区数一致。中间存在 shuffle 的过程。
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
//TODO 创建环境
val sparkConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[*]").setAppName("Operator")
val sc = new SparkContext(sparkConf)
//TODO RDD算子——sortBy
//数字
println("降序排序")
val rdd = sc.makeRDD(List(4,9,1,3,5),2)
val sortByRDD = rdd.sortBy(num => num,false)
// sortByRDD.saveAsTextFile("output")
sortByRDD.collect().foreach(println)
//升序
println("顺序排序(默认)")
val rdd2 = sc.makeRDD(List(("1",1),("20",2),("43",3)),2)
val sortByRDD2 = rdd2.sortBy(t => t._1.toInt)
sortByRDD2.collect().foreach(println)
//TODO 关闭环境
sc.stop()
}
双Value型
(1)intersection
函数签名:def intersection(other: RDD[T]): RDD[T]
函数说明:对源RDD和参数RDD求交集后返回一个新的RDD
(2)union
函数签名:def union(other: RDD[T]): RDD[T]
函数说明:对源RDD和参数RDD求并集后返回一个新的RDD。
(3)subtract
函数签名:def subtract(other: RDD[T]): RDD[T]
函数说明:求差集,以一个RDD元素为主,去除两个RDD中重复元素,将其他元素保留下来。
(4)zip
函数签名:def zip[U: ClassTag](other: RDD[U]): RDD[(T, U)]
函数说明:将两个RDD中的元素,以键值对的形式进行合并。Key为第1个RDD中的元素,Value为第2个RDD中的元素。拉链。
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
//TODO 创建环境
val sparkConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[*]").setAppName("Operator")
val sc = new SparkContext(sparkConf)
//TODO RDD算子——intersection/union/subtract/zip
val rdd1 = sc.makeRDD(List(1,2,3,4,5,6))
val rdd2 = sc.makeRDD(List(2,4,5,7,9,10))
//交集
//要求数据类型一样
println("交集")
val rdd3 = rdd1.intersection(rdd2)
println(rdd3.collect().mkString("."))
//并集
//要求数据类型一样
println("并集")
val rdd4 = rdd1.union(rdd2)
val rdd7 = rdd4.distinct()
println(rdd7.collect().mkString("."))
//差集
//要求数据类型一样
println("差集")
val rdd5 = rdd1.subtract(rdd2)
println(rdd5.collect().mkString("."))
//拉链
//数据类型可以不一样
println("拉链")
val rdd6 = rdd1.zip(rdd2)
println(rdd6.collect().mkString("."))
//TODO 关闭环境
sc.stop()
}
Key-Value型
(1)partitionBy
函数签名:def partitionBy(partitioner: Partitioner): RDD[(K, V)]
函数说明:将数据按照指定Partitioner重新进行分区。
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
//TODO 创建环境
val sparkConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[*]").setAppName("Operator")
val sc = new SparkContext(sparkConf)
//TODO RDD算子——key-value——partitionBy
val rdd = sc.makeRDD(List(1,2,3,4), 2)
val mapRDD = rdd.map((_, 1))
val mapRDD2 = mapRDD.partitionBy(new HashPartitioner(2))
mapRDD2.saveAsTextFile("output")
//TODO 关闭环境
sc.stop()
}
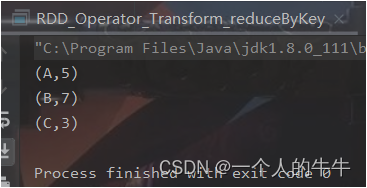
(2)reduceByKey
函数签名:
def reduceByKey(func: (V, V) => V): RDD[(K, V)]
def reduceByKey(func: (V, V) => V, numPartitions: Int): RDD[(K, V)]
函数说明:可以将数据按照相同的Key对Value进行聚合(两两计算)。
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
//TODO 创建环境
val sparkConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[*]").setAppName("Operator")
val sc = new SparkContext(sparkConf)
//TODO RDD算子——key-value——reduceByKey
val rdd = sc.makeRDD(List(("A", 1), ("B", 2), ("C", 3), ("A", 4), ("B", 5)))
val reduceByKeyRDD = rdd.reduceByKey(
(x: Int, y: Int) => {x + y})
reduceByKeyRDD.collect().foreach(println)
//TODO 关闭环境
sc.stop()
}
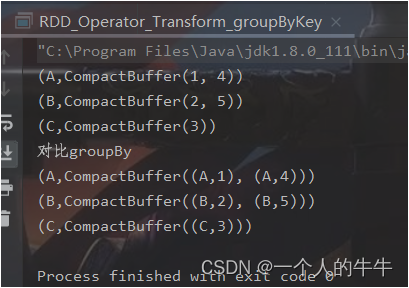
(3)groupByKey
函数签名:
def groupByKey(): RDD[(K, Iterable[V])]
def groupByKey(numPartitions: Int): RDD[(K, Iterable[V])]
def groupByKey(partitioner: Partitioner): RDD[(K, Iterable[V])]
函数说明:将数据源的数据根据key对value进行分组。
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
//TODO 创建环境
val sparkConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[*]").setAppName("Operator")
val sc = new SparkContext(sparkConf)
//TODO RDD算子——key-value——groupByKey
val rdd = sc.makeRDD(List(("A", 1), ("B", 2), ("C", 3), ("A", 4), ("B", 5)))
val groupRDD = rdd.groupByKey()
groupRDD.collect().foreach(println)
//对比groupBy
println("对比groupBy")
val groupRDD2 = rdd.groupBy(_._1)
groupRDD2.collect().foreach(println)
//TODO 关闭环境
sc.stop()
}
(4)aggregateByKey
函数签名:def aggregateByKey[U: ClassTag](zeroValue: U)(seqOp: (U, V) => U, combOp: (U, U) => U): RDD[(K, U)]
函数说明:将数据根据不同的规则进行分区内计算和分区间计算。
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
//TODO 创建环境
val sparkConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[*]").setAppName("Operator")
val sc = new SparkContext(sparkConf)
//TODO RDD算子——key-value——aggregateByKey
//分区内取最大值,分区间相加计算
val rdd = sc.makeRDD(List(
("A", 1), ("B", 2), ("C", 3), ("D", 4), ("A", 5), ("B", 6), ("C", 7), ("A", 8)
), 2)
//第一个:分区内计算规则
//第二个:分区间计算规则
val rdd2 = rdd.aggregateByKey(0)(
(x, y) => math.max(x, y),
(x, y) => x + y
)
rdd2.collect().foreach(println)
//TODO 关闭环境
sc.stop()
}
(5)foldByKey
函数签名:def foldByKey(zeroValue: V)(func: (V, V) => V): RDD[(K, V)]
函数说明:当分区内计算规则和分区间计算规则相同时,aggregateByKey就可以简化为foldByKey。
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
//TODO 创建环境
val sparkConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[*]").setAppName("Operator")
val sc = new SparkContext(sparkConf)
//TODO RDD算子——key-value——foldByKey
//分区内相加计算,分区间相加计算
val rdd = sc.makeRDD(List(
("A", 1), ("B", 2), ("C", 3), ("D", 4), ("A", 5), ("B", 6), ("C", 7), ("A", 8)
), 2)
//第一个:分区内计算规则
//第二个:分区间计算规则
//rdd2 = rdd3 = rdd4 = rdd.foldByKey(0)(_+_).collect().foreach(println)
// val rdd2 = rdd.aggregateByKey(0)(
// (x, y) => x + y,
// (x, y) => x + y
// )
// rdd2.collect().foreach(println)
// val rdd3 = rdd.aggregateByKey(0)(_ + _, _ + _)
// rdd3.collect().foreach(println)
val rdd4 = rdd.foldByKey(0)(_ + _)
rdd4.collect().foreach(println)
// rdd.foldByKey(0)(_+_).collect().foreach(println)
//TODO 关闭环境
sc.stop()
}
(6)combineByKey
函数签名:def combineByKey[C]( createCombiner: V => C, mergeValue: (C, V) => C, mergeCombiners: (C, C) => C): RDD[(K, C)]
函数说明:最通用的对key-value型RDD进行聚集操作的聚集函数(aggregation function)。类似于aggregate(),combineByKey()允许用户返回值的类型与输入不一致。
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
//TODO 创建环境
val sparkConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[*]").setAppName("Operator")
val sc = new SparkContext(sparkConf)
//TODO RDD算子——key-value——combineByKey
//计算不同分区中相同key的平均值
val rdd = sc.makeRDD(List(
("A", 1), ("B", 2), ("C", 3), ("D", 4), ("A", 5), ("B", 6), ("C", 7), ("A", 8)
), 2)
//第一个:将相同key的第一个数据进行结构的转换
//第二个:分区内的计算规则
//第三个:分区间的计算规则
val newRDD = rdd.combineByKey(
v => (v, 1),
(t: (Int, Int), v) => {
(t._1 + v, t._2 + 1)
},
(t1: (Int, Int), t2: (Int, Int)) => {
(t1._1 + t2._1, t1._2 + t2._2)
}
)
val RDD1 = newRDD.mapValues {
case (num, c) => {
num / c
}
}
RDD1.collect().foreach(println)
//TODO 关闭环境
sc.stop()
}
(7)sortByKey
函数签名:def sortByKey(ascending: Boolean = true, numPartitions: Int = self.partitions.length) : RDD[(K, V)]
函数说明:在一个(K,V)的RDD上调用,K必须实现Ordered接口,返回值按照key进行排序。
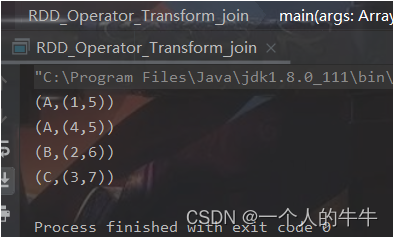
(8)join
函数签名:def join[W](other: RDD[(K, W)]): RDD[(K, (V, W))]
函数说明:在类型为(K,V)和(K,W)的RDD上调用,返回一个相同key对应的所有元素连接在一起的(K,(V,W))的RDD。
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
//TODO 创建环境
val sparkConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[*]").setAppName("Operator")
val sc = new SparkContext(sparkConf)
//TODO RDD算子——key-value——join
val rdd1 = sc.makeRDD(List(
("A", 1), ("B", 2), ("C", 3),("A",4)
))
val rdd2 = sc.makeRDD(List(
("A", 5), ("B", 6), ("C", 7),("D",8)
))
val joinRDD = rdd1.join(rdd2)
joinRDD.collect().foreach(println)
//TODO 关闭环境
sc.stop()
}
(9、10)leftOuterJoin、rightOuterJoin
函数签名:def leftOuterJoin[W](other: RDD[(K, W)]): RDD[(K, (V, Option[W]))]
函数说明:类似于SQL语句的左外连接。
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
//TODO 创建环境
val sparkConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[*]").setAppName("Operator")
val sc = new SparkContext(sparkConf)
//TODO RDD算子——key-value——leftOuterJoin
val rdd1 = sc.makeRDD(List(
("A", 1), ("B", 2), ("C", 3),("A",4)
))
val rdd2 = sc.makeRDD(List(
("A", 5), ("B", 6), ("C", 7),("D",8)
))
val leftRDD = rdd1.leftOuterJoin(rdd2)
val rightRDD = rdd1.rightOuterJoin(rdd2)
println("leftOuterJoin")
leftRDD.collect().foreach(println)
println("rightOuterJoin")
rightRDD.collect().foreach(println)
//TODO 关闭环境
sc.stop()
}
(11)cogroup
函数签名:def cogroup[W](other: RDD[(K, W)]): RDD[(K, (Iterable[V], Iterable[W]))]
函数说明:在类型为(K,V)和(K,W)的RDD上调用,返回一个(K,(Iterable<V>,Iterable<W>))类型的RDD 。
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
//TODO 创建环境
val sparkConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[*]").setAppName("Operator")
val sc = new SparkContext(sparkConf)
//TODO RDD算子——key-value——cogroup
val rdd1 = sc.makeRDD(List(
("A", 1), ("B", 2),("A",4)
))
val rdd2 = sc.makeRDD(List(
("A", 5), ("B", 6),("D",8)
))
val cogroupRDD = rdd1.cogroup(rdd2)
cogroupRDD.collect().foreach(println)
//TODO 关闭环境
sc.stop()
}
reduceByKey和groupByKey的区别?
从shuffle的角度:reduceByKey 和 groupByKey 都存在 shuffle 的操作,但是reduceByKey可以在shuffle前对分区内相同key的数据进行预聚合功能,这样会减少落盘的数据量,而groupByKey只是进行分组,不存在数据量减少的问题,reduceByKey性能比较高。
从功能的角度:reduceByKey其实包含分组和聚合的功能。groupByKey只能分组不能聚合,所以在分组聚合的场合下,推荐使用reduceByKey,如果仅仅是分组而不需要聚合.那么还是只能使用groupByKey。
reduceByKey、foldByKey、aggregateByKey、combineByKey的区别?
reduceByKey: 相同key的第一个数据不进行任何计算,分区内和分区间计算规则相同;
FoldByKey:相同key的第一个数据和初始值进行分区内计算,分区内和分区间计算规则相同;
AggregateByKey:相同key的第一个数据和初始值进行分区内计算,分区内和分区间计算规则可以不相同;
CombineByKey:当计算时,发现数据结构不满足要求时,可以让第一个数据转换结构。分区内和分区间计算规则不相同。
map算子和mapPartitions算子比较
1)数据处理角度:Map算子一个一个的执行;mapPartitions算子以分区为单位进行批处理。
2)功能的角度:Map算子是将数据源中的数据进行转换和改变,不会减少或增多数据;MapPartitions算子传递一个迭代器,返回一个迭代器,没有要求的元素的个数保持不变。
3)性能的角度:Map算子性能比较低;mapPartitions算子性能较高。
4)选取的角度:数据少选择mapPartitions算子,数据多选择map算子。
本文仅仅是学习笔记的记录!!!
边栏推荐
- [二分查找中等题] LeetCode 34. 在排序数组中查找元素的第一个和最后一个位置
- [SQL simple question] leetcode 627. change gender
- Oracle有没有分布式数据库?
- 2513: 小勇学分数(公约数问题)
- Yilingsi T35 FPGA drives LVDS display screen
- 代码审查金字塔
- Portraiture5 new and upgraded leather filter plug-in artifact
- Integrated water conservancy video monitoring station telemetry terminal video image water level water quality water quantity flow velocity monitoring
- 基于.NetCore开发博客项目 StarBlog - (16) 一些新功能 (监控/统计/配置/初始化)
- 二叉树(DAY 82)
猜你喜欢

Worthington果胶酶的特性及测定方案

vector 转 svg 方法

Portraiture5全新升级版磨皮滤镜插件神器

身家破亿!86版「红孩儿」拒绝出道成学霸,已是中科院博士,名下52家公司

抖音服务器带宽有多大,才能供上亿人同时刷?

安全员及环保员岗位职责

Portraiture5 new and upgraded leather filter plug-in artifact

How big is the bandwidth of the Tiktok server for hundreds of millions of people to brush at the same time?

仿知乎论坛社区社交微信小程序

Pytorch损失函数总结
随机推荐
Localstorage and sessionstorage
Boom 3D全新2022版音频增强应用程序App
[simple question of stack and queue] leetcode 232. realize queue with stack, 225. realize stack with queue
Worth more than 100 million! The 86 version of "red boy" refuses to be a Daocheng Xueba. He is already a doctor of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and has 52 companies under his name
day6
Call jshaman's Web API interface to realize JS code encryption.
185. All employees with the top three highest wages in the Department (mandatory)
175. 组合两个表(非常简单)
商城小程序项目完整源码(微信小程序)
C语言const用法详解
localStorage与sessionStorage
An error in the fourth edition of the red book?
在线问题反馈模块实战(十五):实现在线更新反馈状态功能
关于OpenFeign的源码分析
sqlserver select * 能不能排除某个字段
HCIP第十四天笔记
一个测试类了解BeanUtils.copyProperties
[binary search medium] leetcode 34. find the first and last positions of elements in the sorted array
[flask] the server obtains the file requested by the client
Activiti5.22.0扩展支持达国产数据库,以GBase据库为例