当前位置:网站首页>Neck modules of the yolo series
Neck modules of the yolo series
2022-08-04 12:12:00 【Sand side dishes】
学习:【Make YOLO Great Again】YOLOv1-v7Big analysis of the whole series(Neck篇)
本文研究yolo系列的Neck模块.yolov1、yolov2没有使用Neck模块,yolov3开始使用.NeckThe purpose of the module is to fuse the features of different layers to detect large, medium and small objects.
| 模块 | |
| yolov3 | FPN |
| yolov4 | spp+FPN |
| yolov5 | spp+FPN,Concat层后的CBL模块改成了CSP_V5模块 |
| yolox | spp+FPN |
| yolov7 | sppscp+优化的PAN(Concat层前的CBL改成MPConv,Concat层后使用E-ELAN) |
在进行yolo系列NeckBefore module study,先研究FPN、SPP和PAN模块.
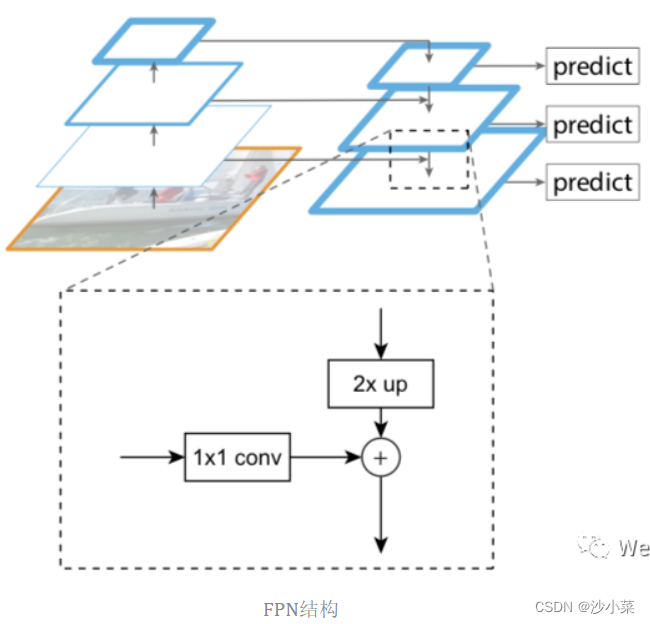
1.FPN(feature pyramid networks)
目的:Improve detection of small targets.
原来很多目标检测算法都是只采用高层特征进行预测,高层的特征语义信息比较丰富,但是分辨率较低,目标位置比较粗略.假设在深层网络中,最后的高层特征图中一个像素可能对应着输出图像20*20的像素区域,那么小于20*20像素的小物体的特征大概率已经丢失.与此同时,低层的特征语义信息比较少,但是目标位置准确,这是对小目标检测有帮助的.FPN将高层特征与底层特征进行融合,从而同时利用低层特征的高分辨率和高层特征的丰富语义信息,并进行了多尺度特征的独立预测,对小物体的检测效果有明显的提升.
2.SPP(Spatial Pyramid Pooling)
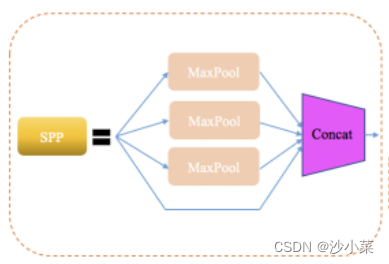
SPP,即空间金字塔池化.SPPThe purpose is to solve the problem of arbitrary size of input data.SPP网络用在YOLOv4The purpose of isIncrease the receptive field of the network
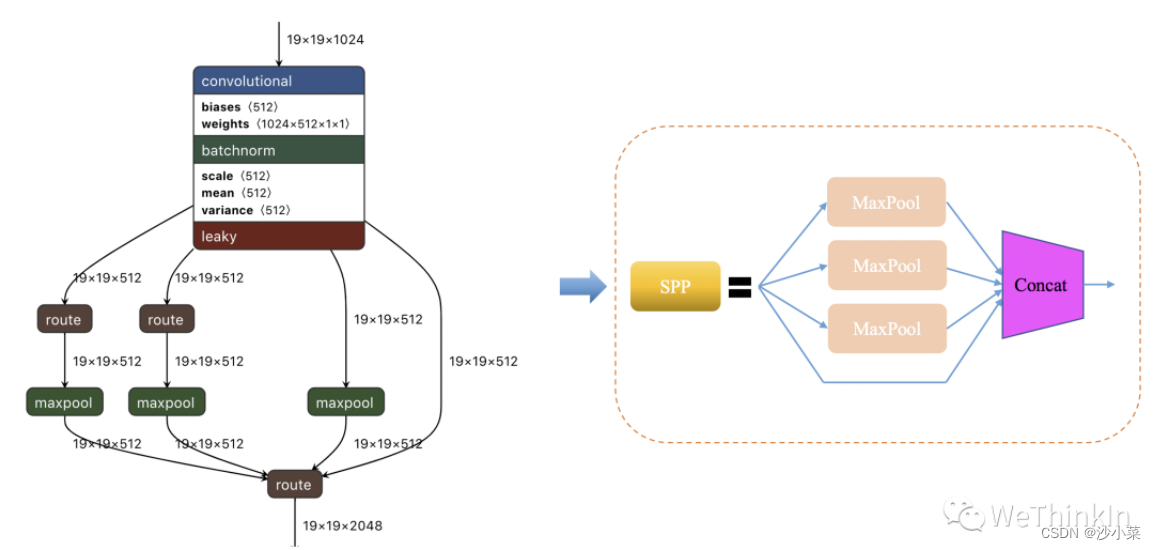
SPP的使用方法:
- First divide the input:Divide the input features into different parts:最左边有16个蓝色小格子的图,It means to split from the input features16份,16X256中的256表示的是channel,即SPP对每一层都分成16份(不一定是等比分).中间的4个绿色小格子和右边1个紫色大格子也同理,That is, the input features are divided into separately4X256和1X256份.(Note that how many portions are divided into the above can be customized)
- Pool each feature:一般选择MAX Pooling,即对每一份进行最大池化.看上图,通过SPP层,The input features are transformed into 16X256+4X256+1X256 = 21X256的矩阵.
- A fully connected layer is connected behind:连接一个1X10752的全连接层.This solves the problem of arbitrary input data size.
SPPMedium convolution kernel 尺寸、and step size calculation method:



假设输入数据大小是 (7,11), 池化数量 (4,4):
那么核大小为 (2,3), 步长大小为 (2,3), padding 为 (1,1), 得到池化后的矩阵大小的确是 4∗4.
SPP的pytorch实现:
#coding=utf-8
import math
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F
# 构建SPP层(空间金字塔池化层)
class SPPLayer(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_levels, pool_type='max_pool'):
super(SPPLayer, self).__init__()
self.num_levels = num_levels
self.pool_type = pool_type
def forward(self, x):
num, c, h, w = x.size() # num:样本数量 c:通道数 h:高 w:宽
for i in range(self.num_levels):
level = i+1
kernel_size = (math.ceil(h / level), math.ceil(w / level))
stride = (math.ceil(h / level), math.ceil(w / level))
pooling = (math.floor((kernel_size[0]*level-h+1)/2), math.floor((kernel_size[1]*level-w+1)/2))
# 选择池化方式
if self.pool_type == 'max_pool':
tensor = F.max_pool2d(x, kernel_size=kernel_size, stride=stride, padding=pooling).view(num, -1)
else:
tensor = F.avg_pool2d(x, kernel_size=kernel_size, stride=stride, padding=pooling).view(num, -1)
# 展开、拼接
if (i == 0):
x_flatten = tensor.view(num, -1)
else:
x_flatten = torch.cat((x_flatten, tensor.view(num, -1)), 1)
return x_flattenSPPCSP
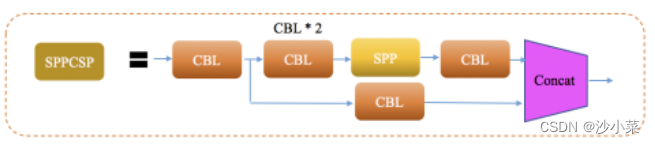
SPP的优化,在SPP模块基础上在最后增加concat操作,与SPP模块之前的特征图进行融合,更加丰富了特征信息.
3.PANet
网络结构如下图所示,与FPN相比,PANet 在UpSample之后又加了DownSample的操作.PANetCrazy fusion of features from different levels,其在FPN模块的基础上增加了自底向上的特征金字塔结构,保留了更多的浅层位置特征,将整体特征提取能力进一步提升.
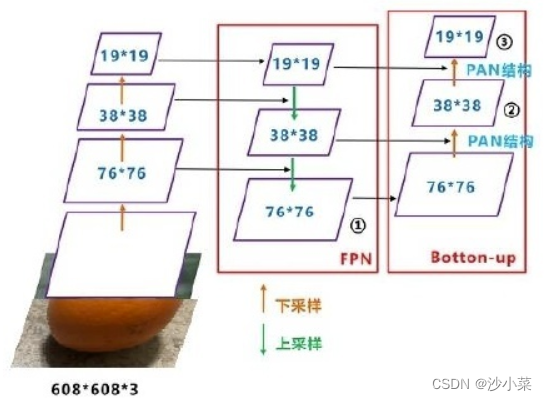
PAN模块的优化:
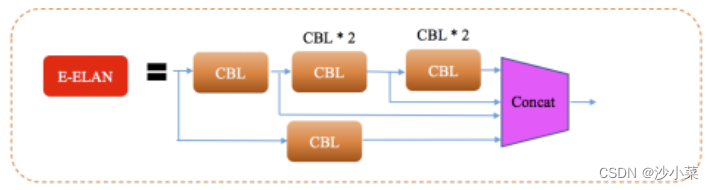
PAN模块在每个ConcatIntroduce one after the layerE-ELAN结构,使用expand、shuffle、merge cardinality等策略实现在不破坏原始梯度路径的情况下,提高网络的学习能力.
4.yolov3
yolov3的NECK模块引入了FPN的思想,并对原始FPN进行修改.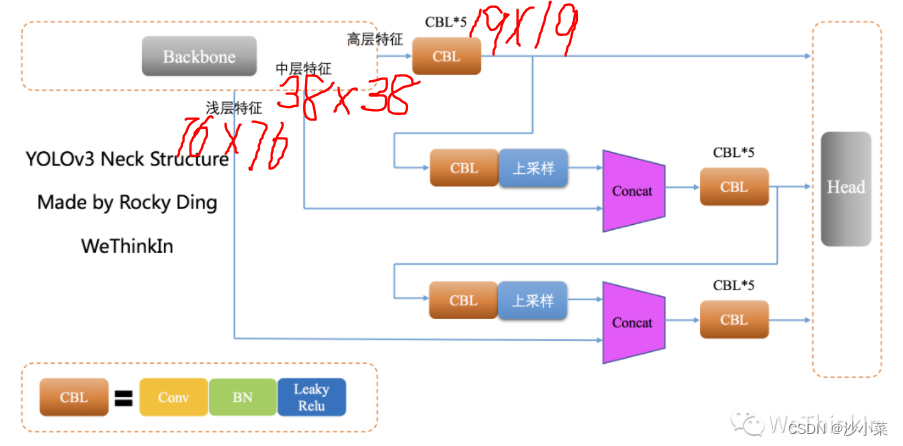
YOLOv3设置了三个不同的尺寸,分别是19*19,38*38,76*76
YOLOv3采用全卷积的思路,在Neck侧也不例外(YOLOv1-v2中采用池化层做特征图的下采样, v3中采用卷积层来实现).
5.yolov4
yolov4的Neck模块主要包含了SPP模块和PAN模块.

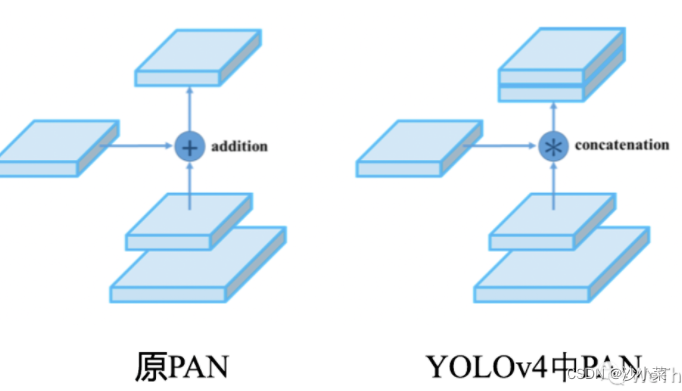
YOLOv4引入PAN时,特征图最后的融合操作相比于原论文发生了变化,从add操作改为concat操作,增加了特征图的通道数:
6. yolov5
YOLOv5的Neck侧也使用了SPP模块和PAN模块,但是在PAN模块进行融合后,将YOLOv4中使用的CBL模块Replace with referenceCSPnet设计的CSP_v5结构,加强网络特征融合的能力.
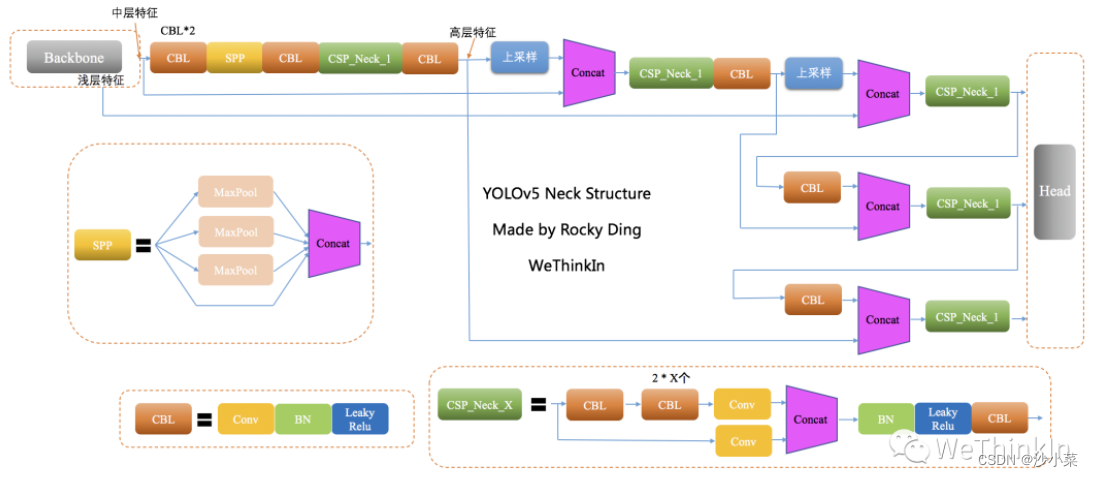
7.yolovx
YOLOx的Neck侧依然使用了YOLOv3的结构,并且使用了SPP模块.
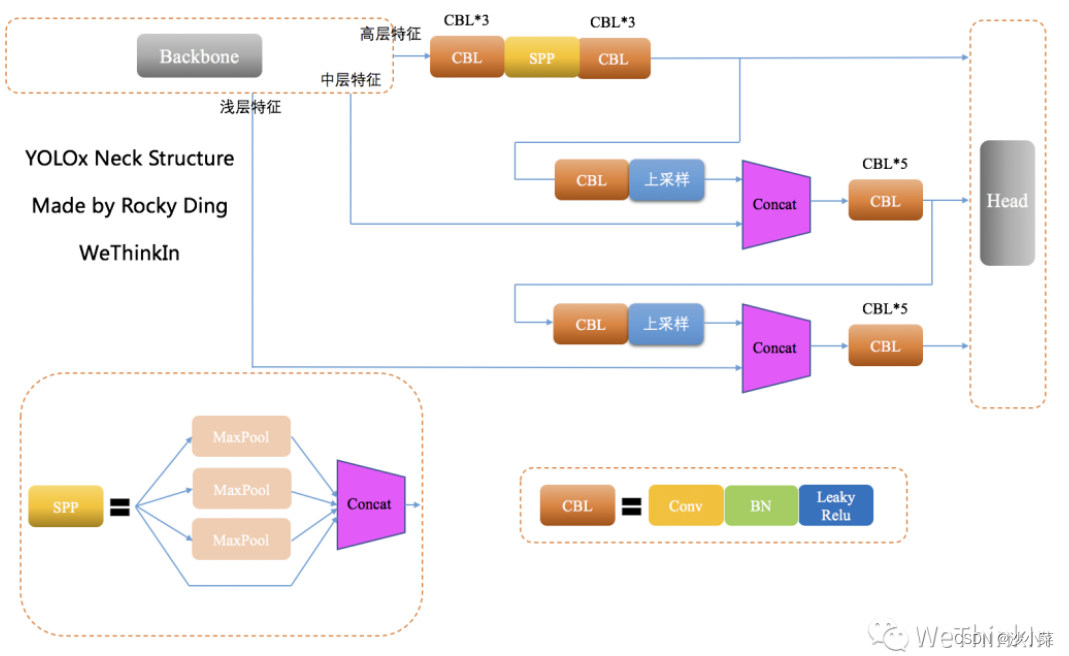
在Neck侧,yolox和yov3的差别在于:Used on high-level feature branchesSPP模块:

8.yolov7
YOLOv7的Neck侧主要包含了SPPSCP模块和优化的PAN模块.
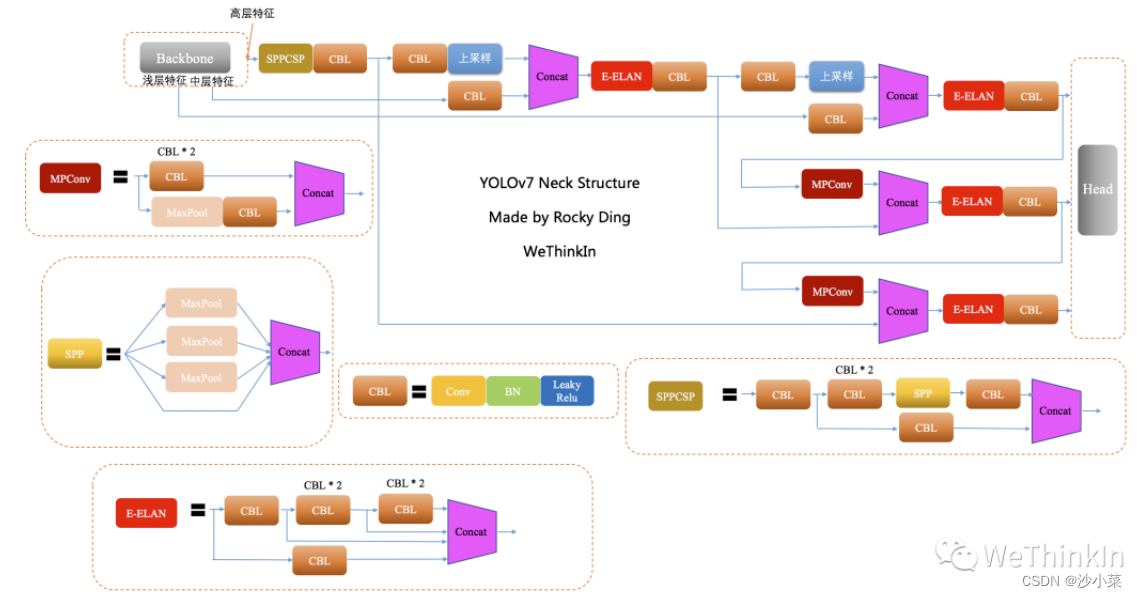
SPPCSP模块在SPP模块基础上在最后增加concat操作,与SPP模块之前的特征图进行融合,更加丰富了特征信息.
PAN模块引入E-ELAN结构,使用expand、shuffle、merge cardinality等策略实现在不破坏原始梯度路径的情况下,提高网络的学习能力.
边栏推荐
- 小程序在政务服务平台建设中如何发挥价值
- 知道创宇EDR系统实力通过中国信通院端点检测与响应产品能力评测
- 【目标检测】yolov2特征提取网络------Darknet19结构解析及tensorflow和pytorch实现
- 力扣解法汇总1403-非递增顺序的最小子序列
- Based on the BiLSTM regression forecast method
- 考研概率论与数理统计(知识点梳理)
- 电源测试之输出动态响应(Output Dynamic Response Test)
- 独立站卖家如何使用 WhatsApp Business API 建立有意义的客户关系?
- 国际原子能机构总干事警告称扎波罗热核电站安全形势已“完全失控”
- 免费翻译软件哪个好用
猜你喜欢

技术分享| 融合调度系统中的电子围栏功能说明

如何做好企业数字化转型?这10份靠谱案例收藏了(附下载)

Leetcode brush questions - 543. Diameter of binary trees, 617. Merging binary trees (recursive solution)

国际原子能机构总干事警告称扎波罗热核电站安全形势已“完全失控”
涨姿势了!原来这才是多线程正确实现方式

A Survey of Multi-Label Classification under Supervised and Semi-Supervised Learning

监督和半监督学习下的多标签分类综述
Redis(一)安装与配置

开发小程序插件如何实现盈利?

考研概率论与数理统计(知识点梳理)
随机推荐
Redis (1) installation and configuration
傅里叶级数与傅里叶变换学习
[牛客网]OR63删除公共字符
到底什么是JS原型
请 AI 画家弄了个 logo,网友热议:画得非常好,下次别画了!
COVID-CT新冠肺炎检测(DenseNet网络)
力扣解法汇总1403-非递增顺序的最小子序列
ECCV 2022 | 通往数据高效的Transformer目标检测器
yolo系列的head模块
数据库对象
监督和半监督学习下的多标签分类综述
节流函数(每隔一段时间就会执行一次)
Flutter强大的下拉筛选菜单gzx_dropdown_menu
深度学习------pytorch-gpu环境搭建
数据库表列类型;DML_添加数据;DDL_修改,删除数据库表
隐私计算与数据流通:关系、作用及功能
防抖函数封装
Share | technology integration electronic fence function of scheduling system
#夏日挑战赛#OpenHarmony 给你的输入法加点彩—星球崛起
子查询