当前位置:网站首页>聊聊异步编程的 7 种实现方式
聊聊异步编程的 7 种实现方式
2022-07-04 15:17:00 【Young丶】
最近有很多小伙伴给我留言,能不能总结下异步编程,今天就和大家简单聊聊这个话题。
早期的系统是同步的,容易理解,我们来看个例子
同步编程
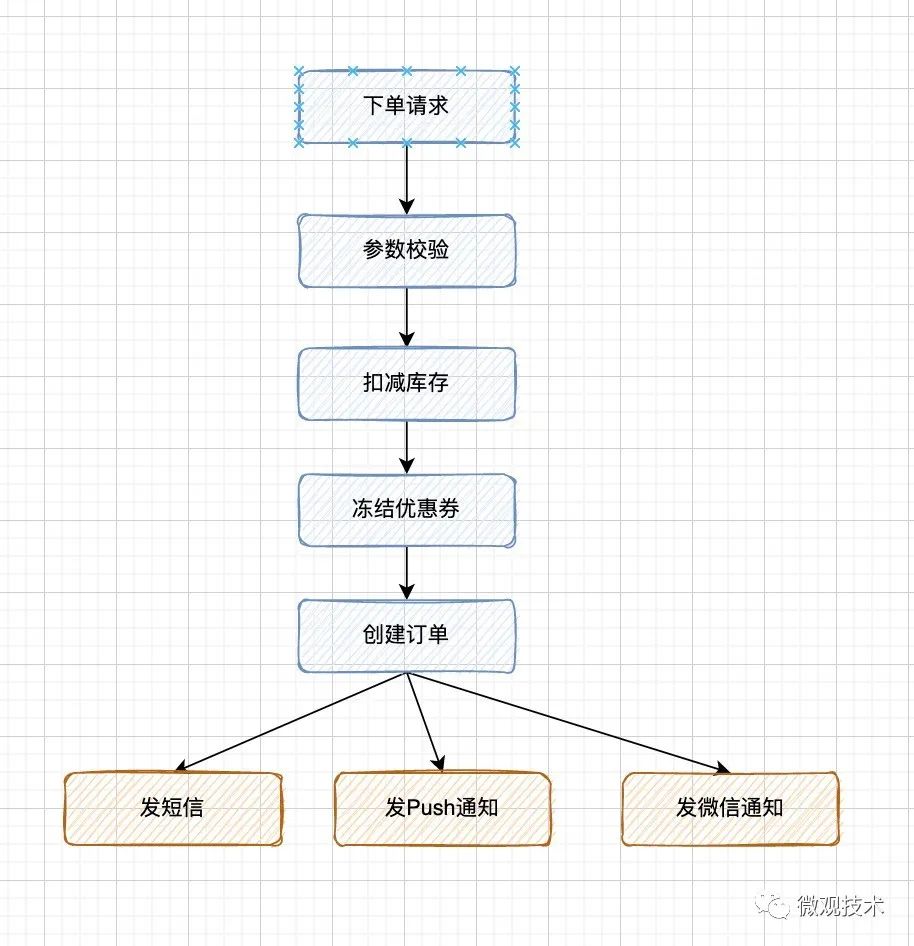
当用户创建一笔电商交易订单时,要经历的业务逻辑流程还是很长的,每一步都要耗费一定的时间,那么整体的RT就会比较长。
于是,聪明的人们开始思考能不能将一些非核心业务从主流程中剥离出来,于是有了异步编程雏形。
异步编程是让程序并发运行的一种手段。它允许多个事件同时发生,当程序调用需要长时间运行的方法时,它不会阻塞当前的执行流程,程序可以继续运行。
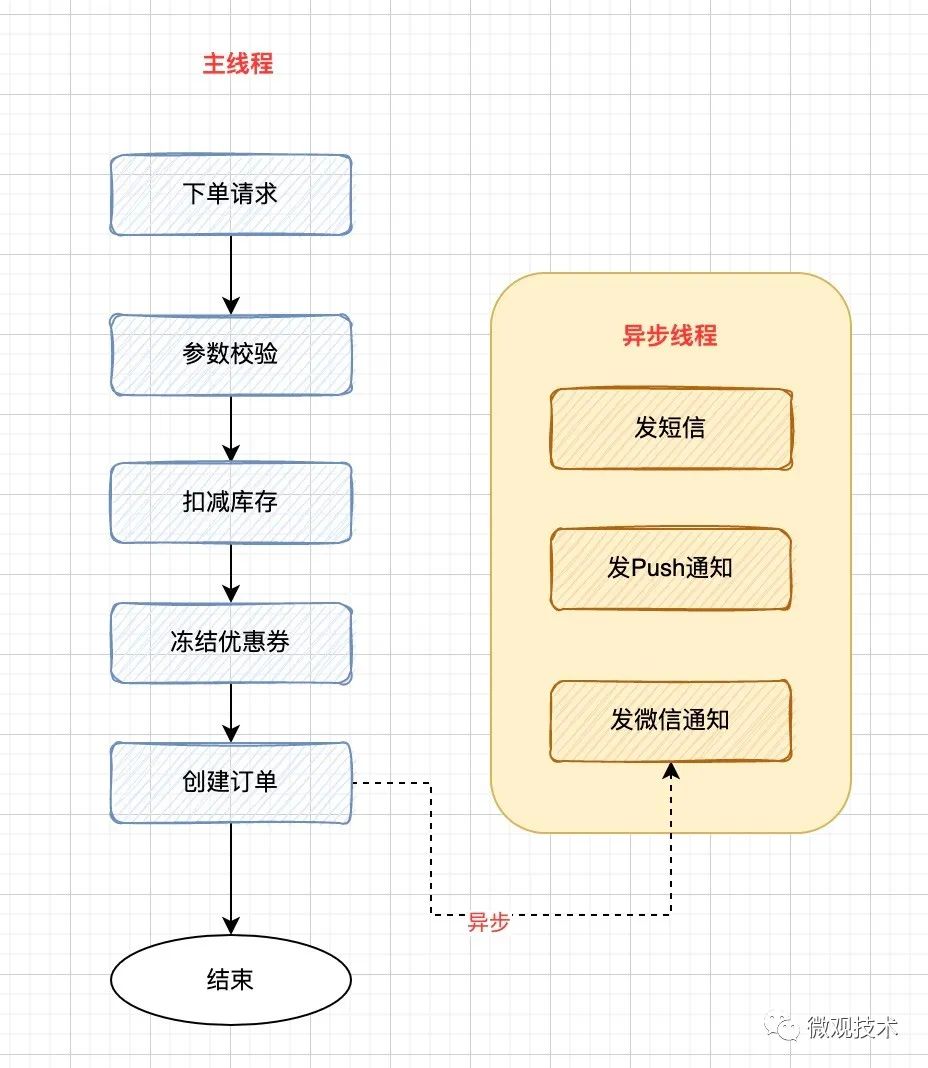
核心思路:采用多线程优化性能,将串行操作变成并行操作。异步模式设计的程序可以显著减少线程等待,从而在高吞吐量场景中,极大提升系统的整体性能,显著降低时延。
接下来,我们来讲下异步有哪些编程实现方式
一、线程 Thread
直接继承 Thread类 是创建异步线程最简单的方式。
首先,创建Thread子类,普通类或匿名内部类方式;然后创建子类实例;最后通过start()方法启动线程。
public class AsyncThread extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("当前线程名称:" + this.getName() + ", 执行线程名称:" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "-hello");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 模拟业务流程
// .......
// 创建异步线程
AsyncThread asyncThread = new AsyncThread();
// 启动异步线程
asyncThread.start();
}
当然如果每次都创建一个 Thread线程,频繁的创建、销毁,浪费系统资源。我们可以采用线程池
@Bean(name = "executorService")
public ExecutorService downloadExecutorService() {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(20, 40, 60, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(2000),
new ThreadFactoryBuilder().setNameFormat("defaultExecutorService-%d").build(),
(r, executor) -> log.error("defaultExecutor pool is full! "));
}
将业务逻辑封装到 Runnable 或 Callable 中,交由 线程池 来执行
二、Future
上述方式虽然达到了多线程并行处理,但有些业务不仅仅要执行过程,还要获取执行结果。
Java 从1.5版本开始,提供了 Callable 和 Future,可以在任务执行完毕之后得到任务执行结果。
当然也提供了其他功能,如:取消任务、查询任务是否完成等
Future类位于java.util.concurrent包下,接口定义:
public interface Future<V> {
boolean cancel(boolean mayInterruptIfRunning);
boolean isCancelled();
boolean isDone();
V get() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException;
V get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException;
}
方法描述:
- cancel():取消任务,如果取消任务成功返回true,如果取消任务失败则返回false
- isCancelled():表示任务是否被取消成功,如果在任务正常完成前被取消成功,则返回 true
- isDone():表示任务是否已经完成,如果完成,返回true
- get():获取执行结果,这个方法会产生阻塞,会一直等到任务执行完毕才返回
- get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit):用来获取执行结果,如果在指定时间内,还没获取到结果,就直接返回null
代码示例:
public class CallableAndFuture {
public static ExecutorService executorService = new ThreadPoolExecutor(4, 40,
0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>(1024), new ThreadFactoryBuilder()
.setNameFormat("demo-pool-%d").build(), new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy());
static class MyCallable implements Callable<String> {
@Override
public String call() throws Exception {
return "异步处理,Callable 返回结果";
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Future<String> future = executorService.submit(new MyCallable());
try {
System.out.println(future.get());
} catch (Exception e) {
// nodo
} finally {
executorService.shutdown();
}
}
}
Future 表示一个可能还没有完成的异步任务的结果,通过 get 方法获取执行结果,该方法会阻塞直到任务返回结果。
三、FutureTask
FutureTask 实现了 RunnableFuture 接口,则 RunnableFuture 接口继承了 Runnable 接口和 Future 接口,所以可以将 FutureTask 对象作为任务提交给 ThreadPoolExecutor 去执行,也可以直接被 Thread 执行;又因为实现了 Future 接口,所以也能用来获得任务的执行结果。
FutureTask 构造函数:
public FutureTask(Callable<V> callable)
public FutureTask(Runnable runnable, V result)
FutureTask 常用来封装 Callable 和 Runnable,可以作为一个任务提交到线程池中执行。除了作为一个独立的类之外,也提供了一些功能性函数供我们创建自定义 task 类使用。
FutureTask 线程安全由CAS来保证。
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
// FutureTask包装callbale任务,再交给线程池执行
FutureTask<Integer> futureTask = new FutureTask<>(() -> {
System.out.println("子线程开始计算:");
Integer sum = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= 100; i++)
sum += i;
return sum;
});
// 线程池执行任务, 运行结果在 futureTask 对象里面
executor.submit(futureTask);
try {
System.out.println("task运行结果计算的总和为:" + futureTask.get());
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
executor.shutdown();
Callable 和 Future 的区别:Callable 用于产生结果,Future 用于获取结果
如果是对多个任务多次自由串行、或并行组合,涉及多个线程之间同步阻塞获取结果,Future 代码实现会比较繁琐,需要我们手动处理各个交叉点,很容易出错。
四、异步框架 CompletableFuture
Future 类通过 get() 方法阻塞等待获取异步执行的运行结果,性能比较差。
JDK1.8 中,Java 提供了 CompletableFuture 类,它是基于异步函数式编程。相对阻塞式等待返回结果,CompletableFuture 可以通过回调的方式来处理计算结果,实现了异步非阻塞,性能更优。
优点:
- 异步任务结束时,会自动回调某个对象的方法
- 异步任务出错时,会自动回调某个对象的方法
- 主线程设置好回调后,不再关心异步任务的执行
泡茶示例:
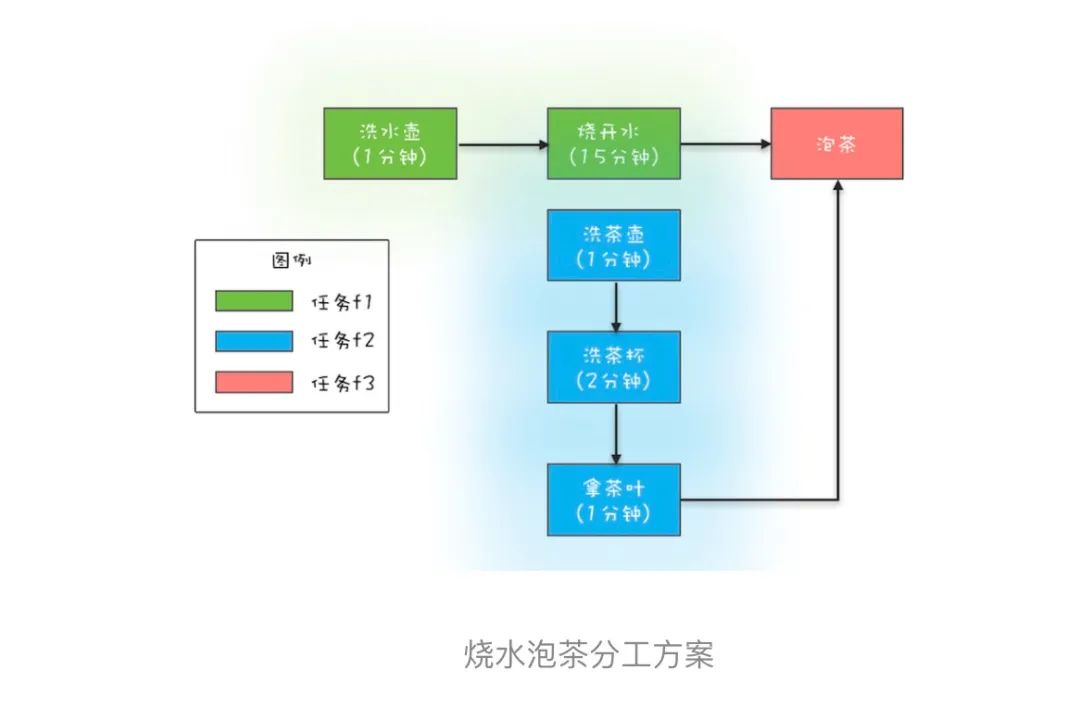
(内容摘自:极客时间的《Java 并发编程实战》)
//任务1:洗水壶->烧开水
CompletableFuture<Void> f1 =
CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("T1:洗水壶...");
sleep(1, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
System.out.println("T1:烧开水...");
sleep(15, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
});
//任务2:洗茶壶->洗茶杯->拿茶叶
CompletableFuture<String> f2 =
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("T2:洗茶壶...");
sleep(1, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
System.out.println("T2:洗茶杯...");
sleep(2, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
System.out.println("T2:拿茶叶...");
sleep(1, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
return "龙井";
});
//任务3:任务1和任务2完成后执行:泡茶
CompletableFuture<String> f3 =
f1.thenCombine(f2, (__, tf) -> {
System.out.println("T1:拿到茶叶:" + tf);
System.out.println("T1:泡茶...");
return "上茶:" + tf;
});
//等待任务3执行结果
System.out.println(f3.join());
}
CompletableFuture 提供了非常丰富的API,大约有50种处理串行,并行,组合以及处理错误的方法。
更多内容移步之前写的一篇文章,搞定 CompletableFuture,并发异步编程和编写串行程序还有什么区别?
五、 SpringBoot 注解 @Async
除了硬编码的异步编程处理方式,SpringBoot 框架还提供了 注解式 解决方案,以 方法体 为边界,方法体内部的代码逻辑全部按异步方式执行。
首先,使用 @EnableAsync 启用异步注解
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableAsync
public class StartApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(StartApplication.class, args);
}
}
自定义线程池:
@Configuration
@Slf4j
public class ThreadPoolConfiguration {
@Bean(name = "defaultThreadPoolExecutor", destroyMethod = "shutdown")
public ThreadPoolExecutor systemCheckPoolExecutorService() {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(3, 10, 60, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>(10000),
new ThreadFactoryBuilder().setNameFormat("default-executor-%d").build(),
(r, executor) -> log.error("system pool is full! "));
}
}
在异步处理的方法上添加注解 @Async ,当对 execute 方法 调用时,通过自定义的线程池 defaultThreadPoolExecutor 异步化执行 execute 方法
@Service
public class AsyncServiceImpl implements AsyncService {
@Async("defaultThreadPoolExecutor")
public Boolean execute(Integer num) {
System.out.println("线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + " , 任务:" + num);
return true;
}
}
用 @Async 注解标记的方法,称为异步方法。在spring boot应用中使用 @Async 很简单:
- 调用异步方法类上或者启动类加上注解 @EnableAsync
- 在需要被异步调用的方法外加上 @Async
- 所使用的 @Async 注解方法的类对象应该是Spring容器管理的bean对象;
六、Spring ApplicationEvent 事件
事件机制在一些大型项目中被经常使用,Spring 专门提供了一套事件机制的接口,满足了架构原则上的解耦。
ApplicationContext 通过 ApplicationEvent 类和 ApplicationListener 接口进行事件处理。如果将实现 ApplicationListener 接口的 bean 注入到上下文中,则每次使用 ApplicationContext 发布 ApplicationEvent 时,都会通知该 bean。本质上,这是标准的观察者设计模式。
ApplicationEvent 是由 Spring 提供的所有 Event 类的基类
首先,自定义业务事件子类,继承自 ApplicationEvent,通过泛型注入业务模型参数类。相当于 MQ 的消息体。
public class OrderEvent extends AbstractGenericEvent<OrderModel> {
public OrderEvent(OrderModel source) {
super(source);
}
}
然后,编写事件监听器。ApplicationListener 接口是由 Spring 提供的事件订阅者必须实现的接口,我们需要定义一个子类,继承 ApplicationListener。相当于 MQ 的消费端
@Component
public class OrderEventListener implements ApplicationListener<OrderEvent> {
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(OrderEvent event) {
System.out.println("【OrderEventListener】监听器处理!" + JSON.toJSONString(event.getSource()));
}
}
最后,发布事件,把某个事件告诉所有与这个事件相关的监听器。相当于 MQ 的生产端。
OrderModel orderModel = new OrderModel();
orderModel.setOrderId((long) i);
orderModel.setBuyerName("Tom-" + i);
orderModel.setSellerName("judy-" + i);
orderModel.setAmount(100L);
// 发布Spring事件通知
SpringUtils.getApplicationContext().publishEvent(new OrderEvent(orderModel));
加个餐:
[消费端]线程:http-nio-8090-exec-1,消费事件 {"amount":100.0,"buyerName":"Tom-1","orderId":1,"sellerName":"judy-1"}
[生产端]线程:http-nio-8090-exec-1,发布事件 1
[消费端]线程:http-nio-8090-exec-1,消费事件 {"amount":100.0,"buyerName":"Tom-2","orderId":2,"sellerName":"judy-2"}
[生产端]线程:http-nio-8090-exec-1,发布事件 2
[消费端]线程:http-nio-8090-exec-1,消费事件 {"amount":100.0,"buyerName":"Tom-3","orderId":3,"sellerName":"judy-3"}
[生产端]线程:http-nio-8090-exec-1,发布事件 3
上面是跑了个demo的运行结果,我们发现无论生产端还是消费端,使用了同一个线程 http-nio-8090-exec-1,Spring 框架的事件机制默认是同步阻塞的。只是在代码规范方面做了解耦,有较好的扩展性,但底层还是采用同步调用方式。
那么问题来了,如果想实现异步调用,如何处理?
我们需要手动创建一个 SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster,并设置 TaskExecutor,此时所有的消费事件采用异步线程执行。
@Component
public class SpringConfiguration {
@Bean
public SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster applicationEventMulticaster(@Qualifier("defaultThreadPoolExecutor") ThreadPoolExecutor defaultThreadPoolExecutor) {
SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster simpleApplicationEventMulticaster = new SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster();
simpleApplicationEventMulticaster.setTaskExecutor(defaultThreadPoolExecutor);
return simpleApplicationEventMulticaster;
}
}
我们看下改造后的运行结果:
[生产端]线程:http-nio-8090-exec-1,发布事件 1
[生产端]线程:http-nio-8090-exec-1,发布事件 2
[生产端]线程:http-nio-8090-exec-1,发布事件 3
[消费端]线程:default-executor-1,消费事件 {"amount":100.0,"buyerName":"Tom-2","orderId":2,"sellerName":"judy-2"}
[消费端]线程:default-executor-2,消费事件 {"amount":100.0,"buyerName":"Tom-1","orderId":1,"sellerName":"judy-1"}
[消费端]线程:default-executor-0,消费事件 {"amount":100.0,"buyerName":"Tom-3","orderId":3,"sellerName":"judy-3"}
SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster 这个我们自己实例化的 Bean 与系统默认的加载顺序如何?会不会有冲突?
查了下 Spring 源码,处理逻辑在 AbstractApplicationContext#initApplicationEventMulticaster 方法中,通过 beanFactory 查找是否有自定义的 Bean,如果没有,容器会自己 new 一个 SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster 对象注入到容器中。
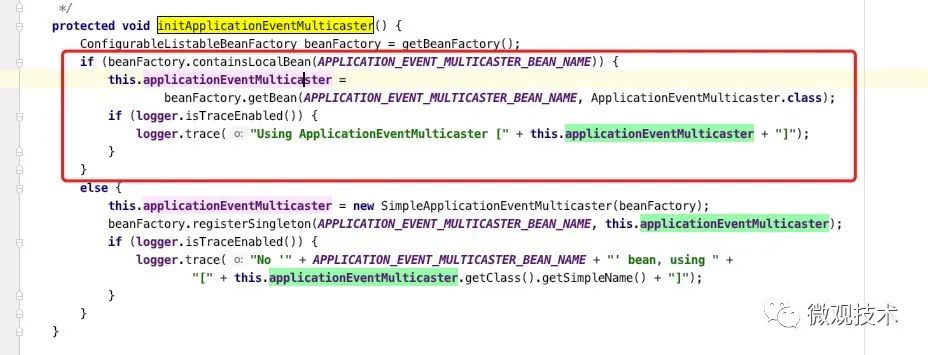
代码地址:https://github.com/aalansehaiyang/wx-project
七、消息队列
异步架构是互联网系统中一种典型架构模式,与同步架构相对应。而消息队列天生就是这种异步架构,具有超高吞吐量和超低时延。
消息队列异步架构的主要角色包括消息生产者、消息队列和消息消费者。
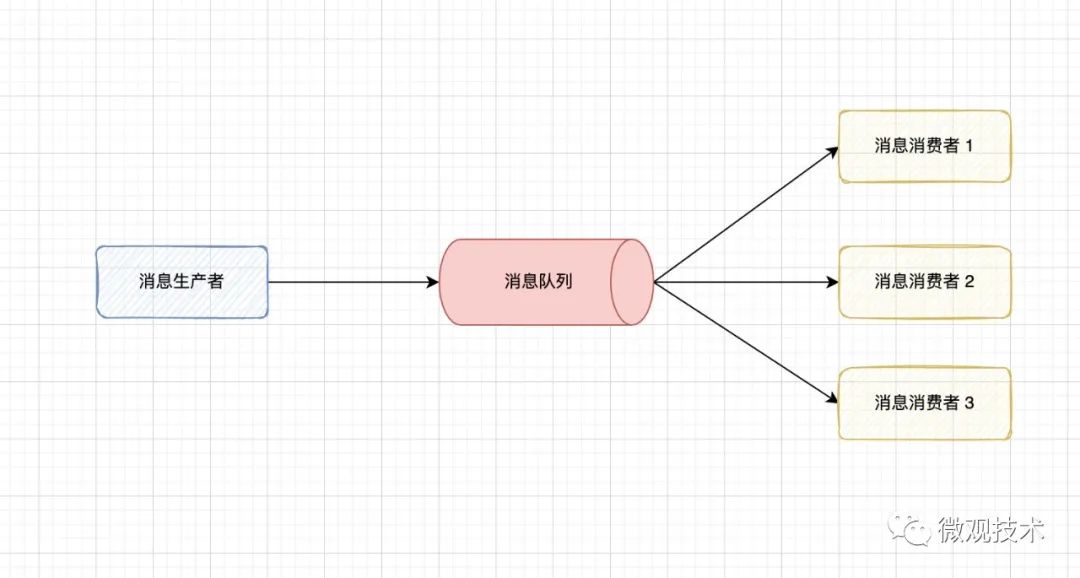
消息生产者就是主应用程序,生产者将调用请求封装成消息发送给消息队列。
消息队列的职责就是缓冲消息,等待消费者消费。根据消费方式又分为点对点模式和发布订阅模式两种。
消息消费者,用来从消息队列中拉取、消费消息,完成业务逻辑处理。
当然市面上消息队列框架非常多,常见的有RabbitMQ、Kafka、RocketMQ、ActiveMQ 和 Pulsar 等
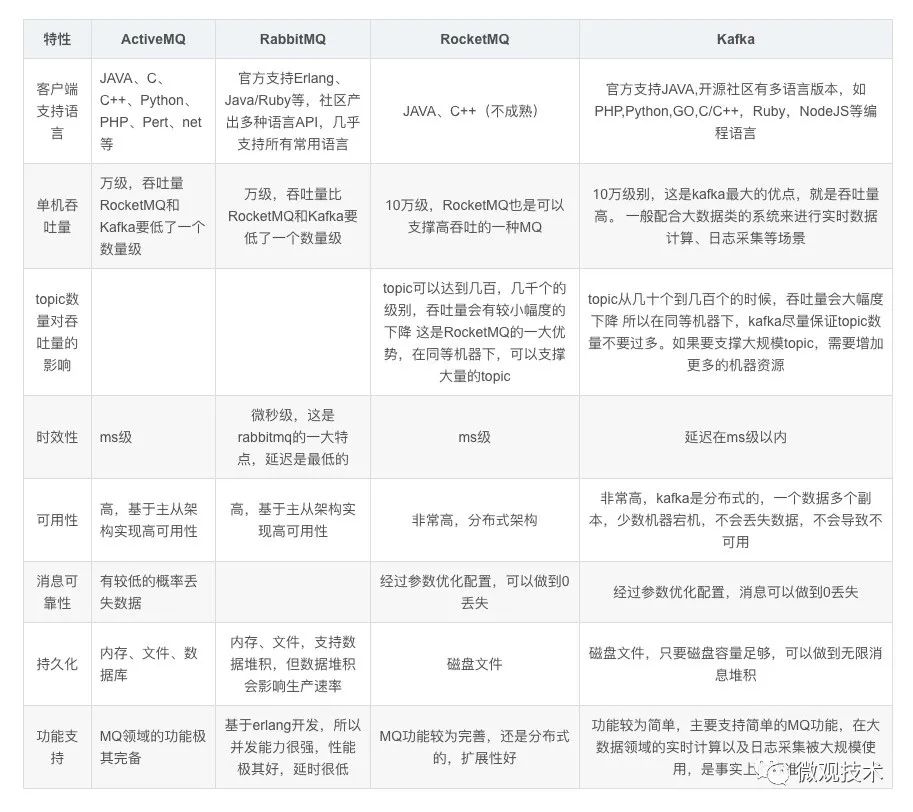
不同的消息队列的功能特性会略有不同,但整体架构类似,这里就不展开了。
我们只需要记住一个关键点,借助消息队列这个中间件可以高效的实现异步编程。
边栏推荐
- [Acwing] 58周赛 4489. 最长子序列
- 手里10万元存款买什么理财产品收益最高?
- c# 实现定义一套中间SQL可以跨库执行的SQL语句
- tp配置多数据库
- Research Report on market supply and demand and strategy of China's Sodium Tetraphenylborate (cas+143-66-8) industry
- 容器环境minor gc异常频繁分析
- Is it safe for Anxin securities to open an account online? Is the account opening fee charged
- 基于check-point机制的任务状态回滚和数据分块任务
- Sql实现Split
- APOC custom functions and procedures
猜你喜欢

Solution du système de gestion de la chaîne d'approvisionnement du parc logistique intelligent

昆明三环闭合工程将经过这些地方,有在你家附近的吗?

周大福践行「百周年承诺」,真诚服务推动绿色环保
Go development: how to use go singleton mode to ensure the security of high concurrency of streaming media?

Smart Logistics Park supply chain management system solution: digital intelligent supply chain enables a new supply chain model for the logistics transportation industry

智慧物流园区供应链管理系统解决方案:数智化供应链赋能物流运输行业供应链新模式
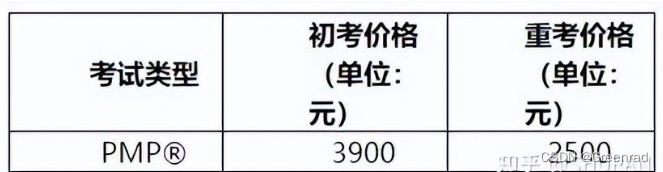
Learn more about the basic situation of 2022pmp examination

DIY a low-cost multi-functional dot matrix clock!
基于wifi控制的51单片机温度报警器

Software Engineer vs Hardware Engineer
随机推荐
Understand asp Net core - Authentication Based on jwtbearer
How to implement a delay queue?
[Acwing] 58周赛 4489. 最长子序列
Hair and fuzz interceptor Industry Research Report - market status analysis and development prospect forecast
[Chongqing Guangdong education] National Open University spring 2019 1248 public sector human resource management reference questions
js中的数组筛选fliter
China Indonesia adhesive market trend report, technological innovation and market forecast
~88 running people practice
APOC自定义函数和过程
GO开发:如何利用Go单例模式保障流媒体高并发的安全性?
嵌入式软件架构设计-函数调用
Market trend report, technical innovation and market forecast of electrochromic glass and devices in China and Indonesia
Median and order statistics
表单传递时,如何隐式将值传过去
线程池的使用和原理
Visual studio 2019 (localdb) mssqllocaldb SQL Server 2014 database version is 852 and cannot be opened. This server supports 782
Research Report on market supply and demand and strategy of China's well completion equipment industry
C# 实现 FFT 正反变换 和 频域滤波
从数数开始
Array filter fliter in JS