当前位置:网站首页>Package details
Package details
2022-06-11 09:19:00 【lwj_ 07】
notes : There are three examples of homework at the end
encapsulation
1.1、 Three characteristics of object-oriented : encapsulation 、 Inherit 、 polymorphic 、
With encapsulation , To inherit , With inheritance , There is polymorphism .
1.2、 The first feature of object orientation : encapsulation .
What is encapsulation ? What's the role ?
Many real examples in real life are encapsulated , for example :
mobile phone , The TV , Computers have a hard shell on the outside , encapsulated ,
Protect internal components , Ensure that the internal components are safe . In addition, after encapsulation ,
For our users , We can't see the complex structure inside , We
There is no need to care about how complicated it is inside , We only need to operate a few on the shell
Button to complete the operation .
So what does encapsulation do ?
The first function : Ensure the safety of the internal structure
The second function : Shielding is complicated , Exposure is simple
At the code level , What's the use of encapsulation ?
Data in a class body , Suppose after encapsulation , For the caller of the code ,
You don't need to care about the complex implementation of the code , Just go through a simple entrance
Visited , in addition , The data with higher security level in the class body is encapsulated , Outsiders
Members are not allowed to visit at will , To ensure data security .
What are the disadvantages of code without encapsulation :

// Access... In an external program Person Data in this type .
public class PersonTest01
{
public static void main(String[] args){
// establish Person object
Person p1 =new Person();
// The age of the interviewer
// Accessing the properties of an object , There are usually two operations , One is to read data , One is to change the data .
// Reading data
System.out.println(p1.age); // read (get Said to get )
// Modifying data
p1.age =50;
// Read again
System.out.println(p1.age);
// stay PersonTest In this external program, you can now set attributes at will age operational .
// Random modification leads to data insecurity
p1.age =-100;
System.out.println(p1.age);
}
}Packaged Person:
// Packaged Person
public class Person
{
// private For private , After being modified by this keyword , This data can only be accessed in this class .
private int age;
}// Access... In an external program Person Data in this type .
public class PersonTest01
{
public static void main(String[] args){
// establish Person object
Person p1 =new Person();
// Person Of age, Completely inaccessible from the outside , But it's a little too safe .
// age Cannot access , The meaning of this program is not great .
// Reading data
System.out.println(p1.age); // read (get Said to get ) The result is wrong
// Modifying data
p1.age =50;
// Read again
System.out.println(p1.age); // The result is wrong
// Modify the data again
p1.age =-100;
System.out.println(p1.age); // The result is wrong
}
}
Modified encapsulation code :【 First understand the instance method Revise 】
java There are requirements in the development specification ,set Methods and get Method should satisfy the following format :
get Method requirements :
public return type get+ Attribute names are capitalized ( No arguments ){
return xxx;
}
set Method requirements :
public void set+ Attribute name is capitalized ( There is a parameter ){
xxx = Parameters ;
}
Focus on
The encapsulated code implements two steps :
First step : Property privatization (private)
The second step : One attribute provides two external set and get Method , External programs can only pass through set Methods to modify , Only through get
Method reading , Can be in set Set up checkpoints in the method to ensure the security of data .Just a little bit more :
set and get Methods are instance methods , You can't take static
No static The method of is called instance method , The instance method must be called first new objectset and get There are strict specification requirements when writing methods
public class Person
{
// private For private , After being modified by this keyword , This data can only be accessed in this class .
private int age;
// Provide simple access to the outside world
// Write a method dedicated to reading .(get)
// Write a method dedicated to writing .(set)
// get and set The method should not take static, Defined as instance method
//[ What you read and revise is your age No object, no age ]
// Format : [ List of modifiers ] return type Method name ( Formal parameter type ){}
// get Take the data
public int getAge(){
return age; // return The data type and " Return type of method " identical ,age by int So the method is int
}
// set Modifying data
public void setAge(int nianLing){
age =nianLing;
}
}// Access... In an external program Person Data in this type .
public class PersonTest01
{
public static void main(String[] args){
// establish Person object
Person p1 =new Person();
// Take the data
int nianling =p1.getAge(); // The return value must require a variable of the same type to receive
System.out.println(nianling); // 0 The default value is
// The above codes are combined System.out.println(p1.getAge());
// Modifying data
p1.setAge(123);
// When reading data again
System.out.println(p1.getAge()); // 123
// Be careful : I found that I could change my age to -100 It's not very realistic [ unsafe ]
// Then we need to set Method set up a checkpoint at the entrance
p1.setAge(-100);
System.out.println(p1.getAge()); // -100
}
}set Method set up a checkpoint at the entrance :
public class Person
{
// private For private , After being modified by this keyword , This data can only be accessed in this class .
private int age;
// Provide simple access to the outside world
// Write a method dedicated to reading .(get)
// Write a method dedicated to writing .(set)
// get and set The method should not take static, Defined as instance method
//[ What you read and revise is your age No object, no age ]
// Format : [ List of modifiers ] return type Method name ( Formal parameter type ){}
// get Take the data
public int getAge(){
return age; // return The data type and " Return type of method " identical ,age by int So the method is int
}
// set Modifying data
public void setAge(int nianLing){
// Can you in this set Method set up a level on the location !!!
// Yes, it was int nianLing Make conditional restrictions
if (nianLing<0||nianLing>150)
{
System.out.println(" Sorry, the age is illegal , Please re-enter !");
return;
}
age =nianLing;
}
}Example method ( No static Methods )
Objects are called instances
Strength is related to : Instance variables 、 Example method
Instance variables are object variables . Instance methods are object methods
step : All instances related need to be new object , adopt " quote ." The way to visit
The code is shown as follows :
public class OOTest02
{
public static void main(String[] args){
// with static Method call ( Common method )
// Class name . It can be omitted ( In the same class )
dosome();
// Without static Method call ( Example method or Object methods ) You need to create the object first Re pass " quote ." Method call
OOTest02 o =new OOTest02();
o.doOther();
}
// with static
public static void dosome(){
System.out.println("do some");
}
// This method doesn't have static, This method is called : Example method ( Object methods )
public void doOther(){
System.out.println("do other.....");
}
}
Null pointer problems caused by instance methods
public class OOTest03
{
public static void main(String[] args){
User u =new User();
u.eat();
// The reference becomes null No longer point to the heap User object
u=null;
// The invocation of an instance method must also have the existence of an object Therefore, a null pointer exception occurs in the above case
u.eat();
}
public static void doSome(){
System.out.println("do some");
}
}
class User
{
// Instance variables
int id;
// Example method ( Object related methods There must be an object )
//( Such as : having dinner So the object is people or animal To play basketball ---> object people ... So you need to call first new An object )
//【 The common method only needs " Class name ." To make the call 】
public void eat(){
System.out.println(" Eat something ");
}
}

Homework 1:
Please encapsulate... Through code , Realize the following requirements :
Write a class Book, Representative textbook :
1. With attributes : name (title) 、 the number of pages (pageNum)
2. The number of pages cannot be less than 200 page , Otherwise, an error message will be output , And give default values 200
3. Provide assignment and value taking methods for each attribute
4. There is a way :detail, It is used to output the name and pages of each textbook on the console
5. Writing test classes BookTest To test : by Book The properties of the object are given initial values , And call Book Object's detail
public class HomeWork
{
public static void main(String[] args){
Book b =new Book("java Introductory textbook ",160);// [ There are constructors Parameters are passed directly to attributes through the constructor ]
b.detail();
// Take the name or Take pages
String i=b.getTitle();
System.out.println(i);
// Modify name or Change the number of pages
b.setTitle("python.");
System.out.println(b.getTitle());
}
}
class Book
{
private String title;
private int pageNum;
// Construction method No parameter
public Book(){
}
// There are parameter constructors
public Book(String t,int p){
title =t;
pageNum =p;
}
// set and get Method
public String getTitle(){
return title;
}
public void setTitle(String t){
title =t;
}
public int getpageNum(){
return pageNum;
}
public void setTitle(int p){
if (p<200||p<0)
{
System.out.println(" The number of pages in this book cannot be less than 200 page Default assignment 200 page .");
pageNum =200;
return;
}
pageNum =p;
}
public void detail(){
System.out.println(" Book title :"+this.title+" Book pages :"+this.pageNum);
}
}

In the parameterless constructor and There are parameter constructors that can also modify data or define conditions
public class HomeWork
{
public static void main(String[] args){
Book b1 =new Book();
// Don't pass it on Modifying attribute data in a parameterless constructor
String i =b1.getTitle();
System.out.println(i);
// Then read the data
int b =b1.getpageNum();
System.out.println(b);
}
}
class Book
{
private String title;
private int pageNum;
// Construction method No parameter
public Book(){
title =" Unknown course ";
pageNum =360;
}
// There are parameter constructors
public Book(String t,int p){
title =t;
pageNum =p;
}
// set and get Method
public String getTitle(){
return title;
}
public void setTitle(String t){
title =t;
}
public int getpageNum(){
return pageNum;
}
public void setpageNum(int p){
if (p<200||p<0)
{
System.out.println(" The number of pages in this book cannot be less than 200 page Default assignment 200 page .");
pageNum =200;
return;
}
pageNum =p;
}
public void detail(){
System.out.println(" Book title :"+this.title+" Book pages :"+this.pageNum);
}
}
Homework 2:
Write a name for Account Class simulation account .
The properties and methods of this class are as follows .
This class includes properties : Account id, balance balance, Annual interest rate annualInterestRate:
Included methods : Each attribute of set and get Method . Method of withdrawal withdraw(), Method of deposit deposit()
Write a test program
(1) Create a Customer, Name is Jane Smith, He has an account number for 1000, The balance is 2000, The annual interest rate is 1
(2) Yes Jane Smith operation :
Deposit in 100 element , Take it out again 960 element , Take it out again 2000.
Print Jane Smith Basic information of
The information is shown below :
Successfully deposited : 100
Successfully removed : 960
Lack of balance , Failed to withdraw money
public class HomeWork01
{
public static void main(String[] args){
Account a =new Account("Jane Smith",2000,1);
System.out.println(a.getId());
a.deposit(100);
a.withdraw(960);
a.withdraw(2000);
}
}
class Account
{
private String id;
private int balance;
private int annualInterestRate;
public Account(){
}
public Account(String id,int balance,int annualInterestRate){
this.id =id;
this.balance =balance;
this.annualInterestRate =annualInterestRate;
}
public String getId(){
return id;
}
public void setId(String id){
this.id =id;
}
public int getBalance(){
return balance;
}
public void setId(int balance){
this.balance =balance;
}
public int getAnnualInterestRate(){
return annualInterestRate;
}
public void setAnnualInterestRate(int annualInterestRate){
this.annualInterestRate =annualInterestRate;
}
// Method of deposit
public void deposit(int money){
int money1 =money+this.balance;
this.balance =money1;
System.out.println(" Successfully deposited :"+money);
}
// Method of withdrawal
public void withdraw(int money){
int money2 =this.balance-money;
if (money2<0)
{
System.out.println(" Lack of balance , Failed to withdraw money ");
return;
}
this.balance =money2;
System.out.println(" Successfully removed :"+money);
}
}
Homework 3:
( encapsulation ) A class is known Student The code is as follows :
class Student{
String name;
int age;
String address ;
String zipCode ;
String mobile;
requirement :
1、 hold student All properties are private , And provide get/set Methods and appropriate construction methods .
2、 by student Class to add a - individual getPostAddress Method , Ask to return student Object's ” Address " and ” Zip code ”
Be careful : The address here is : address, It's not a memory address .
public class HomeWork
{
public static void main(String[] args){
// No arguments
Student s1 =new Student();
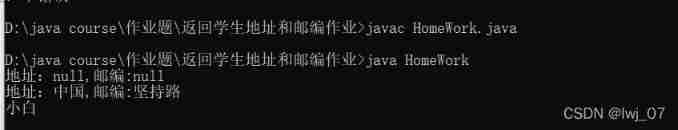
System.out.println(s1.getPostAddress());
// Ginseng
Student s2 =new Student(" The small white ",0," China "," Stick to the road ",null);
System.out.println(s2.getPostAddress());
// Call to read the name getName
System.out.println(s2.getName());
}
}
class Student
{
private String name;
private int age;
private String address ;
private String zipCode ;
private String mobile;
// Parameterless construction method
public Student(){
}
// There are parameter construction methods ( The passed value is assigned to the private variable first )
public Student(String name,int age,String address,String zipCode,String mobile){
this.name =name;
this.age =age;
this.address =address;
this.zipCode =zipCode;
this.mobile =mobile;
}
public String getName(){
return name;
}
public void setName(String name){
this.name =name;
}
public String getAddress(){
return address;
}
public void setAddress(String address){
this.address =address;
}
public String getZipCode(){
return zipCode;
}
public void setZipCode(String zipCode){
this.zipCode =zipCode;
}
public String getPostAddress(){
//return " Address :"+this.address+", Zip code :"+this.zipCode; // this Omission this In fact, it is the same as quoting s1 equally
return " Address :"+this.getAddress()+", Zip code :"+this.getZipCode(); // ditto
}
} 
边栏推荐
- 报错RuntimeError: BlobReader error: The version of imported blob doesn‘t match graph_transformer
- Automation operation and maintenance articles collection
- Tissu. JS définit dynamiquement la taille de la police
- openstack详解(二十二)——Neutron插件配置
- 报错Version mismatch between installed depthai lib and the required one by the scrip.
- 1400. 构造 K 个回文字符串
- 矩阵求逆操作的复杂度分析(逆矩阵的复杂度分析)
- [image processing] spatial domain image enhancement
- OpenCV OAK-D-W广角相机测试
- 1854. the most populous year
猜你喜欢

MSF给正常程序添加后门

CUMT学习日记——ucosII理论解析—任哲版教材

报错RuntimeError: BlobReader error: The version of imported blob doesn‘t match graph_transformer

Output image is bigger (1228800b) than maximum frame size specified in properties (1048576b)
机器学习笔记 - 深度学习技巧备忘清单

ArcGIS 10.9.1 地质、气象体元数据处理及服务发布调用

Type-C Bluetooth speaker single port rechargeable OTG solution

考研數學 【數列極限證明題】題型方法總結

Some learning records I=

机器学习笔记 - 使用TensorFlow的Spatial Transformer网络
随机推荐
ERP体系的这些优势,你知道吗?
面试题 17.10. 主要元素
Type-C Bluetooth speaker single port rechargeable OTG solution
Sword finger offer 18 Delete the node of the linked list
【分享】企業如何進行施行規劃?
【ERP体系】专业技术层面的评估,你了解多少?
自动化运维文章大合集
OpenCV CEO教你用OAK(五):基于OAK-D和DepthAI的反欺骗人脸识别系统
报错[error] input tesnor exceeds available data range [NeuralNetwork(3)] [error] Input tensor ‘0‘ (0)
Do you know these advantages of ERP system?
Install jupyter in the specified environment
从企业评价的方历来看ERP软件成功与失利
2095. delete the intermediate node of the linked list
矩阵求逆操作的复杂度分析(逆矩阵的复杂度分析)
Clothing ERP: how do enterprises carry out implementation planning?
OpenCV OAK相机对比及介绍
剑指 Offer II 041. 滑动窗口的平均值
Talk about how to customize data desensitization
Thread theory
Award winning survey streamnational sponsored 2022 Apache pulsar user questionnaire