One 、 Preparation of compiling and debugging environment
Because I just downloaded vscode The environment has already been configured , Here is a general description of the process , Download and install first vscode Medium C/C++ plug-in unit , Note that compilation and debugging tools are not included , There are only a few code tips for editing .
After the installation windows Version of GCC——MingW, And configure environment variables , The final will be MingW Path configuration to vscode Of launch.json In file . Here I directly use the GUI configuration .
Use g++ --version Check whether the installation is successful .

because menu This project already has makefile File to describe his compilation process , We use it directly in the project path make Instruction to compile the entire project .
But because of MingW Own problems , We need to MingW/bin In the directory MingW-32-makefile.exe Renamed make.exe, otherwise windows Will not recognize make command .

After compiling, we execute the generated test.exe file , Simple operation menu This project .
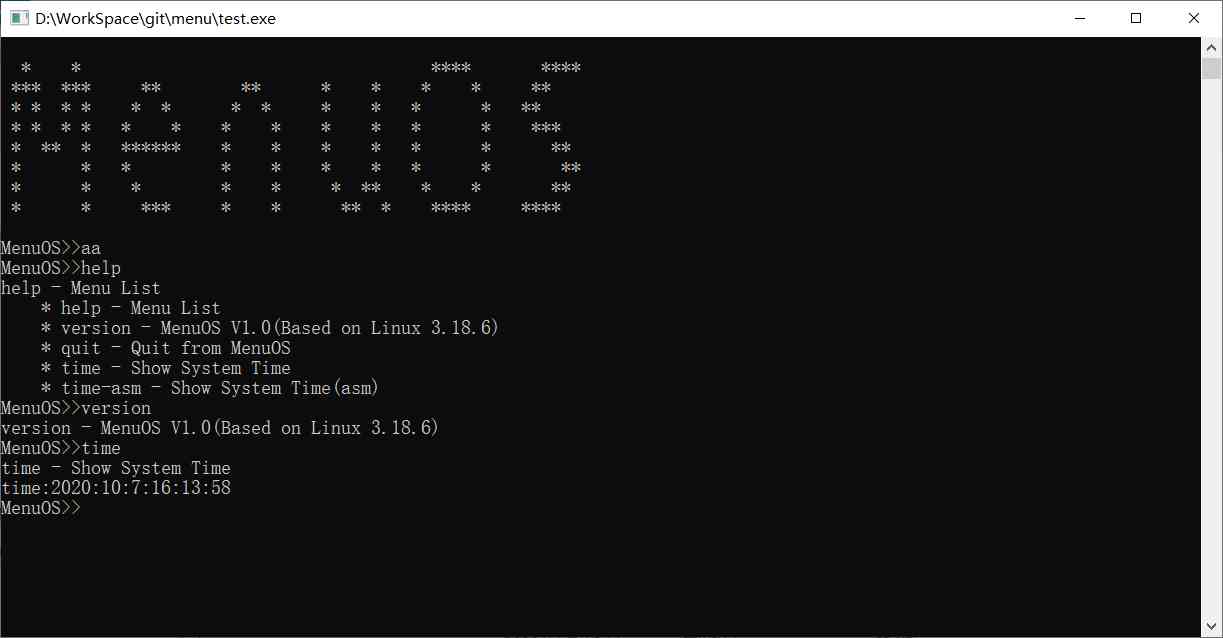
So far, we have completed the configuration of the environment and simply run menu engineering .
Two 、 From the perspective of software engineering menu engineering .
Next, we analyze it one by one .
1、lab1:
Any software starts with a very small prototype , After that, developers will continue to develop on the basis of the previous , Finally achieve the goal defined in the requirements analysis ,
So almost all software is iterative , In each iteration, add new functions or modify them bug. there lab1 It's what the whole project looks like at the beginning .
2、lab2:
stay lab2 in , The project had its original function , Recognition help,quit And other undefined instructions . The key is , There's a comment at the head of the entire file , Explains some information about the project .
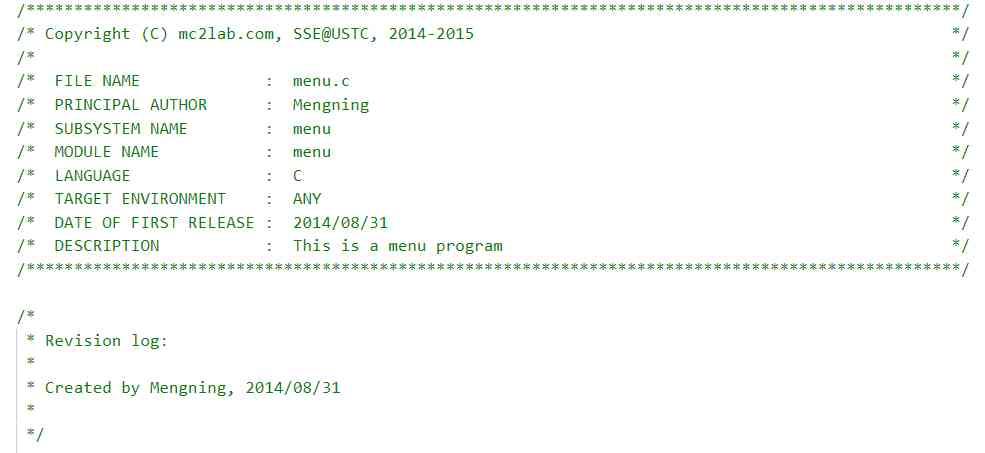
3、lab3.1:
stay lab3.1 in , Mr. Meng abstracted the command , The command is defined as a structure , Put the name of the order 、 Description and specific actions are organized together , At the same time, different commands are organized together through a linked list . The idea of modularity is embodied here .
What needs to be noted is :
The function pointer is used here , Although different commands operate differently, they provide the same interface , This makes c Although language does not have the nature of object-oriented, it still achieves the idea of polymorphism .
meanwhile , Using function pointers makes it easy for us to expand the command array at a later stage head[ ] You just need to add your own behavior , There's no need to modify other code . To a certain extent, it embodies the opening and closing principle of software engineering ,
Open to expansion , Turn off for changes .
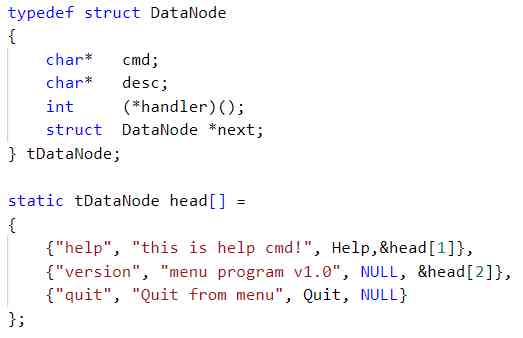
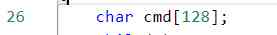
Here's another little detail , stay lab2 in , The maximum length of the command is defined directly by a number , And here we use the macro definition , Eliminated magic number, It enhances the readability of the code and makes it easy to modify .
The following figure for lab2 How to define in :
For a moment lab3.1 How to define in :

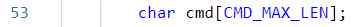
4、lab3.2:
stay lab3.2 in , Mr. Meng will query and display all commands in the linked list. These two behaviors are abstracted into two new functions . The purpose is to facilitate the later modification of these two behaviors ,
For example, we don't use linked list storage commands , When using a red black tree or hash table , It just needs to be modified FindCmd This function can , Without modification main Code in function , It realizes the decoupling between the query command operation and the whole process control .
Another advantage is that we can reuse this function in other projects , If necessary . The idea of modularity is embodied here .
The following figure for FindCmd The definition of and in main Call in function :

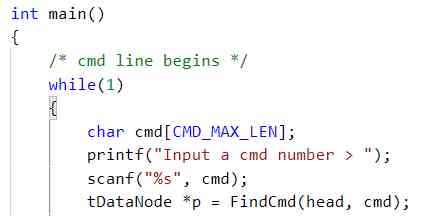
5、lab3.3:
stay lab3.3 in , Mr. Meng put the definition of linked list and related operations in a separate file , The decoupling of linked list operation and main program control process is realized . Here's still the idea of modularity , Easy to maintain and debug programs .

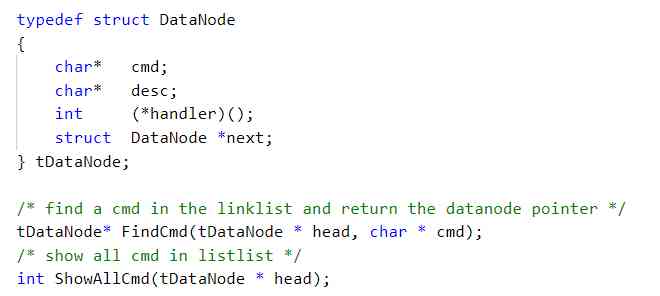
6、lab4:
In this version , Mr. Meng introduced a reusable linked list , Abstract the reusable part of various operations of the linked list , Easy to continue to use in other projects . This part is about the use of reusable interfaces .
At the same time, a simple unit test is carried out on the related operations of the linked list , Make sure the module is correct . The value here is , The node type of reusable linked list is tLinkTableNode*, And the node type that actually stores data is tDataNode*,
To solve this problem , Mr. Meng will operate the linked list tDataNode* Cast type to tLinkTableNode*, So that the business part of the data on the linked list operation of the shield , At the same time, it also decouples the business from the reusable interface .
Here are two examples of strong rotation :
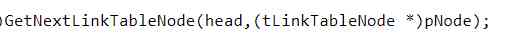
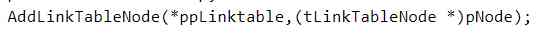
7、lab5.1 & lab5.2
In both versions ,FindCmd Function adds callback Mechanism , In other words, a function is passed in when the function passes parameters , You can then use this function in the calling function .
Use callback Are the benefits of , It can make the program more flexible and increase the reusability , At the same time, it can enhance the function function .
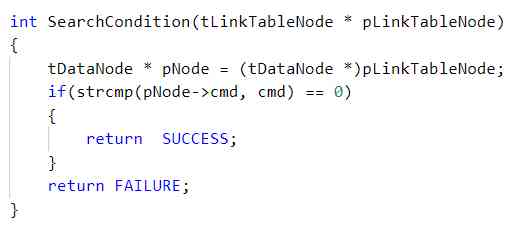
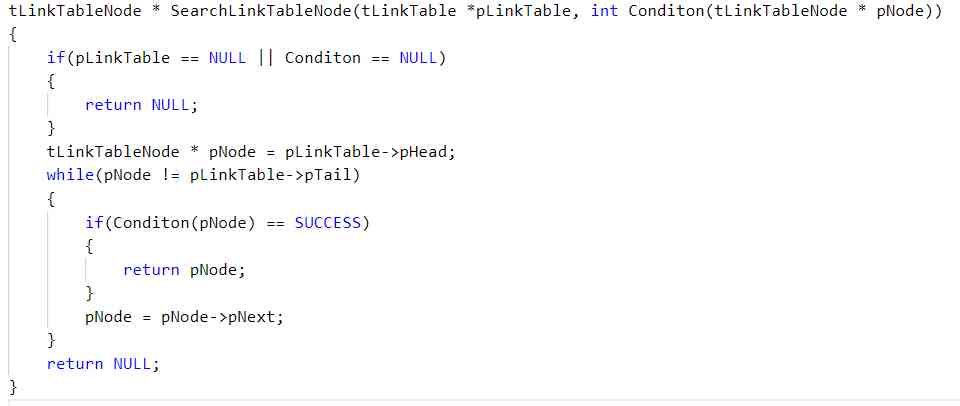
In this case , We can only modify... According to different search criteria SearchCondition The code in the function can achieve the purpose , Without modification SearchLinkTableNode function .
If it's not used here callback, We have to modify SearchLinkTableNode The code in , To a certain extent, it violates the principle of opening and closing .
There's another one that can better reflect callback Examples of the benefits of mechanisms . stay C++ Stl Built in to traverse Stl Function of the container for_each(_InIt _First, _InIt _Last, _Fn _Func).
The first two parameters are the start iterator and the termination iterator to traverse , The third parameter is the action to be performed during traversal , It could be a function .
Because you can do a lot of actions during traversal , For example, output containers , Summation of containers, etc , If not applicable callback,Stl Each traversal action needs to be operated accordingly ,
But in the use of callback after ,Stl Just write an action to traverse the container , Specific actions can be made by Stl User defined and passed in .
Because in lab5.1 Global variables are used for command comparison in , It makes the module that only uses data coupling become public coupling .
So in lab5.2 In the version , Will be used to compare cmd Parameterize and set its type to void* , While reducing the degree of coupling , Completed the business to the reusable interface shielding .
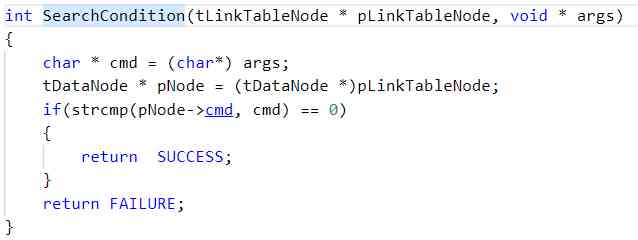
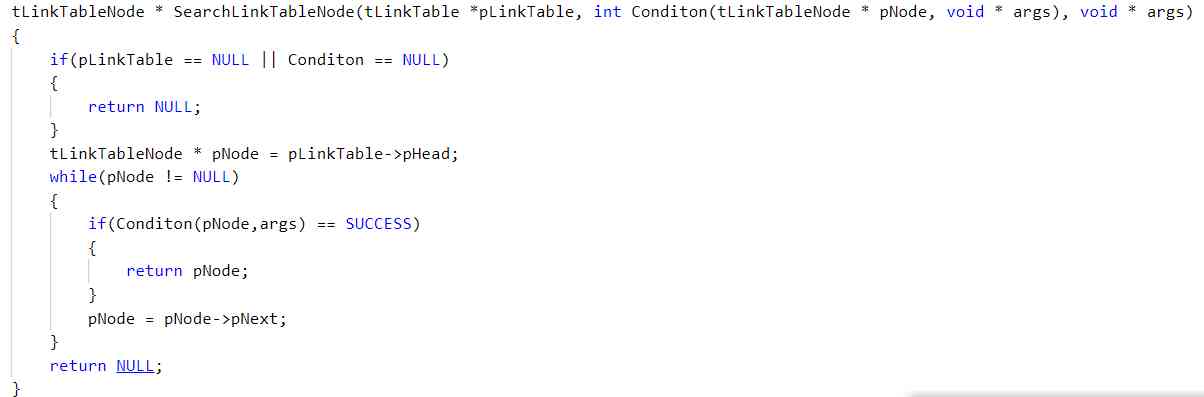
stay 5.x The version also added makefile file , It is convenient to compile the whole project .
8、lab7.1 & lab7.2
stay 7.1 in , Mr. Meng added a lock mechanism to the linked list operation , Ensure that the entire list operation function is reentrant , It is convenient for multithreaded software to call them .
meanwhile , It also abstracts the former process control part from the main function into ExecuteMenu function , Continue decoupling . Will also menu The definition and implementation of is separated into .c and .h file , take menu Designed as a separate module .
stay 7.2 Joined the readme.txt, The function and compiling method of the whole module are explained .
3、 ... and 、 summary :
Through this example , I have a deeper understanding of software engineering . The background of software engineering is the growing scale of software , More and more changes , Make the whole software project difficult to maintain and manage .
The emergence of software engineering is to solve these problems , So that developers can be more leisurely in the face of change , Improve the reusability of software modules .menu Although the project code is not much , But it embodies abstract ideas in many places ,
What this brings us is that —— In software design and Implementation , Consider the abstraction of the interface more than the concrete implementation , And consider which parts are likely to change , Which parts can be reused .
