当前位置:网站首页>[opencv] - Operator (Sobel, canny, Laplacian) learning
[opencv] - Operator (Sobel, canny, Laplacian) learning
2022-07-29 08:22:00 【I love to learn food】
At the beginning :
This blog mainly introduces the three operators involved in edge detection , Namely Sobel operator 、Canny operator 、Laplacian operator ). Last blog python edition CV The usage of these three operators is also introduced .
List of articles
First, let's introduce the steps of edge detection :
(1) wave filtering
The algorithm of edge detection is mainly based on the first and second derivatives of image intensity , But derivatives are usually sensitive to noise , Therefore, filters must be used to improve the performance of noise related edge detectors . Common filtering methods mainly include Gaussian filtering , That is, the discrete Gaussian function is used to generate a set of normalized Gaussian kernels , Then, each point of the image gray matrix is weighted and summed based on Gaussian kernel function .
(2) enhance
The basis of edge enhancement is to determine the change value of neighborhood intensity of each point in the image . The enhancement algorithm can highlight the points with significant changes in the intensity value of the neighborhood of image gray points . In specific programming, the gradient amplitude is used to determine
(3) testing
Enhanced image , Often, the gradient value of many points in the neighborhood is relatively large , And in a particular application , These points are not the edge points to be found , So we should use some method to choose these points . In practical engineering , The commonly used method is to detect by thresholding
1、sobel operator
1.1 sobel The basic concept of operator
Sobel Operator is a discrete differential operator mainly used for edge detection . It combines Gaussian smoothing kernel differential derivation , Used to calculate the myopic gradient of image gray function . Use this operator at any point in the image , Will produce a gradient vector or its normal vector for
1.2 sobel The calculation of the operator
(1) Respectively in x and y Derivation in two directions
Level change : take I With an odd size kernel Gx Convolution . such as , When the kernel size is 3 when ,Gx Calculated results of :
G x = I 3 − I 1 + 2 ∗ I 6 − 2 ∗ I 4 + I 9 − I 7 Gx=I3-I1+2*I6-2*I4+I9-I7 Gx=I3−I1+2∗I6−2∗I4+I9−I7
Vertical change : take I Convolution with an odd sized kernel . such as , When the kernel size is 3 when ,Gx Calculated results of :
G y = I 3 − 2 ∗ I 2 − I 1 + I 9 + 2 ∗ I 8 + I 7 Gy=I3-2*I2-I1+I9+2*I8+I7 Gy=I3−2∗I2−I1+I9+2∗I8+I7
(2) At every point in the image , Combine the above two to find the approximate gradient :
G = s q r t ( G x 2 + G y 2 ) G=sqrt(Gx^2+Gy^2) G=sqrt(Gx2+Gy2)
Sometimes the following formula can be used instead :
G = ∣ G x ∣ + ∣ G y ∣ G=|Gx|+|Gy| G=∣Gx∣+∣Gy∣
1.3 Use Sobel operator :Sobel() function
void Sobel(InputArray src,OutputArray dst,int ddepth,int dx,int dy,
int kszie=3,double scale=1,double delta=0,
int borderType=BORDER_DEFAULT);
The first parameter : The input image , fill Mat The type is enough
The second parameter : Target image , The output parameters of the function , Need the same size and type as the source image
The third parameter : The depth of the output image , The following combinations are supported :
- if src.depth()=CV_8U, take ddepth=-1/CV_16S/CV_32F/CV_64F
- if src.depth()=CV_16U/CV_16S, take ddepth=-1/CV_32F/CV_64F
- if src.depth()=CV_32F, take ddepth=-1/CV_32F/CV_64F
- if src.depth()=CV_64F, take ddepth=-1/CV_64F
Fourth parameter :x The order of difference in the direction
Fifth parameter :y The order of difference in the direction
Sixth parameter : Nuclear size , take 1,3,5,7
Seventh parameter :double Type of scale, Optional scaling factor when calculating derivative values , The default value is 1, Indicates that scaling is not applied by default .
Eighth parameter :double Type of delta, It means storing in the target map
The ninth parameter : The boundary model . Have default values :BORDER_DEFAULT
Additional explanation :
(1) When the kernel size is 3 when ,Sobel The kernel may produce obvious errors . therefore OpenCV Provides Scharr function , But this function only works on the size of 3 The kernel of . Than Sobel The result of the function is more accurate

(2)Sobel Operator combines Gaussian smoothing kernel differentiation , So the result will be more noise resistant :
Calculate the image X Derivative of direction , take 【xorder=1,yorder=0,ksize=3】, Corresponding kernel :

Calculate the image Y Derivative of direction , take 【xorder=0,yorder=1,ksize=3】, Corresponding kernel :

1.4 The sample program
#include<opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include<opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp>
#include<opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
int main()
{
// establish grad_x and grad_y matrix
Mat grad_x, grad_y;
Mat abs_grad_x, abs_grad_y, dst;
// Load the original drawing
Mat src = imread("E:\\Pec\\fushiyuan.jpg");
imshow("【 The original picture 】", src);
// seek X Directional gradient
Sobel(src, grad_x, CV_16S, 1, 0, 3, 1, 1, BORDER_DEFAULT);
// White to black is a positive number , Black to white is a negative number , All negative numbers will be truncated to 0, So take the absolute value
convertScaleAbs(grad_x, abs_grad_x);
imshow("【 design sketch 】X Direction Sobel", abs_grad_x);
// seek Y Directional gradient
Sobel(src, grad_y, CV_16S, 0, 1, 3, 1, 1, BORDER_DEFAULT);
// White to black is a positive number , Black to white is a negative number , All negative numbers will be truncated to 0, So take the absolute value
convertScaleAbs(grad_y, abs_grad_y);
imshow("【 design sketch 】Y Direction Sobel", abs_grad_y);
// Merge gradients
addWeighted(abs_grad_x, 0.5, abs_grad_y, 0.5, 0, dst);
imshow("【 design sketch 】 Main topic direction ", dst);
waitKey(0);
}

2、canny operator
2.1 Canny Steps of edge detection
(1)【 First step 】 Image graying
canny The image processed by the algorithm is a gray image , So if the camera captures a color image , First of all, you have to do graying . Grayscale a color image , It is a weighted average based on the sampling values of each channel of the image .
G a r y = ( R + G + B ) / 3 Gary=(R+G+B)/3 Gary=(R+G+B)/3
(2)【 The second step 】 Eliminate noise
In general , Convolution noise reduction using Gaussian smoothing filter , The following shows a size=5 Gaussian kernel example :

(3)【 The third step 】 Calculate the gradient amplitude and direction
here : according to Sobel Filter steps to operate , sobel operator (Sobel
operator) It is one of the operators of image processing , Mainly used for edge detection . Technically, it is a discrete difference operator , Used to calculate the myopic value of the gradient of the image brightness function .
Using a pair of convolution arrays ( Act on respectively x and y Direction )

Use the following formula to calculate the gradient assignment and direction , The angle taken in the gradient direction is generally 0°,45°,90°,135°

(3)【 The third step 】 Non maximum suppression
This step excludes edge pixels , Only some thin lines are retained ( Candidate edges ). In the calculated amplitude image , There may be situations where multiple large values are close , But there is only one real edge point , In this case, non maximum suppression , Find the local maximum , Thus, most non edge points can be eliminated .
(4)【 Step four 】 Lag threshold
This is the last step ,Canny Use hysteresis threshold , Hysteresis threshold requires two thresholds ( High threshold and low threshold ):
- If the amplitude of a pixel position exceeds the high threshold , The pixel is retained as an edge pixel
- If the amplitude of a pixel position is less than the low threshold , This pixel is excluded
- If the amplitude of a pixel position is between two thresholds , The pixel is only retained when connected to a pixel higher than the high threshold
2.2 Canny edge detection :Canny() function
void Canny(InputArray image,OutputArray edges,double threshold1,double threshold2,int apertureSize=3,
bool L2gradient=false)
- The first parameter : The input image , Source image , fill Mat Class , And it needs to be a single channel 8 For image
- The second parameter : Output edge graph , Need the same size and type as the source image
- The third parameter : The first hysteresis threshold
- Fourth parameter : The second hysteresis threshold
- Fifth parameter :int Type of apertureSize, Show application Sobel The aperture size of the operator , Its default value 3
- Sixth parameter :bool Type of L2gradient, An identifier for calculating the gradient amplitude of an image , Have default values false
Be careful : Function threshold 1 And thresholds 2 The smaller values of the two are used for edge connection , Larger values are used to control the initial segment of the strong edge , The recommended threshold ratio is 2 :1 To 3 :1 Between
2.3 The sample program
#include<opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include<opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp>
#include<opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
int main()
{
// Load the original drawing
Mat src = imread("E:\\Pec\\ Thanos .jpg");
Mat src1 = src.clone();
imshow("【 The original picture 】", src);
Mat dst,dst1, edge, gray;
// Create with src Matrices of the same type and size
dst.create(src.size(), src1.type());
// Convert the original image to gray image
cvtColor(src1, gray, COLOR_BGR2GRAY);
// First use 3x3 Kernel to reduce noise
blur(gray, edge, Size(3, 3));
// function Canny operator
Canny(gray, edge, 3, 9, 3);
// take dst All elements in the are set to 0
dst = Scalar::all(0);
dst1 = Scalar::all(0);
gray.copyTo(dst, edge);
src1.copyTo(dst1, edge);
imshow("【 Color inspection chart 】", dst1);
imshow("【 Gray scale detection diagram 】", dst);
waitKey(0);
return 0;
}
3、Laplacian operator
3.1 Laplacian Introduction to operators
Laplacian Operator is n A second order differential operator in a dimensional Euclidean space , Defined as gradient grad Divergence of div. So if f It's a second-order differentiable real function , be f The Laplace operator of is defined as follows :
(1)f It's the Laplace operator , It is also a Cartesian coordinate system xi Summation of all unmixed second-order partial derivatives in
(2) As a second-order differential operator , Laplacian put C The function maps to C function . According to the principle of image processing , The second derivative can be used to detect edges . Because the image is “ A two-dimensional ”, You need to take the derivative in two directions .

3.2 Laplace transform :Laplacian() function
void Laplacian(InputArray src,OutputArray dst,int ddepth,int ksize=1,double scale=1,double delta=0,
intborderType=BORDER_DEFAULT);
The first parameter : The input image , fill Mat The type is enough
The second parameter : Target image , The output parameters of the function , Need the same size and type as the source image
The third parameter : The depth of the target image
- if src.depth()=CV_8U, take ddepth=-1/CV_16S/CV_32F/CV_64F
- if src.depth()=CV_16U/CV_16S, take ddepth=-1/CV_32F/CV_64F
- if src.depth()=CV_32F, take ddepth=-1/CV_32F/CV_64F
- if src.depth()=CV_64F, take ddepth=-1/CV_64F
Fourth parameter :int Type of ksize, The aperture size of the filter used to calculate the second derivative , Size must be positive odd , The default value is 1
Fifth parameter :double Type of scale, Optional scale factor when calculating Laplacian value , The default value is 1
Sixth parameter :doubel Type of delta, Indicates that the result is stored in the target graph , The default value is 0
Seventh parameter : The boundary model , The default value is BORDER_DEFAULT
Be careful :Laplacian() Function mainly uses sobel The operation of the operator .
3.3 The sample program
#include<opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include<opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp>
#include<opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
int main()
{
Mat src_gray,dst, abs_dst;
// Load the original drawing
Mat src = imread("E:\\Pec\\fushi.jpg");
imshow("【 The original picture 】", src);
// Using Gaussian filtering to eliminate noise
GaussianBlur(src, src, Size(3, 3), 0, 0, BORDER_DEFAULT);
// Turn to grayscale
cvtColor(src, src_gray, COLOR_RGB2GRAY);
// Use Laplace function
Laplacian(src_gray, dst, CV_16S, 3, 1, 0, BORDER_DEFAULT);
// Calculate the absolute value , And convert the result into 8 position
convertScaleAbs(dst, abs_dst);
imshow("【 design sketch 】", abs_dst);
waitKey(0);
return 0;
}

边栏推荐
- Day6: using PHP to write landing pages
- Segment paging and segment page combination
- TCP——滑动窗口
- Reading of false news detection papers (3): semi supervised content-based detection of misinformation via tensor embeddings
- 分段分页以及段页结合
- Unicode private use areas
- Usage of torch.tensor.to
- Day6: use PHP to write file upload page
- Importerror: no module named XX
- Privacy is more secure in the era of digital RMB
猜你喜欢

STM32 detection signal frequency

node:文件写入数据(readFile、writeFile),覆盖与增量两种模式

Second week of postgraduate freshman training: convolutional neural network foundation

SQL 面试碰到的一个问题

Application scheme of charging pile
![[beauty of software engineering - column notes] 22 | how to do a good job in technology selection for the project?](/img/1a/72bfb3fef59c54188a823ead3a5390.png)
[beauty of software engineering - column notes] 22 | how to do a good job in technology selection for the project?

Unity Shader学习(六)实现雷达扫描效果
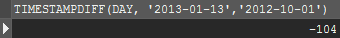
Time function in MySQL

Node: file write data (readfile, WriteFile), two modes: overwrite and increment

Solve the problem of MSVC2017 compiler with yellow exclamation mark in kits component of QT
随机推荐
简易计算器微信小程序项目源码
Phy6252 is an ultra-low power Bluetooth wireless communication chip for the Internet of things
(Video + graphic) machine learning introduction series - Chapter 5 machine learning practice
Alibaba political commissar system - Chapter 1: political commissars are built on companies
Intelligent temperature control system
Windows 安装 MySQL 5.7详细步骤
Four pin OLED display based on stm32
RPC和REST
分段分页以及段页结合
leetcode hot 100(刷题篇9)(301/45/517/407/offer62/MST08.14/)
Tensorboard use
Day6: use PHP to write file upload page
110道 MySQL面试题及答案 (持续更新)
【OpenCV】-算子(Sobel、Canny、Laplacian)学习
Day4: the establishment of MySQL database and its simplicity and practicality
STM32 serial port garbled
Lora opens a new era of Internet of things -asr6500s, asr6501/6502, asr6505, asr6601
Dp4301-sub-1g highly integrated wireless transceiver chip
Simulation of four way responder based on 51 single chip microcomputer
[beauty of software engineering - column notes] "one question and one answer" issue 3 | 18 common software development problem-solving strategies