当前位置:网站首页>2021:Greedy Gradient Ensemble for Robust Visual Question Answering
2021:Greedy Gradient Ensemble for Robust Visual Question Answering
2022-06-27 03:17:00 【weixin_ forty-two million six hundred and fifty-three thousand 】
Abstract
Language bias is a key problem in visual question answering , That is, data set bias is often used instead of image information to make final decisions , This leads to poor performance and insufficient visual interpretation of the model's data distributed outside the region . This paper presents a new depolarization framework --Greedy Gradient Ensemble(GGE), Combining multiple bias models for model learning to remove bias . Due to greedy strategy ,GGE Forcing biased models to preferentially over fit biased data distributions , Make the basic model focus on examples where biased models are difficult to solve . Experiments show that our method makes better use of visual information , And in datasets that do not use additional annotations VQA-CP It has achieved the most advanced performance .
One 、 Introduce
Language bias , That is, models often use the surface correlation between questions and answers to train models , Without considering visual information . The popular solutions to this problem can be divided into : Based on Integration 、 Based on Grounding 、 Based on counterfactual . The method based on integration is similar to the reweighting and resampling in traditional long tail classification , It reweights the sample by only the branch of the problem ; The grounded model emphasizes the better use of image information according to the visual interpretation of human annotations ; The newly proposed counterfactual based method further combines these two kinds of work and achieves better performance . and , The existing methods can not make full use of visual and linguistic information , For example, the improvement of accuracy of grounding based methods does not come from the appropriate visual basis , But from some unknown regularization effect .
Through experimental analysis , There are actually two kinds of linguistic prejudice :a) The statistical distribution gap between training and testing ,b) given QA Semantic relevance of pairs , Pictured 1 Shown .

We proposed Greedy Gradient Ensemble(GGE), A model agnostic depolarization framework , It inherits the bias model and the basic model of gradient descent in function space . The key idea of our method is to use the over fitting phenomenon in deep learning . The biased part of the data is greedily over fitted by the biased features , Therefore, we can use more ideal data distribution to learn the basic model of expectation , And focus on examples where the biased model is difficult to solve .
Two 、 Related work
3、 ... and 、VQA A priori of language in
The following conclusions can be drawn from the experiment :1) A good correct rate does not guarantee that the system can use the visual information well in the answer classifier , Grounding supervision or problem only regularization may encourage the model to take advantage of the opposite language bias , Not the visual information of the root .2) Distribution bias and correlation bias are VQA Complementary aspects of language bias in , A single integration branch cannot model these two biases .
Four 、 Method
4.1 Greedy Gradient Ensemble
(X,Y) Represents a training set ,X Represents the observation space ,Y Represents the label space , According to the previous VQA Method , The classification of binary cross entropy loss is mainly considered :

The baseline model directly minimizes the prediction f(X;sita) And labels Y The loss between :
![]()
The bias that makes the model easy to over fit the dataset , So it has bad generalization ability .
hypothesis B It is a set of bias features that can be extracted based on prior knowledge , We fit the bias model and the basic model to the label Y:

hi Represents a bias model that determines the characteristics of bias . Ideally , We want the biased part of the data to be fitted only by the biased model , Therefore, the basic model can learn the unbiased data distribution , To achieve this goal , We have put forward GGE, Biased models have a high degree of finiteness in fitting data .
In function space , Suppose there is Hm, Hope to find hm+1 Add to Hm Make the loss lower . Theoretically ,hm+1 The expected direction is L stay Hm The negative derivative at :
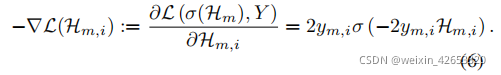
We take the negative gradient as the pseudo label of classification , And optimize the new model hm+1 Of BCE Loss :
![]()
After integrating all bias models , The basic model of expectations f To optimize :
![]()
In the test phase, only the basic model is used to predict .
More intuitively , For a sample that is easily fitted by the biased model , Its loss −∇L(HM) The negative gradient of ( That is, the pseudo label of the basic model ) Will become relatively small .f(X;θ) More attention will be paid to the previous integrated bias classifier HM Difficult samples
In order to adapt the above normal form to batch random gradient attenuation (Batch SGD), We implement two optimal scheduling GGE- Iteration and GGE-together, about GGE-iter, Each model is updated iteratively in a specific data batch iteration .GGE-tog It optimizes the paranoid model and the basic model :
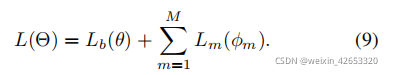
4.2 Robust VQA Of GGE Realization
We define two biased characteristics : Distribution bias and shortcut prejudice .
(1) Distribution bias
We define the distribution bias as the answer distribution of the training set based on the question type :
![]()
The reason for calculating samples based on the problem type is to keep the type information while reducing the distribution bias .
(2)Shortcut prejudice
Indicates the semantic relevance of a particular question and answer pair , We will solve the problem shortcut Prejudice is a problem only branch :
![]()
To verify our proposed distribution bias and shortcut Prejudice is complementary , We designed three versions of GGE To deal with a collection of different language biases .

(1)GGE-D
Model only integrated model distribution bias , Pictured 2b, The loss of the basic model is :
![]()
(2)GGE-Q
Using only one problem-based branch is shortcut prejudice , Pictured 2c, The only thing that optimizes the labeled answer first is the question branch :![]()
The loss of the basic model is :![]()
(3)GGE-DQ
Use distribution bias and questions shortcut prejudice , Pictured 2d,Bq The loss is :
![]()
The loss of the basic model is :![]()
4.3 Connect to enhanced
Enhancement is a widely used integration strategy to solve classification problems , The main idea of reinforcement is to integrate multiple high biases 、 A combination of low variance weak classifiers , Become a low - prejudice 、 And low variance strong classifiers . Every basic learner must be weak enough , otherwise , The first few classifiers will easily over fit the training data , However , The fitting ability of neural network is too strong , Cannot be a high bias and low variance enhancement strategy , It is difficult to use depth models as weak learners . In this paper , Our method takes advantage of this over fitting phenomenon , Make the bias weak feature over fit the bias distribution . In the test phase, the basic model trained by the gradient of the bias model .
5、 ... and 、 experiment
5.1 Evaluation indicators
A new indicator -- Correctly predicted but inappropriate grounding CPIG To assess visual grounding , Definition 1-CPIG by CGR( Correct grounding for correct prediction ):

In order to quantitatively evaluate whether the model uses visual information to answer the decision , We introduced CGW( Proper grounding , But wrong predictions ):![]()
For a clearer comparison , We will CGR and CGW The difference is expressed as CGD( Correct grounding ):
![]()
CGD Only evaluate whether the visual information is obtained in the answer decision , This is parallel to accuracy .CGD The key idea is that a model does use visual information , It's not just about providing the right predictions based on the right visual areas , And because of the inappropriate visual area, it will also lead to the wrong answer . In the table 2 in ,UpDn,HINTinv and CSS-Vinv Achieve comparable performance in accuracy , But in CGD A significant decrease in , It caters to our analysis : These models do not make full use of visual information when making answer decisions .

5.2 Compare with the latest model
The best model GGE-DQ Compare with the most advanced bias reduction technology , Including methods based on visual grounding HINT, SCR, Integration based approach AdvReg, RUBi, LMH, MFH, Problem coding based approach GVQE, DLP, A counterfactual based approach CF-VQA, CSS And the recently proposed regularization method MFE.
stay VQA-CP Test focus ,GGE-DQ State of the art performance without additional comments , be better than UpDn Accuracy rate 17%,CGD13%, Verified GGE The effects of answer classification and visual grounding ability . In the same basic model UpDn under , Our approach achieves the best performance , Even competitive performance with using a strong base model .
For the performance of the problem type , synthesis GGE Reduced bias and improved performance across all problem types , Especially other Class problem .CF-VQA stay Y/N The best in the world , But it is worse than our method on all other indicators .LMH, LMH-MFE, and LMH-CSS stay Num It is superior to other methods ,LMH-CSS The overall accuracy is even slightly higher than GGE-DQ, Because in Num High accuracy on . Compare LM and LMH, stay Num A marked increase in , Because of the regularization of entropy , However , The method of entropy regularization is VQA v2 Up and down almost 10%, It indicates that these models may over correct bias and make extensive use of “ The opposite language bias ”.
5.3 Ablation Experiment

The first set of ablation is to verify whether greedy integration can ensure that biased data can be learned with bias model . We compare the other two integration strategies ,SUM-DQ Directly summarize the outputs of the bias model and the basic model ,LMH+RUBi combination LMH Distribution bias and RUBi Of shortcut prejudice . surface 5 Shown ,SUM-DQ Even worse than the baseline , meanwhile LMH+RUBi The accuracy of LMH similar , About than GGE-DQ Bad 6%, Express GGE Biased model learning that can really force biased data to be serialized . Based on distribution or shortcut Examples where the bias is easy to predict will be well fitted by the corresponding bias model . therefore , The underlying model must pay more attention to difficult examples , And consider more visual information to make the final decision .

In the second set of experiments , Compare distribution bias with shortcut prejudice , chart 3 The example analysis shows that GGE-D Only unified forecast , Major improvements Y/N In the table 5 in .Bq The working principle of is like “ Hard case mining ”, But it also introduces some noise ( For example, in this example “ Mirror image ” and “ no ”) Due to the inverse distribution deviation . Reduce in the first stage Bd The discovery of hard cases can be further encouraged , And force the underlying model to capture visual information . In the figure 3 in , The correct answer has a higher degree of confidence , And the highest predictions are based on images . As shown in the table 5 Shown ,GGE-DQ Higher than the single bias version 10%. This well validates our claim , Distribution deviation and shortcut Deviation is two complementary aspects of language deviation .
5.4 GGE Generalization
(1) Self Integration
GGE The performance of depends largely on the biased characteristics of the pre training , This feature requires prior knowledge of the task or dataset . For further discussion GGE Generalization , We tested a more flexible self integration GGE-SF.GGE-SF Characterizing common expressions as prejudices , Instead of pre training, there are only problem branches , The bias is predicted to be :
![]()
cs A classifier that represents a biased model , Training process and GGE-Q equally .
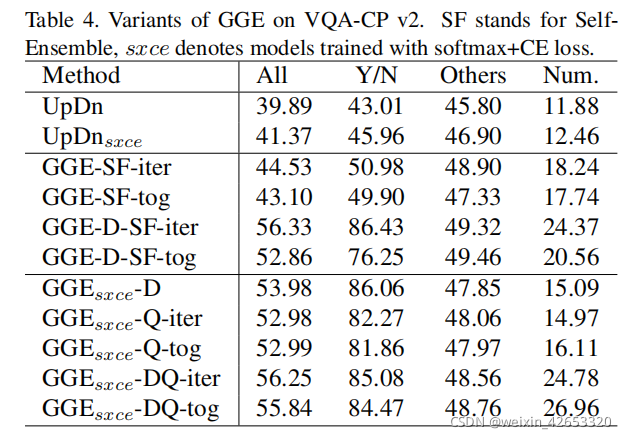
As shown in the table 4, Even without the biased features of pre training ,GGE-SF Still over baseline , Means that as long as the task or data set has enough bias , The basic model can also be regarded as a biased model . Besides , If we first use... Before self integration GGE-D Eliminate distribution bias ,GGE-D-SF Its performance can also be compared with the most advanced existing methods .
(2) Generalization of loss function
To make a fair comparison of previous work , We use Sigmoid+BCE Conduct the above experiment , actually ,GGE The classification loss is unknowable , In the table 4 Provides information about Softmax+CE Additional experiments of loss .
(3) Generalization of the basic model
GGE The choice of the basic model is also unknowable , Provide BAN and S-MRL Additional experiments as a basic model .
5.5 Qualitative assessment

chart 4 Express GGE-DQ How to use visual information for reasoning , We offer three UpDn Examples of failure , The first one is about shortcut prejudice ,UpDn Our predictions are not based on correct visual grounding ; The second example is about distribution bias ,UpDn Correctly capture the visual area but still answer questions based on distribution bias ; The last example is in addition to y/n outside , Reduce the language a priori ,UpDn Only based on language context in the water Answered boat, However GGE-DQ Provides the correct answer tv and television, And there are more obvious visual areas . These examples qualitatively verify the improvement of prediction accuracy and visual interpretation .
6、 ... and 、 summary
In this paper, several robust methods are analyzed VQA Methods , A new framework is proposed to reduce language bias . We proved that VQA The language bias of can be divided into distribution bias and shortcut prejudice , Then a greedy gradient integration strategy is proposed to gradually eliminate these two biases . The experimental results show that our bias decomposition is reasonable and GGE The effectiveness of the . We believe that GGE The idea behind it is valuable , And it may become a general method of data set deviation . some time , We're going to expand GGE To solve the deviation problem of other tasks , Provide more rigorous analysis to ensure the convergence of the model , And learn to automatically detect different types of deviation features without prior knowledge .
边栏推荐
- resnet152 辣椒病虫害图像识别1.0
- Flink学习4:flink技术栈
- Learning Tai Chi Maker - mqtt (VII) advanced mqtt theme
- SQLite reader plug-in tests SQLite syntax
- LeetCode 785:判断二分图
- SAI钢笔工具如何使用,入门篇
- 2021:Graphhopper: Multi-Hop Scene Graph Reasoning for Visual Question Answering
- Learn Tai Chi maker mqtt (IX) esp8266 subscribe to and publish mqtt messages at the same time
- IDEA中好用的插件
- Window 加密壳实现
猜你喜欢

Flink学习3:数据处理模式(流批处理)

TechSmith Camtasia latest 2022 detailed function explanation Download

元透实盘周记20220627

How does source insight (SI) display the full path? (do not display omitted paths) (turn off trim long path names with ellipses)

Mmdetection uses yolox to train its own coco data set

Record the method of reading excel provided by unity and the solution to some pits encountered
Mmdetection valueerror: need at least one array to concatenate solution

Pat grade a 1018 public bike management

2021:Greedy Gradient Ensemble for Robust Visual Question Answering

PAT甲级 1020 Tree Traversals
随机推荐
Pat grade a 1025 pat ranking
2022茶艺师(高级)上岗证题库模拟考试平台操作
事业观、金钱观与幸福观
对数器
PAT甲级 1018 Public Bike Management
PAT甲级 1024 Palindromic Number
Window 加密壳实现
Flink学习1:简介
Getting started with Scala_ Immutable list and variable list
2022 operation of simulated examination platform for tea artist (Senior) work license question bank
ESP8266
servlet与JSP期末复习考点梳理 42问42答
栈溢出漏洞
Introduction to stm32
Mmdetection valueerror: need at least one array to concatenate solution
投资理财产品的钱有保障吗?会不会没有了?
学习太极创客 — MQTT 第二章(一)QoS 服务质量等级
Servlet and JSP final review examination site sorting 42 questions and 42 answers
Flink learning 3: data processing mode (stream batch)
SQLite reader plug-in tests SQLite syntax