当前位置:网站首页>We should make clear the branch prediction
We should make clear the branch prediction
2022-07-02 01:13:00 【Basketball fans who write code】
The English name of branch prediction is 「Branch Prediction」
You can Google Search for this keyword on , You can see a lot about branch prediction , But find out how branch prediction works , That's the point .

The impact of branch prediction on the program
Let's take a look at the following two pieces of code
Code 1
#include <algorithm>
#include <ctime>
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
// Generate data
const unsigned arraySize = 32768;
int data[arraySize];
for (unsigned c = 0; c < arraySize; ++c)
data[c] = std::rand() % 256;
// !!! With this, the next loop runs faster.
//std::sort(data, data + arraySize);
// Test
clock_t start = clock();
long long sum = 0;
for (unsigned i = 0; i < 100000; ++i) {
for (unsigned c = 0; c < arraySize; ++c) { // Primary loop
if (data[c] >= 128) sum += data[c];
}
}
double elapsedTime = static_cast<double>(clock()-start) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC;
std::cout << elapsedTime << '\n';
std::cout << "sum = " << sum << '\n';
}Execution results
@ubuntu:/data/study$ g++ fenzhi.cpp && ./a.out
21.6046
sum = 314931600000 Code 2
#include <algorithm>
#include <ctime>
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
// Generate data
const unsigned arraySize = 32768;
int data[arraySize];
for (unsigned c = 0; c < arraySize; ++c)
data[c] = std::rand() % 256;
// !!! With this, the next loop runs faster.
std::sort(data, data + arraySize);
// Test
clock_t start = clock();
long long sum = 0;
for (unsigned i = 0; i < 100000; ++i) {
for (unsigned c = 0; c < arraySize; ++c) { // Primary loop
if (data[c] >= 128) sum += data[c];
}
}
double elapsedTime = static_cast<double>(clock()-start) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC;
std::cout << elapsedTime << '\n';
std::cout << "sum = " << sum << '\n';
}Execution results :
@ubuntu:/data/study$ g++ fenzhi.cpp && ./a.out
8.52157
sum = 314931600000After the first code generates a random array , No sorting , The second code sorts random arrays , There is a great difference in the execution time .

therefore , What happened to them ?
The reasons for their different results , Namely Branch prediction , Branch prediction is CPU A prediction of a program by a processor , and CPU Architecture related , Many processors now have branch prediction function .
CPU While executing this code
if (data[c] >= 128) sum += data[c];CPU There will be a prediction mechanism in advance , For example, the previous execution results are true, Then next time, judge if When , It will default to be true To deal with it , Let the following instructions enter the pre installation in advance .
Of course , This judgment will not affect the actual result output , This judgment is only for CPU Execute code in parallel .
CPU The execution of an instruction is divided into several stages

Since it is implemented in stages , That is what we normally say pipeline( Pipeline execution ).
The assembly line workers only need to complete the content they are responsible for , There is no need to care about other people to deal with .
If I have a piece of code , as follows :
int a = 0;
a += 1;
a += 2;
a += 3;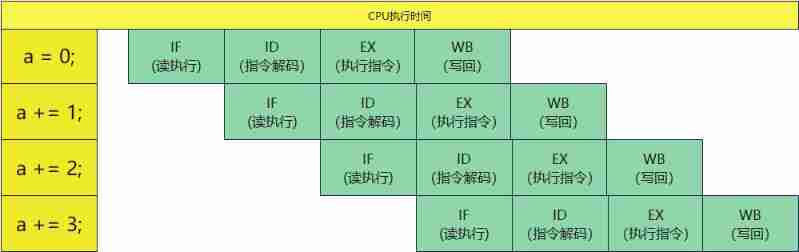

From this picture we can see , We think it's implementation a = 0 After the end , Will execute a+=1.
But the actual CPU It's execution a=0 After the implementation of the first article of , Go ahead immediately a+=1 The first instruction of .
That's why , The execution speed has been greatly improved .
But for if() Language , When there is no branch prediction , We need to wait if() The next code can only be executed after the execution results appear .

If there is branch prediction

By comparison, we can find that , If there is branch prediction , It makes the execution speed faster .

So if you predict Failure , Will it affect the execution time , The answer is yes .
In the previous example , Without sorting the array , Most branch predictions will fail , At this time, the instruction will be retrieved and executed again after the execution , It will seriously affect the execution efficiency .
And in the example after sorting , Branch prediction has been in a successful state ,CPU The execution speed of has been greatly improved .

If the performance degradation caused by branch prediction is solved
There must be a certain decrease in branch prediction , The way to improve performance is not to use this damn if sentence .
such as , The above code , We can change it to this
#include <algorithm>
#include <ctime>
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
// Generate data
const unsigned arraySize = 32768;
int data[arraySize];
for (unsigned c = 0; c < arraySize; ++c)
data[c] = std::rand() % 256;
// !!! With this, the next loop runs faster.
//std::sort(data, data + arraySize);
// Test
clock_t start = clock();
long long sum = 0;
for (unsigned i = 0; i < 100000; ++i) {
for (unsigned c = 0; c < arraySize; ++c) { // Primary loop
int t = (data[c] - 128) >> 31;
sum += ~t & data[c];
}
}
double elapsedTime = static_cast<double>(clock()-start) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC;
std::cout << elapsedTime << '\n';
std::cout << "sum = " << sum << '\n';
} such as , The absolute value code we see , It also uses such ideas
/**
* abs - return absolute value of an argument
* @x: the value. If it is unsigned type, it is converted to signed type first.
* char is treated as if it was signed (regardless of whether it really is)
* but the macro's return type is preserved as char.
*
* Return: an absolute value of x.
*/
#define abs(x) __abs_choose_expr(x, long long, \
__abs_choose_expr(x, long, \
__abs_choose_expr(x, int, \
__abs_choose_expr(x, short, \
__abs_choose_expr(x, char, \
__builtin_choose_expr( \
__builtin_types_compatible_p(typeof(x), char), \
(char)({ signed char __x = (x); __x<0?-__x:__x; }), \
((void)0)))))))
#define __abs_choose_expr(x, type, other) __builtin_choose_expr( \
__builtin_types_compatible_p(typeof(x), signed type) || \
__builtin_types_compatible_p(typeof(x), unsigned type), \
({ signed type __x = (x); __x < 0 ? -__x : __x; }), other)Of course , You can write like this
int abs(int i){
if(i<0)
return ~(--i);
return i;
} So , At the end of the computer is mathematics
Reference resources :
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/11227809/why-is-processing-a-sorted-array-faster-than-processing-an-unsorted-array/11227902#11227902
https://blog.csdn.net/loongshawn/article/details/118339009
https://blog.csdn.net/DBC_121/article/details/105360658
边栏推荐
- Xinniuniu blind box wechat applet source code_ Support flow realization, with complete material pictures
- 2022 high altitude installation, maintenance and removal of test question simulation test platform operation
- gradle
- Based on Simulink and FlightGear, the dynamic control of multi rotor UAV in equilibrium is modeled and simulated
- Picture puzzle wechat applet source code_ Support multi template production and traffic master
- @Valid parameter verification does not take effect
- [eight sorting ③] quick sorting (dynamic graph deduction Hoare method, digging method, front and back pointer method)
- [eight sorts ②] select sort (select sort, heap sort)
- Iclr2022 | spherenet and g-spherenet: autoregressive flow model for 3D molecular graph representation and molecular geometry generation
- Advanced skills of testers: a guide to the application of unit test reports
猜你喜欢
![[eight sorts ④] merge sort, sort not based on comparison (count sort, cardinal sort, bucket sort)](/img/0d/22f3f65ab9422383df9a55d0724d59.jpg)
[eight sorts ④] merge sort, sort not based on comparison (count sort, cardinal sort, bucket sort)
gradle
测试人进阶技能:单元测试报告应用指南

Sql--- related transactions

Study note 2 -- definition and value of high-precision map

AIX存储管理之卷组属性的查看和修改(二)

学习笔记25--多传感器前融合技术

How to compress video size while adding watermark with one click?
![[dynamic planning] interval dp:p3205 Chorus](/img/25/3dc7132e1aaa5c0eca87382692fc12.jpg)
[dynamic planning] interval dp:p3205 Chorus
Promise and modular programming
随机推荐
Edge extraction edges based on Halcon learning_ image. Hdev routine
S32Kxxx bootloader之UDS bootloader
gradle
Principle of finding combinatorial number and template code
Day 13 of hcip (relevant contents of BGP agreement)
什么是商业养老保险?商业养老保险安全靠谱吗?
Datawhale community blackboard newspaper (issue 1)
Basic number theory -- Gauss elimination
Iclr2022 | spherenet and g-spherenet: autoregressive flow model for 3D molecular graph representation and molecular geometry generation
New version of free mobile phone, PC, tablet, notebook four terminal Website thumbnail display diagram online one click to generate website source code
XMind思维导图
Global and Chinese market of wireless chipsets 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
Leetcode 45 Jumping game II (2022.02.14)
ECS project deployment
Basic usage of shell script
Cat Party (Easy Edition)
Infiltration records of CFS shooting range in the fourth phase of the western regions' Dadu Mansion
Appium inspector can directly locate the WebView page. Does anyone know the principle
What are the differences between software testers with a monthly salary of 7K and 25K? Leaders look up to you when they master it
AIX存储管理之卷组的创建(一)