当前位置:网站首页>Heuristic merge, DSU on Tree
Heuristic merge, DSU on Tree
2022-08-02 02:46:00 【xingxg.】
目录
梦幻布丁
启发式合并
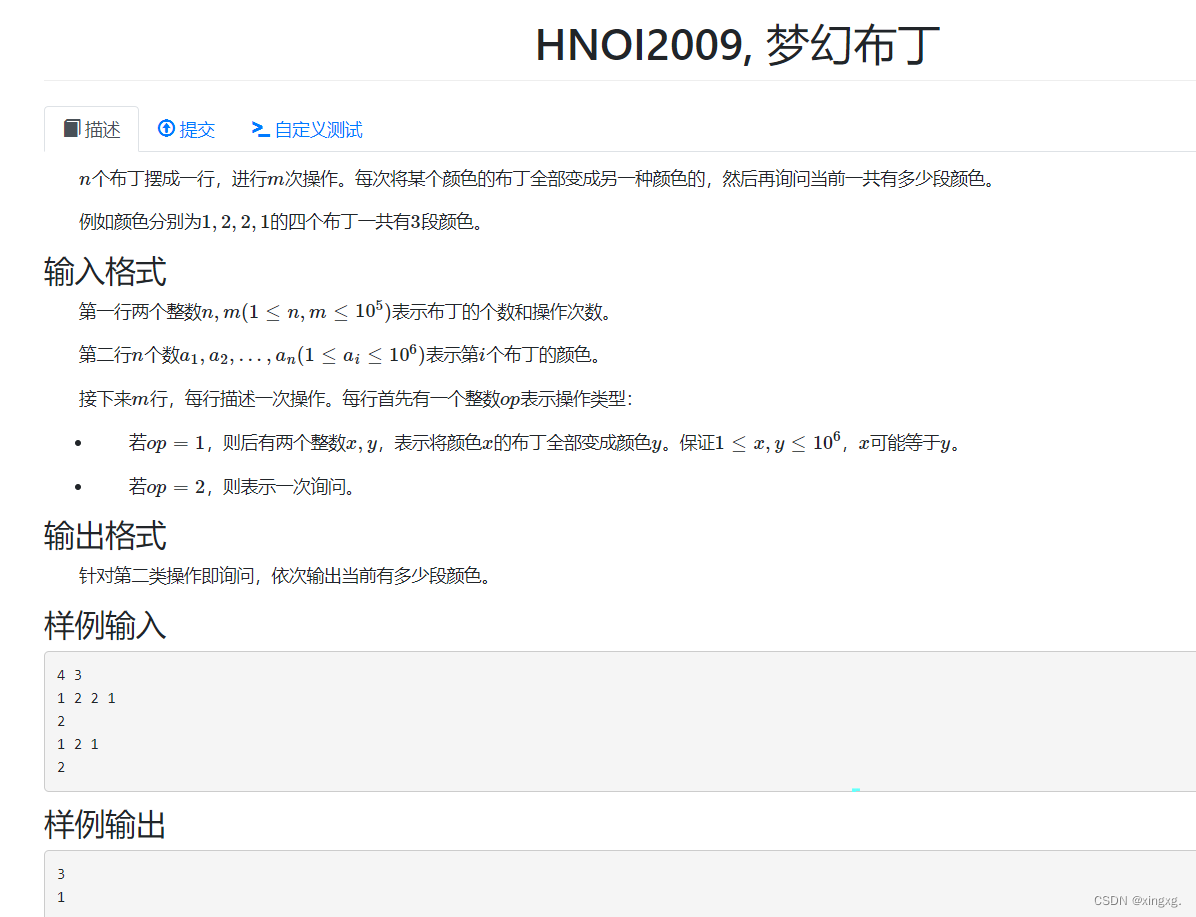
point
pos[i] : Store the color asi的点的坐标, Then why is there in the code behind int col = a[pos[y][0]], 而不直接 int col = y 呢?, Because during the heuristic merge process,To determine the size of the two sets,有个swap操作,两个vector进行swap,pos[x] 和 pos[y] Element exchange in ,但x还是x,y还是y,所以刚开始时, pos[i] Stored is indeed the color fori的点的坐标,But not necessarily later.
When looking for answers,Not traversing againa[]数组,Rather, when modifying the color of a single point,就修改ans
// problem :
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
#define pb push_back
const int N = 101000;
const int M = 1010000;
int n, m, a[N], ans;
void modify(int p, int col) {
ans -= (a[p] != a[p - 1]) + (a[p] != a[p + 1]);
a[p] = col;
ans += (a[p] != a[p - 1]) + (a[p] != a[p + 1]);
}
std::vector<int> pos[M];
int main(){
scanf("%d %d", &n, &m);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
pos[a[i]].push_back(i); // Record the subscript corresponding to each color
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
ans += (a[i] != a[i - 1]);
for (int i = 1; i <= m; ++i) {
int op;
scanf("%d", &op);
if (op == 2) {
printf("%d\n", ans); // Just go through it once before, I also want to do this every query O(n)
} else {
int x, y;
scanf("%d %d", &x, &y);
if (x == y) continue;
if (pos[x].size() > pos[y].size())
swap(pos[x], pos[y]);
if (pos[y].empty()) continue;
int col = a[pos[y][0]];
for (int p : pos[x]) {
modify(p, col);
pos[y].push_back(p);
}
pos[x].clear();
}
}
return 0;
}好序列
If a point appears only once,Then the sequence containing this point is all“好的”, This problem can be solved with the idea of divide and conquer.
So the question is how to solve it Determine if a point occurs only once
还有一个问题需要解决:如果给定一个序列,And the dots that only appear once are all the way at the end,Then we are divided,时间复杂度也是O(n^2)
It can be traversed from the beginning to the end at the same time,如果在中间,那么虽然O(n)遍历,But the divide and conquer interval is even.If at the beginning and end,Although the division and conquer interval is not uniform,But traversal isO(1)
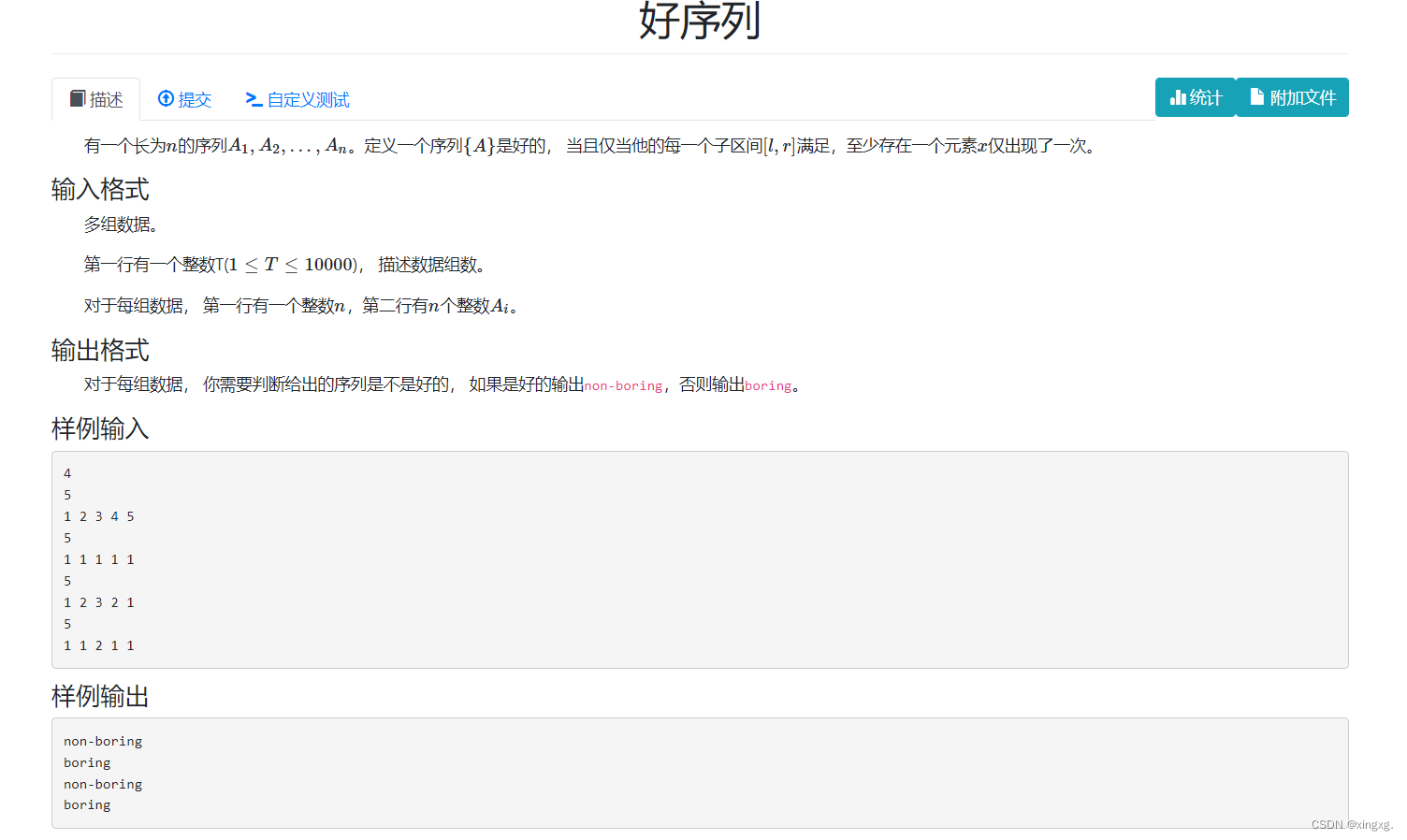
// problem :
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
#define pb push_back
const int N = 201000;
int a[N], pre[N], nxt[N];
bool solve(int l, int r) {
if (l >= r) return true;
for (int pl = l, pr = r; pl <= pr; pl++, pr--) {
if (pre[pl] < l && nxt[pl] > r)
return solve(l, pl - 1) && solve(pl + 1, r);
if (pre[pr] < l && nxt[pr] > r)
return solve(l, pr - 1) && solve(pr + 1, r);
}
return false;
}
bool solve() {
int n; scanf("%d", &n);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
map<int, int> pos;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
if(pos.count(a[i])) pre[i] = pos[a[i]];
else pre[i] = 0;
pos[a[i]] = i;
}
pos.clear();
for (int i = n; i >= 1; --i) {
if (pos.count(a[i])) nxt[i] = pos[a[i]];
else nxt[i] = n + 1;
pos[a[i]] = i;
}
return solve(1, n);
}
int main(){
int tc; scanf("%d", &tc);
for (int i = 1; i <= tc; ++i) {
puts(solve() ? "non-boring" : "boring");
}
return 0;
}CF 600E, Lomsat gelral
You are given a rooted tree with root in vertex 11. Each vertex is coloured in some colour.
Let's call colour cc dominating in the subtree of vertex vv if there are no other colours that appear in the subtree of vertex vv more times than colour cc. So it's possible that two or more colours will be dominating in the subtree of some vertex.
The subtree of vertex vv is the vertex vv and all other vertices that contains vertex vv in each path to the root.
For each vertex vv find the sum of all dominating colours in the subtree of vertex vv.
Input
The first line contains integer n(1 ≤ n ≤ 105)n(1 ≤ n ≤ 105) — the number of vertices in the tree.
The second line contains nn integers ci(1 ≤ ci ≤ n)ci(1 ≤ ci ≤ n), cici — the colour of the ii-th vertex.
Each of the next n − 1n − 1 lines contains two integers xj, yj(1 ≤ xj, yj ≤ n)xj, yj(1 ≤ xj, yj ≤ n) — the edge of the tree. The first vertex is the root of the tree.
Output
Print nn integers — the sums of dominating colours for each vertex.
Examples
input
4
1 2 3 4
1 2
2 3
2 4output
10 9 3 4input
15
1 2 3 1 2 3 3 1 1 3 2 2 1 2 3
1 2
1 3
1 4
1 14
1 15
2 5
2 6
2 7
3 8
3 9
3 10
4 11
4 12
4 13output
6 5 4 3 2 3 3 1 1 3 2 2 1 2 3
Given a rooted tree,root at vertex1.Each vertex has a color.
if at the vertexvThere is no other color than color in the subtree of c出现的次数更多,We call it colorc在顶点vis dominant in the subtree,So it is possible that there are two or more colors that dominate in a subtree of a vertex.
顶点vThe subtrees of are verticesvand all other containing verticesvThe vertices of are on every path to the root.
对于每个顶点v,求顶点vThe sum of all major colors in the subtree.
DSU on Tree DSUMeans and check set,But the funny thing is that this has nothing to do with union checking. Instead, it has a lot to do with heuristic merging.
dfs_solve()中的参数 keep 是保留 , 保留的是cnt数组中的内容,If it is a light son,贡献的cntwill be withdrawn.
主要思想就是:将u和uThe younger sons are all includedu的重儿子. Heavy son because the number of nodes is large,所以Less goes into more,可以节省时间(启发式合并).
// problem :
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
#define pb push_back
int n;
const int N = 101000;
std::vector<int> e[N];
int l[N], r[N], id[N], sz[N], hs[N], tot, c[N];
int cnt[N], maxcnt;
ll sumcnt, ans[N];
void dfs_init(int u, int f) {
l[u] = ++tot;
id[tot] = u;
sz[u] = 1;
hs[u] = -1;
for (auto v : e[u]) {
if (v == f) continue;
dfs_init(v, u);
sz[u] += sz[v];
if (hs[u] == -1 || sz[v] > sz[hs[u]])
hs[u] = v;
}
r[u] = tot;
}
void add(int x) {
x = c[x];
cnt[x]++;
if (cnt[x] > maxcnt) maxcnt = cnt[x], sumcnt = 0;
if (cnt[x] == maxcnt) sumcnt += x;
}
void del(int x) {
x = c[x];
cnt[x]--;
}
void dfs_solve(int u, int f, bool keep) {
for (auto v : e[u]) {
if (v != f && v != hs[u]) {
dfs_solve(v, u, false);
}
}
if (hs[u] != -1)
dfs_solve(hs[u], u, true);
for (auto v : e[u]) {
if (v != f && v != hs[u]) { // v 是轻儿子
// 把vAll points in the subtree are added to the set of heavy sons
for (int x = l[v]; x <= r[v]; ++x)
add(id[x]);
}
}
add(u);
ans[u] = sumcnt;
if (!keep) {
maxcnt = 0;
sumcnt = 0;
// 清空
for (int x = l[u]; x <= r[u]; ++x)
del(id[x]);
}
}
int main(){
scanf("%d", &n);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
scanf("%d", &c[i]);
for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) {
int u, v;
scanf("%d %d", &u, &v);
e[u].push_back(v);
e[v].push_back(u);
}
dfs_init(1, 0);
dfs_solve(1, 0, false);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
printf("%lld ", ans[i]);
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
IOI2011, Race

也是DSU,The code based on the previous question has been modified.But this title is not the solution,Thoughts are still more important.
注意点:
Add the points in the light son to the process of the heavy son,query和add不能同时(一个for)进行.原因是:If querying a point,Just join this point,Then when querying,Can both points are in the light son,Logically, the code we wrote is no longer satisfied.
// problem :
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
#define pb push_back
int n, k;
const int N = 201000;
std::vector<PII> e[N];
map<int, int> val;
int l[N], r[N], id[N], sz[N], hs[N], tot;
ll ans;
int dep1[N];
ll dep2[N];
void dfs_init(int u, int f) {
l[u] = ++tot;
id[tot] = u;
sz[u] = 1;
hs[u] = -1;
for (auto [v, w] : e[u]) {
if (v == f) continue;
dep1[v] = dep1[u] + 1;
dep2[v] = dep2[u] + w;
dfs_init(v, u);
sz[u] += sz[v];
if (hs[u] == -1 || sz[v] > sz[hs[u]])
hs[u] = v;
}
r[u] = tot;
}
void dfs_solve(int u, int f, bool keep) {
for (auto [v, w] : e[u]) {
if (v != f && v != hs[u]) {
dfs_solve(v, u, false);
}
}
if (hs[u] != -1)
dfs_solve(hs[u], u, true);
auto query = [&] (int w) {
// d2 + dep2[w] - 2 * dep2[u] = k
ll d2 = k + 2 * dep2[u] - dep2[w];
if (val.count(d2)){
ll tmp = val[d2] + dep1[w] - 2 * dep1[u];
ans = min(ans, tmp);
}
};
auto add = [&] (int w) {
if (val.count(dep2[w]))
val[dep2[w]] = min(val[dep2[w]], dep1[w]);
else val[dep2[w]] = dep1[w];
};
for (auto [v, w] : e[u]) {
if (v != f && v != hs[u]) {
for (int x = l[v]; x <= r[v]; ++x)
query(id[x]);
for (int x = l[v]; x <= r[v]; ++x)
add(id[x]);
}
}
query(u), add(u);
if (!keep) {
val.clear();
}
}
int main(){
scanf("%d %d", &n, &k);
for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) {
int u, v, w;
scanf("%d %d %d", &u, &v, &w);
u++, v++;
e[u].push_back({v, w});
e[v].push_back({u, w});
}
ans = n + 1;
dfs_init(1, 0);
dfs_solve(1, 0, false);
if (ans == n + 1) printf("-1\n");
else printf("%lld\n", ans);
return 0;
}边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
qt点云配准软件
工程师如何对待开源
VPS8701 电源管理(PMIC) VPS8701
AcWing 1285. Word Problem Solving (AC Automata)
数仓:为什么说 ETL 的未来不是 ELT,而是 EL (T)
使用docker安装mysql
递归检查配置项是否更变并替换
analog IC layout
DVWA安装教程(懂你的不懂·详细)
Qt自定义控件和模板分享
BioVendor Human Club Cellular Protein (CC16) Elisa Kit Research Fields
数值积分方法:欧拉积分、中点积分和龙格-库塔法积分
微信小程序异步回调函数恶梦和解决办法
局部敏感哈希:如何在常数时间内搜索Embedding最近邻
analog IC layout-Design for reliability
Moonbeam and Project integration of the Galaxy, bring brand-new user experience for the community
Nanoprobes纳米探针丨Nanogold偶联物的特点和应用
* 比较版本号
项目场景 with ERRTYPE = cudaError CUDA failure 999 unknown error
灰度传感器、、、diy原理。。图