当前位置:网站首页>An understanding of & array names
An understanding of & array names
2022-07-06 00:19:00 【It's Yi'an】
A strange phenomenon
#include<stdio.h>
int main(void) {
int arr[5] = { 1,2,3,4,5 };
int(*p)[5] = &arr;
printf("%p\n", p); // After running, you will find that these two values are equal
printf("%p\n", *p);
return 0;
}A strange secondary pointer
#include<stdio.h>
int main(void) {
int arr[5] = { 1,2,3,4,5 };
int(*p)[5] = &arr;
// The program runs successfully , And the results are :1
printf("%d\n", **p); // We can know p=&arr
printf("%d\n", **&arr); // Both are secondary pointers
return 0;
}A strange explanation
An explanation of a strange problem
Pointer to array , The designer made this design in order to distinguish it from pointers to elements : A simple array name represents a pointer to the first element of the array , It needs to open up a separate space for storage , At the same time, the value in the array name space is immutable . If you want to represent the address of the entire array , Just above the simple array name , Improved the level , Change to secondary pointer , But don't give space alone .
Design a rule , When addressing an array name , Is to take the address of the first level pointer . You need a variable to store it , Need a space , This is a normal secondary pointer , But there is no separate space here , Just put the array name ( First level pointer ) Occupy space as its space , At the same time, improve its level , Change to secondary pointer , Mark this pointer ( Special secondary pointer ), Make a type to mark / Represents it :type(*)[]. If you want to dereference this secondary pointer , Just lower its level , Become a normal primary pointer
// These are just assumptions , In order to solve *p=p The problem reference comes up with a convincing explanation .
summary : The array name is a pointer constant ,& The array name is to take the address of the first level pointer , A secondary pointer , But it was given a special rule .
Some normal applications
As I understand it ,&arr Is a special secondary pointer , The type is type(*)[ ].
#include<stdio.h>
int main(void) {
int arr[5] = { 1,2,3,4,5 };
int(*p)[5]; // Define a pointer variable of this type
p= &arr; // Give it the value of this type
printf("%d\n",(*p)[1]); //*p Make it a normal first level pointer :arr
printf("%d\n", arr[1]); //arr: Pointer to the first element of the array
printf("%d\n", *(*p + 1));
printf("%d\n", *(*(&arr) + 1)); //p=&arr
printf("%d\n", *(arr + 1)); //*p=arr
printf("%d\n", arr[1]);
// The results are :2
// Is that much easier to understand
return 0;
}边栏推荐
- SQLServer连接数据库读取中文乱码问题解决
- Multithreading and high concurrency (8) -- summarize AQS shared lock from countdownlatch (punch in for the third anniversary)
- LeetCode 1598. Folder operation log collector
- 2022.7.5-----leetcode.729
- 云呐|固定资产管理系统主要操作流程有哪些
- LeetCode 6006. Take out the least number of magic beans
- [Luogu p3295] mengmengda (parallel search) (double)
- Teach you to run uni app with simulator on hbuilderx, conscience teaching!!!
- 行列式学习笔记(一)
- The difference of time zone and the time library of go language
猜你喜欢
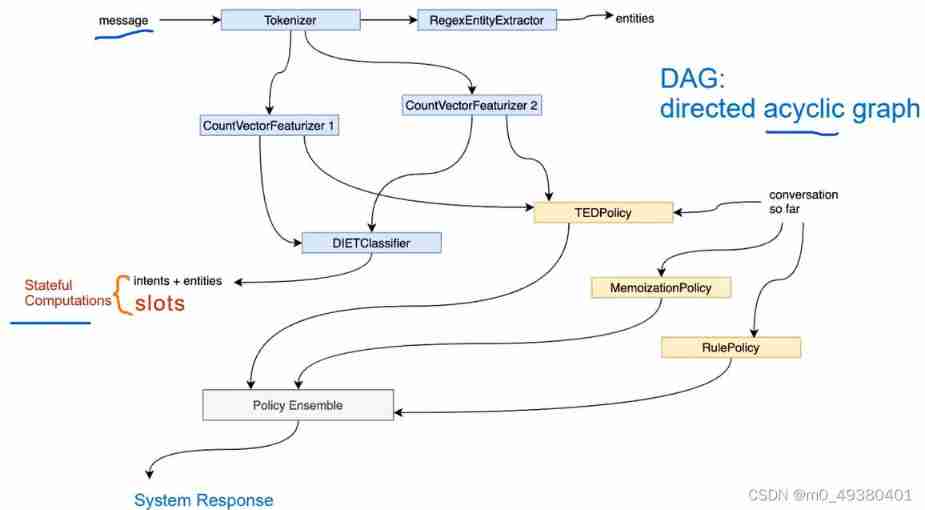
Gavin teacher's perception of transformer live class - rasa project actual combat e-commerce retail customer service intelligent business dialogue robot system behavior analysis and project summary (4
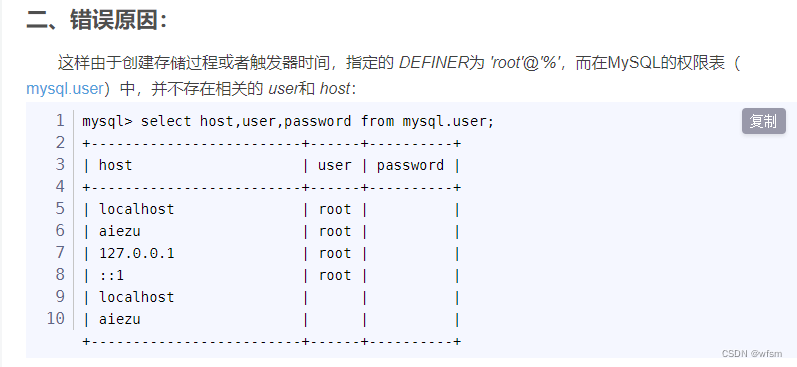
Problems encountered in the database
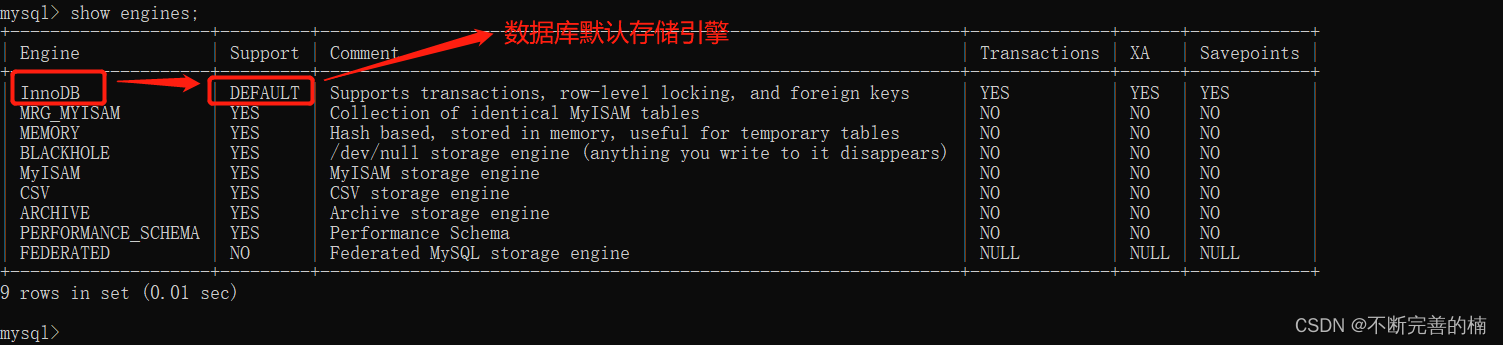
MySQL存储引擎
Gd32f4xx UIP protocol stack migration record
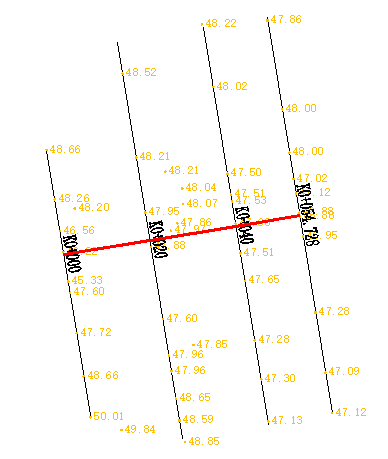
Extracting profile data from profile measurement
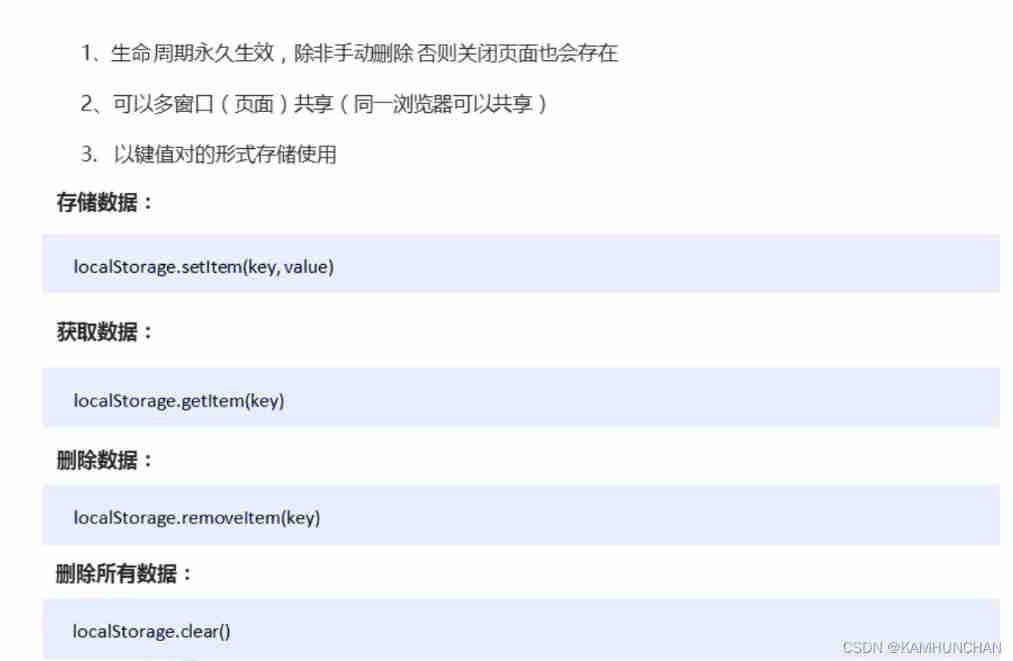
Browser local storage
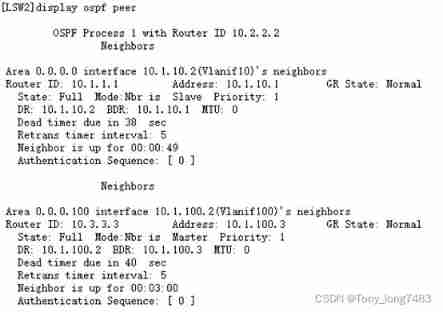
Configuring OSPF GR features for Huawei devices
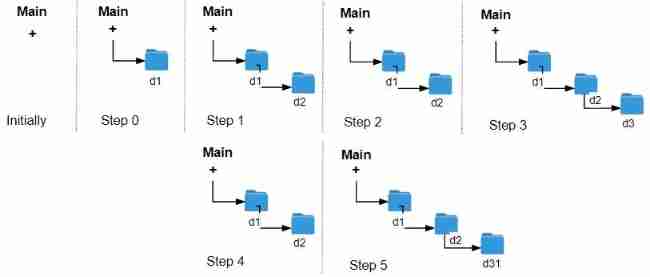
LeetCode 1598. Folder operation log collector
![N1 # if you work on a metauniverse product [metauniverse · interdisciplinary] Season 2 S2](/img/f3/8e237296f5948dd0488441aa625182.jpg)
N1 # if you work on a metauniverse product [metauniverse · interdisciplinary] Season 2 S2
从底层结构开始学习FPGA----FIFO IP核及其关键参数介绍
随机推荐
【NOI模拟赛】Anaid 的树(莫比乌斯反演,指数型生成函数,埃氏筛,虚树)
FFMPEG关键结构体——AVFormatContext
DEJA_ Vu3d - cesium feature set 055 - summary description of map service addresses of domestic and foreign manufacturers
QT -- thread
Mysql - CRUD
[designmode] Decorator Pattern
[Luogu p3295] mengmengda (parallel search) (double)
OpenCV经典100题
USB Interface USB protocol
Codeforces gr19 D (think more about why the first-hand value range is 100, JLS yyds)
如何解决ecology9.0执行导入流程流程产生的问题
单商户V4.4,初心未变,实力依旧!
Global and Chinese market of digital serial inverter 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
[gym 102832h] [template] combination lock (bipartite game)
时区的区别及go语言的time库
Start from the bottom structure and learn the introduction of fpga---fifo IP core and its key parameters
[binary search tree] add, delete, modify and query function code implementation
PV static creation and dynamic creation
Effet Doppler (déplacement de fréquence Doppler)
Classic CTF topic about FTP protocol