What is determinant
The textbook defines the second-order determinant like this .
For a system of binary linear equations :
After elimination, you can get :
\(x\) The same principle can be obtained .
We found that when \(a_{12}a_{21} \neq a_{22}a_{11}\) The equation has a unique solution .
At this time, let's say \(a_{11}a_{22}-a_{12}a_{21}\):
So I didn't understand the use at all .
Now let's introduce a better understanding method .
We know “ A matrix can represent a set of vectors , Matrix representation \(n\) individual \(n\) Dimension vector ”.
That is, each line is treated as a vector , Combine all vectors vertically to determine one \(n\) Dimensional graphics .
Take a look at a two-dimensional picture :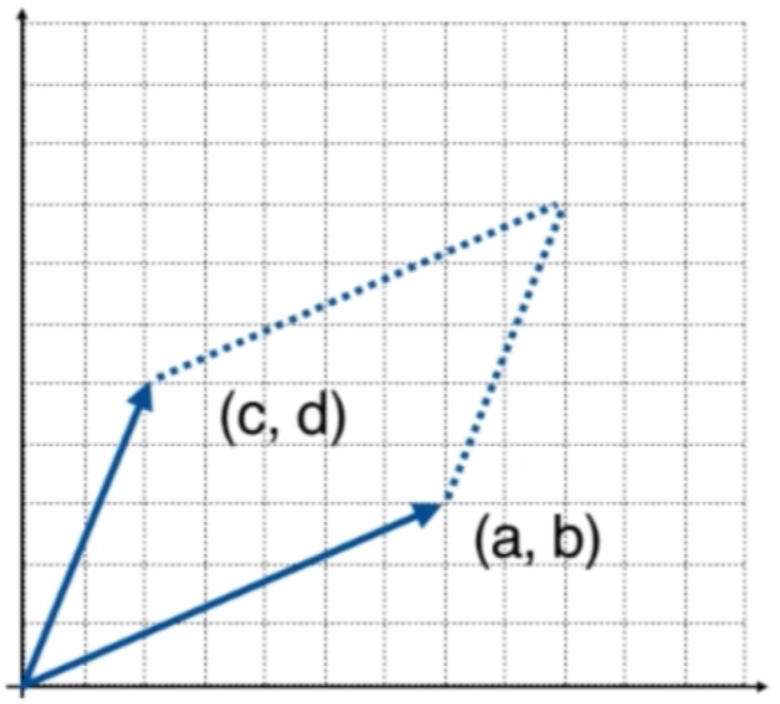
Our second-order determinant is shown in the figure above The area of a parallelogram .
Of course , Two dimensions are areas , Three dimensional is volume , The fourth dimension is ??? ……
The area of the parallelogram above can be expressed as :
be aware , Each row corresponds to a vector in the above figure .
Finding determinant
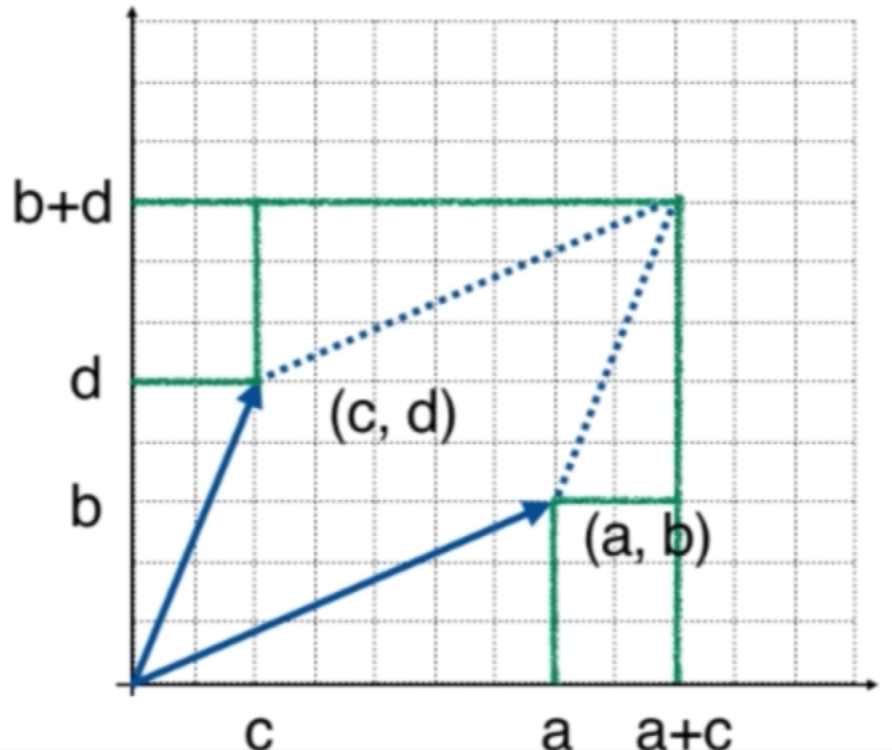
We start with primary school mathematics , First find the area of the parallelogram ( The auxiliary line practice is omitted )
That is to say :
The basic properties of determinants
Let's discuss it with the second-order determinant .
Property one
\(I\) Represents the unit matrix , That makes sense :
All vectors are “ Horizontal and vertical ” And the length is one , The area must be \(1\).
Property two
Exchange the two lines of a determinant , Then the value of the determinant is reversed .
Expressed by mathematical formula :
The proof is simple :
Property three
Express it directly with mathematical formulas .( Chinese is not good )
Simply prove it .
Be careful :\(\det (kA) \neq k\det (A)\)
For the second-order determinant :
From this we can deduce , about \(n\) Determinant of order :
Property 4
One row of the matrix plus one row , Then there are :
prove :