当前位置:网站首页>[binary search tree] add, delete, modify and query function code implementation
[binary search tree] add, delete, modify and query function code implementation
2022-07-05 23:55:00 【UkeLiu】
The basic structure of binary tree is not introduced , Here we mainly serve dry goods , Use code to realize the sorting rules of binary tree , Traversal and insertion , Delete function .
Sort rule
Binary search tree is also called binary search tree 、 Binary sort tree has the following characteristics :
- If its left subtree is not empty , Then the values of the nodes on the left subtree are less than the root node .
- If its right subtree is not empty , Then the values of the nodes on the right subtree are greater than the root node .
- Subtree should also follow the above two points
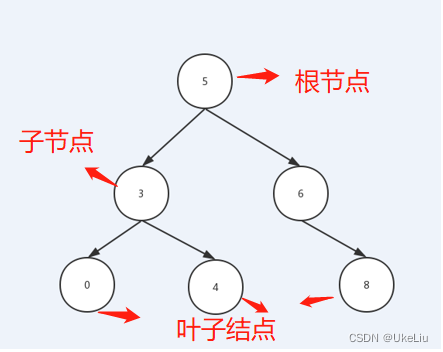
Traversal of binary tree
First, we implement a binary tree in the form of a linked list :
// Define the nodes of the tree
class treeNode{
private int data; // data
private treeNode left; // The left node
private treeNode right; // Right node
private treeNode parent;// Parent node
public treeNode getParent() {
return parent;
}
public void setParent(treeNode parent) {
this.parent = parent;
}
public treeNode(int data, treeNode left, treeNode right) {
this.data = data;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
public treeNode(int data){
this.data = data;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
public int getData() {
return data;
}
public void setData(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
public treeNode getLeft() {
return left;
}
public void setLeft(treeNode left) {
this.left = left;
}
public treeNode getRight() {
return right;
}
public void setRight(treeNode right) {
this.right = right;
}
}
// Method of outputting node data
public void print(treeNode treeNode){
System.out.println(treeNode.getData());
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test the data
treeNode H=new treeNode('H',null,null);
treeNode K=new treeNode('k',null,null);
treeNode G=new treeNode('G',H,K);
treeNode F=new treeNode('F',G,null);
treeNode E=new treeNode('E',null,F);
treeNode D=new treeNode('D',null,null);
treeNode C=new treeNode('C',D,null);
treeNode B=new treeNode('B',null,C);
treeNode A=new treeNode('A',B,E);
BinaryTree binaryTree = new BinaryTree();
System.out.println(" front ---->");
binaryTree.pre(A);
System.out.println();
System.out.println(" in ---->");
binaryTree.in(A);
System.out.println();
System.out.println(" after ---->");
binaryTree.post(A);
System.out.println();
}
What is implemented here is a binary tree as shown in the figure below :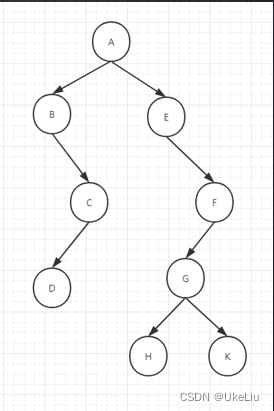
There are three ways to traverse a binary tree :
- The former sequence traversal : Root left and right ( Traverse from the root node of the binary tree , Output... In sequence ), You can understand this by looking at the root node first , There is direct output , Second, look at the left node , There is left node output , Let's see if the left node has a subtree , If so, repeat the above operation , The same is true for the right node , An algorithm idea of recursive backtracking is designed here .
- In the sequence traversal : Left root right
- After the sequence traversal : Left and right
These three traversal methods are actually from top to bottom , From bottom to top , There are also three traversal methods layer by layer , And the pithy formula is about the root , Left root right , Left and right .
Code implementation :
/** * The former sequence traversal Root left and right */
public void pre(treeNode treeNode){
print(treeNode);// Output root node data
if (treeNode.getLeft()!=null){
// The left node is not empty
pre(treeNode.getLeft()); // Recursion looks around the root
}
if (treeNode.getRight()!=null){
// Same as above
pre(treeNode.getRight());
}
}
/** * In the sequence traversal Left root right */
public void in(treeNode treeNode){
if (treeNode.getLeft()!=null){
in(treeNode.getLeft());
}
print(treeNode);
if (treeNode.getRight()!=null){
in(treeNode.getRight());
}
}
/** * In the sequence traversal Left and right */
public void post(treeNode treeNode){
if (treeNode.getLeft()!=null){
post(treeNode.getLeft());
}
if (treeNode.getRight()!=null){
post(treeNode.getRight());
}
print(treeNode);
}
The insertion of a binary tree : The insertion of binary tree is very simple , Because of his characteristics , Let's insert a number , Start at the root node , As long as it is smaller than the root node, go to the left , If it is larger than the root node, go to the right , Compare with the next node , Until the node being compared has no child nodes .
Code :
/** * Binary search tree inserts data * @param root The root node * @param data Inserted value */
public void insert(treeNode root,int data){
// Compare with the root node every time you insert
if (data<root.getData()){
// If it is smaller than the root node, go to the left
if (root.getLeft()==null){
// If it's a leaf node Add the node directly to the left of the leaf node
treeNode treeNode = new treeNode(data, null, null);
treeNode.setParent(root); // Set the parent node of the newly inserted node
root.setLeft(treeNode);
}else {
insert(root.getLeft(),data);
}
}else {
if (root.getRight()==null){
treeNode treeNode = new treeNode(data, null, null);
treeNode.setParent(root);;
root.setRight(treeNode);
}else {
insert(root.getRight(),data);
}
}
}
The deletion of binary trees
Deleting a binary tree is the hardest , But it is not the deletion operation that is rare , It's about the direction of the pointer , The deletion of binary tree can be divided into three cases :
The node to be deleted is the leaf node , In this case , Just delete it directly , Because he has no complicated pointing problem , The time complexity is O(1)
The deleted nodes have left or right subtrees , This situation is also very simple. Just point its child node to its parent node , Time complexity is also O(1)
The deleted node has left and right subtrees , At this time, we need to find its successor node or predecessor node , The next node is the smallest number in his right subtree , The predecessor node is the largest number in the left subtree .
Let's take the following node as an example , Replace the location of the deleted node with a successor node , At this time, the subsequent nodes are also deleted , We also need to consider whether there is a right subtree in the subsequent node , Subsequent nodes are certain that there is no left subtree , Because the successor node is the smallest number of the right subtree of the deleted node , Then we will go to the left , Until the leftmost number is found, it is the successor node .
The code is more complex , I annotated it more carefully , If you have something you don't understand, you can leave a message , See will give you an answer
class treeNode{
private int data; // data
private treeNode left; // The left node
private treeNode right; // Right node
private treeNode parent;// Parent node
public treeNode getParent() {
return parent;
}
public void setParent(treeNode parent) {
this.parent = parent;
}
public treeNode(int data, treeNode left, treeNode right) {
this.data = data;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
public treeNode(int data){
this.data = data;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
public int getData() {
return data;
}
public void setData(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
public treeNode getLeft() {
return left;
}
public void setLeft(treeNode left) {
this.left = left;
}
public treeNode getRight() {
return right;
}
public void setRight(treeNode right) {
this.right = right;
}
}
/** * Use linked list to realize binary tree */
public class BinaryTree {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BinaryTree binaryTree = new BinaryTree();
treeNode root = null;
Scanner cin = new Scanner(System.in);
int t = 1;
System.out.println(" Binary search tree assumes no duplicate child nodes , Repetition can be handled by linked list , Please note that ~~");
System.out.println(" Please enter the root node :");
int rootData = cin.nextInt();
root = new treeNode(rootData);
System.out.println(" Please enter the first " + t + " A little bit : Input -1 End of the said ");
while (true) {
//
int data = cin.nextInt();
if (data == -1)
break;
binaryTree.insert(root, data);
t++;
System.out.println(" Please enter the first " + t + " A little bit : Input -1 End of the said ");
}
binaryTree.show(root); // Find someone else to write a printed binary tree structure , It feels good , It can be clearer
System.out.println(" Delete the test :");
while(true) {
System.out.println(" Please enter the point to delete :-1 End of the said ");
int key = cin.nextInt();
root = binaryTree.delNode(key,root);
binaryTree.show(root);
if(root == null) {
System.out.println(" The tree has no data ~~");
break;
}
}
}
public void print(treeNode treeNode){
System.out.println(treeNode.getData());
}
// Used to get the number of layers of the tree
public int getTreeDepth(treeNode root) {
return root == null ? 0 : (1 + Math.max(getTreeDepth(root.getLeft()), getTreeDepth(root.getRight())));
}
private void writeArray(treeNode currNode, int rowIndex, int columnIndex, String[][] res, int treeDepth) {
// Ensure the input tree is not empty
if (currNode == null)
return;
// First, save the current node to a two-dimensional array
res[rowIndex][columnIndex] = String.valueOf(currNode.getData());
// Calculate the current layer of the tree
int currLevel = ((rowIndex + 1) / 2);
// If you get to the last floor , Then return to
if (currLevel == treeDepth)
return;
// Calculate the current line to the next line , The interval between each element ( The interval between the next row's column index and the current element's column index )
int gap = treeDepth - currLevel - 1;
// Judge the left son , If there is a left son , Record the corresponding "/" And left son's value
if (currNode.getLeft() != null) {
res[rowIndex + 1][columnIndex - gap] = "/";
writeArray(currNode.getLeft(), rowIndex + 2, columnIndex - gap * 2, res, treeDepth);
}
// Judge the right son , If there is a right son , Record the corresponding "\" With the right son's value
if (currNode.getRight() != null) {
res[rowIndex + 1][columnIndex + gap] = "\\";
writeArray(currNode.getRight(), rowIndex + 2, columnIndex + gap * 2, res, treeDepth);
}
}
/** * Show the binary tree * @param root */
public void show(treeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
System.out.println("EMPTY!");
return ;
}
// Get the depth of the tree
int treeDepth = getTreeDepth(root);
// The width of the last line is 2 Of (n - 1) Power multiplication 3, add 1
// As the width of the entire two-dimensional array
int arrayHeight = treeDepth * 2 - 1;
int arrayWidth = (2 << (treeDepth - 2)) * 3 + 1;
// Use an array of strings to store the elements that should be displayed at each location
String[][] res = new String[arrayHeight][arrayWidth];
// Initialize the array , The default is a space
for (int i = 0; i < arrayHeight; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < arrayWidth; j++) {
res[i][j] = " ";
}
}
// Start at the root node , Recursively process the entire tree
writeArray(root, 0, arrayWidth / 2, res, treeDepth);
// here , All the elements that need to be displayed have been stored in a two-dimensional array , It can be spliced and printed
for (String[] line : res) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < line.length; i++) {
sb.append(line[i]);
if (line[i].length() > 1 && i <= line.length - 1) {
i += line[i].length() > 4 ? 2 : line[i].length() - 1;
}
}
System.out.println(sb.toString());
}
}
/** * Binary search tree inserts data * @param root The root node * @param data Inserted value */
public void insert(treeNode root,int data){
// Compare with the root node every time you insert
if (data<root.getData()){
// If it is smaller than the root node, go to the left
if (root.getLeft()==null){
// If it's a leaf node Add the node directly to the left of the leaf node
treeNode treeNode = new treeNode(data, null, null);
treeNode.setParent(root); // Set the parent node of the newly inserted node
root.setLeft(treeNode);
}else {
insert(root.getLeft(),data);
}
}else {
if (root.getRight()==null){
treeNode treeNode = new treeNode(data, null, null);
treeNode.setParent(root);;
root.setRight(treeNode);
}else {
insert(root.getRight(),data);
}
}
}
/** * Binary tree deletes node data * @param data */
public treeNode delNode(int data,treeNode root){
// Find this node . Traverse the tree
treeNode delNode = selectNode(data, root);
// Node not found
if (delNode==null){
System.out.println(" The deleted node does not exist in the tree ");
}
if (root==delNode){
return null;
}
// If this node is a leaf node Just delete
if (delNode.getRight()==null && delNode.getLeft()==null){
treeNode parent = delNode.getParent();
// Judge which side the node is on
if (delNode.getData()< parent.getData()){
// On the left
parent.setLeft(null);
}else {
parent.setRight(null);
}
}else if (delNode.getRight()!=null && delNode.getLeft()!=null){
// Deleted nodes There are two child nodes
// Find subsequent nodes
treeNode successorNode = selectSuccessorNode(delNode);
successorNode.setLeft(delNode.getLeft()); // Point the left subtree of the deleted point to the left of the subsequent node
successorNode.getLeft().setParent(successorNode); // Point the parent node of the left subtree to the successor node
// The left node of the subsequent node must be empty , We need to judge whether the right node of the successor node has a value
if (successorNode.getRight()==null){
// If the successor node has no right node Directly delete the subsequent nodes
if(delNode!=successorNode.getParent()){
// Point the right subtree of the subsequent node to the right subtree of the deleted node
successorNode.setRight(delNode.getRight());
// Point the parent node on the right of the deleted node to the successor node
delNode.getRight().setParent(successorNode);
// Delete subsequent nodes
successorNode.getParent().setLeft(null);
}
}else if (successorNode.getRight()!=null && delNode!=successorNode.getParent()){
// Point the right subtree of the subsequent node to the right subtree of the deleted node
successorNode.setRight(delNode.getRight());
// Point the parent node on the right of the deleted node to the successor node
delNode.getRight().setParent(successorNode);
// Point the parent node of the right subtree of the successor node to the left subtree of the parent node of the successor node
successorNode.getRight().setParent(successorNode.getParent());
// Point the left subtree of the parent node of the successor node to the right subtree of the successor node
successorNode.getParent().setLeft(successorNode.getRight());
}
// Pointer replacement complete The next step is to delete nodes
if (delNode==root){
successorNode.setParent(null);
root=successorNode;
return root;
}
successorNode.setParent(delNode.getParent());
// Determine whether the deleted point is on the left or right of the parent node
if (delNode.getParent().getData()>delNode.getData()){
// On the left
delNode.getParent().setLeft(successorNode);
}else {
delNode.getParent().setRight(successorNode);
}
}else{
// Delete node has only one child
if (delNode.getRight()!=null){
// Only the right node
if (delNode==root){
root=delNode.getRight();
return root;
}
delNode.getRight().setParent(delNode.getParent());
// Determine whether the deleted point is on the left or right of the parent node
if (delNode.getParent().getData()>delNode.getData()){
// On the left
delNode.getParent().setLeft(delNode.getRight());
}else {
delNode.getParent().setRight(delNode.getRight());
}
}else {
// Only the left node
if (delNode==root){
root=delNode.getLeft();
return root;
}
delNode.getLeft().setParent(delNode.getParent());
// Determine whether the deleted point is on the left or right of the parent node
if (delNode.getParent().getData()>delNode.getData()){
// On the left
delNode.getParent().setLeft(delNode.getLeft());
}else {
delNode.getParent().setRight(delNode.getLeft());
}
}
}
return root;
}
/** * There are two ways to delete a binary tree One is to find the predecessor node : Find the number on the left side of the node that is greater than the value of the node * Find the successor node of the node : Find the number of the right node that is the smallest than the node value * This method is used to find subsequent nodes The code of the previous node is the same Just find the direction and change it * @param node * @return */
public treeNode selectSuccessorNode(treeNode node){
// Find the number of all nodes on the right of the node that are smaller than the node
if (node.getRight()==null){
// It indicates that there is no successor node
return node;
}
treeNode cur=node.getRight();
treeNode pre=node.getRight(); // Open an extra space for storage node Because when node When the left node is empty , The previous node is returned
while (cur!=null){
pre=cur;
cur=cur.getLeft();
}
return pre;
}
/** * Find the node that needs to be deleted * @data Node data * @root The root node * @return Deleted nodes */
public treeNode selectNode(int data,treeNode root){
treeNode current=root;
while (current != null){
if (current.getData()<data){
current=current.getRight();
}else if (current.getData()>data){
current=current.getLeft();
}else {
return current;
}
}
return null;
}
}
边栏推荐
- 数据库遇到的问题
- 总结了 800多个 Kubectl 别名,再也不怕记不住命令了!
- 激光slam学习记录
- The use of El cascader and the solution of error reporting
- What are the functions of Yunna fixed assets management system?
- Zhongjun group launched electronic contracts to accelerate the digital development of real estate enterprises
- Laser slam learning record
- 15 MySQL stored procedures and functions
- 18.(arcgis api for js篇)arcgis api for js点采集(SketchViewModel)
- 哪些偏门项目可以做到?自媒体做到月赚一万以上很难吗?
猜你喜欢

Tips for using pads router
Biased sample variance, unbiased sample variance
C reflection and type

云呐|固定资产管理系统主要操作流程有哪些

Bao Yan notebook IV software engineering and calculation volume II (Chapter 8-12)

China Jinmao online electronic signature, accelerating the digitization of real estate business

Use mapper: --- tkmapper
XML configuration file (DTD detailed explanation)
多普勒效应(多普勒频移)

Miaochai Weekly - 8
随机推荐
4点告诉你实时聊天与聊天机器人组合的优势
14 MySQL-视图
14 MySQL view
总结了 800多个 Kubectl 别名,再也不怕记不住命令了!
Zhuan: in the future, such an organization can withstand the risks
提升工作效率工具:SQL批量生成工具思想
[gym 102832h] [template] combination lock (bipartite game)
第16章 OAuth2AuthorizationRequestRedirectWebFilter源码解析
【EF Core】EF Core与C# 数据类型映射关系
开源crm客户关系统管理系统源码,免费分享
[EF core] mapping relationship between EF core and C data type
Rasa 3.x 学习系列-Rasa 3.2.1 新版本发布
Qt 一个简单的word文档编辑器
Russian Foreign Ministry: Japan and South Korea's participation in the NATO summit affects security and stability in Asia
How to improve eloquence
教你在HbuilderX上使用模拟器运行uni-app,良心教学!!!
Bao Yan notebook IV software engineering and calculation volume II (Chapter 8-12)
【NOI模拟赛】Anaid 的树(莫比乌斯反演,指数型生成函数,埃氏筛,虚树)
【luogu CF487E】Tourists(圆方树)(树链剖分)(线段树)
What is a humble but profitable sideline?