当前位置:网站首页>[sort] bucket sort
[sort] bucket sort
2022-07-03 13:20:00 【Programming cheese】
brief introduction
The time complexity of bucket sorting is only O(n) A sort method of , It assumes that the input data is uniformly distributed , We put the data into n A ladle , First sort the data in the bucket , Then traverse the bucket and take out the elements in the bucket in turn to complete the sorting .
Schematic diagram
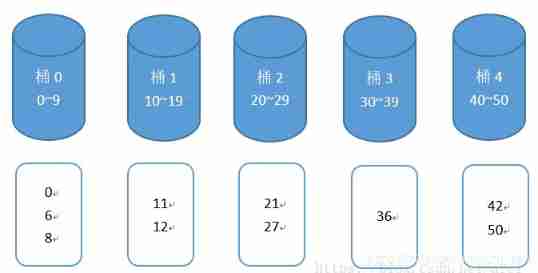
For example, input data :21,8,6,11,36,50,27,42,0,12.
Then put them into the corresponding bucket for sorting , Finally, the sorting can be completed by traversing the bucket in turn and taking out the elements .
analysis
A very important step in bucket sorting is the setting of buckets , We have to depend on the input elements , Choose an appropriate “getBucketIndex” Algorithm , So that the input elements can be correctly put into the corresponding bucket , And ensure that the input data can be put into different barrels as evenly as possible .
In the worst case , That is, all the data is put into a bucket , The self sorting algorithm in bucket is insertion sorting , Then the time complexity is O(n ^ 2) 了 .
secondly , We can find out , The finer the interval is divided , The more barrels there are , In theory, the less elements are divided into each bucket , The easier it is to sort the data in a bucket , The closer the time complexity is to linear .
In extreme cases , It's just that the range is so small that it's only 1, That is, only one element is stored in the barrel , The elements in the bucket no longer need to be sorted , Because they're all the same elements , Now bucket sort is almost the same as counting sort .
Example
Assume that the input elements are evenly distributed floating-point numbers . Counting sort is more suitable for integer cases , If we still want to sort elements in linear time , Then bucket sorting will be a good choice .
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.ListIterator;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Input elements are in [0, 10) In this range
float[] arr = new float[] {
0.12f, 2.2f, 8.8f, 7.6f, 7.2f, 6.3f, 9.0f, 1.6f, 5.6f, 2.4f };
bucketSort(arr);
printArray(arr);
}
public static void bucketSort(float[] arr) {
// Create a new collection of buckets
ArrayList<LinkedList<Float>> buckets = new ArrayList<LinkedList<Float>>();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
// Create a new bucket , And add it to the collection of buckets .
// Because the elements in the barrel will be inserted frequently , So choose LinkedList As the data structure of the bucket
buckets.add(new LinkedList<Float>());
}
// Put all the input data into the bucket and complete the sorting
for (float data : arr) {
int index = getBucketIndex(data);
insertSort(buckets.get(index), data);
}
// Take out all the elements in the bucket and put them in arr Medium output
int index = 0;
for (LinkedList<Float> bucket : buckets) {
for (Float data : bucket) {
arr[index++] = data;
}
}
}
/** * Calculate which bucket the input element should be placed in */
public static int getBucketIndex(float data) {
// The example here is relatively simple , Only the integer part of a floating-point number is used as the index value of its bucket
// In the actual development, it needs to be designed according to the scene
return (int) data;
}
/** * We choose insert sort as the method to sort the elements in the bucket Whenever a new element comes , We all call this method to insert it in the right place */
public static void insertSort(List<Float> bucket, float data) {
ListIterator<Float> it = bucket.listIterator();
boolean insertFlag = true;
while (it.hasNext()) {
if (data <= it.next()) {
it.previous(); // Shift the position of the iterator back to the previous position
it.add(data); // Insert data into the current position of the iterator
insertFlag = false;
break;
}
}
if (insertFlag) {
bucket.add(data); // Otherwise, insert the data into the end of the list
}
}
public static void printArray(float[] arr) {
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
System.out.print(arr[i] + ", ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
Link to the original text :https://blog.csdn.net/afei__/article/details/82965834
边栏推荐
- 【数据库原理及应用教程(第4版|微课版)陈志泊】【第五章习题】
- Luogup3694 Bangbang chorus standing in line
- Sword finger offer 14- ii Cut rope II
- The principle of human voice transformer
- MySQL constraints
- PostgreSQL installation
- 用户和组命令练习
- 【数据库原理及应用教程(第4版|微课版)陈志泊】【第三章习题】
- 2022-02-13 plan for next week
- 71 articles on Flink practice and principle analysis (necessary for interview)
猜你喜欢

The shortage of graphics cards finally came to an end: 3070ti for more than 4000 yuan, 2000 yuan cheaper than the original price, and 3090ti

MySQL functions and related cases and exercises
The difference between stratifiedkfold (classification) and kfold (regression)

Tutoriel PowerPoint, comment enregistrer une présentation sous forme de vidéo dans Powerpoint?
Flink SQL knows why (7): haven't you even seen the ETL and group AGG scenarios that are most suitable for Flink SQL?

【数据库原理及应用教程(第4版|微课版)陈志泊】【第三章习题】

正则表达式
8皇后问题

剑指 Offer 14- II. 剪绳子 II

道路建设问题
随机推荐
【数据库原理及应用教程(第4版|微课版)陈志泊】【第五章习题】
Flink SQL knows why (13): is it difficult to join streams? (next)
Image component in ETS development mode of openharmony application development
luoguP3694邦邦的大合唱站队
The difference between stratifiedkfold (classification) and kfold (regression)
Setting up Oracle datagurd environment
sitesCMS v3.0.2发布,升级JFinal等依赖
Mysql database basic operation - regular expression
双链笔记 RemNote 综合评测:快速输入、PDF 阅读、间隔重复/记忆
2022-02-14 analysis of the startup and request processing process of the incluxdb cluster Coordinator
DQL basic query
Sitescms v3.1.0 release, launch wechat applet
Sword finger offer 11 Rotate the minimum number of the array
Kotlin - improved decorator mode
R语言使用data函数获取当前R环境可用的示例数据集:获取datasets包中的所有示例数据集、获取所有包的数据集、获取特定包的数据集
2022-02-13 plan for next week
C graphical tutorial (Fourth Edition)_ Chapter 17 generic: genericsamplep315
已解决(机器学习中查看数据信息报错)AttributeError: target_names
剑指 Offer 14- II. 剪绳子 II
Smbms project