当前位置:网站首页>Knee joint
Knee joint
2022-06-12 08:31:00 【Neonity】
Knee joint 膝关节
The knee joint is a modified hinge joint between the femur, tibia, and patella. It is the largest synovial joint in the body and allows flexion and extension of the leg as well as some rotation in the flexed position.
膝关节是股骨、胫骨和髌骨之间的,一种改良的屈戌关节[1]。它是身体中最大的滑膜关节,允许腿部弯曲和伸展,以及在弯曲位置进行一些旋转。
Summary 要点
location: two condylar joints between femur and tibia; saddle joint between patella and femur
位置:股骨和胫骨之间的两个髁突关节;髌骨股骨之间的鞍关节blood supply: main supply are the genicular branches of the popliteal artery
血供:主要血供为腘动脉膝支nerve supply: branches from the femoral, tibial, common peroneal, and obturator nerves
神经分布:股神经、胫神经、腓总神经和闭孔神经的分支movement: flexion to 150°, extension to 5-10° hyperextension; rotation whilst in the flexed position to 10° actively and 60° passively
运动:屈曲至150°,伸展至5-10°过伸;当处于弯曲位置时,正向旋转至10°,负向旋转至60°。
Gross anatomy 大体解剖
Articulations 关节
There are two condylar joints between the femur and tibia (tibiofemoral). There are medial and lateral articular facets on the tibial plateau and medial and lateral femoral condyles on the distal femur with are convex and circular shaped.
股骨和胫骨(胫股骨)之间有两个髁突关节。胫骨平台上有内侧和外侧关节面,股骨远端的内侧和外侧髁呈凸面和圆形。
medially: between a narrow and curved femoral condyle, and an oval tibial articular surface with a long anteroposterior length laterally: between a wide and flat femoral condyle; and a circular tibial articular surface which overhangs the shaft posterolaterally the knee menisci are shaped accordingly Saddle joint between the patella and femoral condyles:
内侧:在狭窄弯曲的股骨髁与前后长的椭圆形胫骨关节面之间;外侧:在宽阔平坦的股骨髁之间;以及一个圆形胫骨关节面,该关节面在膝关节半月板的后外侧突出,因此在髌骨和股骨髁之间形成鞍关节:
medial, lateral and odd facet on the posterior surface of the patella articulate with the medial and lateral condyles of the femur on flexion, more parts of the bony surface are exposed to articulation (four below, odd facet) and are more proximal on the patella with extension, the contact area lessens and moves distally
髌骨后表面的内侧、外侧和奇数关节面与股骨屈曲的内侧和外侧髁相连,更多的骨表面部分暴露于关节(下面四个,奇数关节面),并且在髌骨上更近端,随着伸展,接触面积减少并向远侧移动
Menisci 半月板
fibrocartilaginous, C-shaped in appearance and triangular in cross-section the medial meniscus is attached to the medial collateral ligament and the lateral meniscus is attached to the popliteus tendon attached to the femur and tibia via the coronary ligaments
Joint capsule 关节囊
knee capsule on the femur adheres below the epiphyseal line down to the articular margin except in two places posteriorly attached to the intercondylar ridge at the lower limit of the popliteal surface on the lateral condyle it encloses a pit and groove for the popliteus tendon
on the tibia attached around the margins of the tibial plateau except in two places posteriorly to the ridge between the two condyles at the lower end of the groove for the PCL laterally the capsule is not attached to the tibia but is prolonged down over the popliteus tendon
two main gaps one allowing the popliteus to enter one communicating with suprapatellar bursa
Synovial membrane 滑膜
joint capsule is lined by synovial membrane, however, the attachment of the synovial membrane does not coincide with the capsular attachments because of the intra-articular structures the cruciate ligament and popliteus tendon are extrasynovial but intracapsular communicates with the suprapatellar bursa
Fat pads 脂肪垫
There are three anterior fat pads:
infrapatellar fat pad (of Hoffa) posterior suprapatellar (prefemoral or supratrochlear) fat pad anterior suprapatellar (quadriceps) fat pad
Attachments 附件
intracapsular ligaments anterior intermeniscal ligament connect the anterior limbs of the two menisci
anterior (Humphrey) and posterior (Wrisberg) meniscofemoral ligaments: the lateral meniscus is attached to the medial femoral condyle via the anterior and posterior meniscofemoral ligament of Humphrey and Wrisberg
cruciate ligaments: cross each other to form an "x" shape. anterior cruciate ligament: from the anterior tibial plateau to the lateral femoral condyle posterior cruciate ligament: from the posterior intercondylar area to the medial femoral condyle
extracapsular ligaments patellar retinacular ligaments: medial and lateral portions of the quadriceps tendon pass down on either side of the patella and are inserted into the upper extremity of the tibia on either side of the tuberosity, merging into the capsule medial collateral ligament from the medial epicondyle to the medial surface of the tibia, which it is separated from by the passage of the inferior medial genicular arteries attached to the medial meniscus flat band like approximately 12 cm long has superficial and deep parts (thickening of the capsule)
lateral collateral ligament from the lateral epicondyle to the fibular head not attached to the lateral meniscus thin cord like, approximately 5 cm long separated from the tibia within the joint by the popliteus tendon and outside the joint by the inferior lateral genicular artery
oblique popliteal ligament tendinous expansion of the semimembranosus muscle terminating on the popliteal surface of the femur perforated by the middle genicular artery
arcuate popliteal ligament thickened part of the joint capsule that arches over the popliteus tendon as it emerges from the joint capsule and attached to the styloid process of the fibular head
popliteofibular ligament extends from the popliteus tendon near the myotendinous junction to the posterior aspect of the fibular styloid process, posteromedial to the biceps insertion
patella ligament from the apex of the patella to the tibial tuberosity
other anterolateral ligament posterolateral ligamentous complex
tendons popliteal tendon
knee menisci knee capsule knee synovial membrane
Bursa 法氏囊
suprapatellar - superior extension of - the knee joint cavity prepatellar - communicates with the joint cavity, between the lower half of the patella and skin subcutaneous infrapatellar - between the patella ligament and skin deep infrapatellar - between the tibia and patella tendon posterior (between muscle and bone) popliteal - communicates with the joint cavity, beneath the tendon of popliteus lying in the gutter between tibia and head of fibula gastrocnemius bursa beneath the medial head (and usually the lateral head) communicates with the joint cavity
semimembranosus - may communicate with the bursa beneath the medial head of the gastrocnemius
Relations 联系
knee bursae anterior knee fat pads
Blood supply 血供
The knee is supplied by anastomoses of:
five genicular branches of the popliteal artery (main supply) medial and lateral superior genicular arteries encircle the femoral condyle medial and lateral inferior genicular arteries encircle the tibial condyle middle genicular artery supplies the anterior and posterior cruciate ligaments
descending branch of the lateral circumflex femoral artery descending genicular branch of the femoral artery circumflex fibular branches of the posterior tibial artery anterior and posterior recurrent branches of the anterior tibial artery
Innervation
Multiple articular branches are derived from several nerves (Hilton's law):
branches of the femoral nerve to vastus medialis, and also intermedius and lateralis from the sciatic nerve by genicular branches of the tibial and common peroneal nerves from the obturator nerve by a branch from the posterior division
Movements
flexion semimembranosus, semitendinosus, biceps femoris, gracilis, sartorius also gastrocnemius, plantaris and popliteus
extension quadriceps femoris, iliotibial tract also gluteus maximus, tensor fascia latae
internal rotation (when flexed) semimembranosus, semitendinosus, gracilis, sartorius
external rotation (when flexed) biceps femoris
unlocking popliteus externally rotates femur on tibia, locked ligaments loosen, hamstrings can then flex free
locking as the knee moves into full extension, the anterior cruciate ligament becomes taut, with no further extension of the lateral condyle possible passive rotation forwards of the lateral condyle around the radius of the taut anterior cruciate ligament medial femoral condyle is then able to glide backwards into full extension tightening of the oblique popliteal, lateral collateral and medial collateral ligaments purely passive due to the skew pull of the obliquely set ligaments Radiographic features Plain radiograph See knee radiograph (an approach)
Radiographic features
Plain radiograph
See knee radiograph (an approach)
Related pathology
Stieda fracture (MCL avulsion fracture)
Cases and figures
References
Last's Anatomy. Churchill Livingstone. (2011) ISBN:0702033944. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
Butler P, Mitchell A, Healy JC. Applied Radiological Anatomy. Cambridge University Press. (2012) ISBN:0521766664. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
Moore KL, Agur AMR, Dalley AF. Clinically oriented anatomy. LWW. ISBN:1451119453. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
参考资料
屈戊关节: HingeJoint 屈戊关节 就像门的铰链,例如肱骨和尺骨的连结--Osmosis中文
边栏推荐
- (p36-p39) right value and right value reference, role and use of right value reference, derivation of undetermined reference type, and transfer of right value reference
- Py&GO编程技巧篇:逻辑控制避免if else
- Lock mechanism in MySQL
- 三国杀周边--------猪国杀题解
- (p33-p35) lambda expression syntax, precautions for lambda expression, essence of lambda expression
- 判断对象是否为空
- At present, MES is widely used. Why are there few APS scheduling systems? Why?
- Installation series of ROS system (II): ROS rosdep init/update error reporting solution
- Triggers in MySQL
- Install iptables services and open ports
猜你喜欢

余压监控系统保证火灾发生时消防疏散通道的通畅,为大型高层建筑的安全运行和人民生命财产安全保驾护航

Hands on learning and deep learning -- simple implementation of softmax regression

处理异常数据
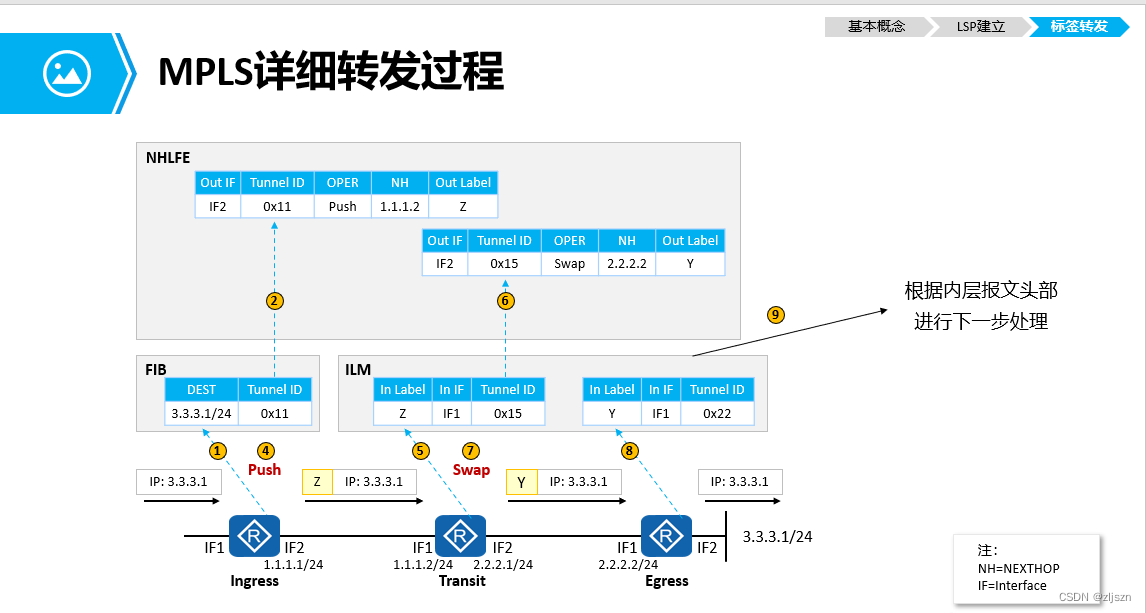
MPLS的原理与配置
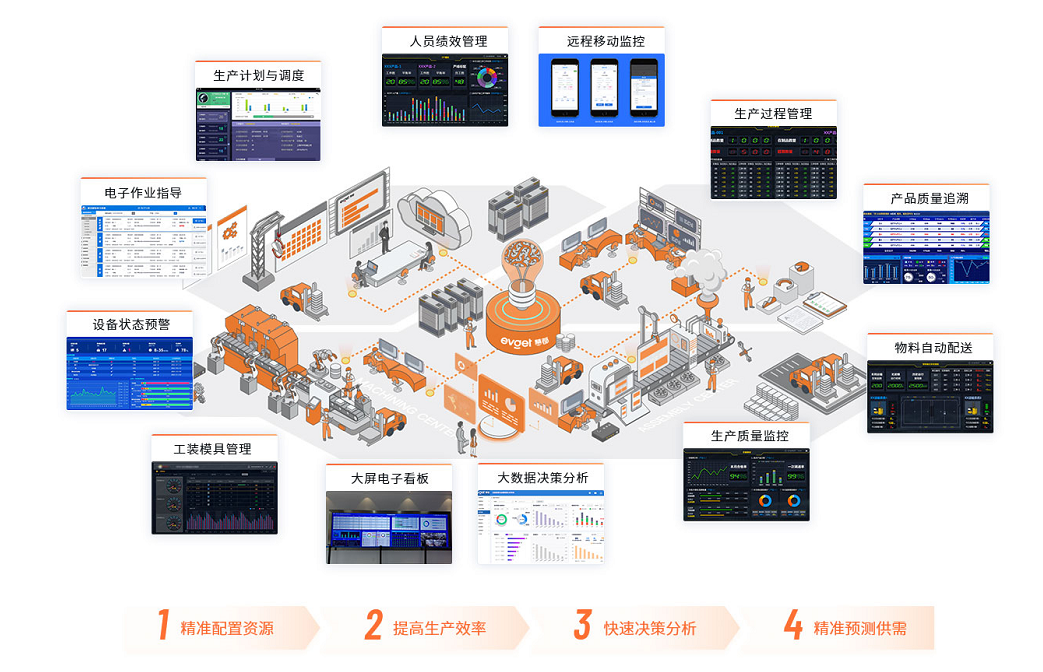
What should be paid attention to when establishing MES system? What benefits can it bring to the enterprise?

网站Colab与Kaggle

In the era of intelligent manufacturing, how do enterprises carry out digital transformation

What kind of sparks will be generated when the remote sensing satellite meets the Beidou navigation satellite?
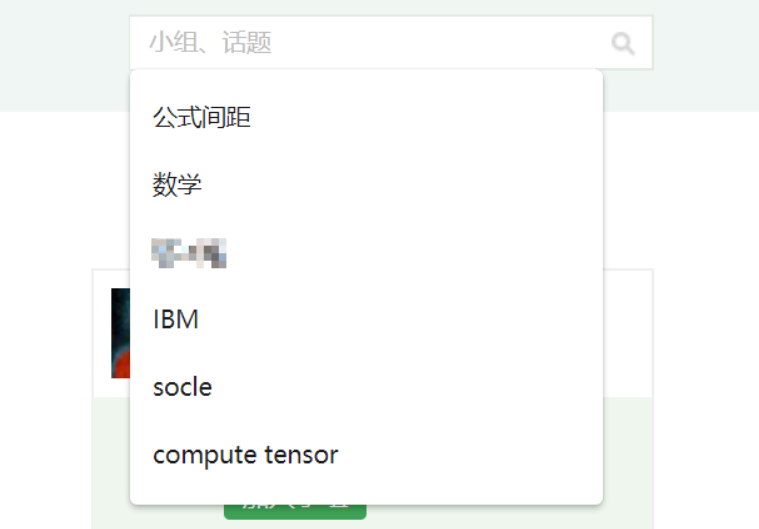
Error: clear the history in the search box in the website?

(p21-p24) unified data initialization method: List initialization, initializing objects of non aggregate type with initialization list, initializer_ Use of Lisy template class
随机推荐
JVM learning notes: three local method interfaces and execution engines
FDA reviewers say Moderna covid vaccine is safe and effective for children under 5 years of age
Convolutional neural network CNN based cat dog battle picture classification (tf2.1 py3.6)
Call method and apply method
JVM学习笔记:垃圾回收机制
【 pointeur avancé Ⅲ】 mise en œuvre de la fonction de tri rapide qsort& fonction de rappel en langage C
x64dbg 调试 EXCEPTION_ACCESS_VIOLATION C0000005
Calling stored procedures in mysql, definition of variables,
(P13)final关键字的使用
Vscode 调试TS
The Three Kingdoms kill the surrounding areas -------- explanation of the pig Kingdom kill problem
Database foundation -- normalization and relational schema
Beidou satellite navigation system foundation part 1
(p27-p32) callable object, callable object wrapper, callable object binder
报错:清除网站内搜索框中的历史记录?
Learning notes (1): live broadcast by Dr. Lu Qi - face up to challenges and grasp entrepreneurial innovation opportunities - face up to challenges and grasp entrepreneurial innovation opportunities -1
vscode 下载慢解决办法
Scope of bean
Record the first step pit of date type
APS软件有哪些排程规则?有何异常处理方案?