当前位置:网站首页>Users, groups, and permissions
Users, groups, and permissions
2022-07-07 12:56:00 【LC181119】
1.Linux Security model
resource allocation :
- Authentication: authentication , Verify user identity
- Authorizaation: to grant authorization , Different users set different permissions
- Accounting | Audition: Audit
1.1 user
Linux Each user in is through User Id (UID) To uniquely identify
- Administrators :root,0
- Ordinary users :1-60000 Automatically assigned
- System users :1-499(CentOS 6 before ),1-999(CentOS 7 in the future )
Allocate permissions to the resources obtained by the daemon
- The logged in user :500+ (CentOS 6 before ),1000+ (CentOS 7 in the future )
Interactive login for users
1.2 User group
- Administrators group :root, 0
- The normal group :
- System group :1-499(CentOS 6 before ), 1-999(CentOS7 in the future ), Divide the permissions of the daemon to obtain resources with
- The normal group :500+(CentOS 6 before ), 1000+(CentOS7 in the future ), For users
1.3 The relationship between users and groups
- The primary group of users (primary group): Users must belong to one and only one main group , By default, users will be created automatically A group with the same name as the user name , As the primary group of users , Because there is only one user in this group , Also known as private group
- Additional groups for users (supplementary group): A user can belong to zero or more secondary groups , Affiliate group
1.4 Security context
2. User and group profiles
2.1 Primary profiles for users and groups
- /etc/passwd: User and its attribute information ( name 、UID、 The main group ID etc. )
- /etc/shadow: User password and its associated attributes
- /etc/group: Group and its attribute information
- /etc/gshadow: Group passwords and their associated attributes
2.2passwd File format
2.3shadow File format
authconfig --passalgo=sha256 --update- Long enough
- Using a digital 、 Capital 、 At least... In lowercase letters and special characters 3 Kind of
- Use random passwords
- Replace regularly , Don't use passwords that have been used recently
2.4group File format
2.5gshdow File format
2.6 Document operation
- vipw and vigr
- pwck and grpck
3. User and group management commands
- useradd
- usermod
- userdel
- groupadd
- groupmod
- groupdel
3.1 The user to create
useradd Command can create new Linux user
useradd [options] LOGIN-u UID-o coordination -u Options , Do not check UID Uniqueness-g GID Specifies that the user belongs to the base group , A group name , It's fine too GID-c "COMMENT“ User's comment information-d HOME_DIR In the specified path ( non-existent ) Catalog for home-s SHELL Indicate the user's default shell Program , The available list is /etc/shells In file-G GROUP1[,GROUP2,...] Specify additional groups for users , The group must exist in advance-N Do not create private group as master group , Use users Group is the main group-r Create system user CentOS 6 Before : ID<500,CentOS7 in the future : ID<1000-m Create a home directory , For system users-M Do not create a home directory , For non system users-p Specify the encrypted password
3.2 User property modification
usermod [OPTION] login-u UID: new UID-g GID: New main group-G GROUP1[,GROUP2,...[,GROUPN]]]: New additional group , The original additional group will be covered ; If you keep the original , At the same timeuse -a Options-s SHELL: New default SHELL-c 'COMMENT': New notes-d HOME: The new home directory will not be created automatically ; To create a new home directory and move home data , Use at the same time -m Options-l login_name: New name-L: lock Designated user , stay /etc/shadow The addition of password column !-U: unlock Designated user , take /etc/shadow Code bar ! Remove-e YYYY-MM-DD: Specify the expiration date of the user account-f INACTIVE: Set an inactive period , That is, the grace period
3.3 Delete user
userdel [OPTION]... Login-f, --force mandatory-r, --remove Delete user home directory and mailbox
3.4 View user related ID Information
id [OPTION]... [USER]u: Show UID-g: Show GID-G: Displays the... Of the group to which the user belongs ID-n: The display name , Need to cooperate ugG Use
3.5 Switch users or execute commands as other users
su [options...] [-] [user [args...]]-l --login su -l UserName amount to su - UserName-c, --command <command> pass a single command to the shell with -c
- su UserName: Non login switch , That is, the configuration file of the target user will not be read , Do not change the current working directory , That is, incomplete switching
- su - UserName: Login switch , Will read the profile of the target user , Switch to your home directory , That is, complete switching
su [-] UserName -c 'COMMAND'3.6 Set the password
passwd [OPTIONS] UserName-d: Delete the specified user password-l: Lock the specified user-u: Unlock the specified user-e: Force user to change password next time login-f: Force operation-n mindays: Specify the minimum service life-x maxdays: Maximum service life-w warndays: How many days in advance to start warning-i inactivedays: Period of inactivity--stdin: Receive user password from standard input ,Ubuntu No such option
3.7 Change user password policy
chage [OPTION]... LOGIN-d LAST_DAY # Time to change password-m --mindays MIN_DAYS-M --maxdays MAX_DAYS-W --warndays WARN_DAYS-I --inactive INACTIVE # Grace period after password expiration-E --expiredate EXPIRE_DATE # User's validity period-l Show password policy
3.8 Other user related commands
- chfn Specify personal information
- chsh Appoint shell, amount to usermod -s
- finger You can view the user's personal information
3.9 Create group
groupadd [OPTION]... group_nameCommon options :
-g GID To specify GID Number ;[GID_MIN, GID_MAX]-r Create system group ,CentOS 6 Before : ID<500,CentOS 7 in the future : ID<1000
3.10 Modify the set of
groupmod [OPTION]... group-n group_name: New name-g GID: new GID
3.11 groups deleting
groupdel [options] GROUP-f, --force Mandatory deletion , Even the user's primary group is forced to delete the group , However, users without a primary group will be unavailable and unable to log in
3.12 Change group password
gpasswd [OPTION] GROUP-a user take user Add to specified group-d user Removes the user from the specified additional group user-A user1,user2,... Set the list of users with administrative rights
3.13 Temporarily switch main group
newgrp [-] [group]3.14 Change and view group members
groupmems [options] [action]-g, --group groupname # Change to the specified group ( Only root)-a, --add username # Specify the user to join the group-d, --delete username # Remove user from group-p, --purge # Clear all members from the group-l, --list # Displays a list of group members
# View the user's group list
groups [OPTION].[USERNAME]...4. File permission management
4.1 File owner and group attribute operation
4.1.1 Set the owner of the file chown
chown [OPTION]... [OWNER][:[GROUP]] FILE...
chown [OPTION]... --reference=RFILE FILE...OWNER # Only modify the ownerOWNER:GROUP # Modify the owner and group at the same time:GROUP # Modify only the group , Colons are also available . Replace--reference=RFILE # Refer to the specified properties , To modify the-R# recursive , Use this option with caution , Very dangerous !
4.1.2 Set the group information of the file chgrp
chgrp [OPTION]... GROUP FILE...
chgrp [OPTION]... --reference=RFILE FILE...4.2 File permissions
4.2.1 File permission description
owner Belong to , ugroup Generic group , gother other , o
The final authority of the user , It's order matching from left to right , namely , owner , Subordinate to the group , others , Once the permissions are matched, they take effect immediately , No more toRight view its permissionsr and w Permission pair root Invalid userAs long as the owner , Group or other One of the three is x jurisdiction ,root You can execute
r Readablew Writablex eXcutable
r You can use file view class tools , such as :cat, You can get its contentw It can be modifiedx You can request the kernel to start this file as a process , That is, it can be executed ( function ) This file ( The contents of this file must be executable )
r have access to ls View in this directoryFile listw You can create files in this directory , You can also delete files in this directory , It has nothing to do with the permission of the deleted filex Sure cd Enter this directory , have access to ls -l View the file metadata in this directory ( Must cooperate with r jurisdiction ), Minimum accessible permissions belonging to the directoryX Just give the catalog x jurisdiction , Do not give files without execution permission x jurisdiction
4.2.2 Modify file permissions chmod
chmod [OPTION]... MODE[,MODE]... FILE...
chmod [OPTION]... OCTAL-MODE FILE...
# Reference resources RFILE File permissions , take FILE It is the same as RFILE
chmod [OPTION]... --reference=RFILE FILE...4.3 Default permissions for new files and directories
- Default permissions for new files : 666-umask, If a bit of the result exists, execute ( Odd number ) jurisdiction , Then its permissions +1, accidentally The number remains the same
- Default permissions for new directories : 777-umask
umask
# Display in mode
umask –S
# The output can be called
umask –pmodify umask
umask #- Global settings : /etc/bashrc
- User Settings :~/.bashrc
4.4 Linux Special permissions on the file system
- SUID Act on binary executables , The user will inherit the rights of the owner of this program
- SGID
- STICKY Act on the directory , Files in this directory can only be deleted by the owner
4.4.1 Special privileges SUID
- Can any executable program file be started as a process , It depends on whether the initiator has execution rights to the program file
- After starting as a process , The owner of the process is the initiator , The group of the process is the group of the initiator
- Permissions for a process to access a file , It depends on the initiator of the process
- Can any executable program file be started as a process : It depends on whether the initiator has execution rights to the program file
- After starting as a process , The owner of the process is the owner of the original program file
- SUID Valid only for binary executables
- SUID Setting on the directory makes no sense
chmod u+s FILE...
chmod 4xxx FILE
chmod u-s FILE...4.4.2 Special privileges SGID
- Can any executable program file be started as a process : It depends on whether the initiator has execution rights to the program file
- After starting as a process , The process belongs to the original program file
SGID Permission setting :
chmod g+s FILE...
chmod 2xxx FILE
chmod g-s FILE...chmod g+s DIR...
chmod 2xxx DIR
chmod g-s DIR...4.4.3 Special privileges Sticky position
chmod o+t DIR...
chmod 1xxx DIR
chmod o-t DIR...4.4.4 Special authority digital method
000 0001 1010 2011 3100 4101 5110 6111 7
4.5 Set file special properties
chattr +i filechattr +a filelsattr4.6 Access control list ACL
4.6.1 ACL Authority function
owner , Custom user , Subordinate to the group | Custom groups , others
4.6.2 ACL Relevant command
- mask Only affect owners and other Maximum permissions for people and groups other than
- mask After logical and operation with the user's permission , To become a limited authority (Effective Permission)
- User or group settings must exist in mask It will take effect only when the permission is set
4.6.3 Backup and restore ACL
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
ISPRS2021/遥感影像云检测:一种地理信息驱动的方法和一种新的大规模遥感云/雪检测数据集
![[statistical learning method] learning notes - support vector machine (I)](/img/3f/56db88d717d7cd6624b3d0867146e9.png)
[statistical learning method] learning notes - support vector machine (I)

Leetcode skimming: binary tree 27 (delete nodes in the binary search tree)
![[爬虫]使用selenium时,躲避脚本检测](/img/3a/85ea729be2aa76c3de4a822ca6939b.png)
[爬虫]使用selenium时,躲避脚本检测
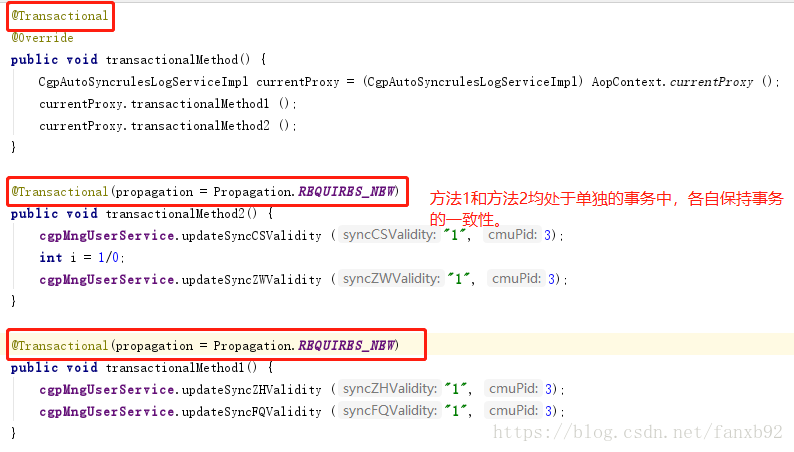
How to apply @transactional transaction annotation to perfection?
处理链中断后如何继续/子链出错removed from scheduling
Leetcode skimming: binary tree 20 (search in binary search tree)
visual stdio 2017关于opencv4.1的环境配置
聊聊Redis缓存4种集群方案、及优缺点对比
![[statistical learning method] learning notes - logistic regression and maximum entropy model](/img/f7/857d053cc2cee81c24919aafab3c6e.png)
[statistical learning method] learning notes - logistic regression and maximum entropy model
随机推荐
智云健康上市:市值150亿港元 SIG经纬与京新基金是股东
test
JS to convert array to tree data
Day-15 common APIs and exception mechanisms
Sorting, dichotomy
测试下摘要
CMU15445 (Fall 2019) 之 Project#2 - Hash Table 详解
layer弹出层的关闭问题
Day22 deadlock, thread communication, singleton mode
Find ID value MySQL in string
怎样重置火狐浏览器
The URL modes supported by ThinkPHP include four common modes, pathinfo, rewrite and compatibility modes
Leetcode skimming: binary tree 21 (verifying binary search tree)
[crawler] avoid script detection when using selenium
visual stdio 2017关于opencv4.1的环境配置
【从 0 开始学微服务】【02】从单体应用走向服务化
AUTOCAD——大于180度的角度标注、CAD直径符号怎么输入?
ip2long与long2IP 分析
Leetcode skimming: binary tree 20 (search in binary search tree)
Cryptography series: detailed explanation of online certificate status protocol OCSP