当前位置:网站首页>Day-17 connection set
Day-17 connection set
2022-07-07 12:36:00 【Xiaobai shelter】
Examination supplement
geter/seter Use of methods
for example Declare a variable private String name;
seter Is to set the attribute value , Therefore, it is necessary to enter , Don't worry if you set it up , No need to participate , Therefore, the return value type is void
public void setName(String name){
this.name=name;
}
geter Is to get the attribute value , Therefore, it is necessary to participate ( Return value ), No input is required , Just get value , It is not to modify the value
public String getName(){
return name;
}
1.LinkedList
① Concept :LinkedList: The bottom layer is a two-way linked list , Because it's not continuous storage , It's just that you can find the address of the next element , So add and delete High efficiency , But the query efficiency is low , Because you can only find one by one from the first
② Common operations :
stay LinkedList list=new LinkedList();
//ArrayList list=new ArrayList();
// Add to tail
list.add(1);
list.add(11);
list.add(2);
list.add(13);
// Add to specified location
//list.add(index,element);
// Add to head
//list.push(e);
//list.addFirst(e);
// Tail add
//list.addLast(e);
// Number
System.out.println(list.size());
// Determine whether it is null
System.out.println(list.isEmpty());
// Delete... According to subscript
list.remove(0);
// Delete according to data
list.remove(new Integer(11));
// Empty
list.clear();
// change
list.set(1, 521);
// obtain
list.get(2);
// Traverse
for(Object object:list){
}
} Insert the code chip here
1.2 Underlying implementation
1.2.1 A linked list consists of nodes , Because it's a two-way list , So there are three attributes in the node
1 Saved data Object
2 Next node object Node type
3 Previous node object Node type
1.2.2 LinkedList class
In order to add more efficiency from beginning to end , stay LinkedList The first and last nodes are saved in the class
1.2.3 add to -add、 obtain -get、
among Get Method just simulates the subscript acquisition method , It is essentially a traversal operation , Just made a certain judgment , Judge whether the first half is fast or the second half is fast
2 Set And sort
Set characteristic Disordered and unrepeatable , Unordered means that the order of addition and extraction are not guaranteed to be the same
HashSet: At the bottom is a hash table
TreeSet: At the bottom are red and black trees , The added elements must be sorted according to a certain format
Numbers : Default from small to large
character string : Per person ASCLL Code to sort
date : Natural date , Yesterday today tomorrow
2.1 TreeSet
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create objects
TreeSet set = new TreeSet();
// add to
set.add(1);
set.add(2);
// because treeSet The elements must be in order , This means that the element types must be unified
// Without unity, there is no comparability , You can't sort
// set.add("xxx");
set.add(22);
set.add(12);
set.add(24);
// Do not repeat , Do not add if repeated
set.add(12);
System.out.println(set.size());
System.out.println(set);
// Delete by content , Cannot delete from index , Because there's no index
set.remove(22);
// Traverse
for (Object object : set) {
System.out.println(object);
}
set = new TreeSet();
// every ASCII Compare
set.add("aadddd");
set.add("aa");
set.add("acadas");
set.add("caa");
set.add("d");
// a,aa,aadddd,acadas,caa,d
System.out.println(set);
set = new TreeSet();
set.add("1");
set.add("2");
set.add("3");
set.add("4");
set.add("5");
set.add("6");
set.add("7");
set.add("8");
set.add("9");
set.add("10");
// [1, 10, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
System.out.println(set);
}
2.2Comparable
Use TreeSet When , The element must implement Comparable Interface , Because when adding , This interface will be called automatically compareTo Methods for comparison
Add string , Numbers , When it comes to dates , Automatically sort , Because Integer,String,Date Both implement the interface and the method
If we want to store custom types , You need to let this class implement the corresponding interfaces and methods to store
2.3 Comparator
Comparator It is also a comparator class Comparable It's also quite , If these two exist at the same time , be Comparator High priority
Comparable: If treeSet When saving our own defined types in , Use Comparable
Comparator : If treeSet When the type we write is not saved in , Then use Comparator To specify the collation
such as Integer The default is ascending sort , If we need to sort in descending order , We can only use Comparator, Because we can't change Integer Source code
But this time Integer There is Comparable The implementation of the interface , Equal to two comparisons exist , however Comparator High priority ,
So it will be sorted according to the rules we define
Opening and closing principle : Turn off for changes , For extension development
2.4List Sort
Here public static void main(String[] args) {
List list = new ArrayList();
list.add(1);
list.add(22);
list.add(3);
list.add(11);
// This method will call the... Of the object Comparable Medium compareTo Method or Comparator Methods in interfaces
// because Integer There is compareTo Method , And in ascending order , That's why you can use sort Method
// For example, if you want to descending order, you can use sort Method overloading
// Collections.sort(list);
Collections.sort(list, new Comparator() {
@Override
public int compare(Object o1, Object o2) {
// o1 Is the element to be added
// o2 It's the elements of the collection
Integer i1 = (Integer) o1;
Integer i2 = (Integer) o2;
// The method return 0 Repeated description , Don't add
// return Greater than 0 Value Indicates that the element to be added is larger than that in the collection , Just put it back
// return Less than 0 Value Indicates that the element to be added is smaller than the element in the collection , Just put it forward
return i2 - i1;
}
});
System.out.println(list);
list = new ArrayList();
list.add(new Student1(18));
list.add(new Student1(11));
list.add(new Student1(15));
list.add(new Student1(4));
// because Student1 It didn't come true comparable Interface So it can't be used sort Method
// Collections.sort(list);
// But you can use overloaded methods
Collections.sort(list,new Comparator () {
@Override
public int compare(Object o1, Object o2) {
return 0;
}
});
}
}
class Student1 {
int age;
public Student1(int age) {
super();
this.age = age;
}
Insert a piece of code into
3 summary
Comparable : If treeSet When saving our own defined types in , Use Comparable
Comparator : If treeSet When the type we write is not saved in , Then use Comparator To specify the collation
such as Integer The default is ascending sort , If we need to sort in descending order , We can only use Comparator, Because we can't change Integer Source code
But this time Integer There is Comparable The implementation of the interface , Equal to two comparisons exist , however Comparator High priority ,
So it will be sorted according to the rules we define
Opening and closing principle : Turn off for changes , For extension development
边栏推荐
- Tutorial on principles and applications of database system (007) -- related concepts of database
- 数据库系统原理与应用教程(008)—— 数据库相关概念练习题
- 金融数据获取(三)当爬虫遇上要鼠标滚轮滚动才会刷新数据的网页(保姆级教程)
- Xiaohongshu microservice framework and governance and other cloud native business architecture evolution cases
- Zhimei creative website exercise
- 2022危险化学品生产单位安全生产管理人员考题及在线模拟考试
- Using stack to convert binary to decimal
- 解决 Server returns invalid timezone. Go to ‘Advanced’ tab and set ‘serverTimezone’ property manually
- SQL Lab (46~53) (continuous update later) order by injection
- visual stdio 2017关于opencv4.1的环境配置
猜你喜欢
Experiment with a web server that configures its own content
跨域问题解决方案
Configure an encrypted web server

SQL lab 11~20 summary (subsequent continuous update) contains the solution that Firefox can't catch local packages after 18 levels
ENSP MPLS layer 3 dedicated line
EPP+DIS学习之路(1)——Hello world!
![[deep learning] image multi label classification task, Baidu paddleclas](/img/dd/6f213a396e8bb240a6872e4c03afab.png)
[deep learning] image multi label classification task, Baidu paddleclas
数据库系统原理与应用教程(009)—— 概念模型与数据模型
Processing strategy of message queue message loss and repeated message sending
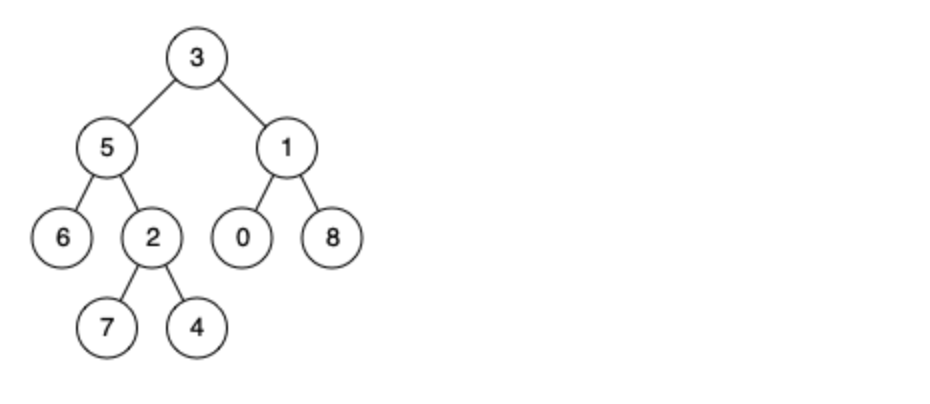
leetcode刷题:二叉树24(二叉树的最近公共祖先)
随机推荐
Idea 2021 Chinese garbled code
ES底层原理之倒排索引
EPP+DIS学习之路(1)——Hello world!
[Q&A]AttributeError: module ‘signal‘ has no attribute ‘SIGALRM‘
2022A特种设备相关管理(锅炉压力容器压力管道)模拟考试题库模拟考试平台操作
编译 libssl 报错
The left-hand side of an assignment expression may not be an optional property access. ts(2779)
H3C HCl MPLS layer 2 dedicated line experiment
AirServer自动接收多画面投屏或者跨设备投屏
The hoisting of the upper cylinder of the steel containment of the world's first reactor "linglong-1" reactor building was successful
Vxlan 静态集中网关
【PyTorch实战】用PyTorch实现基于神经网络的图像风格迁移
Using stack to convert binary to decimal
leetcode刷题:二叉树27(删除二叉搜索树中的节点)
金融数据获取(三)当爬虫遇上要鼠标滚轮滚动才会刷新数据的网页(保姆级教程)
Realize all, race, allsettled and any of the simple version of promise by yourself
leetcode刷题:二叉树25(二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先)
数据库系统原理与应用教程(009)—— 概念模型与数据模型
OSPF exercise Report
数据库系统原理与应用教程(007)—— 数据库相关概念