当前位置:网站首页>Inverted index of ES underlying principle
Inverted index of ES underlying principle
2022-07-07 12:13:00 【Talk about duoxiansen】
Catalog
One 、ElasticSearch Framework principle
1、ElasticSearch Node type of cluster
5、 Use disk cache to retrieve in real time
6、translog Provide disk control
3、 Simple example of inverted index
One 、ElasticSearch Framework principle
1、ElasticSearch Node type of cluster
Elasticsearch An example of is a node , A group of nodes form a cluster .Elasticsearch Nodes in the cluster can be configured in three different ways :
(1)Master node
Master Node control Elasticsearch colony , And be responsible for creating / Delete index , Track which nodes are part of the cluster , And assign partitions to these nodes .
(2)Data node
Data nodes are used to store data and inverted indexes .
(3)Client node
If you will node.master and node.data Set to false, Then configure the node as a client node , And act as a load balancer , Route incoming requests to different nodes in the cluster .
If you are connected to a node as a client , This node is called the coordination node (coordinating node). The coordination node routes the client request to the node of the corresponding partition in the cluster . For read requests , The coordination node selects different partitions each time to provide requests to balance the load .
(4) The storage model
Use a data structure called inverted index , Used to provide low latency search results
Be careful : The operation of indexing data will only occur in the primary partition (primary shard) On , It will not happen in the fragmented copy (Replica) On . If the node to which the request for index data is sent does not have an appropriate partition or the partition is a replica , Then the request will be forwarded to the node containing the primary partition .
2、 Immutability
The inverted index written to disk is immutable , It has the following advantages :
① No need to lock , Improve concurrency , Avoid lock problems
② The data remains the same , Keep it all the time os cache in , as long as cache Enough memory
③filter cache It's always in memory , Because the data doesn't change
④ Can be compressed , save cpu and io expenses
Disadvantage :
① Rebuild the entire index every time
3、 Write and create
1) Modulo operation is performed by the number of main partitions in the index , To determine which fragment the document should be indexed to . shard = hash(document_id) % (num_of_primary_shards)
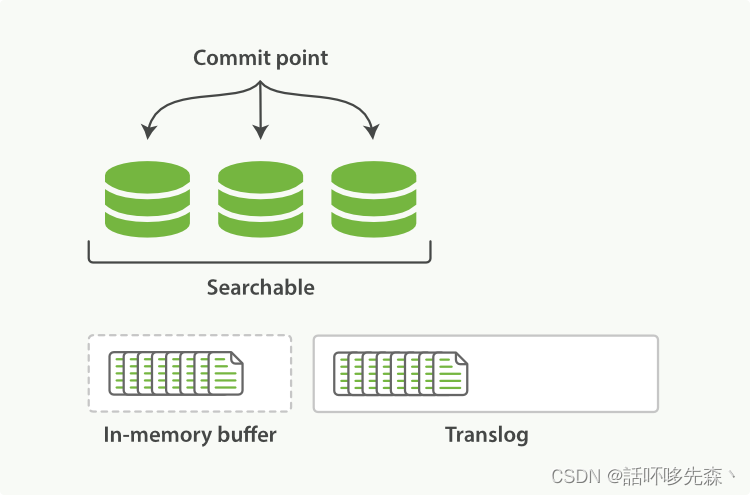
2) When a node receives a request from the coordinating node , The request is written to translog, And add the document to the memory buffer .
If the request is successful on the main slice , The request will be sent in parallel to the replica shard . Only on all master and replica tiles translog By fsync’ed after , The client will receive the confirmation that the request is successful .
- The memory buffer is refreshed at fixed intervals ( The default is 1 second ), And write the content to a new segment in the file system cache . The content of this paragraph has not been fsync’ed( Not written to the file system ), Segments are open , Content can be used to search .
- translog Be emptied , And the file system cache every 30 Every minute fsync, Or when translog Do it once when it gets too big fsync. This process takes place in Elasticsearch called flush. During refresh , The memory buffer is cleared , The content is written to a new file segment (segment). When file segments are fsync’ed And refresh to disk , A new submission point will be created ( In fact, it will update the file offset , The file system does this automatically ). old translog Be deleted , A new start .
4、 Delete and update
Delete : Each submission point includes a .del file , Contains documents that have been deleted on the segment when a document is deleted , It is actually just .del The file is marked for deletion , It can also match queries , But it will be deleted from the result before it finally returns .
to update : The old version of the document is marked for deletion , The new version of the document is indexed in the new segment
5、 Use disk cache to retrieve in real time
1) The newly received data is written into the new index file , Generating inverted indexes is called an end --segment
2) Use one commit Document all in the index segment
3) New data enters memory buffer in
4) Memory buffer Make a new one segment, Brush into the file system cache ,ES You can detect new segment
5) The file system cache is really synchronized to disk ,commit File update
6、translog Provide disk control
To prevent loss ( Host error 、 Disk failure ). When ES Write data to buffer in , It also recorded translog journal
Two 、 Inverted index
1、 word ---- Document matrix
file 1 | file 2 | file 3 | file 4 | file 5 | file 6 | |
word 1 |
|
| ||||
word 2 |
|
| ||||
word 3 |
|
| ||||
word 4 |
|
| ||||
word 5 |
| |||||
word 6 |
|
2、 Inverted index
1)、 Word dictionary (Lexicon): The usual index unit of a search engine is the word , A word dictionary is a string collection of all the words that have appeared in a document collection , Each index entry in a word dictionary records some information about the word itself and points to “ Inverted list ” The pointer to .
2)、 Inverted list (PostingList): The inverted list records the document list of all documents where a word has appeared and the location information of the word in the document , Each record is called an inverted entry (Posting). According to the inverted list , You know which documents contain a particular word .

3、 Simple example of inverted index
Suppose the document collection contains four documents , Create an inverted index of this document collection .
Document number | Document content |
1 | The father of Google Maps job hopping Facebook |
2 | The father of Google Maps joined Facebook |
3 | Google Maps founder Lars left Google to join Facebook |
4 | Lars, the father of Google maps, joins social networking sites Facebook |
1)、 Get keywords — Word segmentation
Meaningless :“ Of ”,“ yes ”,“in”,“too”;
Punctuation 、 Space ;
Uniform case :“a”,“A”. Restore words lives-->live
2)、 Build an indexed list
Article location 、 Frequency of occurrence 、 Position of appearance
3)、 Application reason
Time complexity --1 second
word ID | word | Document frequency | Inverted list (DocID:TF:<Position>) |
1 | 4 | (1:1:<1>),(2:1:<1>),(3:2:<1><6>),(4:1:<1>) | |
2 | Map | 4 | (1:1:<2>),(2:1:<2>),(3:1:<2>),(4:1:<2>) |
3 | The father of | 3 | (1:1:<3>),(2:1:<3>),(4:1:<3>) |
4 | job-hopping | 1 | (1:1:<4>) |
5 | 4 | (1:1:<5>),(2:1:<5>),(3:1:<8>),(4:1:<8>) | |
6 | To join in | 2 | (2:1:<4>),(4:1:<5>) |
7 | founder | 1 | (3:1:<3>) |
8 | Lars | 2 | (3:1:<4>),(4:1:<4>) |
9 | Leave | 1 | (3;1:<5>) |
10 | social contact | 1 | (4:1:<6>) |
11 | Website | 1 | (4:1:<7>) |
With this index system , Search engine can easily respond to user's query , For example, users input query words “Facebook”, Search system search inverted index , You can read the document that contains the word , These documents are the search results provided to users , Using word frequency information 、 Document frequency information can sort these candidate search results , Calculate document and query similarity , Output according to the similarity score from high to low , This is part of the internal process of the search system .
边栏推荐
- 超标量处理器设计 姚永斌 第10章 指令提交 摘录
- Swiftui tutorial how to realize automatic scrolling function in 2 seconds
- Unity map auto match material tool map auto add to shader tool shader match map tool map made by substance painter auto match shader tool
- ES底层原理之倒排索引
- Superscalar processor design yaoyongbin Chapter 10 instruction submission excerpt
- STM32F1与STM32CubeIDE编程实例-315M超再生无线遥控模块驱动
- wallys/Qualcomm IPQ8072A networking SBC supports dual 10GbE, WiFi 6
- Time bomb inside the software: 0-day log4shell is just the tip of the iceberg
- Summed up 200 Classic machine learning interview questions (with reference answers)
- 关于 Web Content-Security-Policy Directive 通过 meta 元素指定的一些测试用例
猜你喜欢
《看完就懂系列》天哪!搞懂节流与防抖竟简单如斯~
![111.网络安全渗透测试—[权限提升篇9]—[Windows 2008 R2内核溢出提权]](/img/2e/da45198bb6fb73749809ba0c4c1fc5.png)
111.网络安全渗透测试—[权限提升篇9]—[Windows 2008 R2内核溢出提权]
![[filter tracking] comparison between EKF and UKF based on MATLAB extended Kalman filter [including Matlab source code 1933]](/img/90/ef2400754cbf3771535196f6822992.jpg)
[filter tracking] comparison between EKF and UKF based on MATLAB extended Kalman filter [including Matlab source code 1933]
Superscalar processor design yaoyongbin Chapter 10 instruction submission excerpt
Explore cloud database of cloud services together
Problem: the string and characters are typed successively, and the results conflict
![[extraction des caractéristiques de texture] extraction des caractéristiques de texture de l'image LBP basée sur le mode binaire local de Matlab [y compris le code source de Matlab 1931]](/img/65/bf1d0f82878a49041e8c2b3a84bc15.png)
[extraction des caractéristiques de texture] extraction des caractéristiques de texture de l'image LBP basée sur le mode binaire local de Matlab [y compris le code source de Matlab 1931]
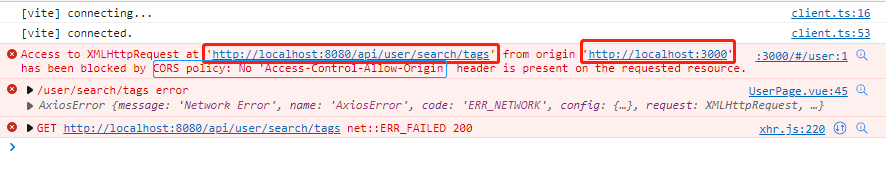
跨域问题解决方案

《通信软件开发与应用》课程结业报告

人大金仓受邀参加《航天七〇六“我与航天电脑有约”全国合作伙伴大会》
随机推荐
Ask about the version of flinkcdc2.2.0, which supports concurrency. Does this concurrency mean Multiple Parallelism? Now I find that mysqlcdc is full
Cenos openssh upgrade to version 8.4
平安证券手机行开户安全吗?
源代码防泄密中的技术区别再哪里
[filter tracking] strapdown inertial navigation pure inertial navigation solution matlab implementation
EPP+DIS学习之路(1)——Hello world!
Review and arrangement of HCIA
Flet tutorial 17 basic introduction to card components (tutorial includes source code)
wallys/Qualcomm IPQ8072A networking SBC supports dual 10GbE, WiFi 6
How to understand the clothing industry chain and supply chain
Improve application security through nonce field of play integrity API
110.网络安全渗透测试—[权限提升篇8]—[Windows SqlServer xp_cmdshell存储过程提权]
Fleet tutorial 19 introduction to verticaldivider separator component Foundation (tutorial includes source code)
【滤波跟踪】基于matlab捷联惯导仿真【含Matlab源码 1935期】
【纹理特征提取】基于matlab局部二值模式LBP图像纹理特征提取【含Matlab源码 1931期】
Solve the problem that vscode can only open two tabs
110. Network security penetration test - [privilege promotion 8] - [windows sqlserver xp_cmdshell stored procedure authorization]
[extraction des caractéristiques de texture] extraction des caractéristiques de texture de l'image LBP basée sur le mode binaire local de Matlab [y compris le code source de Matlab 1931]
千人規模互聯網公司研發效能成功之路
牛客网刷题网址