当前位置:网站首页>Introduction and application of smoothstep in unity: optimization of dissolution effect
Introduction and application of smoothstep in unity: optimization of dissolution effect
2022-07-07 12:02:00 【Blowing breeze and three drops of water】
Unity in SmoothStep Introduction and Application : Optimization of dissolution effect
Last article Use RampTex To add a unsatisfactory edge color change to the dissolve effect , In this article, we will further optimize , And do some simple analysis of the corresponding principle .
Today's main content is as follows :
- Introduction to difference function :
smoothstep - Use the difference function to improve the dissolution effect
- Realize further optimization of the scheme
Old rules , Let's see the end result first :

Introduction to difference function : smoothstep
smoothstep(edge_low, edge_up, x) function :
[edge_low, edge_up]Is a specified range of differencesxIs any real number- The result of the function is :
if x < edge_low; return 0.if x > edge_up; return 1.- If
xbe inedge_lowandedge_upBetween , Then return toxstay[0, 1]Mapping values in the range- For example, the specified range is
[0, 10],x=5, We map it to[0, 1]after , The corresponding mapping value is0.5 - For example, the specified range is
[0, 100],x=5, We map it to[0, 1]after , The corresponding mapping value is0.05 - In essence, I will
[edge_low, edge_up]Mapping to[0, 1], And then findxstay[0, 1]Mapping values in - Note that the instructions here use Linear mapping , and
smoothstepLinear mapping is not used , But after linear mapping, use curve to smooth the result , This result is not much different from linear mapping , We can simply use linear mapping to understand
- For example, the specified range is
xThe mapping of functions within the scope is :- The linear mapping function is : k 1 = ( x − a ) ( b − a ) { a < = x < = b } k_{1}=\dfrac{(x-a)}{(b-a)}\{a<=x<=b\} k1=(b−a)(x−a){ a<=x<=b}
- First line linear mapping , get
xThe mapping value of k 1 k_1 k1 - Then use the curve to smooth this value : k = 3 k 1 2 − 2 k 1 3 { a < x < b } k=3k_{1}^{2}-2k_{1}^{3}\{a<x<b\} k=3k12−2k13{ a<x<b}
The code implementation is as follows :
float smoothstep (float edge0, float edge1, float x)
{
if (x < edge0)
return 0;
if (x > edge1)
return 1;
// Linear mapping
x = (x - edge0) / (edge1 - edge0);
// smooth
return x * x * (3 - 2 * x);
}
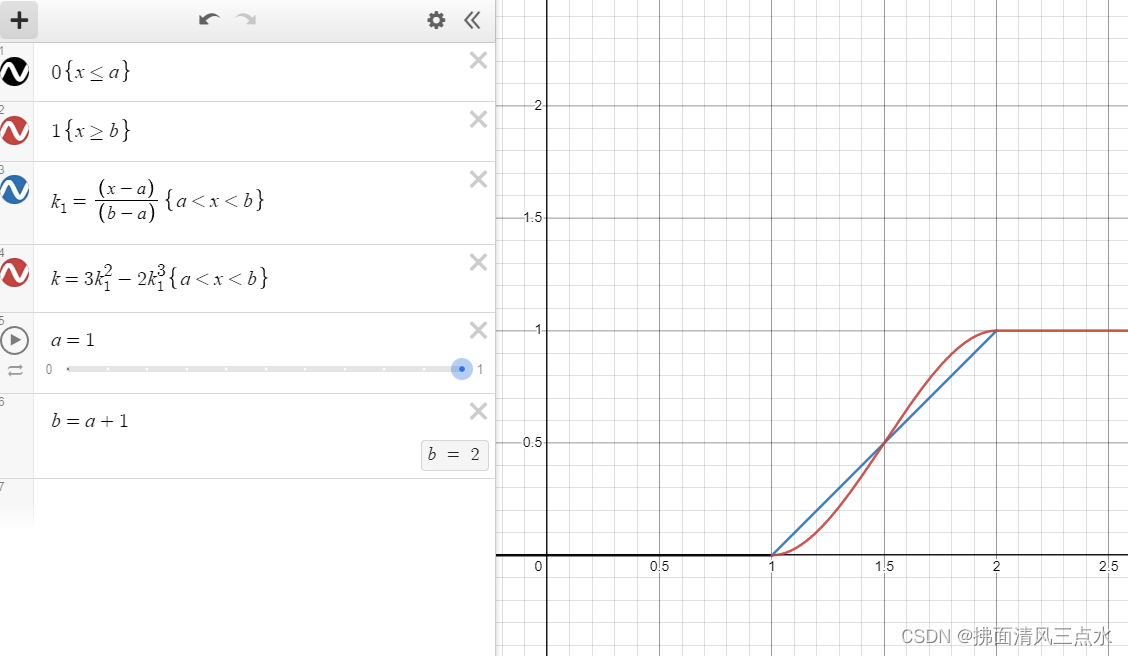
The above figure shows the use of smoothstep Function , The specified range is [a=1, b=a+1=2], You can see :
- When
x <= 1when , Function value is0 - When
x >= 2when , Function value is1 - When
1 < x < 2when , The function value is scaled to[0, 1]Between- The blue lines are linear mappings
- The red line is the result of smoothing with curve after linear mapping
- Generally speaking, there is little difference between the two
Use the difference to improve the scheme
We don't set how many circles there are this time , Completely based on RampTex The gradient level of , RampTex How many layer , How many layers are there on our edge .
in other words , We need to RampTex Mapped to the small area of the dissolution edge , As specified in our last article 0~0.12 Range .
To put it simply , It's about putting RampTex Draw this 0~0.12 Within the scope of .
Here we use 0~0.1.
In mathematical terms , Is to be in [0, 1] Noise texture value in this range , Mapped to the edge [0, 0.1] within , Combined with the difference function introduced above , Our goal is :
// x=dissolveCol.r, {0<=x<=1}
smoothsetp(0, 0.1, x)
Of course , there [0, 0.1] It's not the dissolving edge .
In the previous post , We introduced , dissolveCol.r < _DissolveThreshold Is to dissolve pixels , So from dissolveCol.r == _DissolveThreshold The first pixel is the pixel that dissolves the edge , As for the final range , We need to specify ourselves , For example, the value here is 0.1.
So our call needs to be optimized as :
// x=dissolveCol.r, Sample self noise texture , {0<=x<=1}
// a=_DissolveThreshold, b=_DissolveThreshold+0.1
// among a Is the lower bound of dissolution , b Is the width of the edge of the dissolved pixel
y = smoothsetp(a, b, x)
The above call means :
We need to calculate the dissolution value x, The new sampling coordinates are obtained by processing the difference function y, adopt y stay RampTex After sampling the color, it is attached to the primary color of the object :
x < a: This pixel dissolves , abandon , Don't mindx > b: At this point, the function returns1, stay RampTex Black is sampled on , Because the black value is 0, It is equivalent to that the last pixel keeps the primary colora < x < b: At this time, the function returns a new one after linear mapping and smoothing[0, 1]Mapping values between- What we should pay attention to here is : because
xItself is in[0, 1]Between , Processed resultsyStill processing[0, 1]Between , So it is easy to misunderstand , Need to know - None of the conditions here involve
=Part of , Because in shader Dealing with boundaries , One pixel has little difference , And there may be performance differences
- What we should pay attention to here is : because
After this little treatment , We can be within the specified width pixels of the edge position , Draw completely RampTex Represents the color of the .
Realize further optimization of the scheme
You think it's over ? naive …
because RampTex It is essentially a one-dimensional texture , So our first optimization is , Replace its sampler , This can improve certain performance :
sampler _RampTex;
fixed4 rampColor = tex1D(_RampTex, smoothstep(_DissolveThreshold, _DissolveThreshold + 0.1, dissolveCol.r));
The second optimization has been mentioned above , We are in the difference , Used smoothstep function , This function will do linear mapping first , Then smooth the curve , However, there is little difference between the result of smooth curve and that of linear mapping , But there is an additional curve calculation , So when our requirements are not particularly high , Just use the result of linear mapping .
First, let's introduce the function : saturate.
saturate(x) The delta function is going to be :
- When
x <= 0when , Function value is0 - When
x >= 1when , Function value is1 - When
0 < x < 1when , returnx
Then realize linear mapping and use saturate:
// k = (x - a) / (b - a);
k = (dissolveCol.r - _DissolveThreshold) / (_DissolveThreshold + 0.1 - _DissolveThreshold);
fixed4 rampColor = tex1D(_RampTex, saturate(k));
All right. , At this point, our dissolution effect is finally introduced .
Here is the complete code :
Shader "Dissolve"
{
Properties
{
[NoScaleOffset]_MainTex ("Texture", 2D) = "white" {}
_DissolveTex("DissolveTex", 2D) = "white" {}
_DissolveThreshold("DissolveThreshold", Range(0, 1)) = 0
_RampTex("RampTex", 2D) = "" {}
}
SubShader
{
Tags { "RenderType"="Opaque" }
LOD 100
Pass
{
CGPROGRAM
#pragma vertex vert
#pragma fragment frag
#include "UnityCG.cginc"
struct appdata
{
float4 vertex : POSITION;
float2 uv : TEXCOORD0;
};
struct v2f
{
float4 uv : TEXCOORD0;
float4 vertex : SV_POSITION;
};
sampler2D _MainTex;
float4 _MainTex_ST;
sampler2D _DissolveTex;
float4 _DissolveTex_ST;
fixed _DissolveThreshold;
sampler _RampTex;
v2f vert (appdata v)
{
v2f o;
o.vertex = UnityObjectToClipPos(v.vertex);
// o.uv.xy = TRANSFORM_TEX(v.uv, _MainTex);
o.uv.xy = v.uv;
o.uv.zw = TRANSFORM_TEX(v.uv, _DissolveTex);
return o;
}
fixed4 frag (v2f i) : SV_Target
{
fixed4 dissolveCol = tex2D(_DissolveTex, i.uv.zw);
// Sample color from noise texture , If the value [ Less than threshold ] Then discard this segment
// For example, the threshold is 0.1, All pixels sampled on the noise texture r Less than 0.1 All the fragments will be discarded
// That is, the dark color on the noise texture (->0) Start dissolving first , A pale color (->1) Finally dissolve
clip(dissolveCol.r - _DissolveThreshold);
// fixed4 rampColor = tex1D(_RampTex, smoothstep(_DissolveThreshold, _DissolveThreshold + 0.1, dissolveCol.r));
// k = (x-a)/(b-a);
// k = (dissolveCol.r - _DissolveThreshold) / (_DissolveThreshold + 0.1 - _DissolveThreshold)
fixed4 rampColor = tex1D(_RampTex, saturate((dissolveCol.r - _DissolveThreshold) * 10));
fixed4 col = tex2D(_MainTex, i.uv.xy);
col += rampColor;
return col;
}
ENDCG
}
}
}
summary
After the introduction of three articles , We know each other completely Unity How to make and optimize the dissolution effect in .
In the whole process , We not only understand the principle of dissolution effect itself , Also through this special effect , Touched in Shader Noise texture and gradient texture are common in , And use these two tools to optimize the dissolution effect .
At the same time, we also analyzed Shader Commonly used smoothstep Functions and saturate function , In short, the harvest is full .
Okay , That's what we're talking about today , I hope that's helpful .
边栏推荐
- 正在运行的Kubernetes集群想要调整Pod的网段地址
- [extraction des caractéristiques de texture] extraction des caractéristiques de texture de l'image LBP basée sur le mode binaire local de Matlab [y compris le code source de Matlab 1931]
- SwiftUI Swift 内功之如何在 Swift 中进行自动三角函数计算
- <No. 8> 1816. 截断句子 (简单)
- Detailed explanation of debezium architecture of debezium synchronization
- Hi3516全系统类型烧录教程
- Cmu15445 (fall 2019) project 2 - hash table details
- R语言使用quantile函数计算评分值的分位数(20%、40%、60%、80%)、使用逻辑操作符将对应的分位区间(quantile)编码为分类值生成新的字段、strsplit函数将学生的名和姓拆分
- 正在運行的Kubernetes集群想要調整Pod的網段地址
- Blog moved to Zhihu
猜你喜欢
软件内部的定时炸弹:0-Day Log4Shell只是冰山一角
Hi3516全系统类型烧录教程
SwiftUI 4 新功能之掌握 WeatherKit 和 Swift Charts
![112.网络安全渗透测试—[权限提升篇10]—[Windows 2003 LPK.DDL劫持提权&msf本地提权]](/img/b6/6dfe9be842204567096d1f4292e8e7.png)
112.网络安全渗透测试—[权限提升篇10]—[Windows 2003 LPK.DDL劫持提权&msf本地提权]

百度数字人度晓晓在线回应网友喊话 应战上海高考英语作文
Talk about SOC startup (IX) adding a new board to uboot
Talk about SOC startup (x) kernel startup pilot knowledge

核舟记(一):当“男妈妈”走进现实,生物科技革命能解放女性吗?
30. Few-shot Named Entity Recognition with Self-describing Networks 阅读笔记

Reasons for the failure of web side automation test
随机推荐
[data clustering] realize data clustering analysis based on multiverse optimization DBSCAN with matlab code
zero-shot, one-shot和few-shot
Camera calibration (1): basic principles of monocular camera calibration and Zhang Zhengyou calibration
Internet Protocol
Matlab implementation of Huffman coding and decoding with GUI interface
正在运行的Kubernetes集群想要调整Pod的网段地址
In depth learning autumn recruitment interview questions collection (1)
[filter tracking] comparison between EKF and UKF based on MATLAB extended Kalman filter [including Matlab source code 1933]
Onedns helps college industry network security
30. Few-shot Named Entity Recognition with Self-describing Networks 阅读笔记
Cmu15445 (fall 2019) project 2 - hash table details
Stm32f1 and stm32subeide programming example -max7219 drives 8-bit 7-segment nixie tube (based on SPI)
Flet教程之 17 Card卡片组件 基础入门(教程含源码)
Use references
SwiftUI Swift 内功之如何在 Swift 中进行自动三角函数计算
Neural approvals to conversational AI (1)
The road to success in R & D efficiency of 1000 person Internet companies
[shortest circuit] acwing1128 Messenger: Floyd shortest circuit
超标量处理器设计 姚永斌 第8章 指令发射 摘录
Mise en œuvre du codage Huffman et du décodage avec interface graphique par MATLAB