当前位置:网站首页>Camera calibration (1): basic principles of monocular camera calibration and Zhang Zhengyou calibration
Camera calibration (1): basic principles of monocular camera calibration and Zhang Zhengyou calibration
2022-07-07 11:47:00 【@BangBang】
Why do I need to calibrate the camera
The mathematical meaning of camera :
- The real world is three-dimensional , Taking photos is two-dimensional
- The camera (
As a generalized function): Input 3D scene , The output is a two-dimensional picture ( Gray value ) - The color chart is
RGBThree channels , Each channel can be considered as a gray image function ( The mapping relationship ) It's irreversible, That is to say, we cannot recover the three-dimensional world from two-dimensional photos ( Two dimensional photos have no depth information )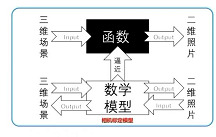
The significance of camera calibration
Camera calibration : Use a pattern Calibration board to solve the process of camera parameters- A simplified mathematical surface model is used to represent the complex three-dimensional to two-dimensional imaging process
- Camera parameters include :
Inside the camera( The focal length )、Camera external parameters( rotate 、 Translation matrix ),Lens distortion parameters purpose : Distortion correction , Binocular vision , Structured light , Three dimensional reconstruction ,SLAM, Camera calibration is required , Only after obtaining the parameters of the camera can it be applied
Coordinate system transformation
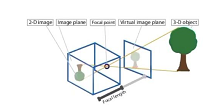
Principle of pinhole imaging
Pinhole imaging instructions
- Simple without lens
- There is a small light source ( candle )
- Real world 3D object , Send light through the aperture ( Pinhole )
- The other side of the camera , Like plane position , Get a real image of handstand
Introduction to coordinate system
Must know terminology :
World coordinate system (World Coords): The position of the point in the real world , Describe the location of the camera , The unit is mCamera coordinate system (Camera Coords):With the camerasensorCenter as origin , Resume camera coordinate system , Company mImage physical coordinate system :The two-dimensional coordinate system obtained after small hole imaging , The unit is mm, The coordinates of new year's day are the points in the graph C C CPixel coordinate system (Pixel Coords): The imaging point is in the camerasensorThe number of rows and columns of the upper pixel , Without any physical unitsPrincipal point: Intersection of optical axis and image plane , The points in the picturep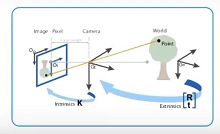
In a binocular or multiocular system , The world coordinate system does not coincide with the camera coordinate system , You need to rotate the world coordinate system through the matrix R Peaceshift matrix T, To the camera coordinate system .
In the above two-dimensional plane , O i O_{i} Oi Is the origin of the image coordinate system , O d O_{d} Od Is the pixel coordinate system , The pixel coordinate system is slightly offset from the origin of the image coordinate system .
(1) World coordinate system to camera coordinate system
spot p Representation in different coordinate systems
- World coordinate system (World Coords): P ( x w , y w , z w ) P(x_{w},y_{w},z_{w}) P(xw,yw,zw)
- Camera coordinate system (World Coords): P ( x c , y c , z c ) P(x_{c},y_{c},z_{c}) P(xc,yc,zc)
The transformation matrix between the world coordinate system and the camera coordinate system :
- R R R: The rotation matrix of the camera coordinate system relative to the world coordinate system
- T T T: The translation matrix of the camera coordinate system relative to the world coordinate system
Mathematical expression of transformation relation :
[ x c y c z c 1 ] = [ R 3 × 3 T 3 × 1 O 1 ] ⋅ [ x w y w z w 1 ] \begin{bmatrix} x_c \\ y_c \\ z_c \\ 1 \\ \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} R_{3\times3} & T_{3\times1} \\ O & 1 \\ \end{bmatrix} \cdot \begin{bmatrix} x_w \\ y_w \\ z_w \\ 1 \\ \end{bmatrix} ⎣⎢⎢⎡xcyczc1⎦⎥⎥⎤=[R3×3OT3×11]⋅⎣⎢⎢⎡xwywzw1⎦⎥⎥⎤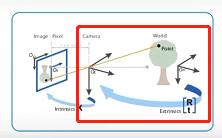
World coordinate system By rotating the matrix R And offset matrix T, Convert to Camera coordinate system , If the world coordinate system coincides with the camera coordinate system , be R It's an identity matrix ,T It's a zero matrix , In this way, the real world point , Convert to a point in the camera coordinate system
(2) Camera coordinate system to image coordinate system
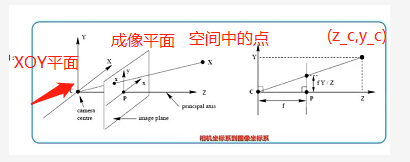
- Suppose the point on the camera p ( x c , y c , z c ) p(x_c,y_c,z_c) p(xc,yc,zc) The imaging point in the image coordinate system is p ′ ( x , y ) p^{'}(x,y) p′(x,y)
- Based on the principle of small hole imaging
- A point in space is imaged in a plane , And X c Y XcY XcY Plane ( The lens ) parallel , From the origin f f f The plane of the
- Take a section Z c Y ZcY ZcY, You can get the right figure , The black dot in the right figure ( z c , y c ) (z_c,y_c) (zc,yc), According to the similar triangle relationship, we can calculate :
y y c = f z c \frac{y}{y_c}=\frac{f}{z_c} ycy=zcf - Take a section X c Y XcY XcY, According to the similar triangle relationship, we can calculate :
x x c = y y c \frac{x}{x_c}=\frac{y}{y_c} xcx=ycy - Combine two triangular transformation relations , Yes :
x x c = y y c = f z c \frac{x}{x_c}=\frac{y}{y_c}=\frac{f}{z_c} xcx=ycy=zcf
After simplification, we can get :
x = f z c ⋅ x c x=\frac{f}{z_c} \cdot x_{c} x=zcf⋅xc
y = f z c ⋅ y c y=\frac{f}{z_c} \cdot y_{c} y=zcf⋅yc
- In matrix form :
z c ⋅ [ x y 1 ] = [ f 0 0 0 0 f 0 0 0 0 1 0 ] ⋅ [ x c y c z c 1 ] z_{c}\cdot \begin{bmatrix} x \\ y \\ 1 \\ \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} f &0&0&0 \\ 0 &f&0&0 \\ 0 &0&1&0 \\ \end{bmatrix} \cdot \begin{bmatrix} x_c \\ y_c \\ z_c \\ 1 \\ \end{bmatrix} zc⋅⎣⎡xy1⎦⎤=⎣⎡f000f0001000⎦⎤⋅⎣⎢⎢⎡xcyczc1⎦⎥⎥⎤
(3) Image coordinate system to pixel coordinate system conversion
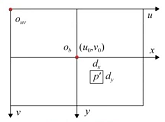
Above picture , Image midpoint O b O_b Ob Represents the origin of the image coordinate system , top left corner O u v O_{uv} Ouv Represents the origin of the pixel coordinate system
Transformation of coordinate system :
- Point of image coordinate system p ′ ( x , y ) p^{'}(x,y) p′(x,y) To the pixel coordinate system ( u , v ) (u,v) (u,v) Transformation
- The origin of the image coordinate system is sensor In the middle of , The unit is mm
- The origin of the pixel coordinate system is sensor Top left corner of , Unit is Pixel, That is, the number of rows and columns of pixels
- The transformation relationship between them :
u = x d x + u 0 , v = y d y + v 0 u=\frac{x}{dx} + u_0 ,v=\frac{y}{dy} + v_0 u=dxx+u0,v=dyy+v0 - In matrix form :
[ u v 1 ] = [ 1 d x 0 u 0 0 1 d y v 0 0 0 1 ] ⋅ [ x y 1 ] \begin{bmatrix} u \\ v \\ 1 \\ \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} \frac{1}{dx} &0&u_0 \\ 0 &\frac{1}{dy}&v_0 \\ 0 &0&1 \\ \end{bmatrix} \cdot \begin{bmatrix} x \\ y \\ 1 \\ \end{bmatrix} ⎣⎡uv1⎦⎤=⎣⎡dx1000dy10u0v01⎦⎤⋅⎣⎡xy1⎦⎤- d x d_x dx, d y d_y dy: yes sensor Gu you parameter , Represents the number of millimeters per pixel
- u 0 u_0 u0, v 0 v_0 v0: Represents the origin of the image coordinate system ( Light heart ) The offset from the origin of the pixel coordinate system
Sum up : Conversion formula from camera coordinate system to pixels :
[ u v 1 ] = [ 1 d x 0 u 0 0 1 d y v 0 0 0 1 ] ⋅ 1 z c ⋅ [ f 0 0 0 0 f 0 0 0 0 1 0 ] ⋅ [ x c y c z c 1 ] \begin{bmatrix} u \\ v \\ 1 \\ \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} \frac{1}{dx} &0&u_0 \\ 0 &\frac{1}{dy}&v_0 \\ 0 &0&1 \\ \end{bmatrix} \cdot \frac{1}{z_c} \cdot \begin{bmatrix} f &0&0&0 \\ 0 &f&0&0 \\ 0 &0&1&0 \\ \end{bmatrix} \cdot \begin{bmatrix} x_c \\ y_c \\ z_c \\ 1 \\ \end{bmatrix} ⎣⎡uv1⎦⎤=⎣⎡dx1000dy10u0v01⎦⎤⋅zc1⋅⎣⎡f000f0001000⎦⎤⋅⎣⎢⎢⎡xcyczc1⎦⎥⎥⎤
You can get :
u = f x ∗ x c z c + u 0 u=f_x * \frac{x_c}{z_c}+ u_0 u=fx∗zcxc+u0
v = f y ∗ y c z c + v 0 v=f_y * \frac{y_c}{z_c}+ v_0 v=fy∗zcyc+v0
- In the above formula : f x = f d x f_x=\frac{f}{dx} fx=dxf, f y = f d y f_y=\frac{f}{dy} fy=dyf, Focal length divided by the size of a single pixel
- During camera calibration , f , d x , d y f,dx,dy f,dx,dy Cannot be calibrated , f x , f y f_x,f_y fx,fy It can be obtained by calibration
(4) Complete coordinate system conversion
Conversion from world coordinate system to pixel coordinate system
[ u v 1 ] = [ 1 d x 0 u 0 0 1 d y v 0 0 0 1 ] ⋅ [ x y 1 ] \begin{bmatrix} u \\ v \\ 1 \\ \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} \frac{1}{dx} &0&u_0 \\ 0 &\frac{1}{dy}&v_0 \\ 0 &0&1 \\ \end{bmatrix} \cdot \begin{bmatrix} x \\ y \\ 1 \\ \end{bmatrix} ⎣⎡uv1⎦⎤=⎣⎡dx1000dy10u0v01⎦⎤⋅⎣⎡xy1⎦⎤- d x d_x dx, d y d_y dy: yes sensor Gu you parameter , Represents the number of millimeters per pixel
- u 0 u_0 u0, v 0 v_0 v0: Represents the origin of the image coordinate system ( Light heart ) The offset from the origin of the pixel coordinate system
Sum up : Conversion formula from camera coordinate system to pixels :
z c ⋅ [ u v 1 ] = [ 1 d x 0 u 0 0 1 d y v 0 0 0 1 ] ⋅ [ f 0 0 0 0 f 0 0 0 0 1 0 ] ⋅ [ R 3 × 3 T 3 × 1 O 1 ] ⋅ [ x w y w z w 1 ] = M 1 M 2 [ x w y w z w 1 ] z_c\cdot\begin{bmatrix} u \\ v \\ 1 \\ \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} \frac{1}{dx} &0&u_0 \\ 0 &\frac{1}{dy}&v_0 \\ 0 &0&1 \\ \end{bmatrix} \cdot \begin{bmatrix} f &0&0&0 \\ 0 &f&0&0 \\ 0 &0&1&0 \\ \end{bmatrix} \cdot \begin{bmatrix} R_{3\times3} & T_{3\times1} \\ O & 1 \\ \end{bmatrix} \cdot \begin{bmatrix} x_w \\ y_w \\ z_w \\ 1 \\ \end{bmatrix} = M_1M_2 \begin{bmatrix} x_w \\ y_w \\ z_w \\ 1 \\ \end{bmatrix} zc⋅⎣⎡uv1⎦⎤=⎣⎡dx1000dy10u0v01⎦⎤⋅⎣⎡f000f0001000⎦⎤⋅[R3×3OT3×11]⋅⎣⎢⎢⎡xwywzw1⎦⎥⎥⎤=M1M2⎣⎢⎢⎡xwywzw1⎦⎥⎥⎤
- Inside the camera : The focal length of the camera , Relative offset of pixel coordinates
M 1 = [ f x 0 u 0 0 f y v 0 0 0 1 ] M_1= \begin{bmatrix} f_x &0&u_0 \\ 0 &f_y&v_0 \\ 0 &0&1 \\ \end{bmatrix} M1=⎣⎡fx000fy0u0v01⎦⎤ - Camera external parameters : The conversion relationship between the world coordinate system and the camera coordinate system , The pose matrix of the camera in the world coordinate system
M 2 = [ R 3 × 3 T 3 × 1 ] = [ r 11 r 12 r 13 t 1 r 21 r 22 r 23 t 2 r 31 r 32 r 33 t 3 ] M_2=\begin{bmatrix} R_{3\times3} & T_{3\times1} \\ \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} r_{11}&r_{12}&r_{13}&t_{1} \\ r_{21}&r_{22}&r_{23}&t_{2} \\ r_{31}&r_{32}&r_{33}&t_{3} \\ \end{bmatrix} M2=[R3×3T3×1]=⎣⎡r11r21r31r12r22r32r13r23r33t1t2t3⎦⎤
Lens distortion
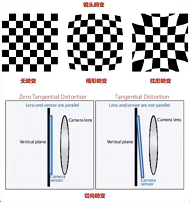
Lens distortion
Ultra wide angle shooting distortion will be more obvious , The more to the edge, the more obvious the distortion
- The error between the actual imaging and the ideal imaging after passing through the lens is the lens distortion
- It is mainly divided into meridional distortion and tangential distortion
Radial distortion - The additive lens shape results in , Along the radial distribution of the lens
- It is divided into barrel distortion and pillow distortion
- The place away from the center of the lens is more curved than the place near the center of the lens
- The distortion at the optical center is 0, The farther away from the optical center, the greater the distortion
- Cheap cameras , Abnormal changes are serious
- Mathematical polynomial description of radial distortion
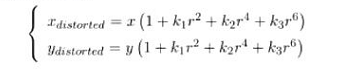
- (x,y) It is a pixel without distortion , ( x d i s t o r t e d , y d i s t o r t e d ) (x_{distorted},y_{distorted}) (xdistorted,ydistorted) Position after distortion
- k 1 , k 2 , k 3 k_1,k_2,k_3 k1,k2,k3: Radial distortion coefficient , The internal reference of the camera , Generally, the first two items are used , Fisheye camera will use the third item
Tangential distortion
- The camera sensor Not parallel to the lens , If the camera is better, there is generally no tangential distortion . Therefore, the influence of radial distortion is generally studied .
- Mathematical representation of distortion :
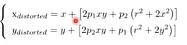
- The two distortions merge :
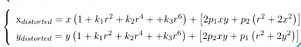
边栏推荐
- R Language Using Image of magick package Mosaic Function and Image La fonction flatten empile plusieurs images ensemble pour former des couches empilées sur chaque autre
- 博客搬家到知乎
- Enclosed please find. Net Maui's latest learning resources
- Distributed database master-slave configuration (MySQL)
- STM32 entry development write DS18B20 temperature sensor driver (read ambient temperature, support cascade)
- How to write test cases for test coupons?
- In my limited software testing experience, a full-time summary of automation testing experience
- 使用MeterSphere让你的测试工作持续高效
- 核舟记(一):当“男妈妈”走进现实,生物科技革命能解放女性吗?
- 【最短路】ACwing 1127. 香甜的黄油(堆优化的dijsktra或spfa)
猜你喜欢
Electron adding SQLite database

Half of the people don't know the difference between for and foreach???
SwiftUI 教程之如何在 2 秒内实现自动滚动功能
Distributed database master-slave configuration (MySQL)

electron添加SQLite数据库

Tsinghua Yaoban programmers, online marriage was scolded?
千人規模互聯網公司研發效能成功之路
【滤波跟踪】基于matlab扩展卡尔曼滤波EKF和无迹卡尔曼滤波UKF比较【含Matlab源码 1933期】

科普达人丨一文弄懂什么是云计算?
STM32F1与STM32CubeIDE编程实例-315M超再生无线遥控模块驱动
随机推荐
Software design - "high cohesion and low coupling"
【滤波跟踪】基于matlab捷联惯导仿真【含Matlab源码 1935期】
相机标定(2): 单目相机标定总结
There are ways to improve self-discipline and self-control
STM32 entry development NEC infrared protocol decoding (ultra low cost wireless transmission scheme)
Creative information was surveyed by 2 institutions: greatdb database has been deployed in 9 places
一起探索云服务之云数据库
Zhou Yajin, a top safety scholar of Zhejiang University, is a curiosity driven activist
Apprentissage comparatif non supervisé des caractéristiques visuelles par les assignations de groupes de contrôle
Common SQL statement collation: MySQL
In my limited software testing experience, a full-time summary of automation testing experience
[question] Compilation Principle
Electron adding SQLite database
The running kubernetes cluster wants to adjust the network segment address of pod
请查收.NET MAUI 的最新学习资源
Have you ever met flick Oracle CDC, read a table without update operation, and read it repeatedly every ten seconds
There are so many factors that imprison you
OneDNS助力高校行业网络安全
Some opinions and code implementation of Siou loss: more powerful learning for bounding box regression zhora gevorgyan
Verilog design responder [with source code]