当前位置:网站首页>High frequency interview questions
High frequency interview questions
2022-07-02 19:05:00 【weixin_ forty-three million seven hundred and sixty-six thousan】
High frequency interview questions
- 1. ArrayList Capacity expansion mechanism of
- 2. Why? HashMap The loading factor is 0.75?
- 3. JDK1.7 HashMap Existing problems and 1.8 The optimization of the ?
- 4. mysql The underlying data structure of the index ?
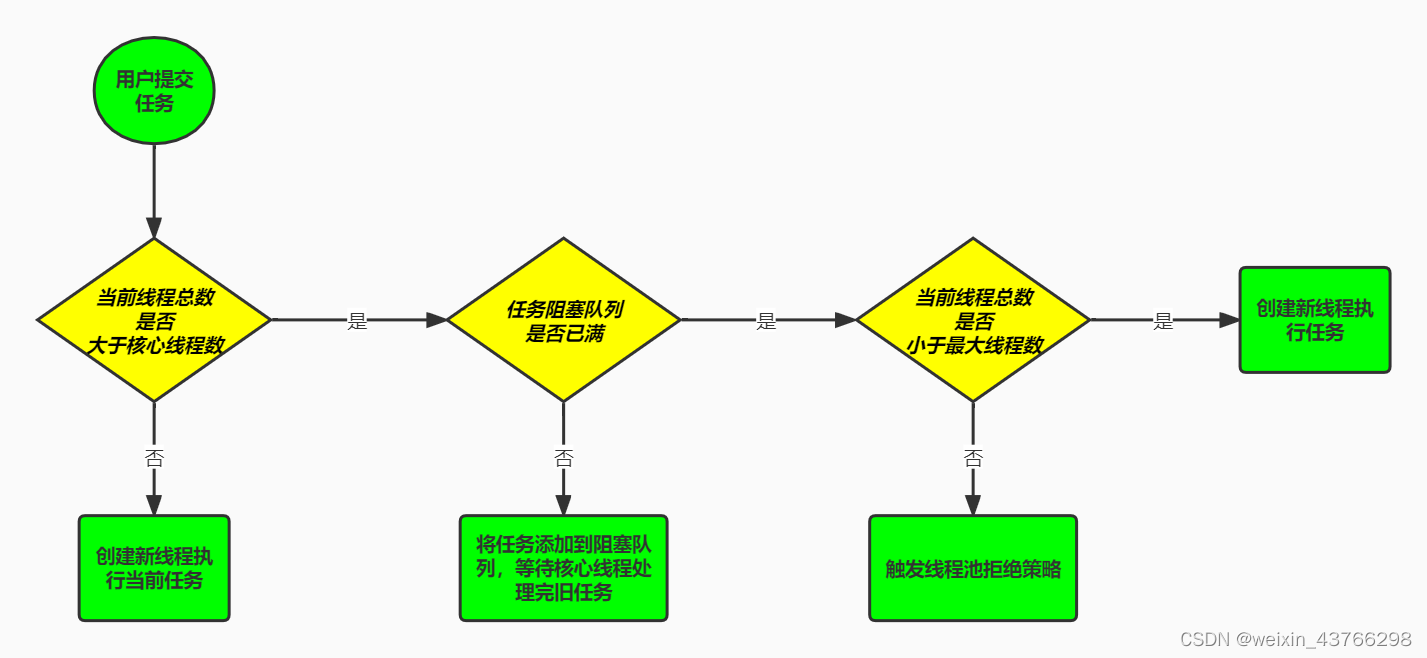
- 5. Thread pool principle ?
- 6. Spring Bean Life cycle of ?
- 7. spring Of bean Is it thread safe ?
- 8. How to understand java Polymorphism, one of the three characteristics of object-oriented ?
- 9. synchronized What is the underlying principle of keywords ?
- 10. java Of Lock What is the underlying principle of locks ?
1. ArrayList Capacity expansion mechanism of
- ArrayList The default initialization capacity is 10, The bottom layer is to use a Objcet[] To store elements , towards ArrayList When you add elements , First, let Size( The number of elements contained in the set )+1, If Size+1 Larger than the bottom layer Object[] If the length is, the expansion will be triggered ( The capacity of the new array is larger than that of the old array 1.5 times , If the new capacity is greater than Integer.MAX_VALUE-8, Let the new capacity point to Integer.MAX_VALUE), Last call Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity) Based on the old array, copy a new array with the length of new capacity as ArrayList The underlying array of .
// Default initialization capacity
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10;
// Adding elements may trigger capacity expansion , Low efficiency
public boolean add(E e) {
// Let Size+1 Then check whether the capacity of the underlying array is available , meanwhile modCount++
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1);
elementData[size++] = e;// After passing the inspection , Then add elements to the array
return true;
}
private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) {
ensureExplicitCapacity(calculateCapacity(elementData, minCapacity));
}
private static int calculateCapacity(Object[] elementData, int minCapacity) {
if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) {
return Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity);
}
return minCapacity;
}
private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) {
modCount++;// The number of times the set is modified plus 1
if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)
grow(minCapacity);// If the given capacity is greater than the capacity of the underlying array , Just expand
}
// Expansion method
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
// Take the old array capacity first
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
// Expand the capacity by% on the basis of the old capacity 50, Get new capacity
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
// If the calculated new capacity is less than the given capacity, let the new capacity point to the given capacity
newCapacity = minCapacity;
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
// If the new capacity is greater than Integer.MAX_VALUE-8, Let the new capacity point to Integer.MAX_VALUE
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
2. Why? HashMap The loading factor is 0.75?
The function of loading factor is to judge map Is it necessary to expand capacity , Capacity expansion is a time-consuming operation .
- If the loading factor is too small , such as loadFactor=0.5f, Initial capacity =16 Under the circumstances , Then the element exceeds 16*0.5=8 One will be expanded to 32, Suppose you add a 9 Elements succeeded , Then there will be 23 Array positions are free , The space utilization rate is about 9/23=39%, Therefore, frequent capacity expansion is not only time-consuming but also a waste of space .
- If the loading factor is too large , such as loadFactor=1.0f, Initial capacity =16 Under the circumstances , Then the element exceeds 16 Will trigger capacity expansion , Although the space utilization rate is large , But there will definitely be more conflicts among the elements in the bucket , More and more elements will affect map Query time efficiency .
- summary :loadFactor=0.75f It's a trade-off between the cost of space and time (1+0.5)/ 2 = 0.75
3. JDK1.7 HashMap Existing problems and 1.8 The optimization of the ?
1.7 There is a problem : HashMap As the amount of data increases, the length of the linked list on the hash table will be too long , This leads to lower query efficiency .
1.8 Optimization problem one : The list length is greater than 8 It will be transformed into red and black trees , So as to improve the query efficiency , If the length of the linked list is less than 6 It will change back to the linked list .
// When the length of the data linked list at a single location exceeds 8 The linked list will be converted into a red black tree
static final int TREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 8;
// When the content length of the red black tree in the current position is less than 6 It will change back to the linked list again
static final int UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 6;
// When the linked list of a certain position is converted into a red black tree , If the array length is less than 64 We will expand the capacity first
static final int MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY = 64;
- 1.7 There are two problems : Multithreading , The use of head interpolation in capacity expansion leads to the problem of circular linked list .
The reason for using head insertion : Because HashMap The writers of think that the newly added data is more commonly used , The newly added elements will be easier to find if they are placed in front . - 1.8 Optimization problem two : Adopted The tail interpolation Prevent the generation of circular linked list , The node order will not be reversed after capacity expansion , There is no dead cycle problem .
- 1.7 Single thread Expand the normal transfer node
oldTable : table[0] a -> b -> c
newTable: table[0] c -> b -> a
Entry<K,V> e
Entry<K,V> next
e = a e = b e = c
next -> b next - > c next -> null
a.next = null b.next = a c.next = b
newTable[0] = a newTable[0] = b newTable[0] = c
Linked list results : a -> null b -> a -> null c -> b -> a -> null
- 1.7 Multithreading Abnormal capacity expansion leads to circular linked list
// jdk 1.7 Node transfer method during capacity expansion
void transfer(Entry[] newTable) {
Entry[] src = table;
int newCapacity = newTable.length;
for (int j = 0; j < src.length; j++) {
Entry<K,V> e = src[j];
if (e != null) {
// B1: Both threads enter first if
src[j] = null;
do {
Entry<K,V> next = e.next;
int i = indexFor(e.hash, newCapacity);// set up a b c All on the same bucket
e.next = newTable[i]; // B2: Threads 1 Stop
newTable[i] = e;
e = next;
} while (e != null);
}
}
}
existing : Threads 1 + Threads 2 Concurrent execution
Prerequisite : The linked list elements in the original bucket are Fall in the On the same bucket of the new hash table
hypothesis 2 All threads have added elements , Both trigger the capacity expansion mechanism , Then they all built their own Entry[] newTable
1. Both threads enter B1, It's all in if Code block .
2. The thread 2 To give up CPU Executive power , Threads 1 Carry on
3. Threads 1 Execute to B2( unexecuted ), Threads 1 suspended
4. The thread 1: e->a 、next->b
5. Threads 2 Get it again CPU Executive power , Build a linked list node of the new hash table newTable[0]
6. Threads 2 newTable2[0] -> b -> a After this step, the execution right is lost again
7. Threads 1 Grab CPU Executive power , Carry on B2 Step code
a.next=null; newTable1[0]=a; e=b;
Cycle again : Entry<K,V> next = b.next; // namely next Yes a
b.next = a;
newTable1[0] = b;
e = a;
Cycle again : a.next = newTable1[0] namely a.next = b
This circular linked list is formed :b -> a -> b
4. mysql The underlying data structure of the index ?
Data structure simulation insertion
- B+ Trees stay B Trees On the basis of , Chain pointers are added to all leaf nodes , All leaf nodes form an orderly linked list from small to large , It greatly accelerates the efficiency of interval search , At the same time, non leaf nodes do not store data Index only , All leaf nodes store complete data row information .
- B Tree, no matter it is Leaf node still Nonleaf node It's all stored data, To query the range, you need to recursively traverse , therefore B The efficiency of tree interval search is relatively low .
5. Thread pool principle ?
6. Spring Bean Life cycle of ?

- 1.Spring start-up , To find and load the Spring Managed bean, Conduct Bean Instantiation .
- 2.Bean After instantiation, the Bean References and values are injected into Bean Properties of .
- 3. If Bean Realized BeanNameAware Interface ,Spring take Bean Of Id Pass to setBeanName() Method .
- 4. If Bean Realized BeanFactoryAware Interface ,Spring Will call setBeanFactory() Method , take BeanFactory Container instance incoming .
- 5. If Bean Realized ApplicationContextAware Interface ,Spring Will call Bean Of setApplicationContext() Method , take bean Incoming application context reference .
- 6. If Bean Realized BeanPostProcessor Interface ,Spring Will call their postProcessBeforeInitialization() Method .
- 7. If Bean Realized InitializingBean Interface ,Spring Will call their afterPropertiesSet() Method . Allied , If bean Use init-method Declared initialization method , This method will also be called .
- 8. If Bean Realized BeanPostProcessor Interface ,Spring Will call their postProcessAfterInitialization() Method .
- 9. here Bean Ready , Can be used by the application . They will always reside in the context of the application , Until the application context is destroyed .
- 10. If bean Realized DisposableBean Interface ,Spring Will call its destory() Interface method , Again , If bean Used destory-method Declaration of destruction method , This method will also be called .
7. spring Of bean Is it thread safe ?
stay spring in , It didn't provide Bean Thread security strategy of , therefore spring In container bean Not thread safe .
consider Spring Bean Thread safety or not should be combined Bean Of Scope Scope to analyze , The common scope is singleton and prototype.
prototype( Multiple cases bean): about prototype In scope bean, Because every time getBean When , Will create a new object , There is no... Between threads Bean Sharing issues , therefore prototype In scope bean There is no thread safety issue .
singleton( Single case bean)( Default scope ): about singleton scoped bean, All threads share a singleton instance bean, So there is a thread safety problem , But if it's a single case bean Is a stateless bean, That is, in multithreaded operation, there will be no bean Member variables for operations other than query ( There is no scenario where multiple threads write this member variable at the same time ), So this single example bean It's thread safe .
- Stateful bean: It's an object with instance variables , Can save data , It's not thread safe .
- Stateless bean: Objects without instance variables , Can't save data , It's thread safe .
Solution :
- 1. The simplest solution is to have stateful bean The scope of is defined by singleton Change it to prototype.
- 2. Define a... In the class ThreadLocal Member variables of , Save the member variables that need to be variable in ThreadLocal in , use ThreadLocal Solving thread safety problems , Provide an independent copy of the variable for each thread , Different threads only operate on copy variables on their own threads ( recommend ).
8. How to understand java Polymorphism, one of the three characteristics of object-oriented ?
- Interface oriented programming , Easy to expand , Method input and parameter use interfaces to improve the compatibility of methods .
9. synchronized What is the underlying principle of keywords ?
- synchronized Underlying principle
- monitor, It's built into every object , Every object has a monitor Associated with it ,synchronized stay JVM The implementation in is based on entry and exit monitor To achieve , The bottom is through pairs of MonitorEnter and MonitorExit Instructions to implement , So every one Java The object has become Monitor The potential to . So we can understand monitor It's a synchronization tool .
- monitorenter, If at present monitor The number of entries is 0 when , The thread will enter monitor, And the number of entries +1, So the thread is monitor The owner of the (owner).
- If the thread is already monitor The owner of the , Back in , It's going to take the entry number again +1. It's reentrant .
- monitorexit, perform monitorexit The thread of must be monitor The owner of the , After the command is executed ,monitor The number of entries minus 1, If less 1 The last in number is 0, The thread exits monitor. Other blocked threads can try to get monitor The ownership of the .
- Use javap -v Absolute path \Test.class Decompile Test.class by jvm Instructions .
public class Test {
static long count = 0;
public static final Object LOCK = new Object();
public void lock(){
synchronized (LOCK){
count++;
System.out.println("count = " + count);
}
}
}
public void lock();
descriptor: ()V
flags: ACC_PUBLIC
Code:
stack=4, locals=3, args_size=1
0: getstatic #2 // Field LOCK:Ljava/lang/Object;
3: dup
4: astore_1
5: monitorenter
6: getstatic #3 // Field count:J
9: lconst_1
10: ladd
11: putstatic #3 // Field count:J
14: getstatic #4 // Field java/lang/System.out:Ljava/io/PrintStream;
17: new #5 // class java/lang/StringBuilder
20: dup
21: invokespecial #6 // Method java/lang/StringBuilder."<init>":()V
24: ldc #7 // String count =
26: invokevirtual #8 // Method java/lang/StringBuilder.append:(Ljava/lang/
String;)Ljava/lang/StringBuilder;
29: getstatic #3 // Field count:J
32: invokevirtual #9 // Method java/lang/StringBuilder.append:(J)Ljava/lan
g/StringBuilder;
35: invokevirtual #10 // Method java/lang/StringBuilder.toString:()Ljava/la
ng/String;
38: invokevirtual #11 // Method java/io/PrintStream.println:(Ljava/lang/Str
ing;)V
41: aload_1
42: monitorexit
43: goto 51
46: astore_2
47: aload_1
48: monitorexit
49: aload_2
50: athrow
51: return
- monitorexit The command appears twice , The first 1 The second is synchronous normal exit release lock ; The first 2 The second is to exit the release lock in case of an exception ;
- synchronized Lock optimization
- JDK1.5 Before ,synchronized It's a heavyweight lock , Heavyweights need to depend on the underlying operating system Mutex Lock Realization , Then the operating system needs to switch between user mode and kernel mode , This kind of switching costs a lot , So the performance is relatively poor .
- JDK1.6 after , Began to synchronized To optimize , Added adaptive CAS The spin 、 Lock elimination 、 Lock coarsening 、 Biased locking 、 Lightweight lock these optimization strategies . The level of lock is from no lock , Biased locking , Lightweight lock , Heavyweight locks are gradually upgraded , And it's one-way , There will be no lock degradation .
10. java Of Lock What is the underlying principle of locks ?
- CAS + AQS
边栏推荐
- Obligatoire pour les débutants, cliquez sur deux boutons pour passer à un contenu différent
- 鸿蒙第四次学习
- [100 cases of JVM tuning practice] 03 -- four cases of JVM heap tuning
- Page title component
- 性能测试如何创造业务价值
- Gstore weekly gstore source code analysis (4): black and white list configuration analysis of security mechanism
- Crypto usage in nodejs
- Tips for material UV masking
- 学生抖音宣传母校被吐槽“招生减章”,网友:哈哈哈哈哈哈
- Use MNIST in tensorflow 2_ 784 data set for handwritten digit recognition
猜你喜欢
Google's official response: we have not given up tensorflow and will develop side by side with Jax in the future
How to copy and paste interlaced in Excel
论文导读 | 关于将预训练语言模型作为知识库的分析与批评

开源物联网平台ThingsBoard的安装
Redis (7) -- database and expiration key
Learning summary of MySQL advanced 6: concept and understanding of index, detailed explanation of b+ tree generation process, comparison between MyISAM and InnoDB

聊聊电商系统中红包活动设计
LightGroupButton* sender = static_ cast<LightGroupButton*>(QObject::sender());
SLC、MLC、TLC 和 QLC NAND SSD 之间的区别:哪个更好?

学生抖音宣传母校被吐槽“招生减章”,网友:哈哈哈哈哈哈
随机推荐
【JVM调优实战100例】01——JVM的介绍与程序计数器
Introduction to the paper | application of machine learning in database cardinality estimation
R语言使用epiDisplay包的cox.display函数获取cox回归模型汇总统计信息(风险率HR、调整风险率及其置信区间、模型系数的t检验的p值、Wald检验的p值和似然比检验的p值)、汇总统计
How can retail enterprises open the second growth curve under the full link digital transformation
Page title component
[论文阅读] CA-Net: Leveraging Contextual Features for Lung Cancer Prediction
The difference between promise and observable
27: Chapter 3: develop Passport Service: 10: [registration / login] interface: after the registration / login is OK, save the user session information (uid, utoken) to redis and cookies; (one main poi
How to write controller layer code gracefully?
R语言使用epiDisplay包的lsNoFunction函数列出当前空间中的所有对象、除了用户自定义的函数对象
The R language dplyr package rowwise function and mutate function calculate the maximum value of multiple data columns in each row in the dataframe data, and generate the data column (row maximum) cor
Three ways of function parameter transfer in C language
sql训练2
Obligatoire pour les débutants, cliquez sur deux boutons pour passer à un contenu différent
Novice must see, click two buttons to switch to different content
LightGroupButton* sender = static_ cast<LightGroupButton*>(QObject::sender());
思维意识转变是施工企业数字化转型成败的关键
MySQL advanced learning summary 7: MySQL data structure - Comparison of hash index, AVL tree, B tree and b+ tree
新手必看,點擊兩個按鈕切換至不同的內容
Crypto usage in nodejs