当前位置:网站首页>[point cloud processing paper crazy reading frontier version 10] - mvtn: multi view transformation network for 3D shape recognition
[point cloud processing paper crazy reading frontier version 10] - mvtn: multi view transformation network for 3D shape recognition
2022-07-03 09:09:00 【LingbinBu】
MVTN: Multi-View Transformation Network for 3D Shape Recognition
Abstract
- problem : Among many point cloud processing methods ,Multi-view projection The perspective of methods is often set heuristically or the same for all shapes .
- Method : Put forward a method , Learn how to better set these perspectives .
- details : Introduced Multi-View Transformation Network (MVTN), Used to find for 3D The best angle of view for shape recognition , The design of the whole network is derivable .MVTN It can be trained end-to-end , And use it with any multi perspective network for 3D Shape recognition . This article will MVTN Integrate with a new adaptive multi perspective network , The network can not only handle 3D mesh, You can also handle point clouds .
- Code :https://github.com/ajhamdi/MVTN Pytorch edition

Related work
- MVTN Learn the spatial transformation of input data , No extra supervision is used in the learning process , Nor adjust the learning process .
Method
Overview of Multi-View 3D Recognition
The training of multi view network can be expressed as :
arg min θ C ∑ n N L ( C ( X n ) , y n ) = arg min θ C ∑ n N L ( C ( R ( S n , u 0 ) ) , y n ) \begin{aligned} & \underset{\boldsymbol{\theta}_{\mathbf{C}}}{\arg \min } \sum_{n}^{N} L\left(\mathbf{C}\left(\mathbf{X}_{n}\right), y_{n}\right) \\ =& \underset{\boldsymbol{\theta}_{\mathbf{C}}}{\arg \min } \sum_{n}^{N} L\left(\mathbf{C}\left(\mathbf{R}\left(\mathbf{S}_{n}, \mathbf{u}_{0}\right)\right), y_{n}\right) \end{aligned} =θCargminn∑NL(C(Xn),yn)θCargminn∑NL(C(R(Sn,u0)),yn)
among L L L Is the loss function of a specific task , N N N It's a dataset 3D Number of shapes , y n y_{n} yn It's No n n n individual 3D shape S n \mathbf{S}_{n} Sn Of label. u 0 ∈ R τ \mathbf{u}_{0} \in \mathbb{R}^{\tau} u0∈Rτ Of the entire dataset τ \tau τ Set of scene parameters , These parameters represent the properties that affect the rendered image , Including viewpoint 、 The light 、 Color and background . R \mathbf{R} R It's the renderer , In shape S n \mathbf{S}_{n} Sn And parameters u 0 \mathbf{u}_{0} u0 As input , Get each shape M M M Multiple view images X n \mathbf{X}_{n} Xn. stay MVCNN in , C = MLP ( max i f ( x i ) ) \mathbf{C}=\operatorname{MLP}\left(\max _{i} \mathbf{f}\left(\mathbf{x}_{i}\right)\right) C=MLP(maxif(xi)), f : R h × w × c → R d \mathbf{f}: \mathbb{R}^{h \times w \times c} \rightarrow \mathbb{R}^{d} f:Rh×w×c→Rd It's a 2D CNN backbone; stay ViewGCN in , C = MLP ( c a t G C N ( f ( x i ) ) ) \mathbf{C}=\operatorname{MLP}\left(\right. cat \left._{\mathrm{GCN}}\left(\mathbf{f}\left(\mathbf{x}_{i}\right)\right)\right) C=MLP(catGCN(f(xi))), c a t G C N cat _{\mathrm{GCN}} catGCN It is the aggregation of view features learned from graph convolution network . θ C \boldsymbol{\theta}_{\mathbf{C}} θC It's a multi view network C \mathbf{C} C Parameters of . In the experimental part , Scene parameters u \mathbf{u} u Expressed as the camera angle pointing to the center of the target azimuth (azimuth) Elevation angle (elevation) angles, therefore τ = 2 M \tau=2M τ=2M

Multi-View Transformation Network (MVTN)
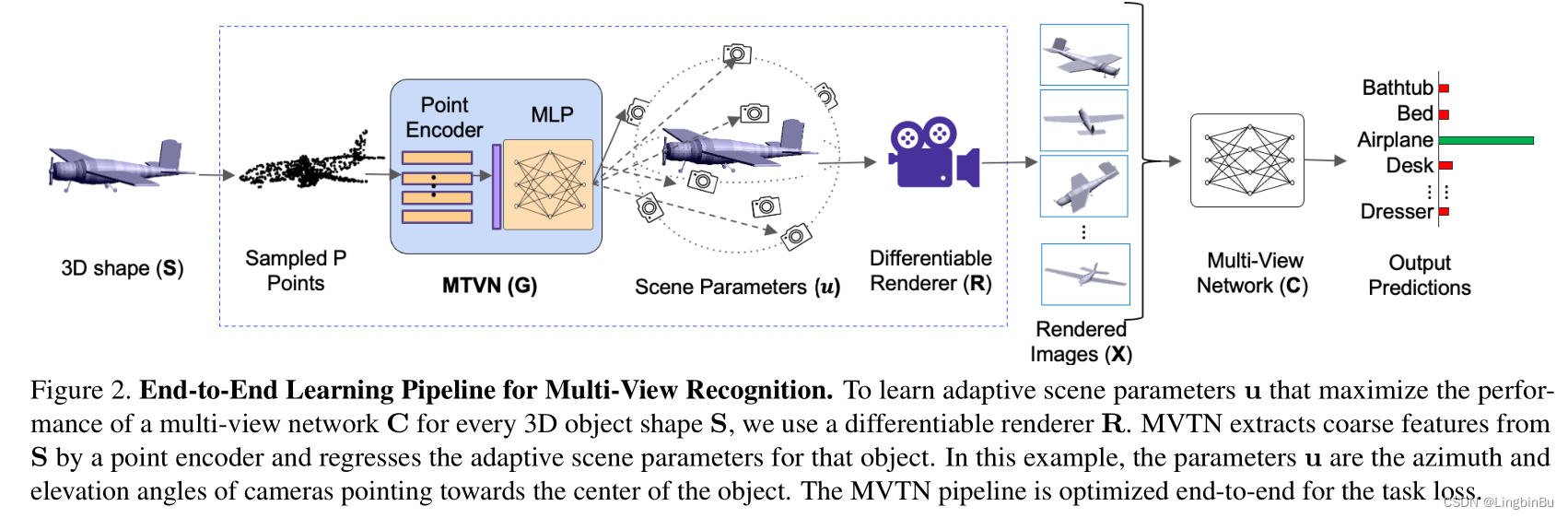
Previous multi view methods are based on images X \mathbf{X} X As 3D Unique representation of shape , among X \mathbf{X} X Is to use fixed scene parameters u 0 \mathbf{u}_0 u0 Got . contrary , This paper considers a more general case , take u \mathbf{u} u Set the boundary to ± u bound \pm \mathbf{u}_{\text {bound }} ±ubound Variables in , among u bound \mathbf{u}_{\text {bound }} ubound Positive number , The allowable range of scene parameters is defined . Put the... Of each azimuth and elevation u bound \mathbf{u}_{\text {bound }} ubound Set as 18 0 ∘ 180^{\circ} 180∘ and 9 0 ∘ 90^{\circ} 90∘.
Differentiable Renderer
Renderers R \mathbf{R} R With 3D shape S \mathbf{S} S(mesh or point cloud) And scene parameters u \mathbf{u} u As input , The output is corresponding to M M M Images { x i } i = 1 M \left\{\mathbf{x}_{i}\right\}_{i=1}^{M} { xi}i=1M. because R \mathbf{R} R Derivable , gradient ∂ x i ∂ u \frac{\partial \mathbf{x}_{i}}{\partial \mathbf{u}} ∂u∂xi It can be back propagated from each image to the whole scene parameters , Therefore, we can construct an end-to-end learning framework .
When S \mathbf{S} S Expressed as 3D mesh when , R \mathbf{R} R There are two components :rasterizer and shader. First , At a given camera angle of view and will face After assigning to pixels ,rasterizer take mesh Transform from the world coordinate system to the view coordinate system . then shader according to face The assignment of creates multiple values for each pixel , And fuse these values .
When S \mathbf{S} S When expressed as point cloud , R \mathbf{R} R have access to alpha-blending mechanism.
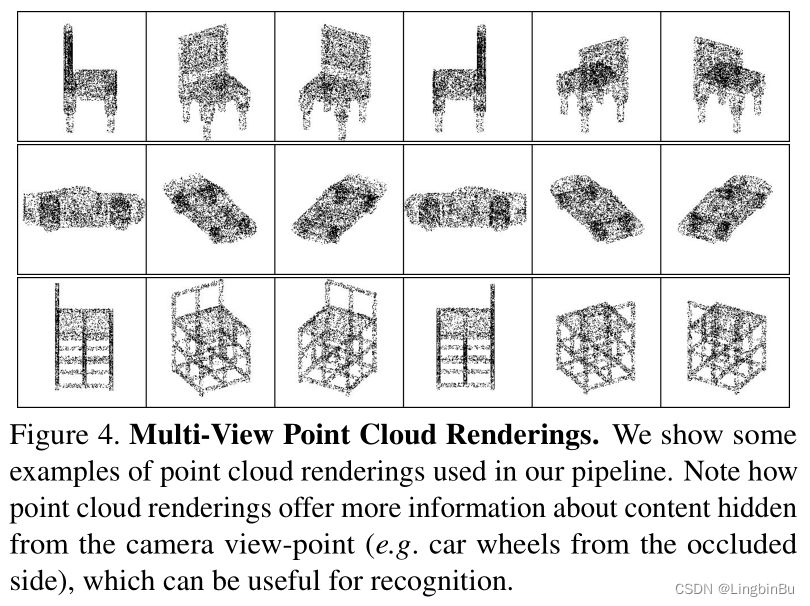
View-Points Conditioned on 3D Shape
Through the study Multi-View Transformation Network (MVTN) G ∈ R P × 3 → R τ \mathbf{G} \in \mathbb{R}^{P \times 3} \rightarrow \mathbb{R}^{\tau} G∈RP×3→Rτ And parameters θ G \boldsymbol{\theta}_{\mathbf{G}} θG, take u \mathbf{u} u Designed to 3D A function of shape , among P P P From the shape S \mathbf{S} S Number of sampling points .MVTN The training of can be expressed as :
arg min θ C , θ G ∑ n N L ( C ( R ( S n , u n ) ) , y n ) s. t. u n = u bound ⋅ tanh ( G ( S n ) ) \begin{aligned} \underset{\boldsymbol{\theta}_{\mathbf{C}}, \boldsymbol{\theta}_{\mathrm{G}}}{\arg \min } & \sum_{n}^{N} L\left(\mathbf{C}\left(\mathbf{R}\left(\mathbf{S}_{n}, \mathbf{u}_{n}\right)\right), y_{n}\right) \text { s. t. } \quad \mathbf{u}_{n}=\mathbf{u}_{\text {bound }} \cdot \tanh \left(\mathbf{G}\left(\mathbf{S}_{n}\right)\right) \end{aligned} θC,θGargminn∑NL(C(R(Sn,un)),yn) s. t. un=ubound ⋅tanh(G(Sn))
among G \mathbf{G} G Yes 3D Shape coding , Predict task specific multiview Networks C \mathbf{C} C Optimal viewpoint of . because G \mathbf{G} G The goal of is only to predict the viewpoint, so G \mathbf{G} G Its structure is very simple , And very light . meanwhile , stay G \mathbf{G} G A simple point encoder is also used in ( such as PointNet Medium shared MLP), Used to process from S \mathbf{S} S Got P P P A little bit , And the generated dimension is b b b Of coarse Shape features . then shallow MLP From this global shape feature, the scene parameters are regressed u n \mathbf{u}_n un, In order to predict parameters u \mathbf{u} u The value of is forced into ± u bound \pm \mathbf{u}_{\text {bound }} ±ubound Within the scope of , Used tanh Function will u \mathbf{u} u Zoom to ± u bound \pm \mathbf{u}_{\text {bound }} ±ubound Inside .
MVTN for 3D Shape Classification
In order to MVTN Training , be used for 3D Shape classification , We define a cross entropy loss function , But other loss functions and regular terms can also be used . Multi perspective network ( C \mathbf{C} C) and MVTN( G \mathbf{G} G) Use the same loss function to train together . The advantage of our network structure is that it can handle 3D Point cloud . When S \mathbf{S} S When it is a group of point clouds , Simply put R \mathbf{R} R Defined as a steerable place cloud renderer .
MVTN for 3D Shape Retrieval
We consider the C \mathbf{C} C The feature representation of the last layer in front of the classifier , Use LFDA reduction Project these features to other spaces , And take the processed features as signature Describe a shape . In the test phase , shape signature It is used to retrieve the most similar shape in the test set .
experiment
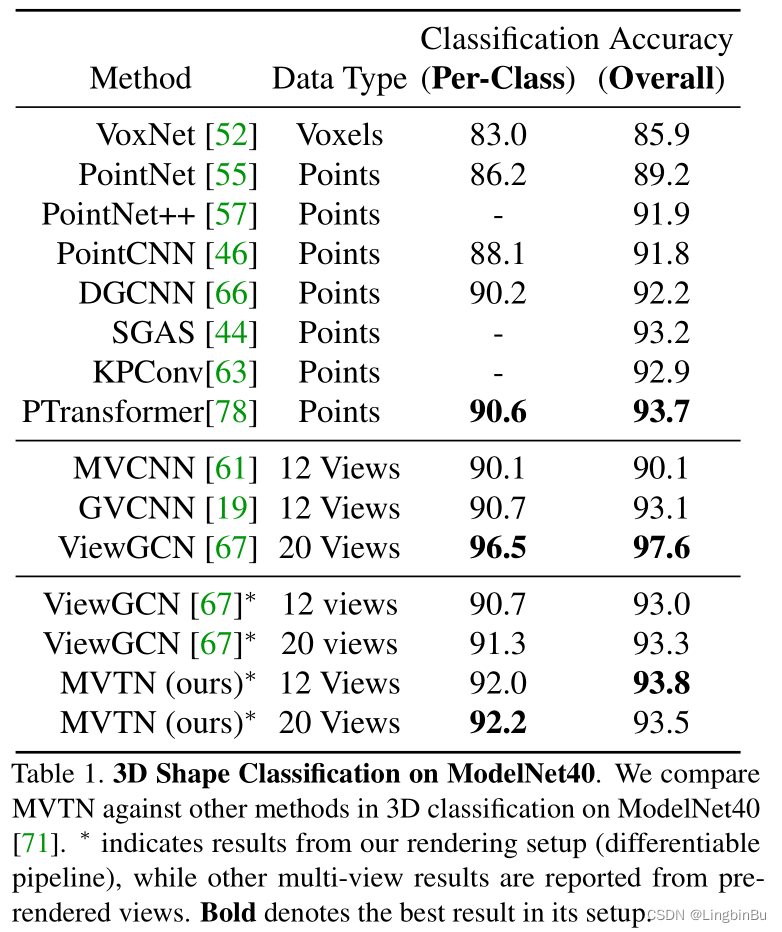
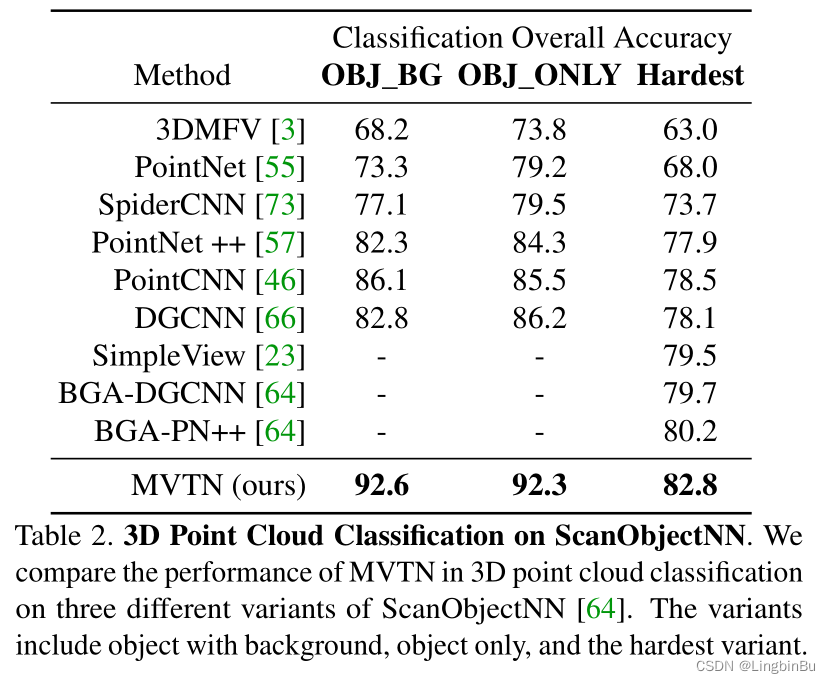
3D Shape Classification
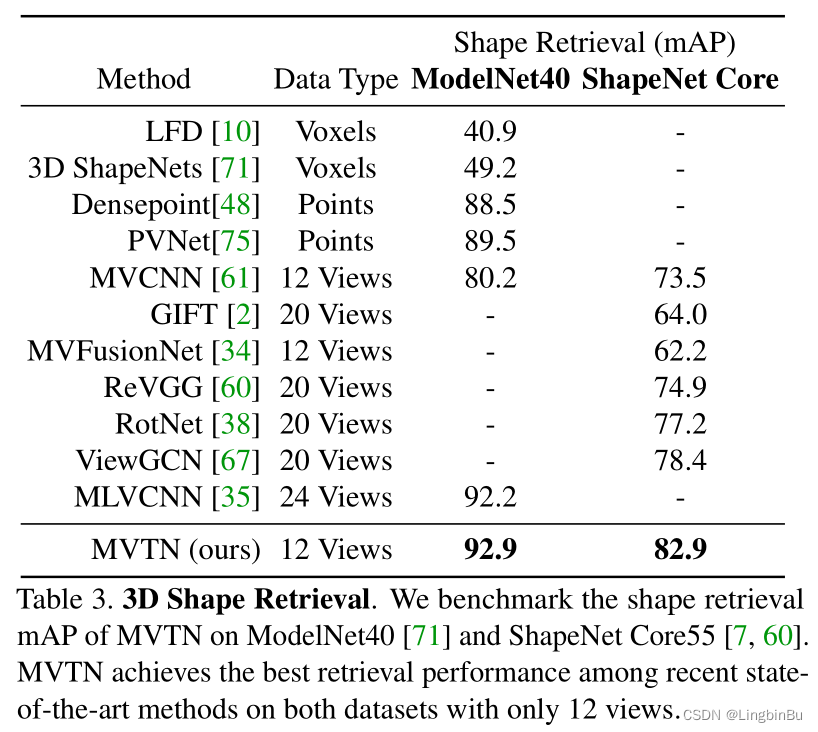
3D Shape Retrieval

Rotation Robustness

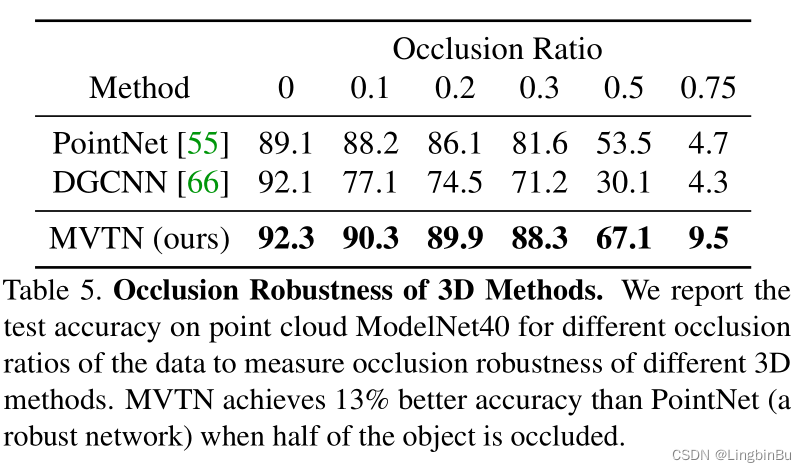
Occlusion Robustness

Ablation Study
Number of Views

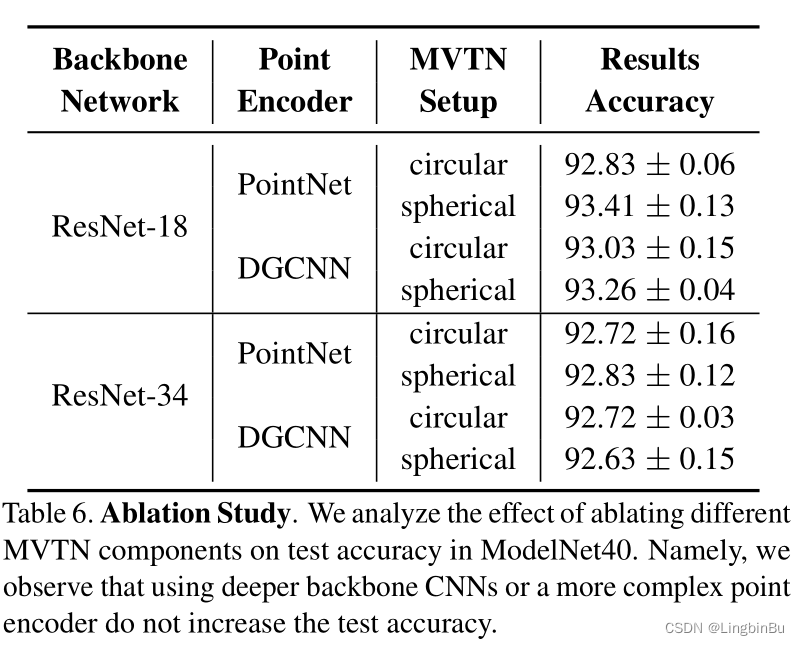
Choice of Backbone and Point Encoders
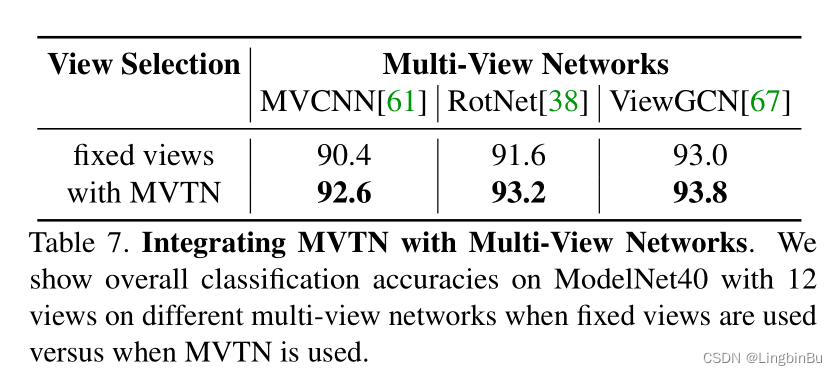
Choice of Multi-View Network
Time and Memory Requirements

边栏推荐
- LeetCode 30. Concatenate substrings of all words
- 数字化转型中,企业设备管理会出现什么问题?JNPF或将是“最优解”
- The method of replacing the newline character '\n' of a file with a space in the shell
- Arbre DP acwing 285. Un bal sans patron.
- I made mistakes that junior programmers all over the world would make, and I also made mistakes that I shouldn't have made
- Tree DP acwing 285 A dance without a boss
- 22-05-26 西安 面试题(01)准备
- 【点云处理之论文狂读经典版13】—— Adaptive Graph Convolutional Neural Networks
- How to delete CSDN after sending a wrong blog? How to operate quickly
- Notes and bugs generated during the use of h:i:s and y-m-d
猜你喜欢

Divide candy (circular queue)

LeetCode 715. Range 模块

How to check whether the disk is in guid format (GPT) or MBR format? Judge whether UEFI mode starts or legacy mode starts?

Excel is not as good as jnpf form for 3 minutes in an hour. Leaders must praise it when making reports like this!

DOM render mount patch responsive system
LeetCode 1089. Duplicate zero

记忆化搜索 AcWing 901. 滑雪

LeetCode 513. Find the value in the lower left corner of the tree

22-06-27 Xian redis (01) commands for installing five common data types: redis and redis
Debug debugging - Visual Studio 2022
随机推荐
Noip 2002 popularity group selection number
Convert video to GIF
Pic16f648a-e/ss PIC16 8-bit microcontroller, 7KB (4kx14)
树形DP AcWing 285. 没有上司的舞会
php public private protected
excel一小时不如JNPF表单3分钟,这样做报表,领导都得点赞!
LeetCode 324. Swing sort II
高斯消元 AcWing 883. 高斯消元解线性方程组
Get the link behind? Parameter value after question mark
AcWing 787. Merge sort (template)
低代码前景可期,JNPF灵活易用,用智能定义新型办公模式
【点云处理之论文狂读经典版11】—— Mining Point Cloud Local Structures by Kernel Correlation and Graph Pooling
First Servlet
Query XML documents with XPath
LeetCode 75. Color classification
We have a common name, XX Gong
Shell script kills the process according to the port number
Tree DP acwing 285 A dance without a boss
I made mistakes that junior programmers all over the world would make, and I also made mistakes that I shouldn't have made
22-05-26 西安 面试题(01)准备