当前位置:网站首页>Talk about the design and implementation logic of payment process
Talk about the design and implementation logic of payment process
2022-07-04 12:56:00 【51CTO】
Novices are afraid of the business that veterans have a headache ;
One 、 Business background
Usually in the business system , Will more or less involve payment related functions ; For some inexperienced students , The most important thing is to face the logic of this kind of payment and settlement , Because of any details in the process , May cause reconciliation exceptions ;
After the error occurs , Then I want to repair the process , The time cost is high , It also involves the leveling of wrong data , Eventually, it is likely to lead to disorderly accounts and unclear results , Then manual intervention is needed ;
In the payment scenario , It not only involves many complex businesses , Settlement rules , Long process , Third party docking , Among them, many technical details are involved , such as : Business management 、 Asynchronous processing 、 Retry mechanism 、 Lock, etc ; Let's analyze the specific detail logic .
Two 、 Payment business
1、 Process disassembly
When facing complex business , The most basic ability is to understand the process into modules , Manage each module , Then consider how to connect the whole process , So as to form ideas and experience to solve problems ;
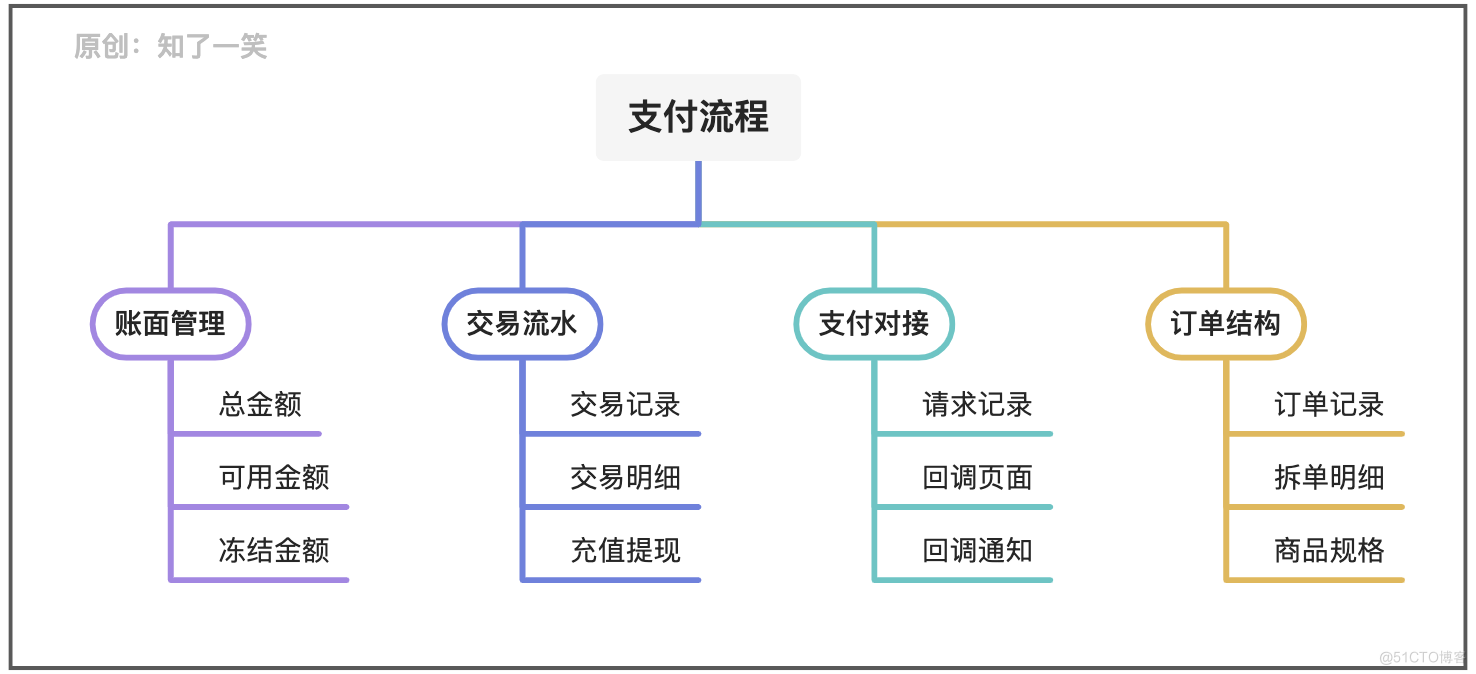
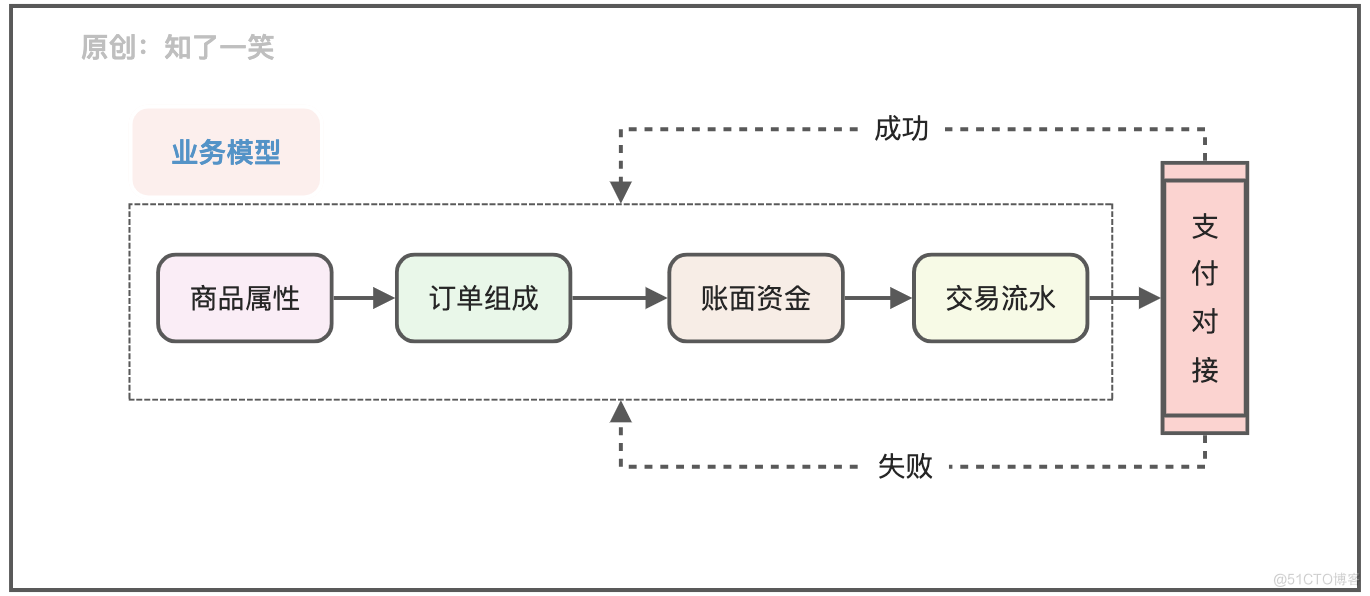
The figure below is a common decomposition of trading scenarios , It can be roughly divided into four modules :
- Book management : For users who have opened the payment function , Must have clear management information ; For example, available , frozen , Bills, etc ;
- Transaction flow : The running records of the whole fund management , Not limited to trading scenarios , And recharge , Withdrawal , Refund, etc ;
- Payment docking : Usually, the payment function in the process is realized by connecting with the third-party payment platform , So make a good record of requests and messages ;
- Order structure : For example, in e-commerce transactions , Order model management , Split order strategy, etc , Specifications of goods paid, etc ;
Here is just an analysis from a conventional transaction process , The actual detailed description will be much more complicated than the legend , Although the business details vary , But the treatment ideas are generally the same ; Then design the flow sequence diagram according to each module , Plan the connection and cooperation between nodes ;
2、 Process sequence
Through the design of sequence diagram , To analyze how each node should handle when connecting and cooperating , In payment business , It is usually divided into before payment 、 Payment docking 、 There are three core stages after payment :
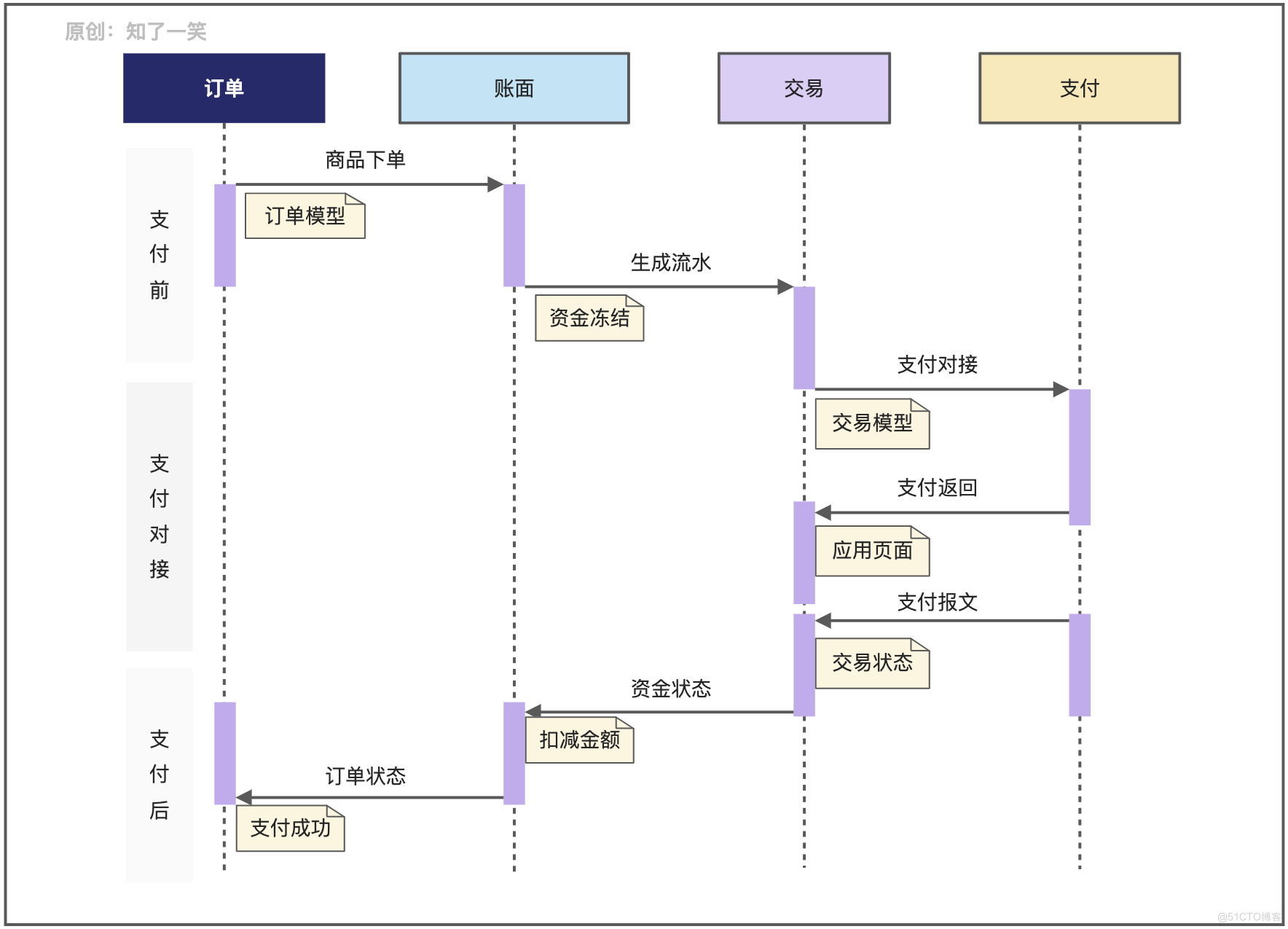
- Before payment : When placing an order , Build order model , Check the inventory according to the splitting rules 、 Commodity status, etc , Then freeze the account funds , Generate transaction flow , At this time, the status is to be paid ;
- Payment docking : After the business model is initialized successfully before payment , Build a third-party payment docking request , Initiate payment process , And record the corresponding request actions and parameters , Waiting for notification of payment results ;
- After payment : According to the success of the payment results , Perform the corresponding business model status update , If the payment is successful, the transaction is recorded 、 Frozen funds 、 Order structure and inventory need to be updated ;
In fact, after having a clear understanding of the business and splitting , Then do a good job in the design of timing process , This has made a complex scene look much simpler , Then it is to design the data structure of each node ;
3、 The structure design
Based on the above business scenario analysis and disassembly , And the presentation of process sequence diagram , It is easy to output a structural design of basic dimensions , The following figure can be used as a reference :
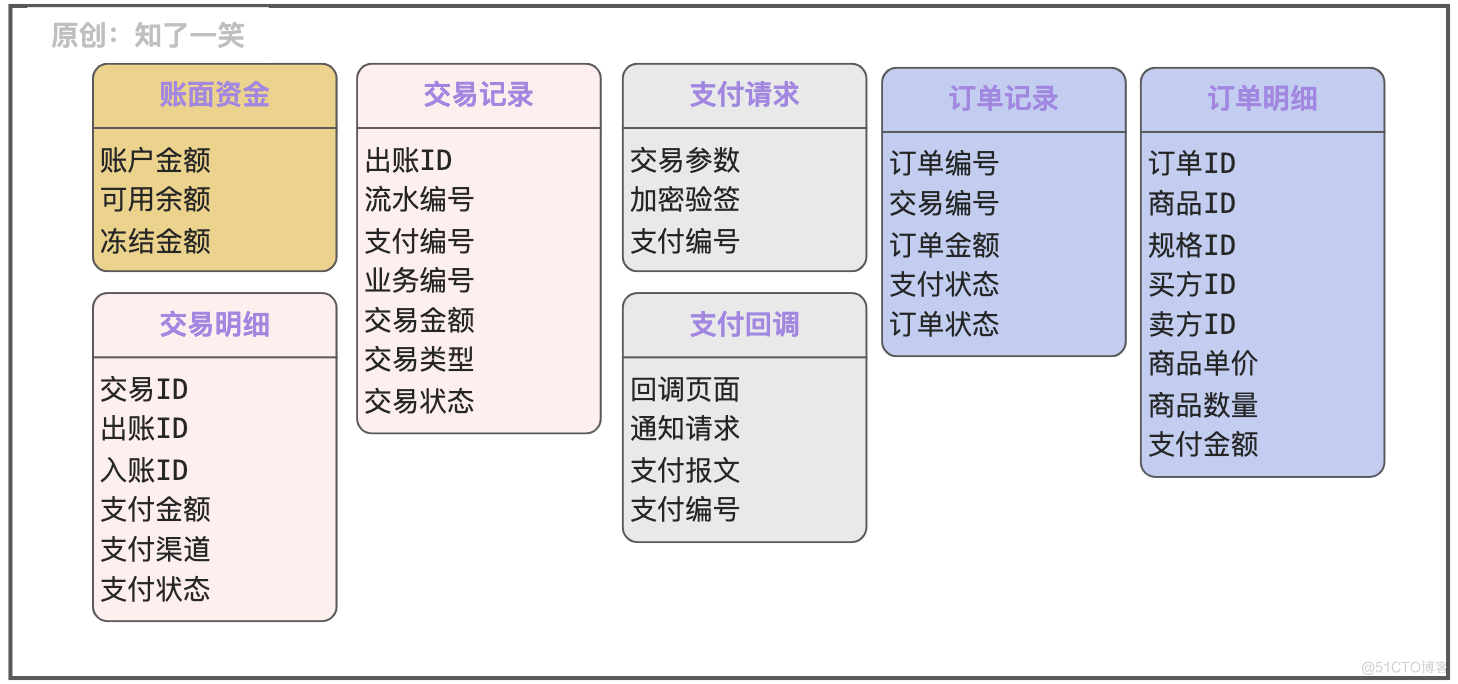
- Book management : Three core dimensions , Amount of account , Available balance , Freezing amount ;
- Transaction records : Store users' transaction actions , However, multiple transaction details may be generated , A typical scenario is to place an order in a shopping cart ;
- Transaction details : Usually because the order is split , As a result, the transaction is split into multiple details , And then pay the funds to different businesses ;
- Payment docking : When requesting a third-party payment platform , Need to record request parameters , And the message of the third party callback notification ;
- Order records : There may be multiple split sub orders in an order , There are also many splitting strategies , Like the warehouse , merchants , Category, etc ;
- The order details : Manage the information of each sub order , Goods ordered 、 specifications 、 round turn 、 The unit price 、 Number 、 Amount, etc. ;
Even if you just look at the simple design above , Can feel the complexity of payment business , What's more, it will be superimposed after preferential rules such as red envelopes or full discounts , Its complexity can be imagined ;
Of course, if there is a clear development specification , In complex versions , All development must output business decomposition ideas , Timing and structure design , Code after unified Review , In this way, even complex businesses will have great quality assurance .
3、 ... and 、 Related business
The above list analyzes the process from the main logic of payment , In fact, the business involved is far more than those mentioned in the process , Take common e-commerce scenarios as an example , There is also commodity management in the transaction 、 Inventory management 、 Physical distribution management , Payment docking will also involve preferential rule embedding and so on ;
Commodity management
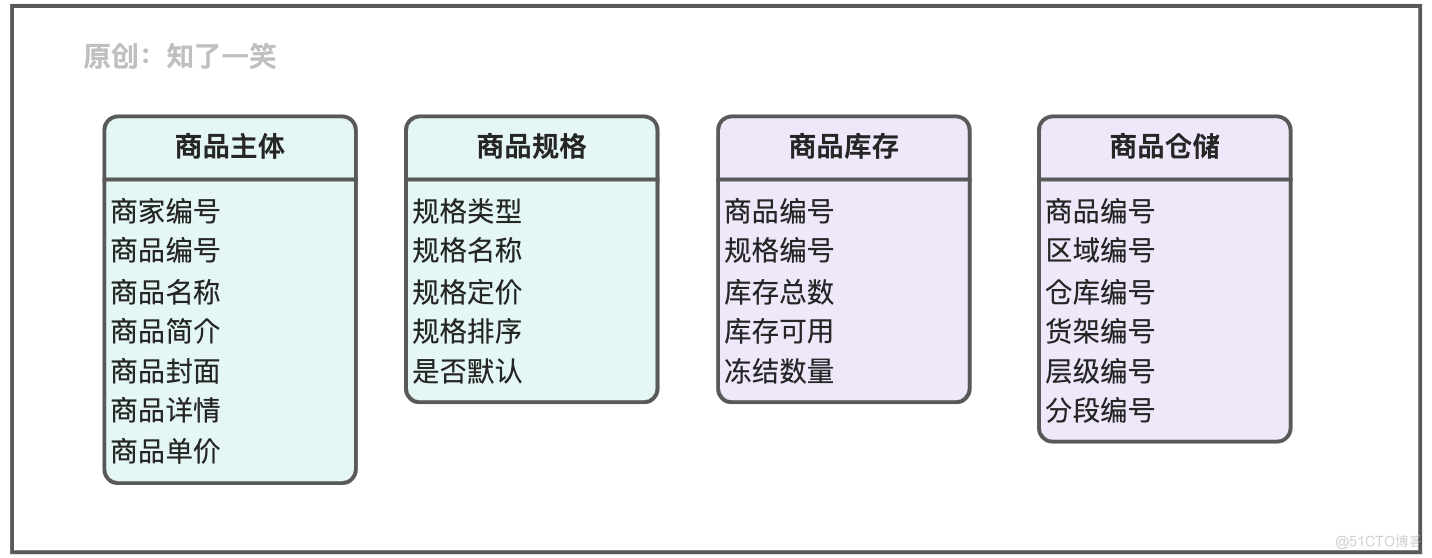
- Commodity subject : Maintain the information of each dimension of goods , And provide various specifications and options , And the basic pricing ladder , Build product details ;
- Warehouse management : After the order is split , You need to verify the storage information according to the commodity number , Carry out corresponding inventory freezing and warehouse delivery after payment ;
Coupon rules

- Coupon subject : In order to adapt to more business scenarios , There need to be many designs for preferential rules , Such as full reduction or discount ratio 、 Price ladder discount 、 Validity limit, etc ;
- Distribution rules : Support daily operational activities , Maintenance of user life cycle , And the transformation of channel flow , Provide the basic ability of user group marketing ;
Here is a brief description of the commodity and coupon business , Are closely related to the payment process , For example, the inventory is insufficient after splitting , This item needs to be removed ; The use strategy of coupons in payment , And how to handle the refund ;
Four 、 practice
Finally, from the perspective of technical implementation , Summarize some key issues in the payment process :
- business model : Have a clear understanding of the business , And can split the core nodes , Design the corresponding process sequence and data structure ;
- Business management : Commonly used in the transaction process TCC Transaction mechanism , namely Try( Preprocessing )、Confirm( confirm )、Cancel( Cancel ) Pattern ;
- Lock and retry : Send the message of successful payment after payment , Then update the business , It is usually necessary to lock the processed order number , Avoid data problems caused by message retry mechanism ;
- Capital settlement : Calculation of amount involved , The problem of accuracy loss cannot occur naturally , In a transaction, it must be ensured that each fund can be verified by reconciliation ;
- Process maintenance : The process itself is difficult to ensure that there are no errors , It needs to be developed , Provide a visual interface of the process , And support the mechanism of manual maintenance ;
Many complex business scenario management , Both need a long-term iterative process , But the premise needs to firmly grasp the core logic ; Understanding business is a process from complexity to simplicity , The realization of business is a process from shallow to deep , Analysis and understanding , To the ground , Then to exploration and innovation .
5、 ... and 、 Reference source code
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
CVPR 2022 | TransFusion:用Transformer进行3D目标检测的激光雷达-相机融合
![[data clustering] section 3 of Chapter 4: DBSCAN performance analysis, advantages and disadvantages, and parameter selection methods](/img/e6/2b46d72049ea50f89d0234eab88439.png)
[data clustering] section 3 of Chapter 4: DBSCAN performance analysis, advantages and disadvantages, and parameter selection methods
16. Memory usage and segmentation
分布式事务相关概念与理论

轻松玩转三子棋
C语言函数
CTF竞赛题解之stm32逆向入门

C#/VB.NET 给PDF文档添加文本/图像水印
DC-5靶机

【云原生 | Kubernetes篇】深入了解Ingress(十二)
随机推荐
MDK在头文件中使用预编译器时,#ifdef 无效的问题
6 分钟看完 BGP 协议。
Backgroundworker usage example
WPF双滑块控件以及强制捕获鼠标事件焦点
C fonctions linguistiques
Why can the implementation class of abstractdispatcherservletinitializer be called when initializing the web container
Detailed explanation of mt4api documentary and foreign exchange API documentary interfaces
【云原生 | Kubernetes篇】深入了解Ingress(十二)
When synchronized encounters this thing, there is a big hole, pay attention!
Valentine's Day confession code
C語言:求100-999是7的倍數的回文數
阿里云有奖体验:用PolarDB-X搭建一个高可用系统
IIS error, unable to start debugging on the webserver
Runc hang causes the kubernetes node notready
在 Apache 上配置 WebDAV 服务器
Golang sets the small details of goproxy proxy proxy, which is applicable to go module download timeout and Alibaba cloud image go module download timeout
C language: find the palindrome number whose 100-999 is a multiple of 7
比量子化学方法快六个数量级,一种基于绝热状态的绝热人工神经网络方法,可加速对偶氮苯衍生物及此类分子的模拟
【FAQ】华为帐号服务报错 907135701的常见原因总结和解决方法
面向个性化需求的在线云数据库混合调优系统 | SIGMOD 2022入选论文解读