当前位置:网站首页>C language function
C language function
2022-07-04 12:39:00 【Wake up after dark】
Catalog
The formal parameter of the function :
One . Library function
 https://cplusplus.com/
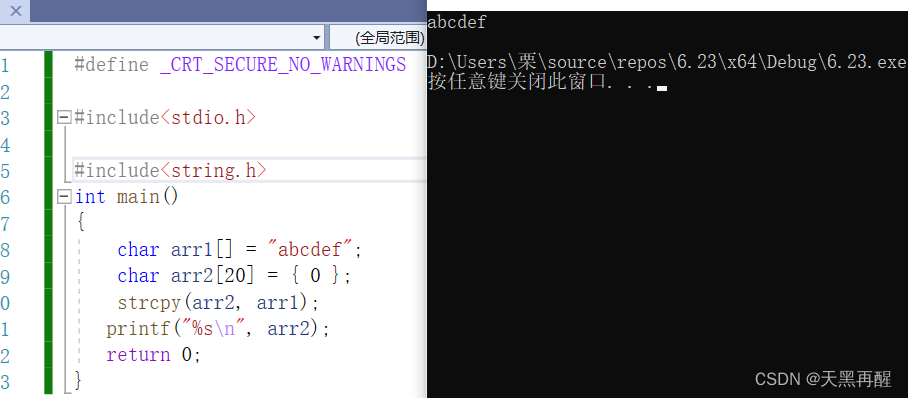
https://cplusplus.com/Such as strcpy( Copy string )char * strcpy ( char * destination, const char * source );
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
int main ()
{
char arr1[]="abcdef"; //a b c d e f
char arr2[20]={0};
strpy(arr1,arr2};
printf("%s\n",arr2);
return 0;
}
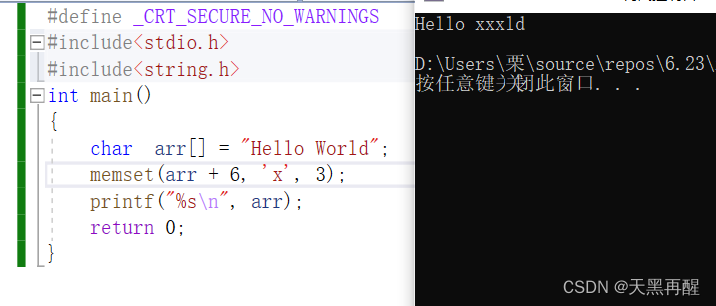
memset( Memory settings )
void * memset ( void * ptr, int value, size_t num );
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
int main()
{
char arr[]="Hello World";
memset(arr+6,'x',3);
//. Memory is set in bytes , And the content of each byte is the same value, Start after the sixth byte , The last three are x
printf("%s\n",arr);
return 0;
} 
Two . Custom function
Like library functions, custom functions are also created by Function name , The return value type and function parameters consist of .
The type of return Function name ( The parameters of the function )
{
Statement item ;
}
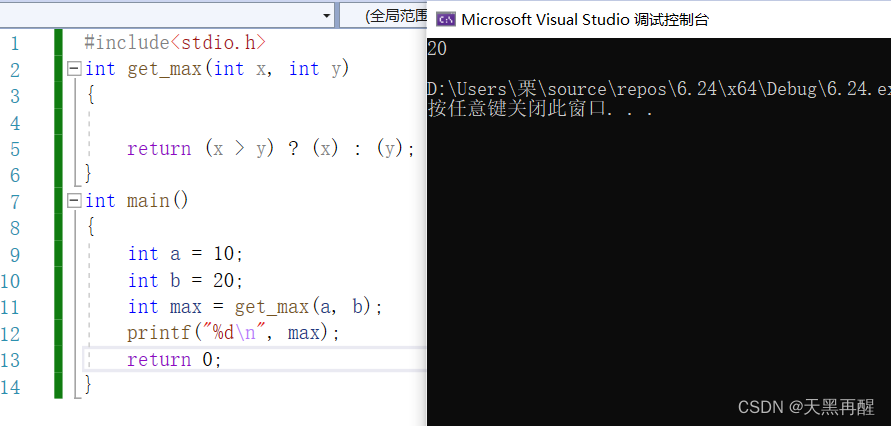
Such as : Write a function to compare the size value between the two .
#include<stdio.h>
int get_max(int x,int y) //int Is the return type get_max Is the function name int x,int y Is the parameter
{
return (x>y) ? (x) : (y); // Statement item
}
int main ()
{
int a=10;
int b=20;
int max = get_max(a,b);
printf("%d\n",max);
return 0;
}
Functions that swap integer variables :
// The wrong form
#include <stdio.h>
// Implemented as a function , But I can't finish the task
void Swap1(int x, int y) {
int tmp = 0;
tmp = x;
x = y;
y = tmp; }
// The right form
#include<stdio.h>
void Swap2(int *px, int *py) // Shape parameter
{
int tmp = 0;
tmp = *px;
*px = *py;
*py = tmp;
}
int main()
{
int a= 4;
int b = 8;
Swap1(a, b); // Value transfer call
printf(" Exchange before :a = %d b = %d\n", a, b);
// Actual parameters
Swap2(&a, &b); // Address call
printf(" After exchanging :a = %d b = %d\n", a, b);
return 0;
}When an argument is passed to a formal parameter , A formal parameter is a temporary copy of an argument , Modification of a parameter does not affect the argument .
swap1: During the call , We will a and b The value of is passed to x,y. Then in the function x,y Exchange values , But it didn't change the original a,b. because x,y It's a parameter , Something destroyed when used up , It is only used to temporarily store the original value , So it can't change at all a,b Value .
swap2: During the call , It's the address , Pass the address to the pointer *px,*py.*px namely a The address of ,*py namely b The address of , Variables are stored in addresses , Then you can locate the original variable according to the pointer .
swap1 and Swap2 Parameters in function x,y,px,py All are Formal parameters . stay main Function passed to swap1 Of a,b He Zhuan to Swap2 Functional &a , &b yes The actual parameter .Swap1 When the function is called , x , y Have your own space , As like as two peas, the same thing is true. . So we can simply think that : After the formal parameter is instantiated, it is actually equivalent to a temporary copy of the argument .
Arguments to functions :
The parameters that are actually passed to the function , It's called the actual parameter .The argument can be : Constant 、 Variable 、 expression 、 Functions, etc .Whatever the type of argument is , When you make a function call , They all have to have certain values , In order to pass these values to the parameter .
The formal parameter of the function :
Formal parameters refer to the variables in brackets after the function name , Because formal parameters are only instantiated when the function is called ( Allocate memory units ), So it's called formal parameter . Formal parameters are automatically destroyed when the function call is completed . So formal parameters are only valid in functions .
Value transfer call :
The formal and actual parameters of a function occupy different memory blocks , Modification of a parameter does not affect the argument .
Address call :
Address call is a way to call a function by passing the memory address of the created variable outside the function to the function parameter .This parameter transfer method can establish a real relationship between the function and the variables outside the function , That is, you can directly operate inside the functionAs a variable outside the function .
Nested calls to functions :
Functions can be called nested , But you can't nest definitions ( A function body cannot contain the definition of another function )
#include <stdio.h>
void new_line()
{
printf("hehe\n");
}
void three_line()
{
int i = 0;
for(i=0; i<3; i++)
{
new_line();
}
}
int main()
{
three_line();
return 0;
}
main Called in the function three_line function ,three_line Every time the function executes the loop, it will call new_line function ,new_line The function prints hehe. So the end result of this program is printing 3 individual hehe. This is the nested call .
Chained access :
Take the return value of one function as the parameter of another function and the return value of one function as the parameter of another function .
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
char arr[20] = "hello";
int ret = strlen(strcat(arr));
printf("%d\n", ret);
return 0;
}
//#include <stdio.h>
//#include <string.h>
//int main()
//{
// char arr[20] = "hello";
// printf("%d\n", strlen(strcat(arr)));
// return 0;
//}#include <stdio.h>
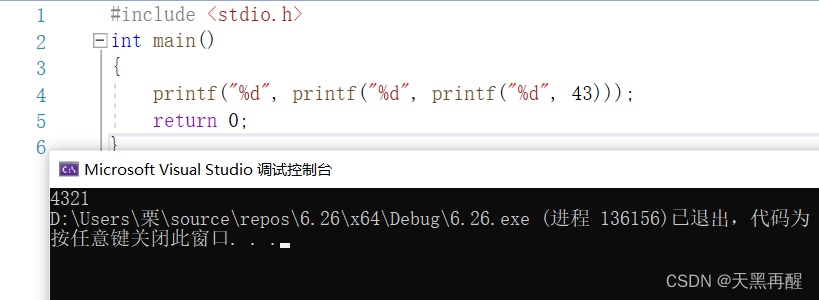
int main()
{
printf("%d", printf("%d", printf("%d", 43)));
return 0;
}Then the final result ?
First, printf The innermost and then outward in turn .
Here is printf The return value of :( It can be done by https://cplusplus.com/ Inquire about )

It roughly means to return the number of printed characters .so Print first 43 , The result is
printf("%d", printf("%d",43));
because '43' It's two characters , therefore printf("%d",43) As the result of the 2. after :
printf("%d",2);
'2' Is a character , So print as 1.
The final result is 4321
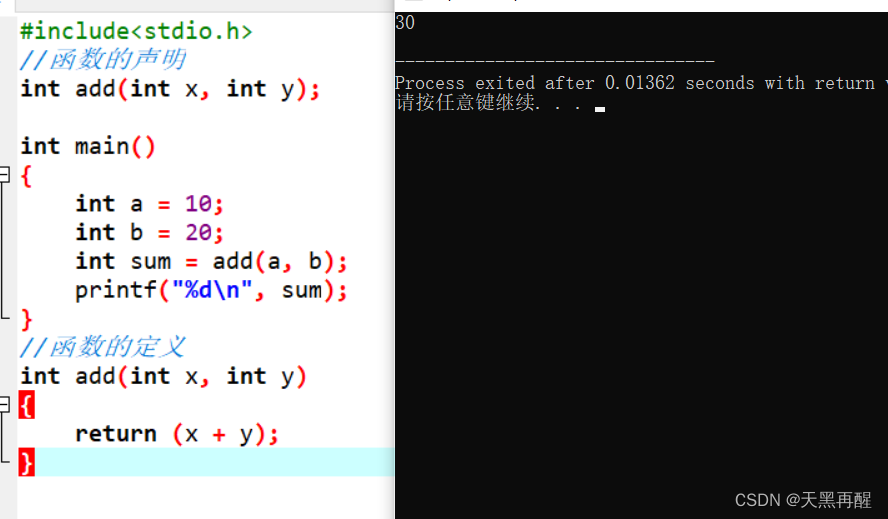
Declaration of functions :
Definition :1. Tell the compiler that there is a function called , What are the parameters , What is the return type . But does it exist , function The statement does not determine .2. The declaration of a function usually precedes the use of the function . To meet the Declare before use .3. The declaration of the function is usually placed in the header file
Definition of function :
Definition : The definition of a function refers to the concrete implementation of a function , Explain the function realization .
#include<stdio.h>
// Declaration of functions
int add(int x,int y);
int main()
{
int a=10;
int b=20;
int sum=add(a,b);
printf("%d\n",sum);
}
// Definition of function
int add(int x,int y)
{
return (x+y);
}
recursive
The programming skill of program calling itself is called recursion ( recursion).Recursion as an algorithm is widely used in programming languages .A procedure or function has direct or indirect meaning in its definition or description Call a method of itself , It usually transforms a large and complex problem into a smaller problem similar to the original problem .The recursion strategy only needs a few programs to describe the repeated calculation needed in the process of solving problems , Greatly reduces the amount of code in the program .Conditions :1. There are restrictions , When this constraint is met , Recursion doesn't continue .2. After each recursive call, it gets closer and closer to this constraint
example : Accept an integer value ( Unsigned ), Print each bit of it in order .
#include <stdio.h>
void print(int n)
{
if(n>9)
{
print(n/10);
}
printf("%d ", n%10);
}
int main()
{
int num = 1234;
print(num);
return 0;
}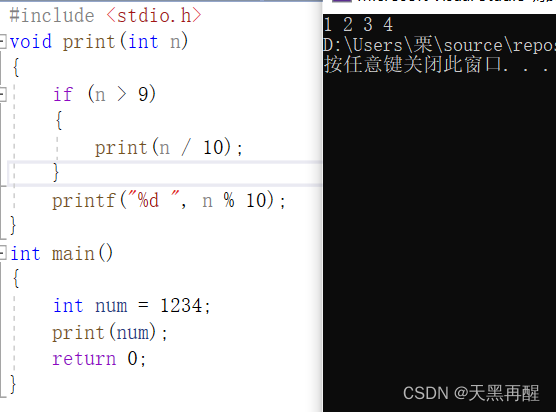
print The function can take num Each bit of is printed out in order .
First num To be an assignment 1234, Get into print In the function . after /10 after 123
Once again into the print The function is followed by 12
next print The function is followed by 1
because 1%10 by 1, Print out 1, Then return to the previous function ,print by 12 In the function of ,12%10 by 2, Print out 2 , Print out accordingly 3 and 4
The process :print(1234)---print(123)4---print(12)3 4---print(1) 2 3 4---print 1 2 3 4
example : Creating temporary variables is not allowed , Use recursive simulation strlen Find the length of the string .
#include <stdio.h>
int my_strlen(char* str)
{
if (*str != '\0')
return 1 + my_strlen(str+1);
}
int main()
{
char arr [] = "abcdef";
int len=my_strlen(arr);
printf("%d\n",len);
return 0;
} 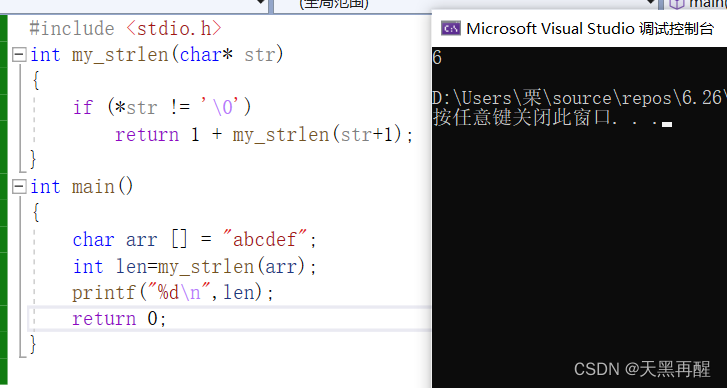
Find the length of the string , encounter \0 Just stop ,\0 A few characters are the length of the string .
At first str yes a It's not equal to \0,str+1 Namely b, Keep going until you meet \0 , Termination code .
iteration :
Iteration is the activity of repeating the feedback process , Its purpose is usually to approach the desired goal or result . Every repetition of a process is called a “ iteration ”, The result of each iteration will be taken as the initial value of the next iteration . Repeat a series of steps , The process of finding out the following quantity from the preceding quantity in turn . Every result of this process , They are all obtained by performing the same operation steps on the previous result .
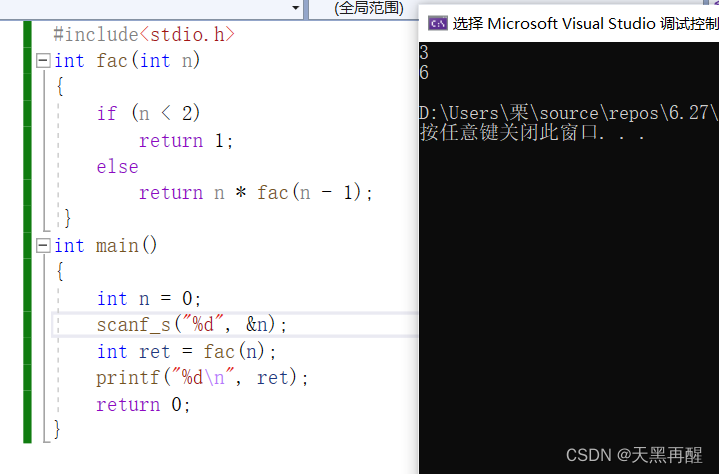
For example, o n The factorial :( The premise is not to consider stack overflow )
#include<stdio.h>
int fac(int n)
{
if (n < 2)
return 1;
else
return n * fac(n - 1);
}
int main()
{
int n = 0;
scanf_s("%d\n", &n);
int ret = fac(n);
printf("%d\n", ret);
return 0;
}
example 2: Please n Fibonacci sequence ( Stack overflow is not considered )
#include <stdio.h>
int count = 0;
int fuc(int n)
{
if (n == 3)
count++;// Record x==3 How many times
if (n <= 2)
return 1;
else
return fuc(n - 2) + fuc(n - 1);
}
int main()
{
int n;
printf(" Please enter a number ");
scanf("%d",&n);
printf(" Fibonacci Series No %d The value of the item %d", n, fuc(n));
printf(" The number of calls is %d", count);
return 0;
}
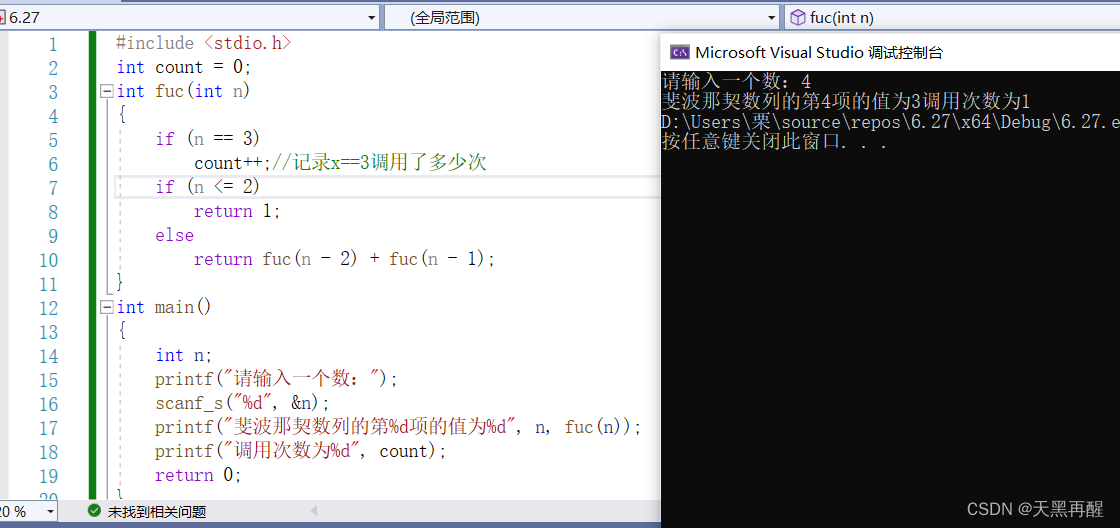
Because stack overflow is not considered , When a large value is entered , Operation is very troublesome , Because it's always circulating , You can change recursion into non recursion .
After factorial change :
#include <stdio.h>
int fac(int n)
{
int result = 1;
while (n > 1)
{
result *= n;
n -= 1;
}
return result;
}
int main()
{
int n;
printf(" Please enter n=>");
scanf("%d",&n);
printf("%d The factorial of is %d",n,fac(n));
return 0;
}Such as n>1, Just put n Multiply the value of to result Inside , then n Decline , Continue to multiply , The cycle goes on , until n<=1 了 , Just return the result . If we type 5,result=1*5=5→result=5*4=20→20*3=60→60*2=120
After the Fibonacci sequence is changed :
#include <stdio.h>
int fuc(int n)
{
int a = 1,b = 1, c = 1;
int i;
while (n>2)
{
c = a + b;
a = b;
b = c;
n--;
}
return c;
}
int main()
{
int n;
printf(" Please enter a number ");
scanf("%d", &n);
printf(" Fibonacci Series No %d The value of the item %ld", n, fuc(n));
return 0;
}Fibonacci sequence :
1 1 2 3 5 8 13 21 34 55
a b c
At first a=1,b=1,c Figure out , And then b The value is assigned to a,c The value is assigned to b, In the calculation c Count it down in turn , Can produce results quickly .
边栏推荐
- First knowledge of spark - 7000 words +15 diagrams, and learn the basic knowledge of spark
- Globalsign's SSL certificate products
- C語言:求100-999是7的倍數的回文數
- [Yunju entrepreneurial foundation notes] Chapter II entrepreneur test 8
- [Yunju entrepreneurial foundation notes] Chapter II entrepreneur test 19
- 0x15 string
- Practical dry goods: deploy mini version message queue based on redis6.0
- French Data Protection Agency: using Google Analytics or violating gdpr
- Unity performance optimization reading notes - Introduction (1)
- [solve the error of this pointing in the applet] SetData of undefined
猜你喜欢

Fly tutorial 02 advanced functions of elevatedbutton (tutorial includes source code) (tutorial includes source code)
Awk getting started to proficient series - awk quick start
![[solve the error of this pointing in the applet] SetData of undefined](/img/19/c34008fbbe1175baac2ab69eb26e05.jpg)
[solve the error of this pointing in the applet] SetData of undefined
![[Yunju entrepreneurial foundation notes] Chapter II entrepreneur test 9](/img/ed/0edff23fbd3880bc6c9dabd31755ac.jpg)
[Yunju entrepreneurial foundation notes] Chapter II entrepreneur test 9
MySQL advanced review

Leetcode day 17
![[Yunju entrepreneurial foundation notes] Chapter II entrepreneur test 6](/img/38/51797fcdb57159b48d0e0a72eeb580.jpg)
[Yunju entrepreneurial foundation notes] Chapter II entrepreneur test 6
Azure solution: how can third-party tools call azure blob storage to store data?
Review of week 278 of leetcode II
![[Yunju entrepreneurial foundation notes] Chapter II entrepreneur test 23](/img/72/a80ee7ee7b967b0afa6018070d03c9.jpg)
[Yunju entrepreneurial foundation notes] Chapter II entrepreneur test 23
随机推荐
2022, 6G is heating up
Entity framework calls Max on null on records - Entity Framework calling Max on null on records
Decrypt the advantages of low code and unlock efficient application development
Iterm tab switching order
Method of setting default items in C # ComboBox control code
《天天数学》连载57:二月二十六日
The solution of permission denied
Global and Chinese market of dental elevators 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
Single spa, Qiankun, Friday access practice
Globalsign's SSL certificate products
PKCs 5: password based cryptography specification version 2.1 Chinese Translation
mm_ Cognition of struct structure
'using an alias column in the where clause in PostgreSQL' - using an alias column in the where clause in PostgreSQL
Data communication and network: ch13 Ethernet
Experiment 7. IPv6
AI should take code agriculture? Deepmind offers a programming version of "Alpha dog" alphacode that surpasses nearly half of programmers!
priority_ queue
TCP slicing and PSH understanding
Paper notes ACL 2020 improving event detection via open domain trigger knowledge
What if the chat record is gone? How to restore wechat chat records on Apple Mobile