当前位置:网站首页>IGMP message (tcp/ip details volume 1/ Volume 2)
IGMP message (tcp/ip details volume 1/ Volume 2)
2022-06-12 15:21:00 【QQ851301776】
Created by QQ:851301776, mailbox :[email protected], Welcome to technical exchange , This blog is mainly my own learning experience , Just to make a little progress every day !
Personal motto :
1. No one was born , As long as it is thick, it will happen .
2. You can have a low degree , You can skip school , But you have to learn
One 、 sketch
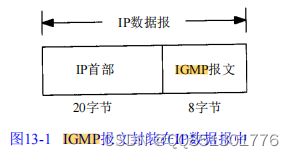
IGMP: Used to support host and router multicast I n t e r n e t Group management protocol
It lets all systems on a physical network know the multicast group that the host is currently in . Multicast routers need this information to know which interfaces multicast datagrams should be forwarded to .
Two 、IGMP message

This is version 1 Of I G M P.I G M P The type is 1 Description is the query message sent by the multicast router , by 2 Description is the report message sent by the host . Check the calculation of sum and I C M P The agreement is the same .
The group address is D class I P Address . Set the group address to in the query message 0, In the report message, the group address is the address of the group to participate .
3、 ... and 、IGMP agreement
1. Join a multicast group
Multicast is based on the concept of a process ( The term process is used to refer to a program executed by the operating system ), The process joins a multicast group on a given interface of a host . The members of a multicast group on a given interface are dynamic — It changes at any time as processes join and leave the multicast group .
The process referred to here must join a multicast group on a given interface in some way . A process can also leave a previously joined multicast group . These are any of the hosts that support multicast A P I Necessary parts . Use the qualifier “ Interface ” Because the members in the multicast group are associated with interfaces . A process can join the same multicast group on multiple interfaces .
This implies that a host identifies a multicast group by group address and interface . The host must keep a table , This table contains all multicast groups containing at least one process and the number of processes in the multicast group .
2.IGMP Reports and queries
Multicast routers use I G M P Message to record the changes of group members in the network connected to the router . The rules of use are as follows :
- When the first process joins a group , The host sends a I G M P The report . If multiple processes of a host join the same group , Send only one I G M P The report . This report is sent to the same interface where the process joined the group .
- When a process leaves a group , The host does not send I G M P The report , Even if the last process in the group leaves . After the host knows that there are no more group members in the determined group , Received later I G M P The report message will not be sent in the query .
- Multicast router sends messages regularly I G M P Query to see if any hosts contain processes belonging to the multicast group . The multicast router must send one to each interface I G M P Inquire about . Because the router wants the host to send back a report for each multicast group it joins , therefore I G M P The group address in the query message is set to 0.
- The host sends I G M P Report in response to a I G M P Inquire about , Send back to each group that contains at least one process I G M P The report .
Use these query and report messages , The multicast router maintains a table for each interface , The table records the multicast group of at least one host on the interface . When the router receives the multicast datagram to be forwarded , It only forwards the datagram to ( Use the corresponding multicast link layer address ) It also has interfaces belonging to that group of hosts .
chart 1 3 - 3 It shows two I G M P message , One is the report sent by the host , The other is the query sent by the router . The router is asking each host on that interface to specify each multicast group it joins .

3. Implementation details
To improve the efficiency of the agreement , There are many implementation details to consider . First , When a host first sends I G M P The report ( When the first process joins a multicast group ) when , There is no guarantee that the report will be received reliably ( Because it uses I P Delivery of services ). The next report will be sent after an interval . This time interval is determined by the host at 0 ~ 1 0 Random selection within seconds .
secondly , When a host receives a query from the router , Do not respond immediately , Instead, some responses are sent after a certain time interval ( use “ Respond to ” Because the host must send a response to each group it participates in ). Since multiple hosts participating in the same multicast group can send a report , Their transmission interval can be set to random delay . All hosts in a physical network will receive all reports sent by other hosts in the same group , Because it's like the picture 1 3 - 3 The destination address in the report shown is the group address . This means that if a host is waiting to send a report , Received the same report from other hosts , Then the response of the host does not need to be sent . Because the multicast router doesn't care how many hosts belong to this group , The only concern is whether the group still has at least one host . You bet , A multicast router doesn't even care which host belongs to a multicast group . It just wants to know if there is at least one host in the multicast group on a given interface .
In a single physical network without any multicast routers , Only I G M P Traffic is when the host joins a new multicast group , Support I P Reports from multicast hosts .
4. Time to live field
In the figure 1 3 - 3 in , We noticed that I G M P Lifetime of reports and queries ( T T L ) All set to 1, This involves I P In the first part T T L Field . An initial T T L by 0 Of multicast datagrams will be restricted to the same host . By default , To transmit multicast datagrams T T L Set to 1, This will restrict multicast datagrams to the same subnet . Bigger T T L Value can be forwarded by multicast router .
Datagrams destined for a multicast address are never generated I C M P A mistake . When T T L The value is 0 when , Multicast routers also do not generate I C M P“ Overtime ” A mistake .
Under normal circumstances , The user process does not care about the T T L. However , One exception is Tr a c e r o u t e Program , It mainly depends on the settings T T L Value to complete . Since the multicast application must be able to set up the TTL value , This means that the programming interface must provide this capability to the user process .
By increasing the T T L The method of value , An application program can realize the extended ring search for a specific server ( e x p a n d i n gring search). The first multicast datagram is T T L be equal to 1 send out . If there is no response , Just try to T T L Set to 2, then 3, wait . In this way , The application can find the nearest server measured in hops .
from 2 2 4 . 0 . 0 . 0 To 2 2 4 . 0 . 0 . 2 5 5 The special address space of is intended for multicast with a range not exceeding 1 Application of skip . No matter T T L What is the value , Multicast routers do not forward datagrams whose destination addresses are any of these addresses .
5. all Host group
In the figure 1 3 - 3 in , We saw the router I G M P The query is sent to the destination I P Address 2 2 4 . 0 . 0 . 1. This address is called all host group addresses . It involves all hosts and routers with multicast capability in a physical network . After the interface is initialized , All hosts on multicast capable interfaces automatically join this multicast group . Members of this group do not need to send I G M P The report .
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢

C escape character

3D reconstruction system | L3 dual view motion recovery structure (SFM binocular SFM)

ROS初学者编写小乌龟以一定速度旋转一定角度的server

解决log4j2漏洞遭到挖矿、僵尸进程病毒攻击

Understanding of Odom coordinate system

Deepin20.6 RTX3080 安装显卡驱动510.60.02、CUDA11.6、PyTorch1.11
Left aligned, right aligned, random number, goto, compare output bool

How to set public IP access on the H3C gr5200 router

粒子滤波学习记录

Solve log4j2 vulnerability and be attacked by mining and zombie process viruses
随机推荐
FIRSTVT和LASTVT白话版
Village to village communication (and collective search)
Scala下载及IDEA安装Scala插件(保姆级教程超详细)
Servlet连接数据库实现用户登录功能
Array related content
C string
USART(RS232422485)、I2C、SPI、CAN、USB总线
Autofac (2)
Introduction to Eureka
[LDA] rough version notes of EM variational reasoning [to be improved
idea 拉取分支代码
The process of generating strong association rules from frequent itemsets
About layoffs in Internet companies
Method reference instance method reference
FIRSTVT and LASTVT vernacular
Microservice fault tolerance
C constant, cannot be changed
Pta: self TEST-1 print Hourglass (20 points)
How to add WWW to the domain name
[jvm learning] parental delegation mechanism and PC register (program counter)