当前位置:网站首页>Source code analysis of the implementation mechanism of multisets in guava class library
Source code analysis of the implementation mechanism of multisets in guava class library
2022-07-04 11:43:00 【Brother Wang_】
Guava Class library Multisets Implementation mechanism
- Multisets data structure , Although it is not often used .
- We know Java Class library Set Cannot store the same element , And the elements inside are out of order ;
- List It can store the same elements , And it's sequential .
- Multisets It can store the same elements , But the order of elements is disordered .
It can also be seen from here ,Multisets Definitely not achieved Java in Set Interface . because Set Interfaces cannot store the same elements Java Medium Set The elements inside are a bit like :[A, C, B], and Multiset Is this : [A ×2, C ×3, B ×5], There is a difference
You need to count the number of times each word appears in an article , We may use the following methods to realize :
public void wordCounts(List words) {
Map<String, Integer> counts = new HashMap<String, Integer>();
for (String word : words) {
Integer count = counts.get(word);
if (count == null) {
counts.put(word, 1);
} else {
counts.put(word, count + 1);
}
}
}
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
How to get the number of a word ? It feels similar to handling , It's annoying , Programmers like to cut corners , ha-ha ! all MutiSet The function of is like this , This collection is in STL It's a long time ago , But it is really used less .
int goodCount = counts.get("XXX");
- 1.
Class graph structure
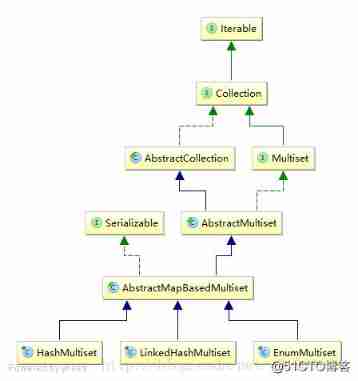
Multiset Interface
- The meaning of processing here is MutliSet As an interface , There are many implementations of interface oriented programming .
- Second, some unique attributes and methods should be added here
public interface Multiset<E> extends Collection<E> {
/**
* multiset, which is given by {@code entrySet().size()}.
*/
@Override
int size();
int count(@Nullable @CompatibleWith("E") Object element);
// Add one or more elements , Embodied in count Count above
int add(@Nullable E element, int occurrences);
int remove(@Nullable @CompatibleWith("E") Object element, int occurrences);
// Set the number of elements
int setCount(E element, int count);
// Conditional setting quantity only oldcount= The number of current elements is set
boolean setCount(E element, int oldCount, int newCount);
// The function of this is not found
Set<E> elementSet();
// This is and HashMap Medium Entry Same , It's convenient for us to check
// The value of the element in the container
Set<Entry<E>> entrySet();
//Entry entry
interface Entry<E> {
E getElement();
int getCount();
@Override
boolean equals(Object o);
@Override
int hashCode();
@Override
String toString();
}
@Override
// TODO(kevinb): caveats about equivalence-relation?
boolean equals(@Nullable Object object);
@Override
Iterator<E> iterator();
@Override
boolean contains(@Nullable Object element);
@Override
boolean containsAll(Collection<< ?> elements);
@Override
boolean add(E element);
@Override
boolean remove(@Nullable Object element);
@Override
boolean removeAll(Collection< ?> c);
}
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
- 24.
- 25.
- 26.
- 27.
- 28.
- 29.
- 30.
- 31.
- 32.
- 33.
- 34.
- 35.
- 36.
- 37.
- 38.
- 39.
- 40.
- 41.
- 42.
- 43.
- 44.
- 45.
- 46.
- 47.
- 48.
- 49.
- 50.
- 51.
- 52.
- 53.
- 54.
- 55.
- 56.
- 57.
- 58.
- 59.
- 60.
- 61.
- 62.
- 63.
- 64.
- 65.
- 66.
- 67.
- 68.
- 69.
AbstractCollection
This is JDK Provide some basic operation libraries , Go and see for yourself ! In the abstract ~ Provides tostring,clear wait , But many of them are template methods , To call the concrete implementation of the subclass
AbstractMultiset abstract
- In the abstract MutliSet Provides some basic operations , The specific implementation will vary according to different subclasses
- A lot of words are written here Multisets. Such an implementation , Improve the effect of reuse , I feel pretty good !
- It's a bit like taking an interface as a parameter of a function , Call the method of the interface , This style of functional programming !
Google Guava Wrote a lot of such methods ! It's really powerful !
Multiset.XXX The method here actually calls the specific implementation !
/**
* An implementation of {@link Multiset#size}.
*/
static int sizeImpl(Multiset< ?> multiset) {
long size = 0;
for (Entry< ?> entry : multiset.entrySet()) {
size += entry.getCount();
}
return Ints.saturatedCast(size);
}
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
This abstract class , Provided with MultiSet Some more relevant operations , It simplifies the implementation of the lower layer .
abstract class AbstractMultiset<E> extends AbstractCollection<E> implements Multiset<E> {
// This transmission this It's fun to write , What is actually called is the subclass this
// Write all the business logic into a public class ..
@Override
public int size() {
return Multisets.sizeImpl(this);
}
@Override
public boolean isEmpty() {
return entrySet().isEmpty();
}
@Override
public boolean contains(@Nullable Object element) {
return count(element) > 0;
}
@Override
public Iterator<E> iterator() {
return Multisets.iteratorImpl(this);
}
@Override
public int count(@Nullable Object element) {
for (Entry<E> entry : entrySet()) {
// This can be avoided null
if (Objects.equal(entry.getElement(), element)) {
return entry.getCount();
}
}
return 0;
}
@Override
public boolean add(@Nullable E element) {
// such add It's all about calling the implementation of subclasses !
// Because of different add stay HashMulitSet and LinkHashMutilset It's not the same
add(element, 1);
return true;
}
// It's left for subclasses to implement
@Override
public int add(@Nullable E element, int occurrences) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
@Override
public boolean remove(@Nullable Object element) {
return remove(element, 1) > 0;
}
@Override
public int remove(@Nullable Object element, int occurrences) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
@Override
public int setCount(@Nullable E element, int count) {
return Multisets.setCountImpl(this, element, count);
}
// What are the advantages of this writing , Reconstruction theory , You can know the function of this at a glance ?
// Get rid of the specific implementation , You can see what this is doing at a glance !
@Override
public boolean setCount(@Nullable E element, int oldCount, int newCount) {
return Multisets.setCountImpl(this, element, oldCount, newCount);
}
@Override
public boolean addAll(Collection< ? extends E> elementsToAdd) {
return Multisets.addAllImpl(this, elementsToAdd);
}
@CanIgnoreReturnValue
@Override
public boolean removeAll(Collection< ?> elementsToRemove) {
return Multisets.removeAllImpl(this, elementsToRemove);
}
@CanIgnoreReturnValue
@Override
public boolean retainAll(Collection< ?> elementsToRetain) {
return Multisets.retainAllImpl(this, elementsToRetain);
}
// This method is useful in many places , Provide a utils Method
@Override
public void clear() {
Iterators.clear(entryIterator());
}
// There are two different types Set, Why ? I went to check this
// Didn't see the specific logic , But it should be useful , With the current object this References to
private transient Set<E> elementSet;
@Override
public Set<E> elementSet() {
Set<E> result = elementSet;
if (result == null) {
elementSet = result = createElementSet();
}
return result;
}
Set<E> createElementSet() {
return new ElementSet();
}
@WeakOuter
class ElementSet extends Multisets.ElementSet<E> {
@Override
Multiset<E> multiset() {
// Here we use this this, It feels so strong
return AbstractMultiset.this;
}
}
// In order to traverse the entrySet, In fact, it is to traverse the data in the container
// In the next combination Map You can see , This is to traverse
//Map And realize the data in ~~
abstract Iterator<Entry<E>> entryIterator();
abstract int distinctElements();
private transient Set<Entry<E>> entrySet;
// Delay initialization , Well done !
@Override
public Set<Entry<E>> entrySet() {
Set<Entry<E>> result = entrySet;
if (result == null) {
entrySet = result = createEntrySet();
}
return result;
}
@WeakOuter
class EntrySet extends Multisets.EntrySet<E> {
@Override
// The current object is of great significance
Multiset<E> multiset() {
return AbstractMultiset.this;
}
@Override
public Iterator<Entry<E>> iterator() {
return entryIterator();
}
@Override
public int size() {
return distinctElements();
}
}
Set<Entry<E>> createEntrySet() {
return new EntrySet();
}
@Override
public boolean equals(@Nullable Object object) {
return Multisets.equalsImpl(this, object);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return entrySet().hashCode();
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return entrySet().toString();
}
}
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
- 24.
- 25.
- 26.
- 27.
- 28.
- 29.
- 30.
- 31.
- 32.
- 33.
- 34.
- 35.
- 36.
- 37.
- 38.
- 39.
- 40.
- 41.
- 42.
- 43.
- 44.
- 45.
- 46.
- 47.
- 48.
- 49.
- 50.
- 51.
- 52.
- 53.
- 54.
- 55.
- 56.
- 57.
- 58.
- 59.
- 60.
- 61.
- 62.
- 63.
- 64.
- 65.
- 66.
- 67.
- 68.
- 69.
- 70.
- 71.
- 72.
- 73.
- 74.
- 75.
- 76.
- 77.
- 78.
- 79.
- 80.
- 81.
- 82.
- 83.
- 84.
- 85.
- 86.
- 87.
- 88.
- 89.
- 90.
- 91.
- 92.
- 93.
- 94.
- 95.
- 96.
- 97.
- 98.
- 99.
- 100.
- 101.
- 102.
- 103.
- 104.
- 105.
- 106.
- 107.
- 108.
- 109.
- 110.
- 111.
- 112.
- 113.
- 114.
- 115.
- 116.
- 117.
- 118.
- 119.
- 120.
- 121.
- 122.
- 123.
- 124.
- 125.
- 126.
- 127.
- 128.
- 129.
- 130.
- 131.
- 132.
- 133.
- 134.
- 135.
- 136.
- 137.
- 138.
- 139.
- 140.
- 141.
- 142.
- 143.
- 144.
- 145.
- 146.
- 147.
- 148.
- 149.
- 150.
- 151.
- 152.
- 153.
- 154.
- 155.
- 156.
- 157.
- 158.
- 159.
- 160.
- 161.
- 162.
- 163.
- 164.
- 165.
- 166.
- 167.
- 168.
- 169.
- 170.
- 171.
AbstractMapBasedMultiset Here is the real feeling , Containers are combined to process data
abstract class AbstractMapBasedMultiset<E> extends AbstractMultiset<E> implements Serializable {
// This is a real container , Combined haha !
private transient Map<E, Count> backingMap;
// Cache size for efficiency . Using it for a long time allows us to avoid the need
// Overflow check , And ensure size() Will work even if
//multiset Once greater than Integer.MAX_VALUE.
private transient long size;
/** Standard constructor. */
protected AbstractMapBasedMultiset(Map<E, Count> backingMap) {
this.backingMap = checkNotNull(backingMap);
this.size = super.size();
}
// Provide a simple traversal Map The interface and hashMap Of EntrySet Allied
@Override
public Set<Multiset.Entry<E>> entrySet() {
return super.entrySet();
}
//entryset The use of the use is to need you this thing
@Override
Iterator<Entry<E>> entryIterator() {
//entrySet() In fact, it provides interface traversal
//hashMap Medium Node<K,V>[] table Arrays provide abstraction
final Iterator<Map.Entry<E, Count>>
backingEntries = backingMap.entrySet().iterator();
//Multiset.Entry<E> Can get map The elements in
return new Iterator<Multiset.Entry<E>>() {
Map.Entry<E, Count> toRemove;
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
return backingEntries.hasNext();
}
@Override
public Multiset.Entry<E> next() {
final Map.Entry<E, Count> mapEntry = backingEntries.next();
toRemove = mapEntry;
// It's right here Multiset.Entry It's abstracted
// Encapsulates some basic methods
/**
*Multisets.AbstractEntry
* public int hashCode() {
* Object e = this.getElement();
* return (e == null?0:e.hashCode()) ^ this.getCount();
*}
*/
return new Multisets.AbstractEntry<E>() {
@Override
public E getElement() {
return mapEntry.getKey();
}
@Override
public int getCount() {
Count count = mapEntry.getValue();
if (count == null || count.get() == 0) {
Count frequency = backingMap.get(getElement());
if (frequency != null) {
return frequency.get();
}
}
return (count == null) ? 0 : count.get();
}
};
}
@Override
public void remove() {
checkRemove(toRemove != null);
size -= toRemove.getValue().getAndSet(0);
backingEntries.remove();
toRemove = null;
}
};
}
@Override
public void clear() {
for (Count frequency : backingMap.values()) {
frequency.set(0);
}
backingMap.clear();
size = 0L;
}
@Override
int distinctElements() {
return backingMap.size();
}
@Override
public int size() {
// This Ints The method is very powerful !
return Ints.saturatedCast(size);
}
// Iterators are implemented here , The parent class also implements , I feel useless haha ! It means the same thing !
@Override
public Iterator<E> iterator() {
return new MapBasedMultisetIterator();
}
/**
* Here is a traverser ,backingMap The value stored in the , Provide delete haha ,
* Deleting duplicate elements is actually reducing the number
*/
private class MapBasedMultisetIterator implements Iterator<E> {
final Iterator<Map.Entry<E, Count>> entryIterator;
Map.Entry<E, Count> currentEntry;
int occurrencesLeft;
boolean canRemove;
MapBasedMultisetIterator() {
this.entryIterator = backingMap.entrySet().iterator();
}
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
return occurrencesLeft > 0 || entryIterator.hasNext();
}
@Override
public E next() {
if (occurrencesLeft == 0) {
currentEntry = entryIterator.next();
occurrencesLeft = currentEntry.getValue().get();
}
occurrencesLeft--;
canRemove = true;
return currentEntry.getKey();
}
@Override
public void remove() {
checkRemove(canRemove);
int frequency = currentEntry.getValue().get();
if (frequency <= 0) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
if (currentEntry.getValue().addAndGet(-1) == 0) {
entryIterator.remove();
}
size--;
canRemove = false;
}
}
@Override
public int count(@Nullable Object element) {
// Function programming , agent Maps Non empty check ! Then or value
Count frequency = Maps.safeGet(backingMap, element);
return (frequency == null) ? 0 : frequency.get();
}
// EH ~ Here is almost what we wrote ! Is it right? ?
@Override
public int add(@Nullable E element, int occurrences) {
if (occurrences == 0) {
return count(element);
}
checkArgument(occurrences > 0, "cannot be negative: %s", occurrences);
Count frequency = backingMap.get(element);
int oldCount;
if (frequency == null) {
oldCount = 0;
backingMap.put(element, new Count(occurrences));
} else {
oldCount = frequency.get();
// So careful ~~Int+Int It is estimated that it will exceed the standard , So convert to long Then I will judge !
long newCount = (long) oldCount + (long) occurrences;
checkArgument(newCount <= Integer.MAX_VALUE, "too many occurrences");
frequency.add(occurrences);
}
size += occurrences;
return oldCount;
}
@Override
public int remove(@Nullable Object element, int occurrences) {
if (occurrences == 0) {
return count(element);
}
checkArgument(occurrences > 0, "occurrences cannot be negative");
Count frequency = backingMap.get(element);
if (frequency == null) {
return 0;
}
int oldCount = frequency.get();
int numberRemoved;
if (oldCount > occurrences) {
numberRemoved = occurrences;
} else {
numberRemoved = oldCount;
backingMap.remove(element);
}
frequency.add(-numberRemoved);
size -= numberRemoved;
return oldCount;
}
// Judge not empty ~ Similar method
private static int getAndSet(@Nullable Count i, int count) {
if (i == null) {
return 0;
}
return i.getAndSet(count);
}
}
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
- 24.
- 25.
- 26.
- 27.
- 28.
- 29.
- 30.
- 31.
- 32.
- 33.
- 34.
- 35.
- 36.
- 37.
- 38.
- 39.
- 40.
- 41.
- 42.
- 43.
- 44.
- 45.
- 46.
- 47.
- 48.
- 49.
- 50.
- 51.
- 52.
- 53.
- 54.
- 55.
- 56.
- 57.
- 58.
- 59.
- 60.
- 61.
- 62.
- 63.
- 64.
- 65.
- 66.
- 67.
- 68.
- 69.
- 70.
- 71.
- 72.
- 73.
- 74.
- 75.
- 76.
- 77.
- 78.
- 79.
- 80.
- 81.
- 82.
- 83.
- 84.
- 85.
- 86.
- 87.
- 88.
- 89.
- 90.
- 91.
- 92.
- 93.
- 94.
- 95.
- 96.
- 97.
- 98.
- 99.
- 100.
- 101.
- 102.
- 103.
- 104.
- 105.
- 106.
- 107.
- 108.
- 109.
- 110.
- 111.
- 112.
- 113.
- 114.
- 115.
- 116.
- 117.
- 118.
- 119.
- 120.
- 121.
- 122.
- 123.
- 124.
- 125.
- 126.
- 127.
- 128.
- 129.
- 130.
- 131.
- 132.
- 133.
- 134.
- 135.
- 136.
- 137.
- 138.
- 139.
- 140.
- 141.
- 142.
- 143.
- 144.
- 145.
- 146.
- 147.
- 148.
- 149.
- 150.
- 151.
- 152.
- 153.
- 154.
- 155.
- 156.
- 157.
- 158.
- 159.
- 160.
- 161.
- 162.
- 163.
- 164.
- 165.
- 166.
- 167.
- 168.
- 169.
- 170.
- 171.
- 172.
- 173.
- 174.
- 175.
- 176.
- 177.
- 178.
- 179.
- 180.
- 181.
- 182.
- 183.
- 184.
- 185.
- 186.
- 187.
- 188.
- 189.
- 190.
- 191.
- 192.
- 193.
- 194.
- 195.
- 196.
- 197.
- 198.
- 199.
- 200.
- 201.
- 202.
- 203.
- 204.
- 205.
- 206.
- 207.
- 208.
- 209.
- 210.
- 211.
- 212.
- 213.
- 214.
Count Save data ~
final class Count implements Serializable {
private int value;
Count(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public int get() {
return value;
}
public void add(int delta) {
value += delta;
}
public int addAndGet(int delta) {
return value += delta;
}
public void set(int newValue) {
value = newValue;
}
public int getAndSet(int newValue) {
int result = value;
value = newValue;
return result;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return value;
}
}
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
- 24.
- 25.
- 26.
- 27.
- 28.
- 29.
- 30.
- 31.
- 32.
- 33.
- 34.
HashMultiset LinkedHashMultiset EnumMultiset
- With the above as a support , The following code is implemented in minutes !
- Use HashMultiset As an example
public final class HashMultiset<E> extends AbstractMapBasedMultiset<E> {
public static <E> HashMultiset<E> create() {
return new HashMultiset<E>();
}
/**
* Creates a new, empty {@code HashMultiset} with the specified expected
* number of distinct elements.
* Use a specific number of sizes
*/
public static <E> HashMultiset<E> create(int distinctElements) {
return new HashMultiset<E>(distinctElements);
}
// Create ha ha with a number of elements astringent
public static <E> HashMultiset<E> create(Iterable< ? extends E> elements) {
HashMultiset<E> multiset = create(Multisets.inferDistinctElements(elements));
Iterables.addAll(multiset, elements);
return multiset;
}
private HashMultiset() {
// Here is the simplest , Haha, this is HashMutiSet, Concrete Map Let subclasses decide !
super(new HashMap<E, Count>());
}
private HashMultiset(int distinctElements) {
// Create an agreed number of
super(Maps.<E, Count>newHashMapWithExpectedSize(distinctElements));
}
/**
* Serialize it , What method does Mi use to virtualize , Just how to restore
*/
@GwtIncompatible // java.io.ObjectOutputStream
private void writeObject(ObjectOutputStream stream) throws IOException {
stream.defaultWriteObject();
Serialization.writeMultiset(this, stream);
}
@GwtIncompatible // java.io.ObjectInputStream
private void readObject(ObjectInputStream stream) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
stream.defaultReadObject();
int distinctElements = Serialization.readCount(stream);
setBackingMap(Maps.<E, Count>newHashMap());
Serialization.populateMultiset(this, stream, distinctElements);
}
private static final long serialVersionUID = 0;
}
static <E> void writeMultiset(Multiset<E> multiset, ObjectOutputStream stream)
throws IOException {
int entryCount = multiset.entrySet().size();
stream.writeInt(entryCount);
for (Multiset.Entry<E> entry : multiset.entrySet()) {
stream.writeObject(entry.getElement());
stream.writeInt(entry.getCount());
}
}
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
- 24.
- 25.
- 26.
- 27.
- 28.
- 29.
- 30.
- 31.
- 32.
- 33.
- 34.
- 35.
- 36.
- 37.
- 38.
- 39.
- 40.
- 41.
- 42.
- 43.
- 44.
- 45.
- 46.
- 47.
- 48.
- 49.
- 50.
- 51.
- 52.
- 53.
- 54.
- 55.
- 56.
- 57.
- 58.
- 59.
- 60.
- 61.
This is the end of the whole project …. Experience it slowly ! Ha, it takes time to understand why others write like this !
边栏推荐
- Understanding of object
- Serialization oriented - pickle library, JSON Library
- [Yunju entrepreneurial foundation notes] Chapter II entrepreneur test 13
- (August 10, 2021) web crawler learning - Chinese University ranking directed crawler
- Summary of collection: (to be updated)
- QQ get group link, QR code
- QQ one click cookie acquisition
- How to judge the advantages and disadvantages of low code products in the market?
- 20 kinds of hardware engineers must be aware of basic components | the latest update to 8.13
- Local MySQL forget password modification method (Windows) [easy to understand]
猜你喜欢

os. Path built-in module
QQ group administrators

Detailed explanation of classic process synchronization problems
![[Yunju entrepreneurial foundation notes] Chapter II entrepreneur test 10](/img/89/1c2f98973b79e8d181c10d7796fbb5.jpg)
[Yunju entrepreneurial foundation notes] Chapter II entrepreneur test 10

JD home programmers delete databases and run away. Talk about binlog, the killer of MySQL data backup
OSI model notes
2018 meisai modeling summary +latex standard meisai template sharing
Digital simulation beauty match preparation -matlab basic operation No. 6
![Entitas learning [3] multi context system](/img/f9/a3ce86ff2121dd1043305b7e834cc5.jpg)
Entitas learning [3] multi context system
![[Yunju entrepreneurial foundation notes] Chapter II entrepreneur test 20](/img/d5/4bce239b522696b5312b1346336b5f.jpg)
[Yunju entrepreneurial foundation notes] Chapter II entrepreneur test 20
随机推荐
netstat
Experiment 7. IPv6
World document to picture
LxC shared directory permission configuration
Heartbeat报错 attempted replay attack
The latest idea activation cracking tutorial, idea permanent activation code, the strongest in history
First knowledge of spark - 7000 words +15 diagrams, and learn the basic knowledge of spark
LxC shared directory addition and deletion
QQ get group settings
template<typename MAP, typename LIST, typename First, typename ... Keytypes > recursive call with indefinite parameters - beauty of Pan China
Simple understanding of seesion, cookies, tokens
Simple understanding of string
Is Sanli futures safe? How to open a futures account? How to reduce the handling charge of futures at present?
[Yunju entrepreneurial foundation notes] Chapter II entrepreneur test 6
[Yunju entrepreneurial foundation notes] Chapter II entrepreneur test 7
Configure SSH certificate login
[Yunju entrepreneurial foundation notes] Chapter II entrepreneur test 10
Summary of Shanghai Jiaotong University postgraduate entrance examination module firewall technology
Solaris 10 network services
Day01 preliminary packet capture