当前位置:网站首页>Polymorphic system summary
Polymorphic system summary
2022-07-04 10:58:00 【Black demon fairy moon】
One 、 polymorphic
Polymorphism can be divided into two kinds : One is method polymorphism , The other is object polymorphism
1. Method polymorphism
Method polymorphism can be divided into two kinds : One is overload , The other is rewriting
heavy load : In the same class , Same method name , The relationship between methods with different parameters , Take the following example to illustrate :
public void f1() {
System.out.println(" Ha ha ha , You are a little pig ");
}
public void f1(int x){
System.out.println(" Ha ha ha ,x It's a little pig ");
}
rewrite : Occurs in two parent and child classes , follow “ With two , A large , Two small rules ”, With two : The method names of subclasses and superclasses are the same 、 Same parameter list , A large : The modifier of the subclass is larger than that of the parent , Two small : The return value type of the subclass is smaller than that of the parent class , The exception thrown by the child class is smaller than that of the parent class
class Father{
public void f1(int s)
{
System.out.println(" Parent class method ");
}
}
class son extends Father{
@Override
public void f1(int s){
System.out.println(" Subclass method ");
}
}
2. Object polymorphism
The basis of object polymorphism is inheritance , There are two kinds of object polymorphism : Transition up and down
Upward transformation : Parent class Parent instance = Subclass instance ( Automatic conversion )
Move down : Subclass Subclass instance =( Subclass ) Parent instance ( Cast )
We need to pay attention to when we are actually programming :90% All of our programming is upward transformation , Only 10% The programming of is a downward transformation , Among them, the downward transformation is basically to add attributes and functions that the parent class does not have .
(1) Upward polymorphism
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
DataBaseMessage dbm=new DataBaseMessage();
WebServerMessage wsm=new WebServerMessage();
print(dbm);
print(wsm);
}
public static void print(Message message){
message.print();
}
}
class Message{
public void print(){
System.out.println("www.mldn.cn");
}
}
class DataBaseMessage extends Message{
@Override
public void print(){
System.out.println("Oracle Database link information ");
}
}
class WebServerMessage extends Message{
@Override
public void print(){
System.out.println("Web Server link information ");
}
}
summary : Upward polymorphism can complete the unification of method parameters ( Receive or return ), For example print In the method , We have only one type of parameter, which is message, But we can use DataBaseMessage, You can also use WebServerMessage. Upward polymorphism requires attention : Inherit + rewrite , Although it is a parent type , But the method of subclass is called .
public static void print(WebServerMessage message){
message.print();
}
public static void print(DataBaseMessage message){
message.print();
}
Someone may come up with : Why not use the method of function overloading ? In this way, you can also realize the corresponding functions, just like the code above , But we should also consider the maintainability of programming . If the method of function overloading is used , Add one... At a time Message Subclasses of , We need to write it again print Overload method of , This is very difficult to maintain !
(2) Downward polymorphism
public class Test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Animal a=new Cat();
a.eat();
}
}
class Animal{
public void eat(){
System.out.println(" Small animals can eat anything ");
}
}
class Cat extends Animal{
public void play(){
System.out.println(" Kitty likes catching butterflies ");
}
public void eat(){
System.out.println(" Xiaomiao likes to eat dried fish ");
}
}
We can see from the above code that we are creating upward polymorphism ,Animal The reference variable of a Called Cat and Animal The common method , But what it does is Cat The function of is “ Xiaomiao likes to eat dried fish ”, But if you want to be Animal Type of a Realization Cat The unique method of play() What shall I do? ? Look at the code below :
public class Test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Animal a=new Cat();
a.eat();
// Then add
Cat c=(Cat)a;
c.play();
}
}
class Animal{
public void eat(){
System.out.println(" Small animals can eat anything ");
}
}
class Cat extends Animal{
public void play(){
System.out.println(" Kitty likes catching butterflies ");
}
public void eat(){
System.out.println(" Xiaomiao likes to eat dried fish ");
}
}
The running result of the program is :
Xiaomiao likes to eat dried fish
Kitty likes catching butterflies
Now someone may have doubts , Why don't I just create one Cat And then call this play() Methods? ? Let's look at the following example , We are Person1 Class Object Class equals Method , According to the rewritten condition equals Method parameters cannot be changed , So what must be passed in is object type , But the incoming obj We also want to use Person1 Inside name,age What about attributes ? We can use downward transformation !
class Person1 extends Object{
String name;
int age;
@override
public boolean equals(Object obj){
/** * Judge whether the two are the same class , such as pa.equals(" Dog ") */
if(!(obj instanceof Person1)){
return false;
}
/** * Judge whether the incoming object is empty, that is null, In this case, a null pointer error will occur */
if(obj==null){
return false;
}
/** * Judge whether they are the same object */
if(this==obj){
return true;
}
Person1 per = (Person1) obj;//obj There's no person Properties of , In order to obtain person Properties of
return this.name.equals(per.name)&&this.age==per.age;
}
But what we need to pay attention to is , Only after the successful upward transformation can we transform downward , Otherwise, the following errors will appear : That is, types cannot be converted to each other
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.ClassCastException: cn.tedu.exercise1.Animal cannot be cast to cn.tedu.exercise1.Cat
summary : Downward polymorphic usage is mainly to increase the functions that the parent class and subclass do not , Two unrelated classes cannot complete downward polymorphism , You must complete up polymorphism before you can complete down polymorphism , Otherwise, there will be an exception that the type cannot be converted . In order to ensure the security of downward transformation, we introduce instanceof The concept of :
instranceof Usage of :
Instance name instanceof Class name :a instanceof A, The return value type is boolean
Animal a=new Cat();
System.out.println(a instanceof Cat);
System.out.println(a instanceof Animal);
The result is the following code ,“instanceof” It is judgement. a yes A Example , We can see a yes Animal Example , It's also Cat Example
true
true
Then we use the following code when transforming downward :
if(a instanceof Cat){
Cat c=(Cat)a;
c.play();
}
We have now received a Animal Variable of type a, We want to use Cat Type of play Method , Let's judge first a Is it right? Cat Class instantiation , If we are going to make a downward transformation .
边栏推荐
- Software testing related resources
- CAPL: on sysVar_ Update difference on sysvar
- Strings and characters
- SSH原理和公钥认证
- TS type gymnastics: illustrating a complex advanced type
- Knapsack problem and 0-1 knapsack problem
- Function introduction of canbedded component
- How to use diff and patch to update the source code
- [Galaxy Kirin V10] [server] failed to start the network
- Canoe: the difference between environment variables and system variables
猜你喜欢
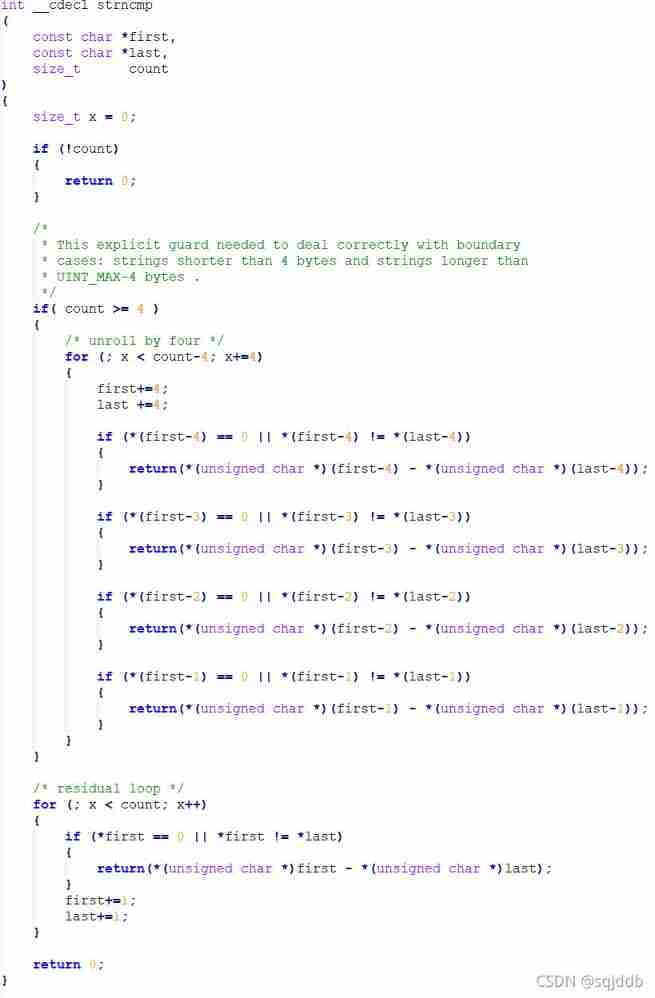
Collection of practical string functions
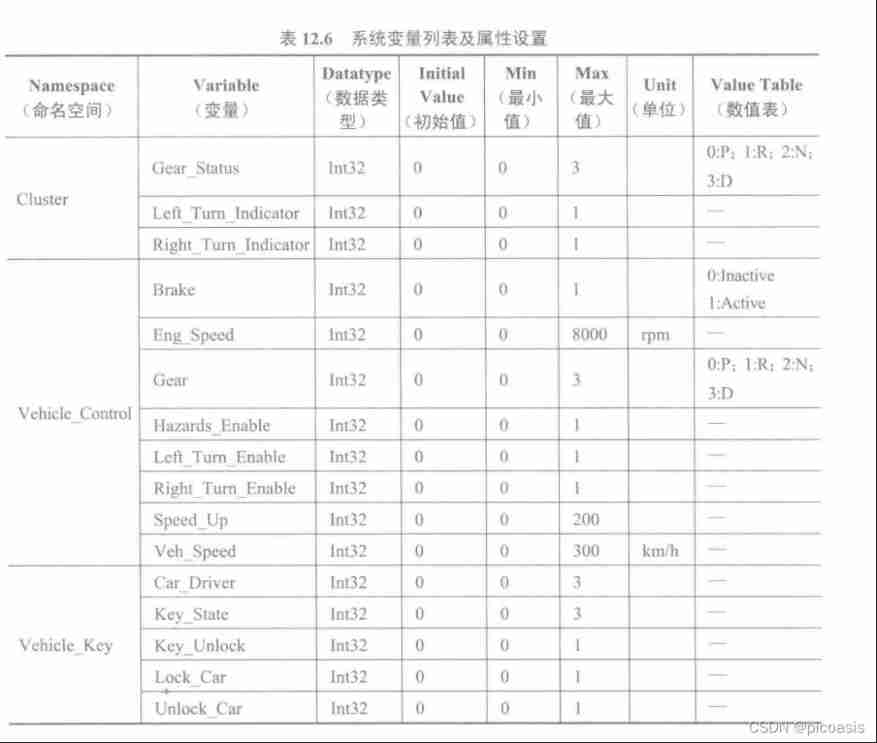
Canoe - the third simulation project - bus simulation - 3-1 project implementation

Canoe - the second simulation engineering - xvehicle - 2panel design (principle, idea)
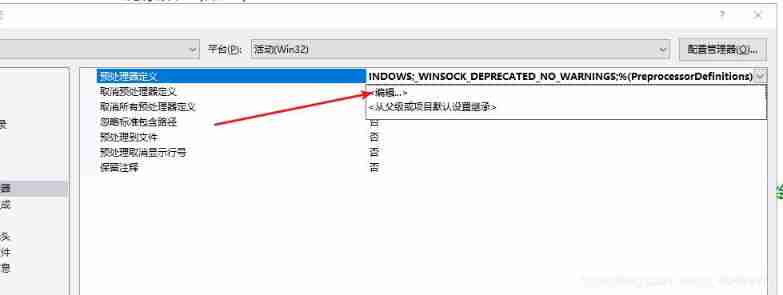
Error C4996 ‘WSAAsyncSelect‘: Use WSAEventSelect() instead or define _ WINSOCK_ DEPRECATED_ NO_ WARN
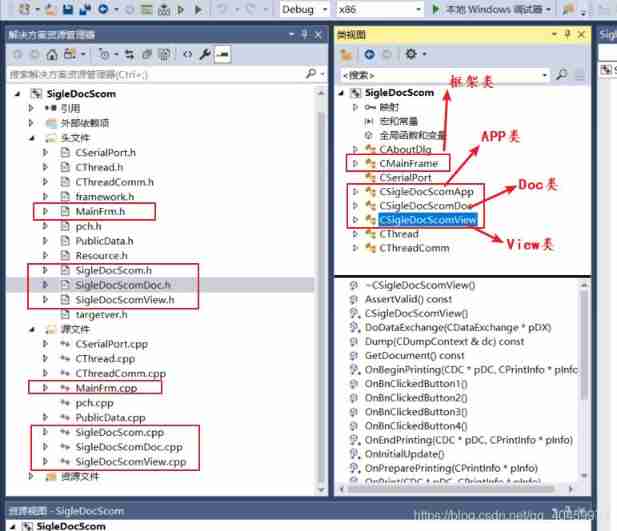
MFC document view framework (relationship between classes)
20 kinds of hardware engineers must be aware of basic components | the latest update to 8.13
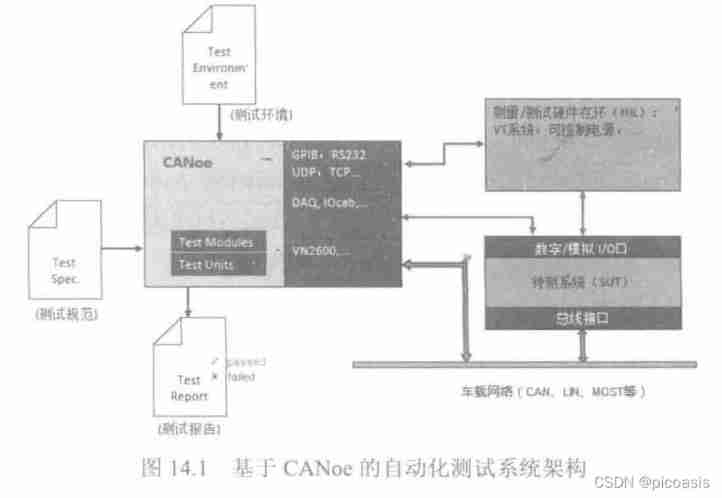
Introduction to canoe automatic test system
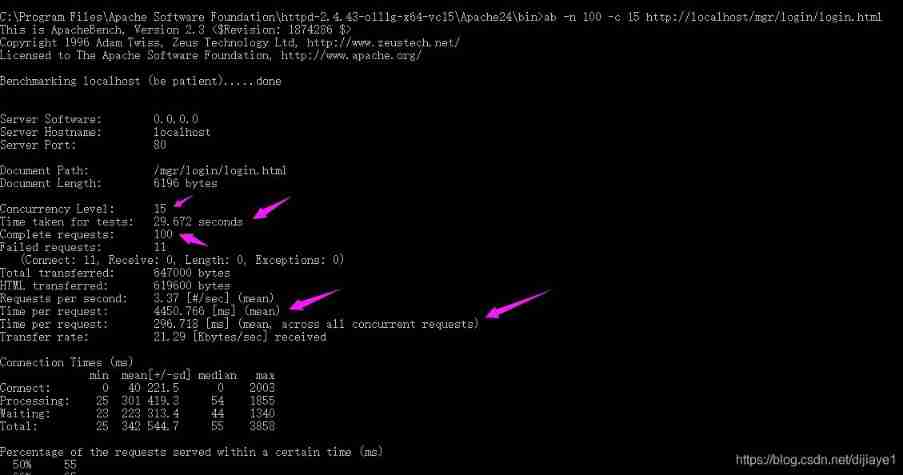
Ten key performance indicators of software applications
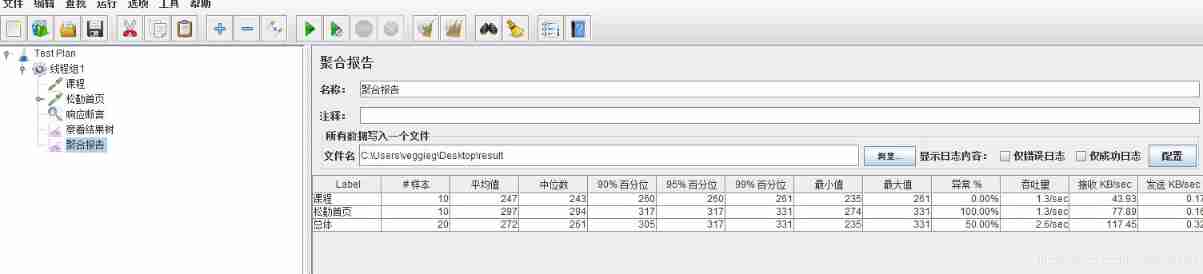
JMeter Foundation
Linked list operation can never change without its roots
随机推荐
[Galaxy Kirin V10] [server] system partition expansion
20 minutes to learn what XML is_ XML learning notes_ What is an XML file_ Basic grammatical rules_ How to parse
3W word will help you master the C language as soon as you get started - the latest update is up to 5.22
Canoe - the third simulation project - bus simulation - 3-2 project implementation
Sword finger offer 05 (implemented in C language)
DNS hijacking
Unittest+airtest+beatiulreport combine the three to make a beautiful test report
Time complexity and space complexity
Error C4996 ‘WSAAsyncSelect‘: Use WSAEventSelect() instead or define _ WINSOCK_ DEPRECATED_ NO_ WARN
Failed to configure a DataSource: ‘url‘ attribute is not specified... Bug solution
Write a program to judge whether the two arrays are equal, and then write a similar program to compare the two vectors.
2022 ape circle recruitment project (software development)
CAPL: on sysVar_ Update difference on sysvar
Discussion | has large AI become autonomous? Lecun, chief scientist of openai
/*Rewrite the program, find the value of the element, and return the iterator 9.13: pointing to the found element. Make sure that the program works correctly when the element you are looking for does
[Galaxy Kirin V10] [desktop] can't be started or the screen is black
Capl: timer event
2、 Operators and branches
XMIND installation
Elevator dispatching (pairing project) ④