当前位置:网站首页>2、 Operators and branches
2、 Operators and branches
2022-07-04 10:38:00 【She was your flaw】
Operators and branches
Operators are divided into : Numeric operators 、 Comparison operator 、 Logical operators 、 Assignment operator
One 、 Mathematical operators :+( Add )、-( reduce )、*( ride )、/( except )、%( Mod 、 modulus )、//( to be divisible by )、**( Power operation )
- +、-、*、/ And in mathematics +、-、×、÷ The function is as like as two peas
print(5 + 2) # 7
print(5 - 2) # 3
print(5 * 2) # 10
print(5 / 2) # 2.5
- % - Mod 、 modulus
x % y — seek x Divide y The remainder of
application 1: Judge whether a number can be divided by another number ( See if the remainder is 0)
print(5 % 2) # 1
print(16 % 2) # 0
print(15 % 5) # 0
application 2: Take the lower digits ( Yes 10 perhaps 10 To the power of )
num = 2398
print(num % 10) # 8
print(num % 100) # 98
num = 4621
print(num % 2) # 1
print(num % 10) # 1
print(num % 20) # 1
print(num % 100) # 21
- // - to be divisible by
x // y - x Divide y The quotient of is rounded to the small
print(5 // 2) # 2; 2 2.5 3
print(1.8 // 2) # 0.0; 0 0.9 1
print(-5 // 2) # -3; -3 -2.5 -2
application : Positive integer to low
num = 23489
print(num // 10) # 2348
print(num // 100) # 234
# practice 2: Gets the tens of the specified positive integer
num = 3945
print(num // 10 % 10) # 4
print(num % 100 // 10) # 4
# practice 3: Get the hundreds of the specified positive integer
num = 3945
print(num // 100 % 10) # 9
print(num % 1000 // 100) # 9
- ** - Power operation
x ** y - seek x Of y Power
print(2 ** 3) # 8
print(5 ** 3) # 125
print(16 ** 0.5) # 4.0
print(27 ** (1/3)) # 3.0
print(2.2 ** 2) # 2.2 * 2.2 = 4.84
print(2.0 ** 2) # 4.0
Two 、 Comparison operator :==( be equal to )、!=( It's not equal to )
Important conclusions : The result of all comparison operations is Boolean
print(10 > 20) # False ( wrong )
print(10 >= 10) # True ( Yes )
print(20 != 10) # True ( Yes )
Be careful :python The comparison operator in can express the range through concatenation like data
age = 16
print(18 <= age <= 28)
3、 ... and 、 Logical operators :and( Logic and operators )、or( Logic or operation )、not( Logic is not )
1.and - Logic and operators
(1) Application scenarios : Equivalent to life and , Used to connect multiple conditions that need to be met at the same time
(2) Operational rules : All two are True The result is True, As long as one is False The result is False
# Conditions 1 and Conditions 2
True and True - True
True and False - False
False and True - False
False and False - False
practice : Write a number that can be simultaneously 3 and 7 The condition of division
num = 67
# Conditions 1: Can be 3 to be divisible by - num % 3 == 0
# Conditions 2: Can be 7 to be divisible by - num % 7 == 0
print(' Whether it can be 3 and 7 to be divisible by :'num % 7==0) and print(num % 3==0) # False
print(' Whether it can be 3 and 7 to be divisible by :'num % 21==0) # False
2.or - Logic or operation
(1) Application scenarios : Equivalent to or in life , It is used when one of the conditions needs to be met
(2) Operational rules : As long as one is True The result is True, All two are False The result is False
# Conditions 1 and Conditions 2
True or True - True
True or False - True
False or True - True
False or False - False
gpa = 4.0
score = 95
# Conditions for scholarship : Grade point higher than 4 Or the score of gymnastics is not lower than 95
# Grade point higher than 4: gpa > 4
# The score of gymnastics is not lower than 95: score >= 95
print(' Can I get a scholarship :', gpa > 4 or score >= 95) # True
practice : Judge whether the specified year is a leap year
# Common leap year : Can be 4 Divisible but not by 100 to be divisible by : year % 4 == 0 and year % 100 != 0
# Leap year of the century : Can be 400 to be divisible by : year % 400 == 0
# Can be 4 to be divisible by : year % 4 == 0
# Can not be 100 to be divisible by : year % 100 != 0
# Can be 400 to be divisible by : year % 400 == 0
year = int(input(' Please enter the year :')) # perhaps year = 2020
print(' Is it a leap year :',(year % 4 == 0 and year % 100 != 0) or year % 400 == 0)
- not - Logic is not
not Conditions - A negative condition
(1) Application scenarios : Negate the specified condition ( Take the opposite ). Generally used for positive conditions, there are many complex situations , When the reverse condition is simple , Conditions are written backwards and then added not
(2) Operational rules : True change False, False change True
not True - False
not False - True
# Older than 18: age > 18
# Be no older than 18: age <= 18、 not age > 18
num = 18
print(num == 18)
print(not num == 18, num != 18)
# practice : Write one that cannot be 3 and 7 The condition of division
# Can be 3 Division cannot be 7 to be divisible by
# Can be 7 Division cannot be 3 to be divisible by
# Can neither be 3 It can't be divided 7 to be divisible by
print(not num % 21 == 0)
4. Short circuit operation
# Conditions 1 and Conditions 2 --- If the condition 1 yes False, So the conditions 2 Not execute
# Conditions 1 or Conditions 2 --- If the condition 1 yes True, So the conditions 2 Not execute
True and print(' And the condition of operation 2') # Both conditions are met
False and print(' And the condition of operation 2') # Conditions 1 dissatisfaction , Direct negation
False or print(' Or the condition of operation 2') # Conditions 1 dissatisfaction , Conditions 2 Satisfy , Choose the conditions 2( If the condition 1 Satisfy , You don't have to look at the conditions 2 Is it true )
- Extension of logical operators - The operand is not a Boolean
data 1 and data 2 - If data 1 The Boolean value of is True, The result is data 2, Otherwise, the result is data 1
data 1 or data 2 - If data 1 The Boolean value of is True, The result is data 1, Otherwise, the result is data 2
print(8 and 7) # 7
print(10 and 7) # 7
print(0 and 7) # 0
print(False and 7) # False
print(8 or 7) # 8
print(0 or 7) # 7
- Boolean value of data - The result of converting data to Boolean ( Of particular importance )
python All types of data in have Boolean values .
All Boolean values corresponding to zero and null values are False, The Boolean values of other data are True.
Common zero and null values : 0、0.0、0.00、’’、""、[]、()、{}、None.
print(bool(0), bool(0.0), bool('')) # False False False
print(bool(12), bool(-9.454), bool('ban')) # True True True
Four 、 Assignment operator :=、+=、*=、/=、%=、//=、**=
( important !) Important conclusions : The function of all assignment operations is to assign values to variables , Will not produce a result .( The expression of assignment operation has no result )
The left side of all assignment operators must be variables
a = 10
10 > 20
# print(a = 10) # Report errors
print(10 > 20)
- =
Use when defining variables or re assigning values to variables
name = 20
num = 10 * 20
2.=、+=、*=、/=、%=、//=、**=
requirement : The variable before the assignment symbol must be a defined variable
Variable += data --- Variable = Variable + data
b = 10
b += 2
print(b) # 12
b -= 3
print(b) # 9
b **= 2
print(b) # 81
b %= 2
print(b) # 1
3. Operator precedence
Mathematical operators > Comparison operator > Logical operators > Assignment operator
# Mathematical operators : ** > * , / , % , // > + , -
# If there are brackets, count the... In the brackets first
b = 10 + 30
c = 10 < 5 * 3 # First calculate c = 10<15 Count again c = True
print(c) # True
Branching structure
1. Process control
1) Sequential structure ( Default ) - The code is executed from top to bottom , Each statement is executed once ;
2) Branching structure - The execution of the code depends on whether the condition is true (if sentence );
3) Loop structure - Let the code repeat (for,while).
print('1') # 1
print('2') # 2
print('3') # 3
2.if Branching structure
(1) if Single branch structure - Perform an operation when conditions are met , If this condition is not satisfied, the operation will not be executed .
a. grammar :
if Conditional statements :
Code segment
b. explain
if - keyword , Fixed writing .
Conditional statements - Any expression with a result , for example : data , Operation expression ( Except assignment ), Function call expression, etc .
: - Fixed writing .
Code segment - That's right. if One or more statements that hold an indent ( At least one ); It is necessary to meet the conditions before executing the code .
c. Execution process
First, judge whether the conditional statement is True( If the result of a conditional statement is not Boolean , Just turn it into Boolean and see ), If True Just execute the code snippet , Otherwise, the code segment will not execute .
a = 100
if a > 10:
print(' Code 1') # Code 1
print(' Code 2') # Code 2
print(' Code 3') # Code 3
print(' Code 4') # Code 4
# practice : If the specified number is even, print ' even numbers '
num = 23
if num % 2 == 0:
print(' even numbers ')
if not num % 2:
print(' even numbers ')
# If the specified number is odd, print ' Odd number '
if num % 2 == 1:
print('646464') # 646464
num = 153
a = num % 10
b = num // 10 % 10
c = num // 100
if a**3 + b**3 + c**3 == num:
print(' This number is narcissus number ') # This number is narcissus number
(2) if Two branch structure - Perform an operation when conditions are met , When this condition is not satisfied, perform another operation
grammar :
''' if Conditional statements : Code segment 1 else: Code segment 2 '''
num = 30
if 220 > num:
print(123) # 123
else:
print(321)
age = 12
if age >= 18:
print(' adult ')
else:
print(' The child ') # The child
(3) if Multi branch structure - Do different things according to different conditions
if - elif - elif - … - else
''' if Conditional statements 1: Code segment 1 elif Conditional statements : Code segment 2 elif Conditional statements 3: Code segment three . . . else: Code segment N '''
score = 98
if 60 > score:
print(' Bad ')
elif score < 80:
print(' commonly ')
elif score < 90:
print(' good ')
# elif score <= 100:
else:
print(' optimal ') # optimal
choice question
print(100 - 25 * 3 % 4)What should be output ? (B)A. 1B. 97C. 25D. 0Which of the following statements is wrong (A).
A. Except for dictionary types , All standard objects can ⽤ Yu Boolean testB. The Boolean value of an empty string is FalseC. The Boolean value of an empty list object is FalseD. The value is 0 The Boolean value of any numeric object of is FalseThe value of the following expression is True Yes. (B).
A. 3>2>2B. 1 and 2 != 1C. not(11 and 0 != 2)D. 10 < 20 and 10 < 5Python No ⽀ The data types held are (A).
A. charB. intC. floatD. list( multi-select )n = 6784, You can get 7 Of ⽅ FA you (C、D).
A. n / 1000 % 100B. n % 1000 / 100C. n // 100 % 10D. n // 10 % 100 // 10shipment ⾏ The following procedure , When typing from the keyboard ⼊12, shipment ⾏ The result is (A).
x = (input()) print(type(x))A. <class 'str'>B. <class 'int'>C. errorD. <class 'dict'>The operation result of the following expression is (D ) .
a = 100 b = False print(a * b > -1)A. FalseB. 1C. 0D. True
Completion
- The function name to view the type of data in the variable is (type()).
- It is known that x = 3 == 3 , Of board ⾏ After the end , Variable x The value of is (True).
- It is known that x = 3 , So clinging ⾏ sentence x += 6 after ,x The value of is (9).
- expression 3 ** 2 The value of is (9), expression 3 * 2 The value of is (6), expression 4 ** 0.5 The value of is (2.0).
Programming questions
Write a judgment ⼀ Whether the number can be at the same time 2 and 5 Divisible conditional statement , And print the corresponding results .
q = 16 print(q % 2 == 0 and q % 5 == 0) # FalseWrite a judgment ⼀ Whether the number can be 2 perhaps 5 to be divisible by , But not both 2 perhaps 5 Divisible conditional statement , And print the corresponding results .
q = 35 input((q % 2 == 0 or q % 5 == 0)and q % 10 != 0) # TrueSuppose today's class time is 15678 second , Program to calculate the class time today ⼩ when , How many minutes? , How many seconds ; With ‘XX
when XX branch XX second ’ Of ⽅ Express .
for example :100 Seconds are expressed as 0 when 1 branch 40 second
time=15678 a=time // 3600 b=(time - a*3600) // 60 c=time - a * 3600 - b * 60 print(a,' when ',b,' branch ',c,' second ') # 4 when 21 branch 18 secondDefine two variables to save ⼀ individual ⼈ Body ⾼ And weight , The programming implementation judges this ⼈ Is your figure normal !
The formula : weight (kg) / ( body ⾼(m) The level of ⽅ value ) stay 18.5 ~ 24.9 It's normal .
Output format : If there is something wrong :True/False
# weight = 47kg height = 1.65 if 18.5 <= 47 / (1.65 ** 2) <= 24.9: print(' normal ') else: print(' Is not normal ') # Is not normalPrint according to the range of grades entered
passperhapsfail,a = 80 if a >=60: print(' pass ') else: print(' fail, ') # passPrint according to the entered age range
adultperhapsA minor, If the age is not within the normal range (0~150) PrintThis is not a person !.age = int(input(' Please enter age ')) if 18 <= age <= 150: print(' adult ') elif 0 < age < 18: print(' A minor ') else: print(' This is not a person ')Enter two integers a and b, if a-b The result is an odd number , The result is output , Otherwise, the prompt message will be output
a-b The result is not an odd number.a = 67 b = 24 if (a - b) % 2==1: print(a - b,' Is odd ') else: print(a-b, ' It's not an odd number ') # 43 Is odd
边栏推荐
- Remove linked list elements
- Dynamic memory management
- How do microservices aggregate API documents? This wave of show~
- Student achievement management system (C language)
- DNS hijacking
- Use the data to tell you where is the most difficult province for the college entrance examination!
- OSPF summary
- Es entry series - 6 document relevance and sorting
- uniapp 小于1000 按原数字显示 超过1000 数字换算成10w+ 1.3k+ 显示
- 如果不知道這4種緩存模式,敢說懂緩存嗎?
猜你喜欢

Remove linked list elements
Network connection (III) functions and similarities and differences of hubs, switches and routers, routing tables and tables in switches, why do you need address translation and packet filtering?
Realsense of d435i, d435, d415, t265_ Matching and installation of viewer environment
On binary tree (C language)

Knapsack problem and 0-1 knapsack problem
![[machine] [server] Taishan 200](/img/e5/69a1a4ca04814a033a77d3cb4601b3.jpg)
[machine] [server] Taishan 200
Four characteristics and isolation levels of database transactions
![[Galaxy Kirin V10] [server] soft RAID configuration](/img/d5/789387613fafc18f623d0cff45093b.jpg)
[Galaxy Kirin V10] [server] soft RAID configuration
Rhcsa day 10 operation
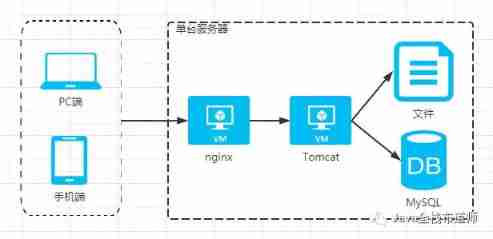
Evolution from monomer architecture to microservice architecture
随机推荐
Debug:==42==ERROR: AddressSanitizer: heap-buffer-overflow on address
Safety reinforcement learning based on linear function approximation safe RL with linear function approximation translation 2
Reprint: summation formula of proportional series and its derivation process
Article publishing experiment
Seven examples to understand the storage rules of shaped data on each bit
System. Currenttimemillis() and system Nanotime (), which is faster? Don't use it wrong!
From programmers to large-scale distributed architects, where are you (I)
Crawl Zhejiang industry and trade news page
Latex insert picture, insert formula
Does any teacher know how to inherit richsourcefunction custom reading Mysql to do increment?
DDL language of MySQL database: create, modify alter, delete drop of databases and tables
Static comprehensive experiment ---hcip1
【FAQ】华为帐号服务报错 907135701的常见原因总结和解决方法
183 sets of free resume templates to help everyone find a good job
RHCE - day one
Press the button wizard to learn how to fight monsters - identify the map, run the map, enter the gang and identify NPC
[FAQ] summary of common causes and solutions of Huawei account service error 907135701
Rhcsa day 10 operation
Development guidance document of CMDB
【Day2】 convolutional-neural-networks