当前位置:网站首页>Digital simulation beauty match preparation -matlab basic operation No. 6
Digital simulation beauty match preparation -matlab basic operation No. 6
2022-07-04 10:56:00 【Eric%258436】
** If there is a mistake , Thank you for correcting **
If there is a mistake , Thank you for correcting , Please send a private message to the blogger , There is a red envelope for hard work , Worship “ one-word teacher ”.
Please find the paragraphs you need according to the table of contents
Introduction : This blog is organized for individuals MATLAB Learning notes , If there is a mistake , Thank you for correcting . System learning , Welcome to continue to pay attention , Follow up updates
Java communication qq Group 383245788
order
The purpose of this article is to record the experience of preparing for the personal digital simulation American competition . Reprint please indicate the source .
MATLAB Basics
●MATLAB yes Matrix Laboratory ( Matrix lab ) Abbreviation .
● Open programming language , It can be used for high-performance engineering calculation .
● The basic data unit is a matrix without dimension limitation .
●MATLAB It's a lot of math 、 Standard guidance tools for elementary and advanced courses in engineering and Science .
● It is often used in industry for product research 、 Development and analysis .
●MATLAB The version number of mainly includes the release time .3 Release in June a , 9 Release in June b.
MATLAB The system mainly consists of five parts , Respectively :
● Desktop tools and development environment : Graphical user interface , Convenient for users MATLAB Functions and files for , Include MATLAB Desktop and command line windows , Editors and debuggers , Code analyzer and help for browsing 、 working space 、 File browser .
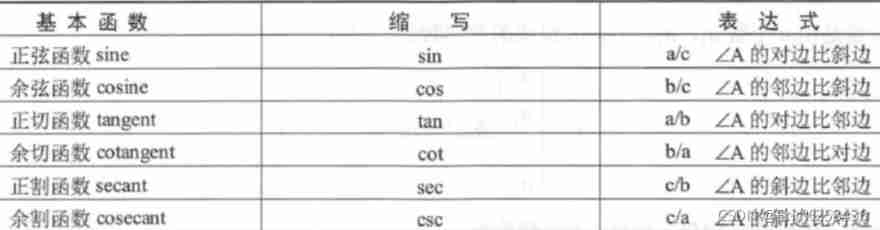
● A library of mathematical functions : Including a large number of computational algorithms , From elementary functions ( Such as addition 、 sine 、 Cosine etc ) To complex higher functions ( Such as matrix inversion 、 Matrix eigenvalues 、 Bessel function and fast Fourier transform ).
● Language :MATLAB Language is an advanced language / Array language , With program flow control 、 function 、 data structure 、 Input and output and object-oriented programming . The user can synchronize the input statement with the execution command in the command line window , To quickly create a rapid abandonment program , It's fine too Write a large and complex M File and then run together , To create complete large-scale applications . Graph processing : Convenient data visualization function , To graphically represent vectors and matrices , You can also perform image processing 、 Graphic labels 、 Animation and expression drawing , And build on MATLAB The complete graphical user interface of the application .
● External interface :MATLAB Language can communicate with C Language and other languages .
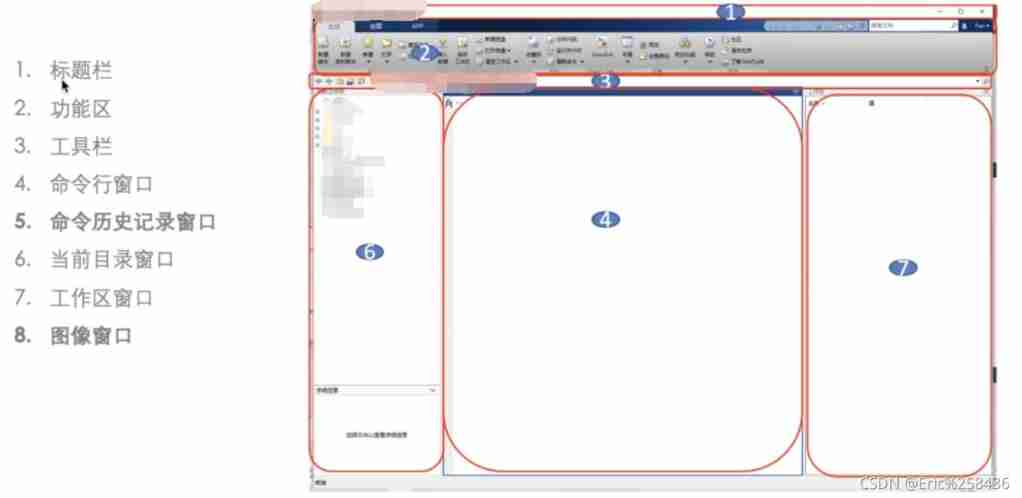
MATLAB Work interface
MATLAB Our working interface is the most direct contact , A preliminary understanding of the components can help you get familiar with MATLAB Use .
MATLAB The working interface is simple , It's mainly made up of the title bar 、 Functional area 、 The toolbar 、 The current directory window (Current Folder, The current folder window )、 Command line window (CommandWindow)、 The workspace window (WorkSpace) And command history window .
MATLAB 2019 The command history window is no longer directly displayed in. You need to input instructions to call up .
Basic operation , newly build , open , Import , Adjust the layout .
help system :1. Query function ( Know the function name ) : help+ Function name
2. MATLAB Online help : helpwin
3. Query function ( I don't know all the function names , Fuzzy query ) : lookfor+ The function of information
4. Memory variable list : who
5. Memory variable information : whos
6. List of files in the directory : what
7. Determine file location : which
8. Variable test function : exist
MATLAB command
Command input prompt “》”
enter Execute a line or a paragraph of command
Do not accept Chinese command input , The path should avoid Chinese
MATLAB The format requirements for commands are relatively strict , Must be entered in the format , If you don't know the format or calling method , You can view the help system .
MATLAB Your commands must be logical , All variables must exist before .
MATLAB Function symbol : as follows> English semicolon ; Do not display results on the command line .
MATLAB Common commands>MATLAB data type
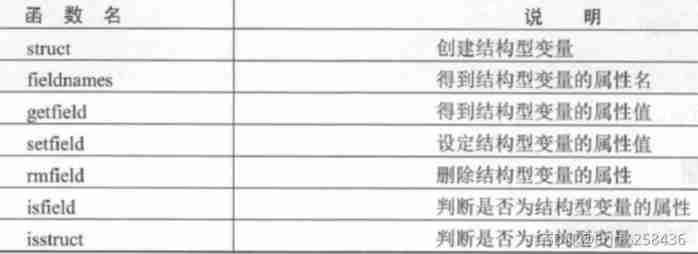
MATLAB The main data types include : Numbers 、 character string 、 vector 、 matrix 、 Unit data and structural data . Matrix is MATLAB The most basic data type in a language , In essence, it's an array . A vector can be thought of as having only one row or one - Columns of the matrix ( Or an array ) ; Numbers can also be seen as matrices , That is, a row column matrix : Strings can also be seen as matrices ( Or an array ), Character matrix ( Or an array ) : Both unit data and structural data can be regarded as multidimensional arrays with arbitrary forms of arrays as elements , It's just that the elements of structured data have attribute names .
You can check Baidu for details , It is different from other programming languages , But not much . There are several more data types . The plural 、 Matrix these can talk with Baidu .Variable name
Variable names must start with a letter , It can be followed by any letter 、 Number or underscore .
Variable names are case sensitive .
No more than name of variable 31 Characters , The first 31 Characters after 1 character will be ignored .
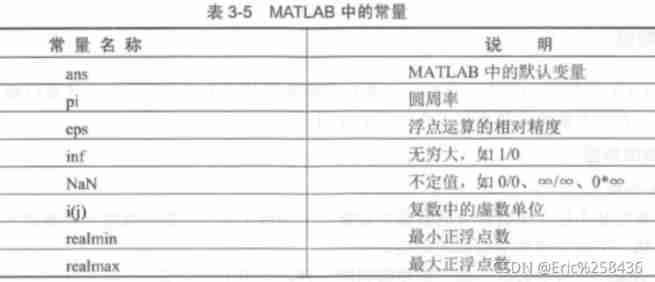
MATLAB Common constants
Basic knowledge of
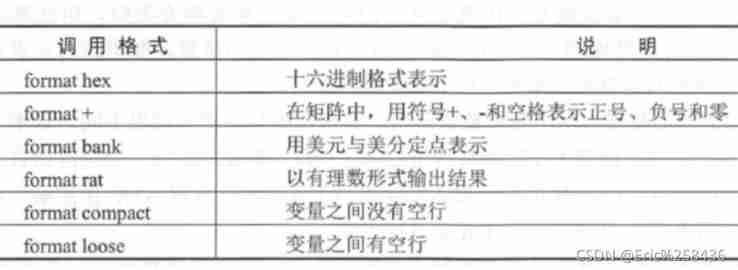
format : Change the form of digital display
Just change the display form , The actual stored value does not change
MATLAB Arithmetic operator
> among , Arithmetic operator plus 、 reduce 、 Multiplication and power and traditional meaning , On top of 、 reduce 、 Multiplication and power are similar , The usage is basically the same , And dot multiplication 、 Operations such as point power have their special side . Point operation refers to the point-to-point operation of elements , That is, the operation between elements in the matrix . Point operation requires that the variables involved in the operation are in the structure . It must be similar .MATLAB The division operation of is special . For simple values , Arithmetic left division is also different from arithmetic right division . Arithmetic right division is the same as traditional division , namely a/b=a+ b; Arithmetic left division is the opposite of traditional division , namely a\b=b Death a. For matrices , Arithmetic right division A/B Solving a linear equation is equivalent to XA=B Solution : Arithmetic left division is equivalent to solving linear equations AX=B Solution . Point left division and point right division are similar to the above point operations , Is the point division of the variable corresponding to the element . stay MATLAB Carry out simple numerical operation under , Just put the expression at the prompt (>>) Then directly enter , And press Enter Press the key .
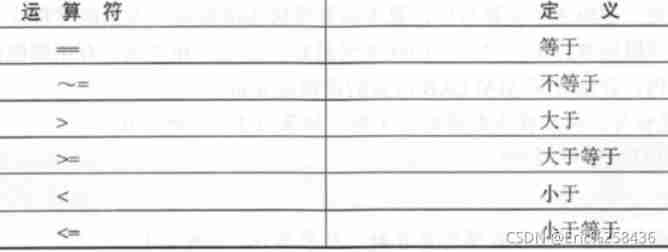
MATLAB Relational operator
These operators are not introduced in detail , I'm not going to introduce , I have a simple understanding of Baidu , Just like other languages , Don't introduce too much .
MATLAB Logical operators
MATLAB Common mathematical functions
Four operations of complex number : High school knowledge , See things for yourself , Advanced operations ,B There are also many station videos , A look at will understand
Trigonometric functions
MATLAB vector
The generation of vectors : Direct input method 、 Colon method and use MATLAB There are three ways to create functions .
- Direct input method . Generate row vectors separated by spaces and commas , Form column vectors separated by semicolons .[1,2,3]、[1 2 3]、[1;2;3]
- Colon method . The basic format is x=first:increment:last, Representation creation - A from first Start , To last end , The increment of the data element is increment Vector . If the increment is 1, . The way to create vectors above is abbreviated as x =first:last.x=1:10、x=0:2:10
- Utilization function linspace Create a vector .linspace By directly defining the number of data elements , Instead of creating vectors in increments between data elements . The calling format of this function is as follows .linspace (first_ value, last_ value, number). This call format represents the creation of a - From the first_value Start last_value end , contain number Vectors of elements .
A reference to a vector element
Vector operations : Four operations and rank conversion
Dot product operation of vector : stay MATLAB in , For vector a、b, Its dot product can be used a.*b obtain , You can also use the command directly dot Work out , The calling format of this command
The cross product of vectors : We know , In space analytic geometry , The result of the cross multiplication of two vectors is one - A vector passing through the intersection of two intersecting vectors and perpendicular to the plane where the two vectors are located . stay MATLAB in , The cross product operation of a vector can be performed by a function cross To achieve .
The mixed product of vectors
MATLAB polynomial
An expression is an algebraic expression , It is made up of numbers and letters , Such as 1,5a,sdef, ax"+b. Formula is divided into monomial formula and polynomial :
- Monomials are numbers Product with letters , A single number or letter is also a monomial , Such as 3ab.N How many? The sum of monomials is called polynomials , Such as 3ab+5cd.
- In Higher Algebra , Polynomials can generally be expressed as : ax" +ax"-+…+a. x+a,. This is a n (>0) Sub polynomial ,a.,a, And so on are the coefficients of polynomials .
stay MATLAB in , The vector composed of the coefficients of the polynomial is expressed as p=ao,.,an_,a,2x’-x2 +3<>[,-1,0,3]. Zero in the coefficient cannot be omitted . Transform the operation on polynomials into the operation on vectors , It is one of the most basic operations in mathematics .
Polynomial creation
Polynomial operations :MATLAB There is no special function for polynomial addition and subtraction , The four operations of polynomials are actually the four operations of coefficients corresponding to polynomials . The four operations of polynomials refer to the addition of polynomials 、 reduce 、 ride 、 In addition to the operation . It should be noted that , Add up 、 The two vectors of subtraction must be equal in size . Different orders , Lower order polynomials must be filled with zeros , Make it have the same order as higher-order polynomials . The addition of polynomials 、 The subtraction operation is directly used “+”、“_” To achieve .
- Multiplication : The multiplication of polynomials uses functions conv(pl,p2) To achieve , Equivalent to performing convolution of two arrays .
- division :deconv
Derivation : Functions for polynomial derivative operations polyder To achieve . Its calling format is :polyder§. among p Is the coefficient vector of a polynomial
Special variables :
Correlation function
matrix
Definition :MATLAB Take matrix as the basic unit of data operation , This makes the matrix operation very simple 、 convenient 、 Efficient . The matrix is made up of mn Number ay(i= 1,2.**,m;j= 1,2…,n) In line m That's ok n Array table , be called mxn matrix , It can also be recorded as a or A(mn). among ,i Number of lines ,j A number of columns . if m=n, Then the matrix is n Order matrix (n Square matrix ).
establish :
It is most convenient to input the matrix directly by line on the keyboard 、 The most common way to create a numerical matrix , Especially suitable for small simple matrices . When creating a matrix in this way , We should pay attention to the following points .
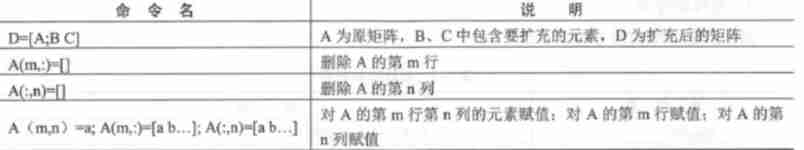
- Enter the matrix with “[ ]” Give it an identifier , All elements of the matrix must be in parentheses .
- There are spaces between the elements of the same row of the matrix ( There is no limit to the number of ) Or comma separated , Lines are separated by semicolons or enter .
- The size of the matrix does not need to be predetermined The righteous .
- Matrix elements can be run Calculate the expression .
- if “[ ]” There is no element in , Represents a null matrix .
- If you don't want to show intermediate results , It can be used “;” end .
In addition to the direct input method , It can also be used M File generation method and text file generation method, etc .
utilize M File creation : When the scale of the matrix is relatively large , The direct input method is clumsy , Travel mistakes are not easy to modify . To solve these problems , The matrix to be input can be written into a text file first according to the format , And put this file as m Give it an extension , namely M file .M The file is a - Can be planted in MATLAB Text files running in the environment , It can be divided into command file and function file . What is mainly used here is imperative M file , Use its simple form to create a large matrix . stay MATLAB Input in the command line window M file name , The large matrix to be input can be input into memory .
Users can directly use functions to generate some specific matrices , The common functions are as follows .
eye(n) // establish nxn Unit matrix .
eye(m,n) // establish mxn The identity matrix of .
eye(size(A)) // Create with A A unit matrix of the same dimension .
ones(n) // establish nxn whole 1 matrix .
ones(m,n) // establish mxn whole 1 matrix .
ones(size(A)) // Create with A All with the same dimension 1 front .
zeros(m,n) // establish mxn whole 0 matrix .
zeros(size(A)) // Create with A All with the same dimension 0 front .
rand(n) // stay [0,1] Create a... In the interval nxn Uniformly distributed random matrix .
rand(m,n) // stay [0,1] Create a... In the interval mxn Uniformly distributed random matrix .
rand(size(A)) // stay [0,1] Create an interval with A A uniformly distributed random matrix with the same dimension .
compan(P) // Creating a coefficient vector is P The adjoint matrix of polynomials .
diag(v) // Create a vector v The elements in are diagonal matrices .
hilb(n) // establish nxn Of Hilbert matrix .
magic(n) // Generate n Second order magic cube matrix .
sparse(A) // The matrix A Convert to sparse matrix form , by A The nonzero elements and subscripts of form a sparse matrix S. if A Itself is a sparse matrix , Then return to A In itself .
Matrix operation
The elements in a matrix are the same as those in a vector , You can extract references 、 Edit and modify .
Modification of matrix elements : After the matrix is established , You also need to modify its elements .
Variable dimension of matrix
The variable dimension of a matrix can be represented by the symbol “:” Law and reshape Function method .reshape The call form of the function is as follows .reshape(X,m,n): Change the dimension of a known matrix into m That's ok n Columns of the matrix .
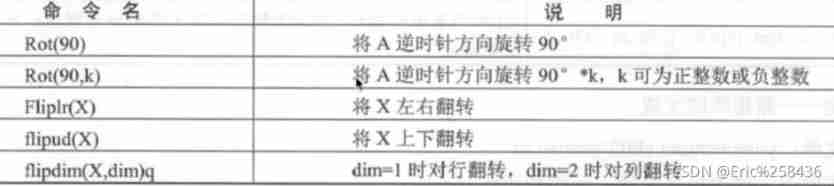
The turn of the matrix / Flip :
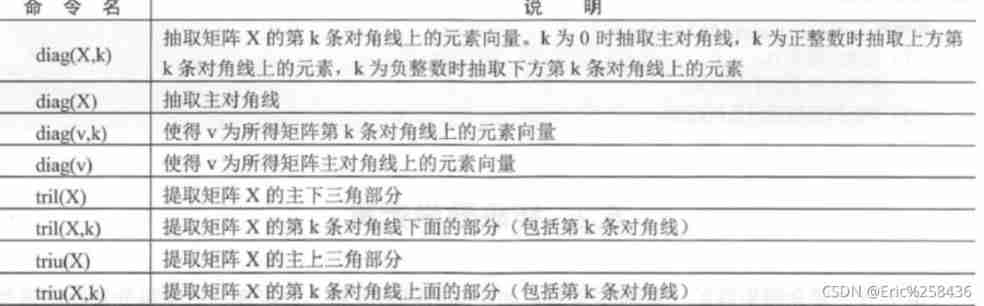
Matrix extraction : The extraction of matrix elements mainly refers to diagonal elements and upper elements ( Next ) Extraction of triangular matrix .
Matrix operation : linear algebra
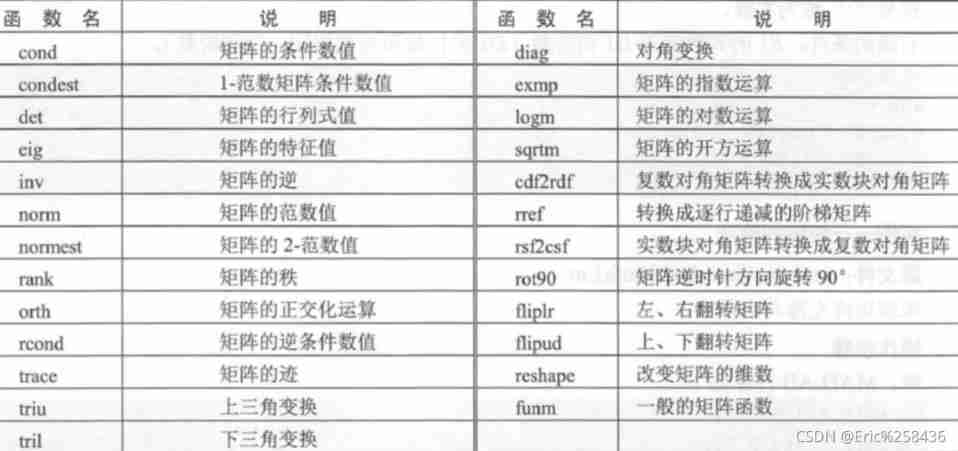
Common functions
Inverse matrix : linear algebra
norm :
Singular value decomposition (SVD) Modern numerical analysis ( Especially numerical calculation ) One of the most basic and important tools , Therefore, it is widely used in practical engineering .
So-called SVD Decomposition means to decompose mxn matrix A Expressed as 3 A matrix product form : USvT, among U by mxm Unitary matrix ,V by nxn Unitary matrix ,S It's a diagonal matrix , Its diagonal elements are matrix A And satisfy s≥s2≥≥s,>s=.≈s,=0,r For matrix A The rank of . stay MATLAB in , This decomposition is through svd Command to achieve .
Symbolic operations
In Mathematics 、 Physics, mechanics and other disciplines and engineering applications , There are often problems with symbolic operations . stay MATLAB in , Symbolic operation is to obtain more accurate numerical solutions , But numerical operations are easier for readers to understand , So in certain circumstances , Use symbols or numerical expressions for different operations .
Symbolic operation is MATLAB Extension of numerical calculation , In the operation process, take the symbolic expression or symbolic matrix as the operation object , The combination of symbolic calculation and numerical calculation is realized , Make the application more flexible .
The conversion between symbolic expression and numerical expression is mainly through function eval and sym Realized . among ,eval Function to convert a symbolic expression to a numeric expression , The function sym Used to convert a numeric expression to a symbolic expression .
The elements in the symbol matrix and symbol vector are symbolic expressions , Symbolic expressions are composed of symbolic variables and numeric values . The elements in the symbolic matrix are any symbolic expression without an equal sign , The length of each symbolic expression can be different . The elements separated by spaces or commas in the symbol matrix specify the elements of different columns , Elements separated by semicolons specify elements in different rows .
There are the following ways to generate a symbolic matrix .
Direct input : When entering the symbol matrix directly , Every row of the sign matrix All should be enclosed in square brackets , And ensure that the length of element strings in each row of the same column is the same , Therefore, insert spaces in shorter strings to make up the length , Otherwise, the program will report an error .Transform numerical matrix into symbolic matrix : stay MATLAB in , Numerical matrices cannot be directly involved in symbolic operations , So we must first convert it into a symbolic matrix . And numerical matrix - equally , The sign matrix can be transposed 、 Inverse and other operations , But the function of symbolic matrix is different from that of numerical matrix . This section will introduce .
Transpose operation of symbolic matrix : The transpose operation of the symbolic matrix can be carried out through the symbol “’” Or functions transpose To achieve .
Determinant operation of symbolic matrix determinant operation of symbolic matrix can be through function determ or det To achieve , Where the matrix must use a square matrix .
Symbol simplification : Symbolic simplification can be achieved through functions simple and simplify To achieve .
The fraction is divided into two parts : The numerator and denominator of the symbolic expression can be solved by the function numden To achieve .
MATLAB Two dimensional drawing
Basic drawing commands
- plot command
plot Command is the most basic drawing command , It is also the most commonly used drawing command . When executed plot On command , The system will automatically create a new graphic window .
If there is a graphic window before , Then the system will draw the graphics on the recently opened graphics window , The original graphics will also be overwritten .
The format of the command can be through help Inquire about , I won't repeat it here . A glance will , Forget to check , Just watch more and remember .X and Y Must be a vector of the same dimension . Draw to X Abscissa 、Y Is the curve of the ordinate .
- If X It's a vector ,Y When it's a matrix .X The dimension of should be the same as Y One dimension of is equal . Draw multiple curves with different colors , The number of curves is equal to Y Another dimension of ,X As the abscissa of the curve .
- If the matrix is a square matrix , draw Y Each column pair of X The curve of .(MATLAB The principle of column priority )
- If X It's a matrix ,Y It's a vector , ditto , But this time Y Abscissa
- If X and Y Is a homodimensional matrix , With X As abscissa 、 With Y The corresponding column element is used as the ordinate to draw the curve ,, The number of curves equals the number of columns .
- linespace Parameters :
LineSpec Is a character vector or string containing symbols , Used to set the shape of the drawn data points 、 Size and color , And the shape of the line between data points 、 thickness 、 Color, etc. . in application ,LineSpec It is a combination of some letters or symbols , It can be omitted . When omitted ,MATLAB The default settings will be used , The curve adopts solid line , Different curves will be colored in a certain order .( Different versions Ben MATLAB The default color order is different ) If you ignore linetype , Specify only tags , Then only the mark is displayed when drawing , Do not show lines .
Example :’ One or’ It's with Red dotted line with circular mark . The basic linetype is given below 、 Marking symbols and colors , More complex ones will be introduced later .
plot(x1 ,y1…n,yn) Draw multiple x、y The corresponding graph , All lines use the same coordinate area .
plot(x1,y1,LineSpec…,xn,yn,LineSpecn) Set the linetype of each line 、 Marking symbols and colors . When use ,X、y、LineSpec Triples and x、y It can be mixed up .- plot(y) establish y A two-dimensional line graph of each value index in the data .
If y It's a real vector , be x The axis scale ranges from 1 To length(y). If y Is a real matrix , Draw the curve of the subscript corresponding to the element value of each column by column , The number of curves is equal to y Columns of . If y It's a complex matrix , Draw the abscissa of the real part of the element by column , Multiple curves whose imaginary part is ordinate . Equivalent to plot(real(y),imag(y)).plot(y,LineSpec) Set the line type 、 Marking symbols and colors .
More linear and marking operations , Look up the documents , Easy to learn , Add a few parameters to achieve , It's simple . Length is too long , What I summarized is not as neat and up-to-date as other people's documents .
- fplot command
Special commands for drawing unary functions .
Adaptively guide the selection of data points .
- The smooth points are sparse
- The steep place is a little dense
Image ratio plot Smoother and more accurate .
Grammar is mostly related to plot be similar , For details, you can check the document .
- ezplot command
Special drawing commands for symbolic functions . This function is not recommended , Functions can be defined by fplot Instead of .
The default domain is [-2Tπ,2π].fun2(x,y) Definition is x and y Implicit functions between .
ezplot(fun2) What you're drawing is fun2(x,y)=0 Image .
ezplot(funx,funy) The default domain of is 0<t<2π.
ezplot(…,fig) Draw the drawing window to fig In the marked picture window , It can be done with . Any combination of input parameters in the above syntax .- subplot command
Split several required windows in the same graphics window .
subplot(m,n,p) command
Divide the current window into mXn A view area , and p Create a coordinate area at the specified location . When numbering , Line first .
'replace’ Parameters , Delete location p Existing coordinate area and create a new coordinate area .
‘align’ Parameters , Default parameters , Create a new coordinate area .
subplot(m,n,p,ax) Set the existing coordinate area ax Convert to sub graph in the same graph window .
subplot(‘Position’ ,pos) stay pos Create a coordinate area at the specified custom location .
1.pos The format is [left bottom width height].
2. 1. If the new coordinate area overlaps with the existing coordinate area , The existing coordinate area will be replaced .
Drawing commands in different coordinate systems
- Polar system
polarplot ( polar: It is not recommended to use , The function can be replaced by the former .)
polarplot(theta,rho) Draw lines in polar coordinates , from theta Represents polar angle , In radians ,rho Indicates pole diameter .theta and rho can Take all as vectors or matrices , You can also use a vector \ A matrix , And plot similar .
polarplot(rho) At equal intervals ( Be situated between 0 and 2π Between ) draw rho Radius value in .
polarplot(z) draw z Complex values in . The module length of the complex number corresponding to the polar diameter , The polar angle corresponds to the principal value of the argument of the complex number .
polarplot(pax,_ ) Use pax Specified coordinate area .
Detailed check help file .- Semi logarithmic coordinate system
Semi logarithmic coordinates are very common in Engineering .semilogx Used to draw x The axis is logarithmic 、y Curve whose axis is linear coordinate .
semilogy Used to draw x The axis is a linear coordinate 、y Curve whose axis is logarithmic coordinate . Logarithm as 10 The common logarithm of the base .
In addition to semi logarithmic coordinate drawing ,MATLAB It also provides drawing commands in the double logarithmic coordinate system loglog, Usage and semilogx Similar .
Check the documents in detail , And plot They are very similar .- Double logarithmic coordinate system
- double y Axis coordinate system
When the ordinate values of the two curves to be represented on the same graph are not the same - Range time , You can use double y Axis coordinates .
plotyy: It is not recommended to use .
yyaxis: Create with two y The figure of the axis .
plotyy Different formats of commands : Use function The specified drawing function generates graphics ,function can Specify as plot,semilogx, semilogy, loglog and stem Function of .
Graphics window
MATLAB Not only good at numerical calculation related to matrix , It also has powerful graphic functions . utilize MATLB It can easily realize the visualization of a large number of data calculation results, and it can also easily modify and edit the graphical interface . The graphics window is MATLB A platform for data visualization . The graphics window and the command line window are independent of each other , You can get various high-quality graphics according to the needs of programmers .
- Creation of graphic window
figure command :
figure: Create with default attribute values - A picture window .-figure(Name,Value): Use one - One or more names - Value to modify the properties of the drawing window for the group parameter .f=figure(_ ): return Figure object , It can be . After use f Query and modify attributes .figure(f): take f Specify as the current drawing window -figure(n): Create a number by Figure(n) Graphics window ,n Is a positive integer .- figure Some of the properties of
Look up the documents- Other relevant orders
set The command can be used to set the attribute values of the graphics window .
get The command can be used to query the attribute value of the graphics window .
close The command can be used to close the graphics window .
clf The command can be used to empty the current drawing window .- Use of toolbars
Adjust the curve , angle , The highlighted , Dimension coordinate values, etc .
Graphic labels
Through previous commands and operations , It is already available in the graphics window , Draw basic graphics . But only with these operations draw graphics , It's just a list of drawing results , Lack of decoration of graphics 、 explain . Missing Title 、 Legend and other information for explanation .MATLAB Provides a large number of functions and commands , You can decorate and annotate two-dimensional graphics . At the same time, it can also complete some special graphics The draw .
- Graph property settings
Coordinate system and axis : function axis() use help Command details
Graphic annotation : fill()、title()、xlable()、text()、gtext() See the name, think of the meaning , Don't understand help
legend command Don't understand help
grid command : Grid line of coordinate area (on,off,minor) Don't understand help- Special graphics :
Two dimensional bar chart :bar/barh
Three dimensional bar chart :bar3/bar3h
Area map :area
The pie chart :pie
Three dimensional pie chart :pie3
two-dimensional histogram :hist/histogram/rose/polarhistogram
Error bar :errorbar
Needle pattern :stem
Arrow diagram :quiver
MATLAB Three dimensional drawing
plot3() function It won't be help
Curve drawing :ezplot3()
3D mesh function :mesh()
Grid generation :meshgrid
Color :hidden function
premium :meshc()
Brother function :meshz()
Brother function :ezmesh() Not recommended
Brother function :fmesh() Instead of ez Function of recommend
3D surface function :surf. spread function surfc and surfl
cylinder :cylinder
sphere :sphere
Contour map :contour3
Sequence and limit
- sum function
s=sum(A,all) Calculation A The sum of all the elements in . This syntax applies to R2018b And higher . Unsupported can be used sum nesting .
s=sum(A,dim) Along the dimension dim Return the sum . If A It's a matrix , that sum(A,2) Calculate lines and .
s=sum(A,vecdim) According to the vector vecdim Dimension pairs specified in A The sum of the elements of . If A It's a matrix , that sum(A,[1 2]) Is to seek A The sum of all the elements in . Apply to R2017b Later versions .
s=sum(_ ,nanflag) can To choose whether to include NaN value ,'includenan’ Meeting Include ,‘omitnan’ It does not include .
nansum Functions can be evaluated without NaN The sum of other elements of the value , And sum(, ‘omitnan’) Equivalent .
cumsum Function can be used to calculate the cumulative sum .
cumsum(A): And sum(A) similar .
cumsum(A,dim): And sum(A,dim) class like .
cumsum( ,direction): Calculate the cumulative sum in the specified direction . The default is ’forward’, 'reverse’ For reverse order .
cumsum(_ ,nanflag): Specifies whether the calculation ignores NaN value .- Other summation functions
cumtrapz Function can be used to calculate cumulative trapezoidal numerical integral .
q=cumtrapz(y) Calculate according to unit spacing by trapezoidal method y Approximate cumulative integral of . If y It's a vector , Then calculate the cumulative integral . If y It's a matrix , Then calculate each - Cumulative integral of column . If y Is a high-dimensional array , Then the pair size is not equal to 1 Calculate the cumulative integral in the first dimension of .
q=cumtrapz(x,y) according to x Specified coordinate or scalar spacing pair y Do integral . If x It's a vector , Then the length must be the same as y The first one of is not equal to 1 The dimensions of are the same . If x It's scalar , Represents spacing , here cumtrapz(x,y)=x*cumtrapz(y).
q=cumtrapz(_ ,dim) Along the dim Calculate the integral of the specified dimension .- prod quadrature
prod Function can be used to find the product of array elements .prod The basic usage of function is the same as sum Function similar to . If you enter an empty matrix , The result is 1. If A by single type , Then the result is single type , If it is other numeric and logical data types , The result will be double type .- Other product functions
cumprod Function can calculate cumulative product , Usage and cumsum similar .
factorial Function can be used to calculate factorial . You can calculate the factorial of scalar , You can also calculate the factorial of a matrix .
gamma Function can be used to calculate gamma The value of a function .- limit
limit Function can be used to find the limit of function .
limit(f,var,a) Calculation function f In variables yar near a The limit of time . Omit var Use the default variable .
limit(f) The calculation function is in 0 The limits of .
limit(f,var,a,left’) Calculation function f In variables var near a The left limit of time .
limit(f,var,a,‘right’ ) Calculation function f In variables var near a The right limit of time .- derivative
According to the definition of derivative , Use limit Function calculates derivative .
diff Function can be used to calculate the derivative of function directly .
dif(,n): Calculation function f Of n Derivative, , The default is 1.
dif(f,var,n): Calculate multivariate functions f About variables x Of n Order partial derivative .- Difference approximate derivative
When the step size is small , The ratio of difference to step length can be approximated as derivative .- Sum of series
symsum Function can be used to calculate the sum of series .
F=syssum(f,k,a,b): Calculation k from a Fetch b when , Series f And . Parameters can be used Inf To represent infinity . If the series does not converge , The result of summation of infinite series is Inf.
F=symsum(f,k): Calculate the sum of indefinite series . The recurrence formula satisfied : F(k+ 1)-F(k)= f(k)
- just so so Sum the sequence of equal ratio and the sequence of equal difference- You can also calculate indefinite integral
symsum(f): Calculation function f The indefinite integral of .
symsum(f, var): Calculate multivariate functions f About variables var The indefinite integral of .MATLAB It is not possible to calculate the sum of all series , If the closed form solution cannot be found , The result is still the original statement .- integral
int Function can be used to calculate definite integral .
int(f,a,b): Calculation function f In the interval [a,b] The definite integral over .
int(f,x,a,b): Calculate multivariate functions about x In the interval [a,b] The definite integral over .
int(f): Calculation function f The indefinite integral of .
int(f,x): Calculation function f About x The indefinite integral of .- Double integral
dblquad Function can be used to calculate double integral , It is not recommended to use .
integral2 Function can realize this function , Replace the former .
q=integral2(fun,xmin,xmax,ymin,ymax) In the plane area xminSx sxmax and ymin sy Symax Upcomputed function z=fun(x,y) Integral .
q=integral2(_, Name,Value) You can add attribute names and values later- Taylor expansion
T=taylor(f,var) Calculation f In variables var=0 Nearby sixth order Taylor expansion .
T=taylor(f,var,a) Calculation f In variables var=a Nearby sixth order Taylor expansion . You can add attribute names and values later . Get more items by adding attributes .- Fourier transform and inverse transform
fourier(f) You can calculate f The Fourier transform of , In the end w Is the transformed variable .
fourier(f,transVar) use transVar Instead of w.
fourier(f,var,transVar) Yes var The variables represented by do Fourier transform .
ifourir(F) It can be used to calculate F Inverse Fourier transform , The variable after inverse transformation is x.
ifourier(F,transVar) And ifourier(F,var,transVar) And fourier similar .- The fast Fourier transform
y=ff(x): Calculate with fast Fourier transform algorithm X Discrete Fourier transform based on Wavelet Transform .
If x It's a vector , Then the Fourier transform of the vector is returned .
If x It's a matrix , Then the Fourier transform of each column is returned .
y=fft(x,n) return n Point discrete Fourier transform , If no n, be Y The size and X identical
If x It's a vector , The length is less than n Then fill 0, Greater than n Then cut off .
If x It's a matrix , Then the Fourier transform of each column is returned .
y-fft(x.n,dim) Return along dimension dim The Fourier transform of .
ft2 Function can be used to calculate two-dimensional Fourier transform .
tshift Function moves the DC component to the center of the spectrum .
ift Functions and ifft2 Function is one-dimensional and two-dimensional inverse fast Fourier transform .
iftshift Function to offset fftshift Translation of function to zero frequency .- Laplace transform
laplace Functions and ilaplace Function can be used to calculate Laplace transform and inverse Laplace transform , Usage and fourier and ifourier similar .
边栏推荐
- [Galaxy Kirin V10] [server] grub default password
- [Galaxy Kirin V10] [desktop] build NFS to realize disk sharing
- [Galaxy Kirin V10] [desktop] login system flash back
- How do microservices aggregate API documents? This wave of show~
- Knapsack problem and 0-1 knapsack problem
- Remove linked list elements
- Performance test process
- From programmers to large-scale distributed architects, where are you (I)
- Canoe - the third simulation project - bus simulation-1 overview
- Sword finger offer 05 (implemented in C language)
猜你喜欢
![[Galaxy Kirin V10] [desktop] printer](/img/ab/066923f1aa1e8dd8dcc572cb60a25d.jpg)
[Galaxy Kirin V10] [desktop] printer

Knapsack problem and 0-1 knapsack problem
![[Galaxy Kirin V10] [desktop] cannot add printer](/img/a6/28e4aa31e805a018e6db2b32ca1be0.jpg)
[Galaxy Kirin V10] [desktop] cannot add printer
Network connection (III) functions and similarities and differences of hubs, switches and routers, routing tables and tables in switches, why do you need address translation and packet filtering?
Software sharing: the best PDF document conversion tool and PDF Suite Enterprise version sharing | with sharing

Application and Optimization Practice of redis in vivo push platform
The most detailed teaching -- realize win10 multi-user remote login to intranet machine at the same time -- win10+frp+rdpwrap+ Alibaba cloud server
Virtual machine configuration network

Recursion and divide and conquer strategy
From programmers to large-scale distributed architects, where are you (I)
随机推荐
What if the book written is too popular? Author of "deep reinforcement learning" at Peking University: then open the download
DML statement of MySQL Foundation
Elevator dispatching (pairing project) ③
Canoe - the third simulation project - bus simulation-1 overview
[Galaxy Kirin V10] [server] NFS setup
Introduction to tree and binary tree
Canoe - the third simulation project - bus simulation - 2 function introduction, network topology
[test theory] test process management
First article
Jemeter plug-in technology
Snake (C language)
[Galaxy Kirin V10] [desktop] build NFS to realize disk sharing
Swagger and OpenAPI
Const's constant member function after the function; Form, characteristics and use of inline function
Canoe - the second simulation engineering - xvehicle - 2 panel design (operation)
JMeter correlation technology
The most ideal automated testing model, how to achieve layering of automated testing
Postman interface test
[Galaxy Kirin V10] [desktop] login system flash back
Using SA token to solve websocket handshake authentication