当前位置:网站首页>Recursion and divide and conquer strategy
Recursion and divide and conquer strategy
2022-07-04 10:25:00 【sqjddb】
* Recursion and divide and conquer strategy
>> The basic idea of recursion and divide and conquer
Sometimes it is difficult to solve a big problem directly , The idea of divide and conquer is : Divide the big problem into smaller ones , In order to break each one , Divide and rule . Apply divide and conquer means repeatedly , Make the sub problem smaller , The solution of the subproblem is usually the same as that of the original problem , Naturally leads to recursive processes . Divide and conquer and recursion are twin brothers , Many efficient algorithms have been produced .
>> The advantages and disadvantages of recursion

>> Conditions for the application of divide and conquer
The problems that can be solved by divide and conquer generally have the following characteristics :
• The problem can be easily solved by reducing its scale to a certain extent
• The problem can be divided into several smaller problems of the same size
• The solution of the subproblem can be combined into the solution of the problem
• The subproblems are independent of each other , I.e. Zi Wen
There are no common sub problems between the questions
>> The idea of balanced subproblem

>> Recursive classic program


①Ackerman function
Ackerman function A(n,m) There are two independent integer variables m>=0,n>=0, Its definition is as follows
A(1,0)=2;
A(0,m)=1 m>=0
A(n,0)=n+2 n>=2
A(n,m)=A(A(n-1,m),m-1) n,m>=1
This is a double recursive function  A(n,m) Each independent variable of defines a univariate function . The third form of recursion defines the function “ Add 2”.
A(n,m) Each independent variable of defines a univariate function . The third form of recursion defines the function “ Add 2”.
m=1 when , because A(1,1)=A(A(0,1),0)=A(1,0)=2
as well as A(n,1)=A(A(n-1),1),0)=A(n-1,1)+2 (n>1), therefore A(n,1)=2n (n>=1), namely A(n,1) Defined the function “ ride 2”
When m=2 when , because A(1,2)=A(A(0,2),1)=A(1,1)=2
A(n,2)=A(A(n-1,2),1)=2A(n-1,2), therefore A(n,2)=2^n
And so on 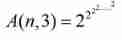
among 2 The number of layers is n.
A(n,4) The growth rate of has become unimaginably fast , It is impossible to write a general term formula to express this function
② The total permutation problem
Design a recursive algorithm to generate n Elements {r1,r2,…,rn} The whole arrangement
R={1,2,3,4}
Output :1234 1243 1324 …… 4312 4132 4123
The procedure is as follows :
Template<class type>
void Perm(Type list[ ], int k, int m)
{
if (k==m)
{
for (int i=0;i<=m;i++)
cout<<list[i];
cout<<endl;
}
else
for(i=k;i<=m;i++)
{
Swap(list[k],list[i]);
Perm(list,k+1,m);
Swap(list[k],list[i]);
}
}
Core statement :
Swap(list[k],list[i]);
Perm(list,k+1,m);
Swap(list[k],list[i]);

The process is tedious , Thinking about the meaning of recursion is of great help in clarifying ideas
③ Integer partition problem
Integer partition problem : Put a positive integer n Expressed as the sum of several positive integers
n=n1+n2+…+nk, n1≥n2≥…≥nk≥1, k≥1
Find out how many ways to divide :
 The procedure is as follows :
The procedure is as follows :
int a(int n, int m)
{
if((n<1) or (m<1))
return 0;
if((n==1) or (m==1))
return 1;
if(n<m)
return q(n,n);
if(n==m)
return q(n,m-1)+1;
return q(n,m-1)+q(n-m,m);
}
④ The hanotta problem
Take the example of Hanoi tower to explain the recursive idea 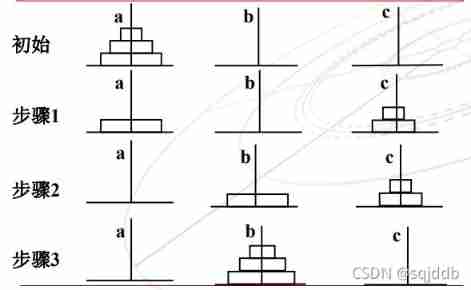
So the core code has three lines , Explain the following :
// Parameter means : hold A Move to according to the rules on B On ,C For the auxiliary tower
Void Hanoi(int n, int A, int B, int C)
{
if(n>0)
{
Hanoi(n-1,A,C,B); // hold n-1 From the A Move to C,B For the auxiliary tower
Move(n,A,B); // Take the biggest one from A Move to B
Hanoi(n-1, C,B,A); // hold n-1 From the C Move to B,A For the auxiliary tower
}
}
Actually Tower of Hanoi's non recursive program It's also worth learning
>> Deep understanding of divide and conquer
The time complexity of the algorithm :
Want to deeply understand the time complexity of the algorithm , Readers are advised to make clear Algorithm time complexity The calculation method of
Good article recommends  The following examples analyze the time complexity of the algorithm , Understand the above k,m The meaning of
The following examples analyze the time complexity of the algorithm , Understand the above k,m The meaning of
① Two point search
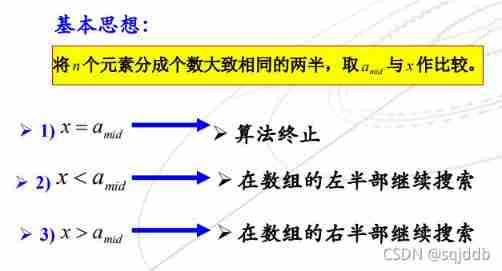


The loop is executed O(logn) Time , The comparison operation in each cycle requires O(1) Time 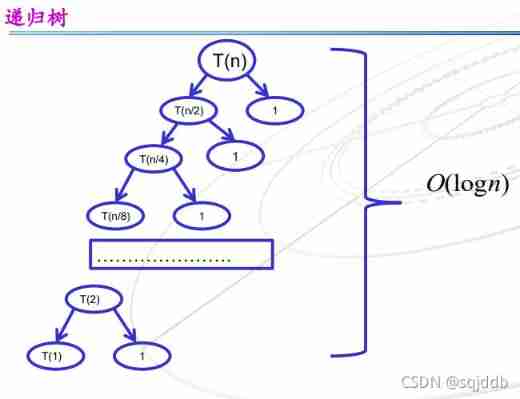
Recursive tree drawing 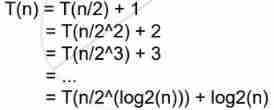

② Multiplication of large integers

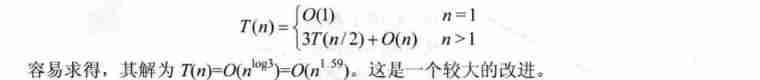 The procedure is as follows :
The procedure is as follows :
③Strassen Matrix multiplication
Matrix multiplication :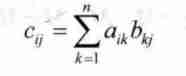
 To reduce time complexity , Made such an attempt :
To reduce time complexity , Made such an attempt :
Strassen To reduce the time complexity

④ Chessboard coverage
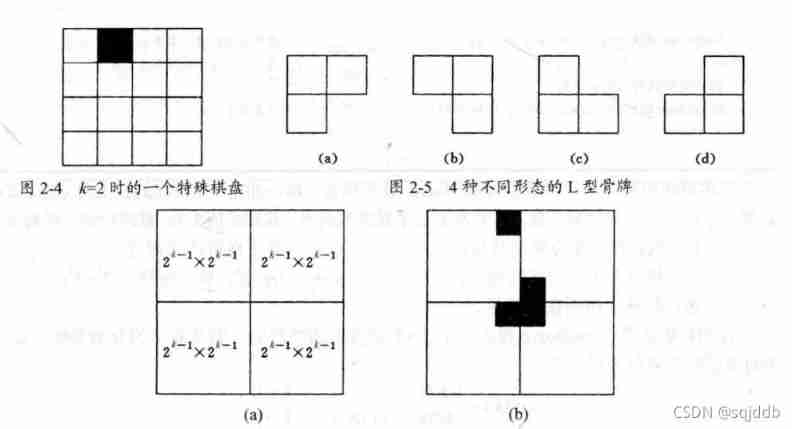


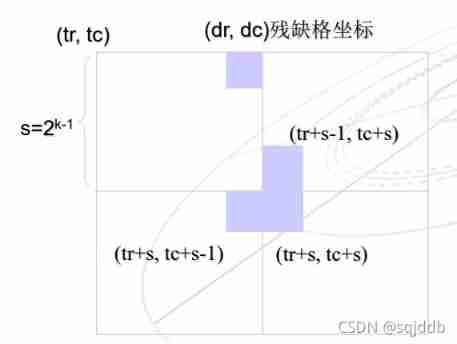
The procedure is as follows : Be careful :tile Global variable
Be careful :tile Global variable
Complexity analysis :
边栏推荐
- Vanishing numbers
- 【FAQ】华为帐号服务报错 907135701的常见原因总结和解决方法
- 转载:等比数列的求和公式,及其推导过程
- Summary of reasons for web side automation test failure
- VLAN part of switching technology
- RHCE day 3
- Rhcsa day 10 operation
- 2020-03-28
- Latex error: missing delimiter (. Inserted) {\xi \left( {p,{p_q}} \right)} \right|}}
- Custom type: structure, enumeration, union
猜你喜欢
Debug:==42==ERROR: AddressSanitizer: heap-buffer-overflow on address
Occasional pit compiled by idea

Application of safety monitoring in zhizhilu Denggan reservoir area

Development guidance document of CMDB
Si vous ne connaissez pas ces quatre modes de mise en cache, vous osez dire que vous connaissez la mise en cache?
Hands on deep learning (39) -- gating cycle unit Gru
DML statement of MySQL Foundation

Basic principle of servlet and application of common API methods
VLAN part of switching technology
【Day1】 deep-learning-basics
随机推荐
基于线性函数近似的安全强化学习 Safe RL with Linear Function Approximation 翻译 1
From programmers to large-scale distributed architects, where are you (2)
BGP advanced experiment
What are the advantages of automation?
BGP ---- border gateway routing protocol ----- basic experiment
[200 opencv routines] 218 Multi line italic text watermark
Map container
Hands on deep learning (45) -- bundle search
Sword finger offer 31 Stack push in and pop-up sequence
Online troubleshooting
2021-08-11 function pointer
Four characteristics and isolation levels of database transactions
Exercise 7-8 converting strings to decimal integers (15 points)
Rhcsa learning practice
Button wizard business running learning - commodity quantity, price reminder, judgment Backpack
Laravel文档阅读笔记-How to use @auth and @guest directives in Laravel
按键精灵打怪学习-识别所在地图、跑图、进入帮派识别NPC
Hands on deep learning (44) -- seq2seq principle and Implementation
Network disk installation
Occasional pit compiled by idea