当前位置:网站首页>Dynamic memory management
Dynamic memory management
2022-07-04 09:47:00 【skeet follower】
Catalog
1. Why dynamic memory management exists
2. The introduction of dynamic memory function
3. Common dynamic memory errors
4.2 The characteristics of flexible arrays
4.3 The use of flexible arrays
4.4 Advantages of flexible arrays
1. Why dynamic memory management exists
Of course, we have mastered the way of memory development :
int a=10;// local variable - Four spaces are opened up in the stack space
int g_a=10;// Global variables - Static zone

But there are two characteristics of the way to open up space :
struct stu{
char name[20];
int age;
}
int main(){
int n=0;
scanf("%d",&n);
struct stu arr[n];
return 0;
}Yes C99 This standard is introduced in , But many compilers do not support this standard , So it will report an error , Therefore, this method is not feasible .
2. The introduction of dynamic memory function
2.1malloc and free
Dynamic memory development function code example :
void* malloc (size_t size);
This function requests a piece of memory Continuously available Space , And return the pointer to this space .
- If the development is successful , Then return a pointer to open a good space .
- If the development fails , Returns a NULL The pointer , therefore malloc The return value of must be checked .
- The type of return value is void* , therefore malloc Function doesn't know the type of open space , Use yourself to decide when using .
void free (void* ptr);
free Function is used to release memory opened dynamically .
- If parameters ptr The pointed space is not opened dynamically , that free The behavior of a function is undefined .
- If parameters ptr yes NULL The pointer , Then the function does nothing .
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
int main()
{
// Apply to memory 10 An integer space
int* p = (int*)malloc(10 * sizeof(int));//int* Force type to integer
if (p == NULL) {
// Failed to open up space , The reason for the printing error
printf("%s\n", strerror(errno));
}
else {
// Normal use space
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
*(p + i) = i;
}
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
printf("%d", *(p + i));
}
}
// When dynamic memory space is not in use
// It should be returned to the operating system
free(p);
p = NULL;
return 0;
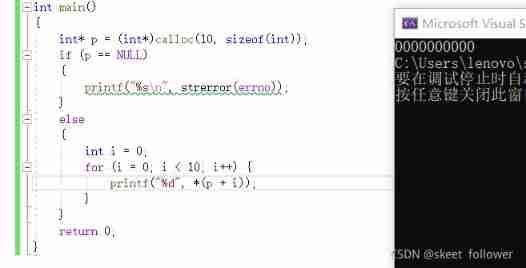
}2.2calloc
calloc Function dynamic memory allocation . The prototype is as follows :
void* calloc (size_t num, size_t size);
- The function is for num Size is size The elements of open up a space , And initialize each byte of the space to 0.
- And functions malloc The only difference is calloc Initializes each byte of the requested space to full before returning the address 0. The code is as follows :
2.3realloc
- realloc Functions make dynamic memory management more flexible .
- Sometimes we find that the application space is too small in the past , Sometimes we think the application space is too large , That's for reasonable time memory , We will make flexible adjustments to the size of memory . that realloc Function can be used to adjust the dynamic memory size . The function prototype as follows :void* realloc (void* ptr, size_t size);
- ptr Is the memory address to be adjusted ,size New size after adjustment , The return value is the starting memory position after adjustment .
- This function adjusts the size of the original memory space , The original data in memory will also be moved to new Space .
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
int main()
{
// Apply to memory 10 An integer space
int* p = (int*)malloc(20);//int* Force type to integer
if (p == NULL) {
// Failed to open up space , The reason for the printing error
printf("%s\n", strerror(errno));
}
else {
// Normal use space
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
*(p + i) = i;
}
}
int* ptr = realloc(p, 40);
if (ptr != NULL) {
p = ptr;
int i = 0;
for (i = 5; i < 10; i++) {
*(p + i) = i;
}
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
printf("%d", *(p + i));
}
}
free(p);
p = NULL;
return 0;
}
3. Common dynamic memory errors
- Yes NULL Dereference operation of pointer
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
int main()
{
int* p = (int*)malloc(40);
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
*(p + i) = i;
}
free(p);
p = NULL;
return 0;
}In case malloc Failed to open up space , be p Will be assigned a null pointer , therefore malloc When using, you must judge whether the return value is a null pointer .
- Cross border access to dynamic open space
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
int main()
{
int* p = (int*)malloc(5 * sizeof(int));
if (p == NULL) {
return 0;
}
else {
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
*(p + i) = i;
}
}
free(p);
p = NULL;
return 0;
}
malloc Only opened up 5 An integer element , and for Loop access 10 Caused cross-border visits , Program crash .
- Use of non dynamic memory free Release
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
int main()
{
int a = 10;
int* p = &a;
*p = 20;
free(p);
return 0;
}
- Use free Release a piece of dynamic memory
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
int main()
{
int* p = (int*)malloc(40);
if (p == NULL) {
return 0;
}
else {
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
*p++ = i;
}
}
free(p);
p = NULL;
return 0;
}
p Changes have taken place in this process , It is not our complete development space , If you want to release, you can only release it from the starting position of the opening , So wrong .
- Multiple releases of the same dynamic memory
void test()
{
int *p = (int *)malloc(100);
free(p);
free(p);// Repeat release
}- Dynamic memory forget to release ( Memory leak )
void test()
{
int *p = (int *)malloc(100);
if(NULL != p)
{
*p = 20;
}
}
int main()
{
test();
while(1);
}No space is released after use , Will continue to consume memory , It may cause the server to crash .
4. Flexible array
4.1 Concept of flexible array
Maybe you've never heard of Flexible array (flflexible array) The concept , But it does exist . C99 in , The most in the structureThe latter element is allowed to be an array of unknown size , This is called 『 Flexible array 』 member
The code is as follows :
typedef struct st_type
{
int i;
int a[];// Flexible array members
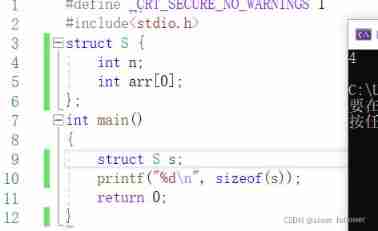
}type_a;4.2 The characteristics of flexible arrays
- A flexible array member in a structure must be preceded by at least one other member .
- sizeof The size of the structure returned does not include the memory of the flexible array .
- Structures that contain flexible array members use malloc () Function to dynamically allocate memory , And the allocated memory should be larger than the size of the structure , Adapt to Expected size of the flexible array .
4.3 The use of flexible arrays
Code 1:
#include<stdio.h>
struct S {
int n;
int arr[0];
};
int main()
{
struct S* s = (struct S*)malloc(sizeof(struct S) + 5 * sizeof(int));
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
s->arr[i] = i;
}
struct S* ps = realloc(s, 44);
if (ps!= NULL) {
s = ps;
for (i = 5; i < 10; i++) {
s->arr[i] = i;
}
}
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
printf("%d", s->arr[i]);
}
free(s);
s = NULL;
return 0;
}Code 2:
#include<stdio.h>
struct S {
int n;
int* arr;
};
int main()
{
struct S* ps = (struct S*)malloc(sizeof(struct S) + 5 * sizeof(int));
ps->arr = malloc(5 * sizeof(int));
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
ps->arr[i] = i;
}
for (i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
printf("%d\n", ps->arr[i]);
}
int* ptr = realloc(ps->arr, 10 * sizeof(int));
if (ptr!= NULL) {
ps->arr = ptr;
for (i = 5; i < 10; i++) {
ps->arr[i] = i;
}
}
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
printf("%d ", ps->arr[i]);
}
free(ps->arr);
free(ps);
ps = NULL;
return 0;
}4.4 Advantages of flexible arrays
By comparing the above code 1 And code 2, Code 1 The implementation of has two benefits :
1. Convenient memory release
2. Conducive to access speed
边栏推荐
- 法向量点云旋转
- 2022-2028 global tensile strain sensor industry research and trend analysis report
- Exercise 9-5 address book sorting (20 points)
- Kubernetes CNI 插件之Fabric
- C language pointer interview question - the second bullet
- Hands on deep learning (33) -- style transfer
- Qtreeview+ custom model implementation example
- Deadlock in channel
- Nuxt reports an error: render function or template not defined in component: anonymous
- Write a mobile date selector component by yourself
猜你喜欢
自动化的优点有哪些?
MySQL develops small mall management system
C语言指针面试题——第二弹
PHP personal album management system source code, realizes album classification and album grouping, as well as album image management. The database adopts Mysql to realize the login and registration f
How can Huawei online match improve the success rate of player matching
ASP. Net to access directory files outside the project website
MATLAB小技巧(25)竞争神经网络与SOM神经网络

C # use gdi+ to add text to the picture and make the text adaptive to the rectangular area
mmclassification 标注文件生成

2022-2028 global optical transparency industry research and trend analysis report
随机推荐
C # use gdi+ to add text with center rotation (arbitrary angle)
2022-2028 global gasket metal plate heat exchanger industry research and trend analysis report
JDBC and MySQL database
Hands on deep learning (33) -- style transfer
Global and Chinese market of wheel hubs 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
Write a jison parser from scratch (3/10): a good beginning is half the success -- "politics" (Aristotle)
Kotlin 集合操作汇总
The child container margin top acts on the parent container
Problems encountered by scan, scanf and scanln in golang
Write a jison parser from scratch (4/10): detailed explanation of the syntax format of the jison parser generator
Summary of the most comprehensive CTF web question ideas (updating)
Lauchpad X | 模式
How does idea withdraw code from remote push
Multilingual Wikipedia website source code development part II
Les différents modèles imbriqués de listview et Pageview avec les conseils de flutter
查看CSDN个人资源下载明细
【leetcode】29. Divide two numbers
Deadlock in channel
2022-2028 global special starch industry research and trend analysis report
Flutter 小技巧之 ListView 和 PageView 的各種花式嵌套
