当前位置:网站首页>Four characteristics and isolation levels of database transactions
Four characteristics and isolation levels of database transactions
2022-07-04 10:21:00 【Java full stack preacher】
Better reading experience : Four characteristics and isolation levels of database transactions
1. brief introduction
1.1. What is the business
Business (Transaction) The database is operated by one or more SQL Statement is an integral unit of work , Either of these operations are completed , Either roll back . A transaction often corresponds to a complete business .
1.2. Transaction key process
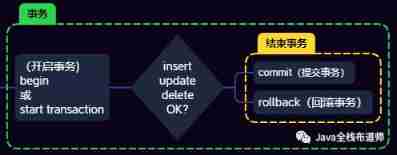
2. Four characteristics of transaction (ACID)
2.1. Atomicity (atomicity)
The transaction is a whole , Can not be further divided ( Just like atoms in chemistry can't be divided anymore ), All requests DML Statement operations must succeed or fail at the same time .
2.2. Uniformity (consistency)
The data before and after the transaction should be consistent . Such as :A Yes 10 Yuan ,B Yes 20 Yuan .B turn 10 Yuan to A, After the transfer A+B Money or 30 element .
2.3. Isolation, ( isolation )
Different transactions are isolated from each other .
2.4. persistence (durability)
When the business is over , Memory data persistent disk .
3. Concurrency issues
3.1. Two kinds of data loss
The first is when two transactions operate on the same data at the same time , When the first transaction rolls back , Override the update data of the second transaction that has been committed , The second transaction causes data loss .
The second refers to when two transactions operate on the same data at the same time , After the first transaction successfully commits the modification result , The modification result that has been committed by the second transaction is covered , Data loss for the second transaction .
3.2. Dirty reading
Dirty read refers to that one transaction reads the data of another uncommitted transaction .
Such as : Business A Read transaction B Uncommitted data , If the business B Not implemented correctly , Roll back , The transaction A What you read is dirty data .
The key point of the problem : Read **「 Not submitted 」** Transaction data .
3.3. It can't be read repeatedly
Non repeatable reading means that a transaction repeatedly reads the same row of data twice , But the results are different .
Such as : During the execution of a transaction , Another transaction commits and modifies the data being read by the current transaction
The key point of the problem : The same transaction occurs more than once **「 The reading conditions are the same 」 The data of , Other affairs are ok 「 Modify this condition 」** The data of .
3.4. Fantasy reading
Unreal reading is that the results of the same two queries of the same transaction are inconsistent .
Such as : During the execution of a transaction , Another transaction adds or deletes data , As a result, the number of the same query results is different for two times .
The key point of the problem : The same transaction occurs more than once **「 Read data with the same conditions 」, Other affairs are ok 「 Add or delete 」** The data of .
*
solve the problem
*
4. Isolation level
There are two types of transactions : Read and write transactions .
4.1. Read uncommitted (Read UnCommitted)
- Multiple transactions can read uncommitted data at the same time
- When a transaction is read, other transactions can also be written
- When a transaction is written, other transactions can also be read
- But not at the same time
Problem solved : Prevent lost updates
4.2. Read submitted (Read Committed)
- Multiple transactions can read committed data at the same time
- When a transaction is read, other transactions can also be written
- When a transaction is written, other transactions prohibit all operations
- But not at the same time
Problem solved : It can effectively prevent dirty reading .
4.3. Repeatable (Repeatable Read)
- Multiple transactions can read committed insert data at the same time , Cannot read the submitted modification data
- When a transaction is read, other transactions can only be read and written
- When a transaction is written, other transactions prohibit all operations
- But not at the same time
Problem solved : It can effectively prevent non repeatable reading and dirty reading (InnoDB The storage engine also solves the unreal reading problem ).
4.4. Serialization (Serializable)
- Transactions can only be executed one after another , Cannot execute concurrently .
Problem solved : It can effectively prevent dirty reading 、 No repeated reading or phantom reading .
But this level can lead to a lot of timeout and lock contention , It is rarely used in practical applications .
5. Some common operations of transactions
5.1. Set transaction auto commit
-- View the current session
show session variables like 'autocommit';
-- View global sessions
show global variables like 'autocommit';
-- Set current session
set session autocommit = 0|1|ON|OFF;
-- Set up global session
set global autocommit = 0|1|ON|OFF;
Options :0|1|ON|OFF
- close :0 and OFF
- Turn on :1 and ON
5.2. Set isolation level
-- View the current session
select @@tx_isolation;
select @@session.tx_isolation;
-- View global sessions
select @@global.tx_isolation;
show global variables like 'tx_isolation';
-- Set current session
set tx_isolation=' Isolation level ';
-- Set up global session
set global transaction isolation level Isolation level ;
Isolation level
- read uncommitted
- read committed
- repeatable read
- serializable
6. summary
Generally speaking , The higher the isolation level of the transaction , The more you can ensure the integrity and consistency of the database , But relatively speaking , Higher isolation level , The greater the impact on concurrency performance . The official default is **「 Repeatable (Repeatable Read)」** But you can also set the isolation level of the database to read committed (Read Committed), It can prevent dirty reading , It also has good concurrency performance , About non repeatable reading 、 The concurrency problems of unreal reading and the second kind of data loss , It can be controlled by adopting pessimistic lock and optimistic lock in the application . 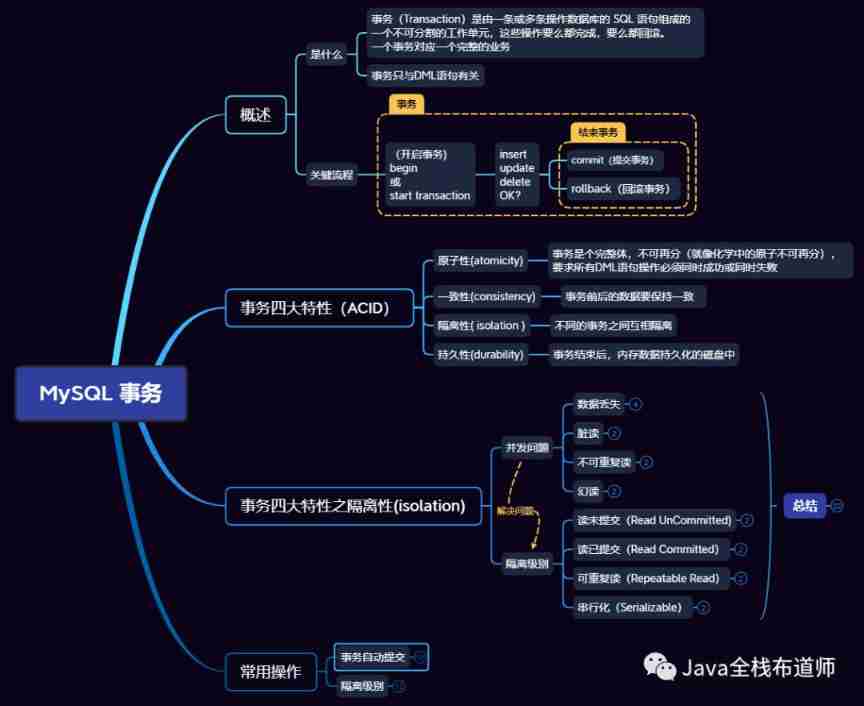 Focus on reading more quality articles Get mind map official account input :dt0010
Focus on reading more quality articles Get mind map official account input :dt0010
One key, three links
边栏推荐
- If you don't know these four caching modes, dare you say you understand caching?
- Qtreeview+ custom model implementation example
- Rhsca day 11 operation
- Realsense d435 d435i d415 depth camera obtains RGB map, left and right infrared camera map, depth map and IMU data under ROS
- System.currentTimeMillis() 和 System.nanoTime() 哪个更快?别用错了!
- Vs201 solution to failure to open source file HPP (or link library file)
- Work order management system OTRs
- Check 15 developer tools of Alibaba
- View CSDN personal resource download details
- Network disk installation
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
uniapp 处理过去时间对比现在时间的时间差 如刚刚、几分钟前,几小时前,几个月前
Development guidance document of CMDB
六月份阶段性大总结之Doris/Clickhouse/Hudi一网打尽
Latex learning insertion number - list of filled dots, bars, numbers
Servlet基本原理与常见API方法的应用
Dynamic memory management
OSPF comprehensive experiment
Latex arranges single column table pictures in double column format articles
AUTOSAR from getting started to mastering 100 lectures (106) - SOA in domain controllers
How to teach yourself to learn programming
Hands on deep learning (38) -- realize RNN from scratch
2. Data type
Doris / Clickhouse / Hudi, a phased summary in June
Check 15 developer tools of Alibaba
Baidu R & D suffered Waterloo on three sides: I was stunned by the interviewer's set of combination punches on the spot
Work order management system OTRs
Vanishing numbers
C language pointer interview question - the second bullet
What are the advantages of automation?
Delayed message center design