当前位置:网站首页>Dark horse notes - Common APIs
Dark horse notes - Common APIs
2022-06-26 13:04:00 【Xiaofu knocks the code】
Catalog
Object Common methods of class
summary : Why splice , To invert a string, it is recommended to use StringBuilder?
Case study : Print the contents of the shaping array
System Common methods of class
1.Object
Object The role of classes :
1.Object The method of class is that all subclass objects can be used directly ;
2. A class either inherits by default Object class , Or indirectly inherited Object class ,Object Class is Java Ancestors in .
Object Common methods of class

toString Meaning of existence
Parent class toString() The meaning of method is to be overridden by subclasses , In order to return the content information of the object , Not address information !
equals Meaning of existence
Parent class equals The meaning of method is to be overridden by subclasses , So that the subclass can customize the comparison rules by itself .
The following is a specific code description toString and equals Method :
import java.util.Objects;
public class Student { //extends Object{
private String name;
private char sex;
private int age;
public Student() {
}
public Student(String name, char sex, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.sex = sex;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public char getSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(char sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
/**
Custom equality rules .
If the contents of two objects are the same, they are considered equal
s1.equals(s2)
Comparator :s1 == this
The comparee : s2 ==> o
*/
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
// 1、 Determine whether the same object is compared , If it's a return true.
if (this == o) return true;
// 2、 If o yes null return false If o Not a student type, return false ...Student != ..Pig
if (o == null || this.getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
// 3、 explain o It must be a student type and not null
Student student = (Student) o;
return sex == student.sex && age == student.age && Objects.equals(name, student.name);
}
/**
Rewrite yourself equals, Customize your own equality rules .
If the contents of two objects are the same, they are considered equal
s1.equals(s2)
Comparator :s1 == this
The comparee : s2 ==> o
*/
/* @Override
public boolean equals(Object o){
// 1、 Judge o Is it the type of student
if(o instanceof Student){
Student s2 = (Student) o;
// 2、 Judge 2 Whether the contents of the objects are the same .
// if(this.name.equals(s2.name) &&
// this.age == s2.age && this.sex == s2.sex){
// return true;
// }else {
// return false;
// }
return this.name.equals(s2.name) && this.age == s2.age
&& this.sex == s2.sex ;
}else {
// Students can only compare with students , Otherwise, the result must be false
return false;
}
}*/
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", sex=" + sex +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
/**
The goal is : master Object Class toString Use of methods .
*/
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student s = new Student(" Zhou Xiong ", ' male ', 19);
// String rs = s.toString();
// System.out.println(rs);
// System.out.println(s.toString());
// Output object variables directly , It can be omitted by default toString Call not written
System.out.println(s);
}
}
import java.util.Objects;
/**
The goal is : master Object Class equals Use of methods .
*/
public class Test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student s1 = new Student(" Zhou Xiong ", ' male ', 19);
Student s2 = new Student(" Zhou Xiong ", ' male ', 19);
// equals The default is comparison 2 Whether the addresses of two objects are the same , After subclass rewriting, it will call the of subclass rewriting to compare whether the content is the same .
System.out.println(s1.equals(s2));
System.out.println(s1 == s2);
System.out.println(Objects.equals(s1, s2));
}
}
2.Objects
Objects summary
Objects Is a utility class , Provides some methods to complete some functions .
When comparing strings, the official , There is no string object equals Method , They chose to Objects Of equals Method to compare .
Objects Common ways to do it :

The following is a specific code description equals and isNull Method :
import java.util.Objects;
/**
The goal is : master objects Common methods of class :equals
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = null;
String s2 = new String("itheima");
// System.out.println(s1.equals(s2)); // Left a hidden danger , The pointer may be null .
System.out.println(Objects.equals(s1, s2)); // More secure , The result is also right !
/**
Objects:
public static boolean equals(Object a, Object b) {
return (a == b) || (a != null && a.equals(b));
}
*/
System.out.println(Objects.isNull(s1)); // true
System.out.println(s1 == null); // true
System.out.println(Objects.isNull(s2)); // false
System.out.println(s2 == null); // false
}
}
summary : What is recommended for content comparison of objects ? Why? ?
1. It is recommended to use Objects Provided equals Method .
2. The result of the comparison is the same , But it's safer .
3.StringBuilder
StringBuilder summary
StringBuilder Is a variable string class , We can think of it as an object container .
effect : Improve string operation efficiency , Such as splicing 、 Modify etc. .
StringBuilder Constructors

/**
The goal is : Learn how to use StringBuilder Operation string , Finally, you need to know why it works well
*/
public class StringBuilderDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); // ""
sb.append("a");
sb.append("b");
sb.append("c");
sb.append(1);
sb.append(false);
sb.append(3.3);
sb.append("abc");
System.out.println(sb);
StringBuilder sb1 = new StringBuilder();
// Support chain programming
sb1.append("a").append("b").append("c").append(" I love you China ");
System.out.println(sb1);
// reverse
sb1.reverse().append("110");
System.out.println(sb1);
System.out.println(sb1.length());
// Be careful :StringBuilder Just a means of splicing strings : Efficient .
// The ultimate goal is to restore String type .
StringBuilder sb2 = new StringBuilder();
sb2.append("123").append("456");
// Return to String type
String rs = sb2.toString();
check(rs);
}
public static void check(String data){
System.out.println(data);
}
}
Main idea : First use StringBuilder Complete the stitching , modify , And then use toString() take StringBuilder The address of the object is returned to String Variable , complete StringBuilder Type to String type .
StringBuilder Common methods
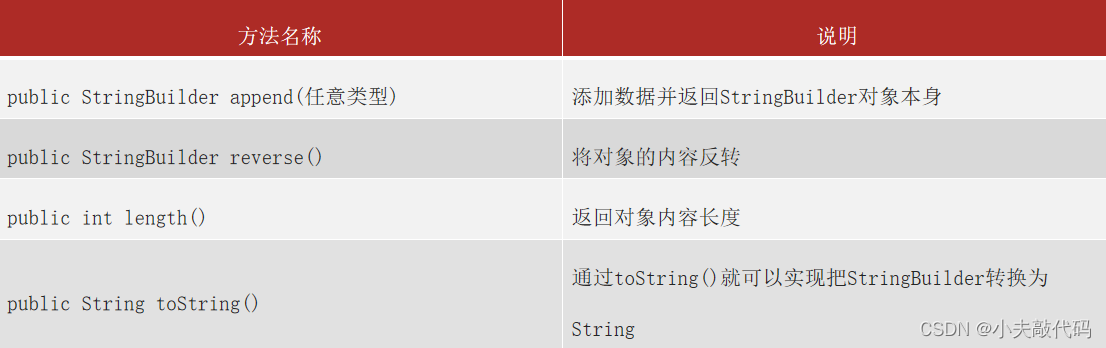
Why? String Use “+” Splicing strings is not as good as using StringBuilder Method ?
Pictured :


summary : Why splice , To invert a string, it is recommended to use StringBuilder?
1.String : Content is immutable 、 Poor string splicing performance .
2.StringBuilder: The content is variable 、 Splicing string has good performance 、 Elegant code .
3. Define the string using String.
4. Splicing 、 Modify the operation string and use StringBuilder
Case study : Print the contents of the shaping array
demand :
Design a method to output the contents of any integer array , The output is required to be in the following format :
“ The contents of the array are :[11, 22, 33, 44, 55]”
analysis :
1、 Define a method , This method is required to receive an array , And output the contents of the array . ---> Do you need parameters ? Do you need a return value type declaration ?
2、 Define a statically initialized array , Call the method , And pass in the array .
public class StringBuilderTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr1 = null;
System.out.println(toString(arr1));
int[] arr2 = {10, 88, 99};
System.out.println(toString(arr2));
int[] arr3 = {};
System.out.println(toString(arr3));
}
/**
1、 Define a method to receive any integer array , Returns the format of the contents of the array
*/
public static String toString(int[] arr){
if(arr != null){
// 2、 Start splicing content .
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("[");
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
sb.append(arr[i] ).append(i == arr.length - 1 ? "" : ", ");
}
sb.append("]");
return sb.toString();
}else {
return null;
}
}
}
4.Math
Math class
1. Contains methods for performing basic number operations ,Math Class does not provide an exposed constructor .
2. How do I use members in a class ? See if the members of the class are static , If it is , Through the class name, you can directly call .

/**
The goal is :Math The use of the class .
Math Used to do mathematical operations .
Math The methods in the class are all static methods , Call directly with the class name .
Method :
Method name explain
public static int abs(int a) To obtain parameters a The absolute value of :
public static double ceil(double a) Rounding up
public static double floor(double a) Rounding down
public static double pow(double a, double b) obtain a Of b The next power
public static long round(double a) Round to the nearest whole
Summary :
remember .
*/
public class MathDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1. Take the absolute value : Return positive number
System.out.println(Math.abs(10)); // 10
System.out.println(Math.abs(-10.3)); // 10.3
// 2. Rounding up : 5
System.out.println(Math.ceil(4.00000001)); // 5.0
System.out.println(Math.ceil(4.0)); // 4.0
// 3. Rounding down :4
System.out.println(Math.floor(4.99999999)); // 4.0
System.out.println(Math.floor(4.0)); // 4.0
// 4. Find the exponential power
System.out.println(Math.pow(2 , 3)); // 2^3 = 8.0
// 5. rounding 10
System.out.println(Math.round(4.49999)); // 4
System.out.println(Math.round(4.500001)); // 5
System.out.println(Math.random()); // 0.0 - 1.0 ( Not before, not after )
// expand : 3 - 9 Random number between (0 - 6) + 3
// [0 - 6] + 3
int data = (int)(Math.random() * 7) + 3;
System.out.println(data);
}
}5.System
System Class Overview
System It's also a tool class , Represents the current system , Provides some system related methods .
System Common methods of class

import java.math.BigDecimal;
import java.math.RoundingMode;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
The goal is :System Use of system classes .
System Represents the current system .( Virtual machine system )
Static methods :
1.public static void exit(int status): End JVM virtual machine , Not 0 Is an abnormal termination .
2.public static long currentTimeMillis(): Get the current system time in milliseconds .( a key )
3. You can make a copy of the array .
arraycopy(Object var0, int var1, Object var2, int var3, int var4);
* Parameter one : Original array
* Parameter two : From which position in the original array to start the assignment .
* Parameter 3 : Target array
* Parameter 4 : To which position in the target array
* Parameter 5 : Assign several .
*/
public class SystemDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(" Program starts ...");
// System.exit(0); // JVM End !
// 2、 Computers believe that time has a origin : return 1970-1-1 00:00:00 The total number of milliseconds to this moment : Time in milliseconds .
long time = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(time);
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
// Calculate the time : Performance analysis
for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) {
System.out.println(" Output :" + i);
}
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println((endTime - startTime)/1000.0 + "s");
// 3、 Make an array copy ( understand )
/**
arraycopy(Object src, int srcPos,
Object dest, int destPos,
int length)
Parameter one : The copied array
Parameter two : Which index location to copy from
Parameter 3 : Copy target array
Parameter 4 : Paste position
Parameter 5 : Number of copied elements
*/
int[] arr1 = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70};
int[] arr2 = new int[6]; // [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0] ==> [0, 0, 40, 50, 60, 0]
System.arraycopy(arr1, 3, arr2, 2, 3);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr2));
System.out.println("-------------------");
double i = 10.0;
double j = 3.0;
//
// System.out.println(k1);
System.out.println(" Program end ....");
}
}
6.BigDecimal
BigDecimal effect
Used to solve the problem of precision distortion of floating-point operation .

BigDecima Commonly used API
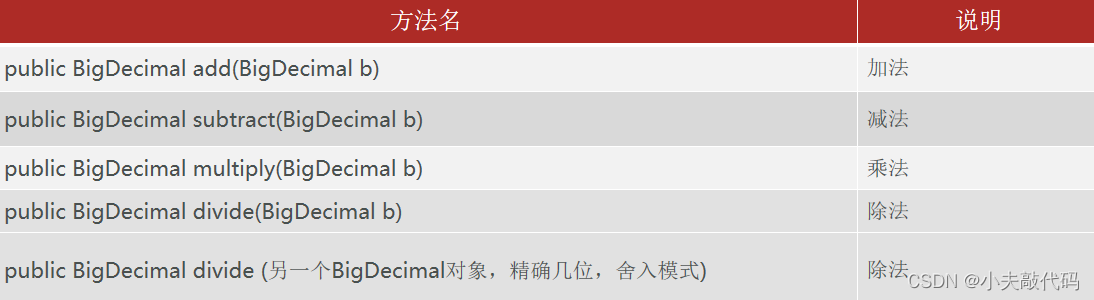
import java.math.BigDecimal;
import java.math.RoundingMode;
import java.text.NumberFormat;
/**
The goal is :BigDecimal Big data .
introduce :
Floating point arithmetic directly + * / Data distortion may occur ( Precision problem ).
BigDecimal It can solve the problem of data distortion of floating-point operation .
BigDicimal class :
package :java.math.
How to create objects ( The best way :)
public static BigDecimal valueOf(double val) : Wrapping floating-point numbers into big data objects .
Method statement
public BigDecimal add(BigDecimal value) Addition operation
public BigDecimal subtract(BigDecimal value) Subtraction
public BigDecimal multiply(BigDecimal value) Multiplication
public BigDecimal divide(BigDecimal value) Division operations
public double doubleValue(): hold BigDecimal convert to double type .
*/
public class BigDecimalDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Floating point arithmetic directly + * / Data distortion may occur ( Precision problem ).
System.out.println(0.09 + 0.01);
System.out.println(1.0 - 0.32);
System.out.println(1.015 * 100);
System.out.println(1.301 / 100);
System.out.println("-------------------------");
double a = 0.1;
double b = 0.2;
double c = a + b;
System.out.println(c);
System.out.println("--------------------------");
// Wrap floating-point data into big data objects BigDeciaml
BigDecimal a1 = BigDecimal.valueOf(a);
BigDecimal b1 = BigDecimal.valueOf(b);
BigDecimal c1 = a1.add(b1);
// BigDecimal c1 = a1.subtract(b1);
// BigDecimal c1 = a1.multiply(b1);
// BigDecimal c1 = a1.divide(b1);
System.out.println(c1);
// Purpose :double
double rs = c1.doubleValue();
System.out.println(rs);
// matters needing attention :BigDecimal Precision operation is a must
BigDecimal a11 = BigDecimal.valueOf(10.0);
BigDecimal b11 = BigDecimal.valueOf(3.0);
/**
Parameter one : Divisor Parameter two : Keep the decimal places Parameter 3 : rounding mode
*/
BigDecimal c11 = a11.divide(b11, 2, RoundingMode.HALF_UP); // 3.3333333333
System.out.println(c11);
System.out.println("-------------------");
}
}Main idea : First create BigDecimal Encapsulate floating point data ( The best way is to call methods ), The result is BigDecimal type , Using variable names .doubleValue() It can be transformed into double type .
边栏推荐
- Openlayers drawing dynamic migration lines and curves
- A must for programmers, an artifact utools that can improve your work efficiency n times
- 倍福PLC基于NT_Shutdown实现控制器自动关机重启
- I - Dollar Dayz
- Go 结构体方法
- opencv高速下载
- Adobe Acrobat prevents 30 security software from viewing PDF files or there are security risks
- code force Party Lemonade
- 倍福PLC基于CX5130实现数据的断电保持
- Electron official docs series: Best Practices
猜你喜欢

Chapter 01_ Installation and use of MySQL under Linux

机组实践实验8——使用CMStudio设计基于基本模型机微程序指令(1)

倍福CX5130换卡对已有的授权文件转移操作

Redis learning - 05 node JS client operation redis and pipeline pipeline

National standard gb28181 protocol easygbs cascaded universal vision platform, how to deal with live message 403?
Echart堆叠柱状图:色块之间添加白色间距效果设置
国标GB28181协议EasyGBS视频平台TCP主动模式拉流异常情况修复

使用SSH密钥对登陆服务器

Solution of Splunk iowait alarm

Software testing - Fundamentals
随机推荐
Explain C language 10 in detail (C language series)
第十章 设置结构化日志记录(二)
ES6模块
First knowledge - Software Testing
【网络是怎么连接的】第二章(中):一个网络包的发出
National standard gb28181 protocol easygbs video platform TCP active mode streaming exception repair
Electron official docs series: Distribution
openlayers 绘制动态迁徙线、曲线
P5733 [deep foundation 6. example 1] automatic correction
UVA5009 Error Curves三分
国标GB28181协议EasyGBS级联宇视平台,保活消息出现403该如何处理?
Vivado 错误代码 [DRC PDCN-2721] 解决
Redis learning - 05 node JS client operation redis and pipeline pipeline
Solution of Splunk iowait alarm
黑马笔记---常用API
使用SSH密钥对登陆服务器
倍福PLC实现绝对值编码器原点断电保持---bias的使用
深度解析当贝盒子B3、腾讯极光5S、小米盒子4S之间的区别
国标GB28181协议EasyGBS视频平台TCP主动模式拉流异常情况修复
面试题积累