当前位置:网站首页>Conditional variables for thread synchronization
Conditional variables for thread synchronization
2022-06-26 03:58:00 【StudyWinter】
1 Basic concepts
The conditional variable itself is not a lock ! But it can also cause thread blocking . Usually used with mutex . Provide a meeting place for multithreading .
Conditional variables are used to wait for threads instead of locking them , Conditional variables are often used with mutexes . The reason why conditional variables are used with mutexes , Mainly because an obvious feature of mutex is that it has only two states : Locked and unlocked , Conditional variables can make up for the lack of mutex by allowing a thread to block and wait for another thread to send a signal , So mutexes and conditional variables are usually used together .
When the conditions are met , Threads usually unlock and wait for the condition to change , Once another thread changes the environment variable , It will notify the corresponding environment variable to wake up one or more threads blocked by this condition variable . These awakened threads will be locked again , And test whether the conditions meet . In general, conditional variables are used for synchronization between threads ; When the conditions are not met , Allow one of the execution flows to hang and wait
Reference resources : Detailed explanation of conditional variables _ The breeze is coming Groot The blog of -CSDN Blog _ Condition variables,
2 Why use conditional variables
When a thread preempts a mutex , Threads A The mutex lock was seized , But the conditions are not met , Threads A Will give up the mutex to other threads , Then wait for other threads to wake him up ; Once the conditions are met , The thread can be awakened , And use the mutex to access the shared area . Through this design, the process can run more stably .
3 Function USES
3.1 pthread_cond_init function
effect : Initialize a conditional variable
int pthread_cond_init(pthread_cond_t *restrict cond,
const pthread_condattr_t *restrict attr);
// ginseng 2:attr Table condition variable properties , Usually the default value , Pass on NULL that will do Static initialization and dynamic initialization
// 1 initiate static
pthread_cond_t cond=PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIZER;
// 2 dynamic initialization
int pthread_cond_init(pthread_cond_t *restrict cond,
const pthread_condattr_t *restrict attr);3.2 pthread_cond_destroy function
effect : Destroy a conditional variable
int pthread_cond_destroy(pthread_cond_t *cond);3.3 pthread_cond_wait function ( a key )
effect :( It's very important Three points )
1 Block wait condition variable cond( ginseng 1) Satisfy
2 Release the mastered mutex ( Unlock mutex ) amount to pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
3 When awakened ,pthread_cond_wait When function returns , Unblock and re apply for mutex
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
int pthread_cond_wait(pthread_cond_t *restrict cond,
pthread_mutex_t *restrict mutex);1.2. Two steps for an atomic operation .
3.4 pthread_cond_timedwait function
effect : Wait for a conditional variable for a limited time
int pthread_cond_timedwait(pthread_cond_t *restrict cond,
pthread_mutex_t *restrict mutex,
const struct timespec *restrict abstime);3.5 pthread_cond_signal function
effect : Wake up at least one thread blocked on a condition variable
int pthread_cond_signal(pthread_cond_t *cond);3.6 pthread_cond_broadcast function
effect : Wake up all threads blocked on condition variables
int pthread_cond_broadcast(pthread_cond_t *cond);
4 Producer consumer model

step :
producer :
(1) The production data ;
(2) Lock pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
(3) Place data in public areas ;
(4) Unlock pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
(5) Notifies threads blocking on condition variables pthread_cond_signal()、pthread_cond_brocadcast();
(6) Generate sequential data in a cycle .
consumer :
(1) Create a lock pthread_mutex_t mutex;
(2) Initialize lock pthread_mutex_init(mutex, NULL);
(3) Lock pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
(4) Wait condition satisfied
pthread_cond_wait(&cond, &mutex);
Block wait condition variable ;
Unlock ;
----10s;
Lock ;
(5) Access shared data ;
(6) Unlock 、 Release condition variable , Release the lock .
Code
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <pthread.h>
// Simulate with conditional variables [ producer - consumer ] problem
// Linked list as shared data , Need to be protected by mutex
struct Msg
{
int val;
struct Msg *next;
};
// Head node
struct Msg *head;
// Statically initialize mutexes and condition variables
pthread_mutex_t lock = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;
pthread_cond_t has_product = PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIZER;
// Producer thread
void *producer(void *arg)
{
struct Msg *mp;
while (1)
{
// To apply for space
mp = malloc(sizeof(struct Msg));
// Simulate the production of a product
mp->val = rand() % 1000 + 1;
printf("---produce----------------------:%d\n", mp->val);
// Lock
int res = pthread_mutex_lock(&lock);
if (res != 0)
{
fprintf(stderr, "pthread_mutex_lock producer error:%s\n", strerror(res));
exit(1);
}
// The first interpolation
mp->next = head;
head = mp;
// Unlock
res = pthread_mutex_unlock(&lock);
if (res != 0)
{
fprintf(stderr, "pthread_mutex_unlock producer error:%s\n", strerror(res));
exit(1);
}
// Will wait for a thread on the condition variable to wake up
res = pthread_cond_signal(&has_product);
if (res != 0)
{
fprintf(stderr, "pthread_cond_signal producer error:%s\n", strerror(res));
exit(1);
}
sleep(rand() % 5);
}
}
// Consumer thread
void *consumer(void *arg)
{
struct Msg *mp;
while (1)
{
// Lock
int res = pthread_mutex_lock(&lock);
if (res != 0)
{
fprintf(stderr, "pthread_mutex_lock consumer error:%s\n", strerror(res));
exit(1);
}
// The header node is empty , Indicates that there are no nodes
while (head == NULL)
{
// Consumer is blocking
res = pthread_cond_wait(&has_product, &lock);
if (res != 0)
{
fprintf(stderr, "pthread_cond_wait consumer error:%s\n", strerror(res));
exit(1);
}
}
// Simulate the consumption of a product
mp = head;
head = head->next;
// Unlock
res = pthread_mutex_unlock(&lock);
if (res != 0)
{
fprintf(stderr, "pthread_mutex_unlock consumer error:%s\n", strerror(res));
exit(1);
}
printf("==Consumer:%lu====%d\n", pthread_self(), mp->val);
// Release
free(mp);
sleep(rand() % 5);
}
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
// Create producer and consumer threads
pthread_t pid, cid;
srand(time(NULL));
// Create a producer thread
int res = pthread_create(&pid, NULL, producer, NULL);
if (res != 0)
{
fprintf(stderr, "pthread_create producer error:%s\n", strerror(res));
exit(1);
}
// Create consumer thread
res = pthread_create(&cid, NULL, consumer, NULL);
if (res != 0)
{
fprintf(stderr, "pthread_create consumer error:%s\n", strerror(res));
exit(1);
}
// Recycling producer threads
res = pthread_join(pid, NULL);
if (res != 0)
{
fprintf(stderr, "pthread_join producer error:%s\n", strerror(res));
exit(1);
}
// Recycle consumer threads
res = pthread_join(cid, NULL);
if (res != 0)
{
fprintf(stderr, "pthread_join consumer error:%s\n", strerror(res));
exit(1);
}
return 0;
}perform

5 Multiple consumers
Producers have shorter breaks , Everything else is the same
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <pthread.h>
// Simulate with conditional variables [ producer - consumer ] problem
// Linked list as shared data , Need to be protected by mutex
struct Msg
{
int val;
struct Msg *next;
};
// Head node
struct Msg *head;
// Statically initialize mutexes and condition variables
pthread_mutex_t lock = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;
pthread_cond_t has_product = PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIZER;
// Producer thread
void *producer(void *arg)
{
struct Msg *mp;
while (1)
{
// To apply for space
mp = malloc(sizeof(struct Msg));
// Simulate the production of a product
mp->val = rand() % 1000 + 1;
printf("---produce----------------------:%d\n", mp->val);
// Lock
int res = pthread_mutex_lock(&lock);
if (res != 0)
{
fprintf(stderr, "pthread_mutex_lock producer error:%s\n", strerror(res));
exit(1);
}
// The first interpolation
mp->next = head;
head = mp;
// Unlock
res = pthread_mutex_unlock(&lock);
if (res != 0)
{
fprintf(stderr, "pthread_mutex_unlock producer error:%s\n", strerror(res));
exit(1);
}
// Will wait for a thread on the condition variable to wake up
res = pthread_cond_signal(&has_product);
if (res != 0)
{
fprintf(stderr, "pthread_cond_signal producer error:%s\n", strerror(res));
exit(1);
}
sleep(rand() % 3);
}
}
// Consumer thread
void *consumer(void *arg)
{
struct Msg *mp;
while (1)
{
// Lock
int res = pthread_mutex_lock(&lock);
if (res != 0)
{
fprintf(stderr, "pthread_mutex_lock consumer error:%s\n", strerror(res));
exit(1);
}
// The header node is empty , Indicates that there are no nodes
while (head == NULL)
{
// Consumer is blocking
res = pthread_cond_wait(&has_product, &lock);
if (res != 0)
{
fprintf(stderr, "pthread_cond_wait consumer error:%s\n", strerror(res));
exit(1);
}
}
// Simulate the consumption of a product
mp = head;
head = head->next;
// Unlock
res = pthread_mutex_unlock(&lock);
if (res != 0)
{
fprintf(stderr, "pthread_mutex_unlock consumer error:%s\n", strerror(res));
exit(1);
}
printf("==Consumer:%lu====%d\n", pthread_self(), mp->val);
// Release
free(mp);
sleep(rand() % 5);
}
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
// Create producer and consumer threads
pthread_t pid, cid;
srand(time(NULL));
// Create a producer thread
int res = pthread_create(&pid, NULL, producer, NULL);
if (res != 0)
{
fprintf(stderr, "pthread_create producer error:%s\n", strerror(res));
exit(1);
}
/***********3 Consumers ****************/
// Create consumer thread
res = pthread_create(&cid, NULL, consumer, NULL);
if (res != 0)
{
fprintf(stderr, "pthread_create consumer error:%s\n", strerror(res));
exit(1);
}
// Create consumer thread
res = pthread_create(&cid, NULL, consumer, NULL);
if (res != 0)
{
fprintf(stderr, "pthread_create consumer error:%s\n", strerror(res));
exit(1);
}
// Create consumer thread
res = pthread_create(&cid, NULL, consumer, NULL);
if (res != 0)
{
fprintf(stderr, "pthread_create consumer error:%s\n", strerror(res));
exit(1);
}
// Recycling producer threads
res = pthread_join(pid, NULL);
if (res != 0)
{
fprintf(stderr, "pthread_join producer error:%s\n", strerror(res));
exit(1);
}
// Recycle consumer threads
res = pthread_join(cid, NULL);
if (res != 0)
{
fprintf(stderr, "pthread_join consumer error:%s\n", strerror(res));
exit(1);
}
return 0;
}perform

6 Advantages of conditional variables
Compare with mutex for , Conditional variables can reduce competition .
If used directly mutex, Except producers 、 Consumers should compete with each other in addition to mutual exclusion , Consumers also need competition and mutual exclusion , But if you ( Linked list ) No data in , Competition and mutual exclusion between consumers are meaningless . With the conditional variable mechanism , Only producers complete production , Will cause competition among consumers . Improved program efficiency .
边栏推荐
- Ten important basic principles of software debugging and testing
- ABP framework Practice Series (III) - domain layer in depth
- 2022.6.23-----leetcode. thirty
- Comparison of static methods and variables with instance methods and variables
- Uni app, the text implementation expands and retracts the full text
- Restful API interface design standards and specifications
- [LOJ 6718] nine suns' weakened version (cyclic convolution, arbitrary modulus NTT)
- WebRTC系列-网络传输之7-ICE补充之偏好(preference)与优先级(priority)
- 用eclipse连mysql数据库出错然后出现图中的话是咋回事呀
- EF core Basics
猜你喜欢

Open Camera异常分析(一)

After a test of 25K bytes, I really saw the basic ceiling

ABP framework Practice Series (I) - Introduction to persistence layer

Optimization - multi objective planning

(15)Blender源码分析之闪屏窗口显示菜单功能

ABP framework Practice Series (II) - Introduction to domain layer
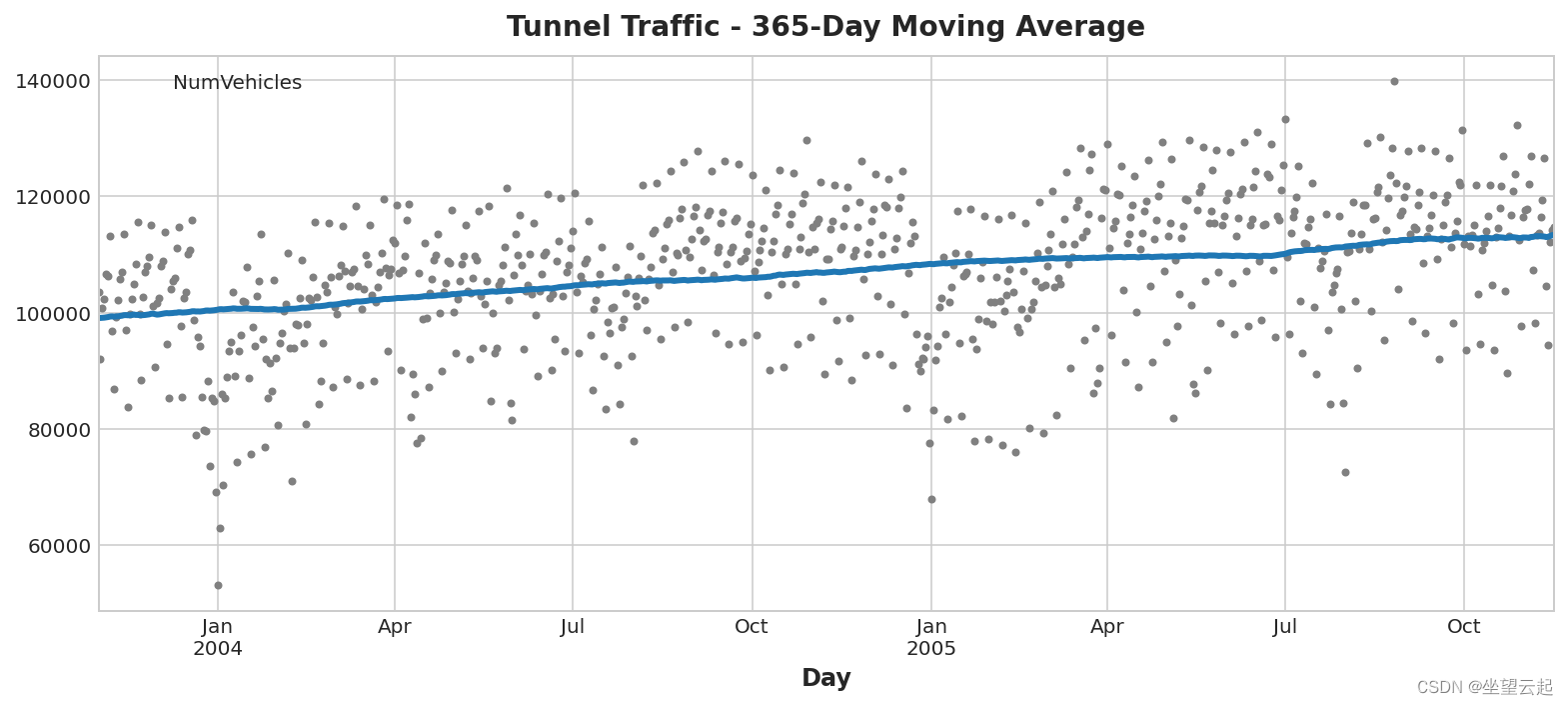
机器学习笔记 - 时间序列的趋势分量

. Net core learning journey
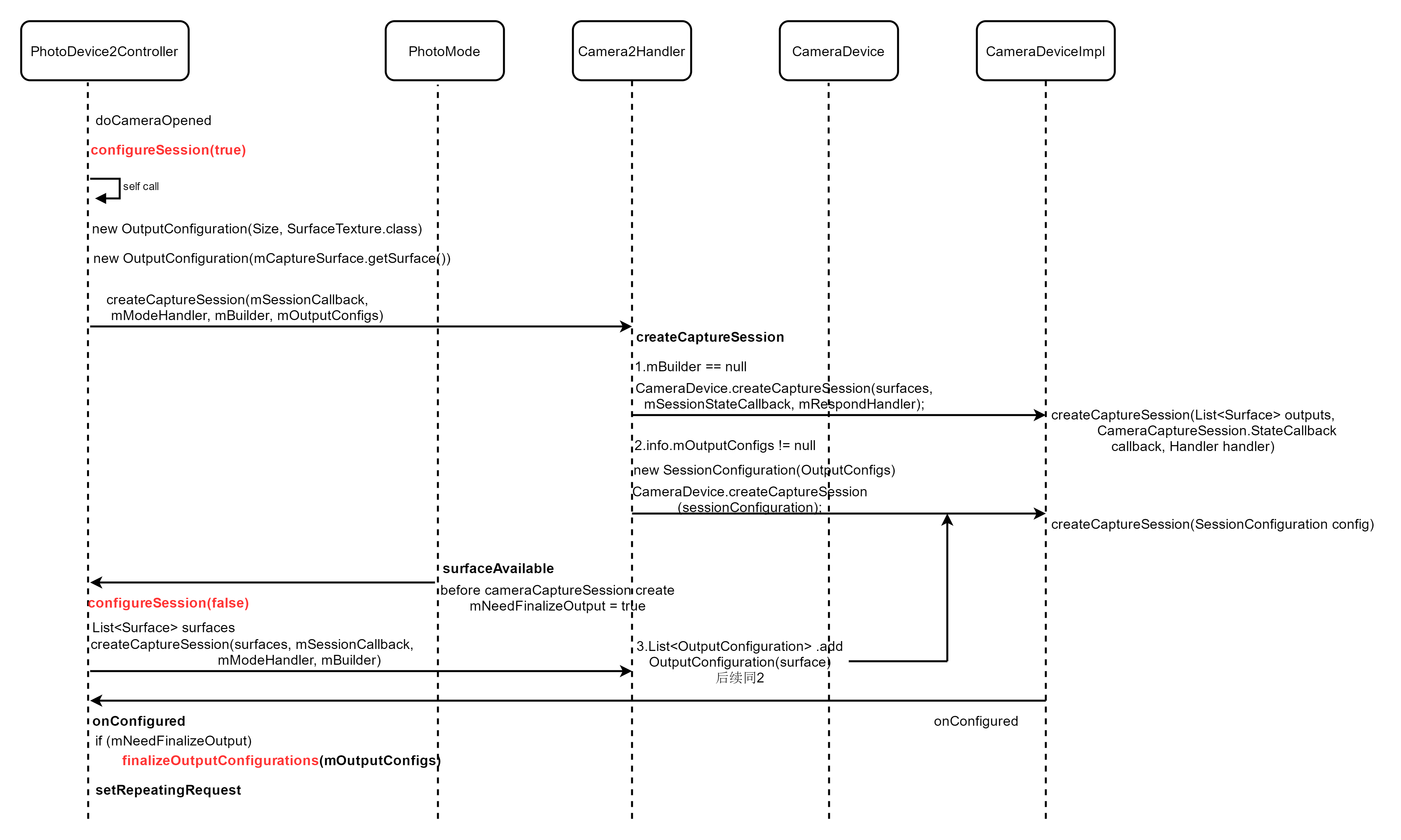
Camera-CreateCaptureSession

Evaluation - analytic hierarchy process
随机推荐
Dix critères de base importants pour les essais de débogage de logiciels
Uni app QR code scanning and identification function
线程同步之读写锁
Binary search method
169. 多数元素
Slide the menu of uni app custom components left and right and click switch to select and display in the middle
YOLOv5改进:更换骨干网(Backbone)
2022.6.23-----leetcode. thirty
xml 解析bean工具类
XML parsing bean tool class
商城风格也可以很多变,DIY 了解一下
Quanergy welcomes Lori sundberg as chief human resources officer
Part 4: drawing quadrilateral
Machine learning notes - trend components of time series
But the Internet began to have a new evolution and began to appear in a new state
Uni app custom selection date 1 (September 16, 2021)
軟件調試測試的十大重要基本准則
Uni app swiper rotation chart (full screen / card)
Lua语法讲解
User control custom DependencyProperty