当前位置:网站首页>Go language implementation principle -- map implementation principle
Go language implementation principle -- map implementation principle
2022-07-05 23:12:00 【There is too much uncertainty in life】
Contents of this article
Map Realization principle
1、 summary
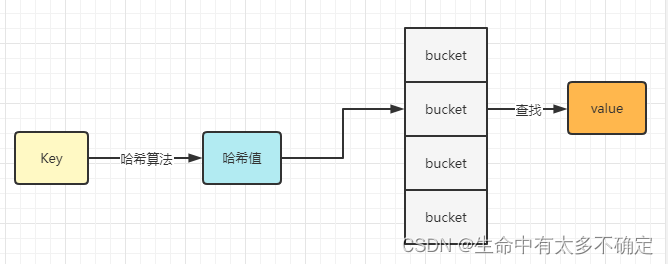
Map This data structure exists in many languages , Its query efficiency is very high , The complexity of time is O(1) The level of , The underlying principle uses a hash table , By calculation key Of hash value , Find where it is bucket, And then through bucket Look for it value, The flow is shown in the following figure
2、 Hash collision
because bucket There is a limited number of , and k-v There will be more and more right ones , therefore , Find the corresponding... Through the hash value bucket There may be multiple hash values corresponding to one bucket The situation of , This is it. hash Collision . To solve this problem , Can pass Zipper method or Open address method To solve such problems
2.1、 Zipper method
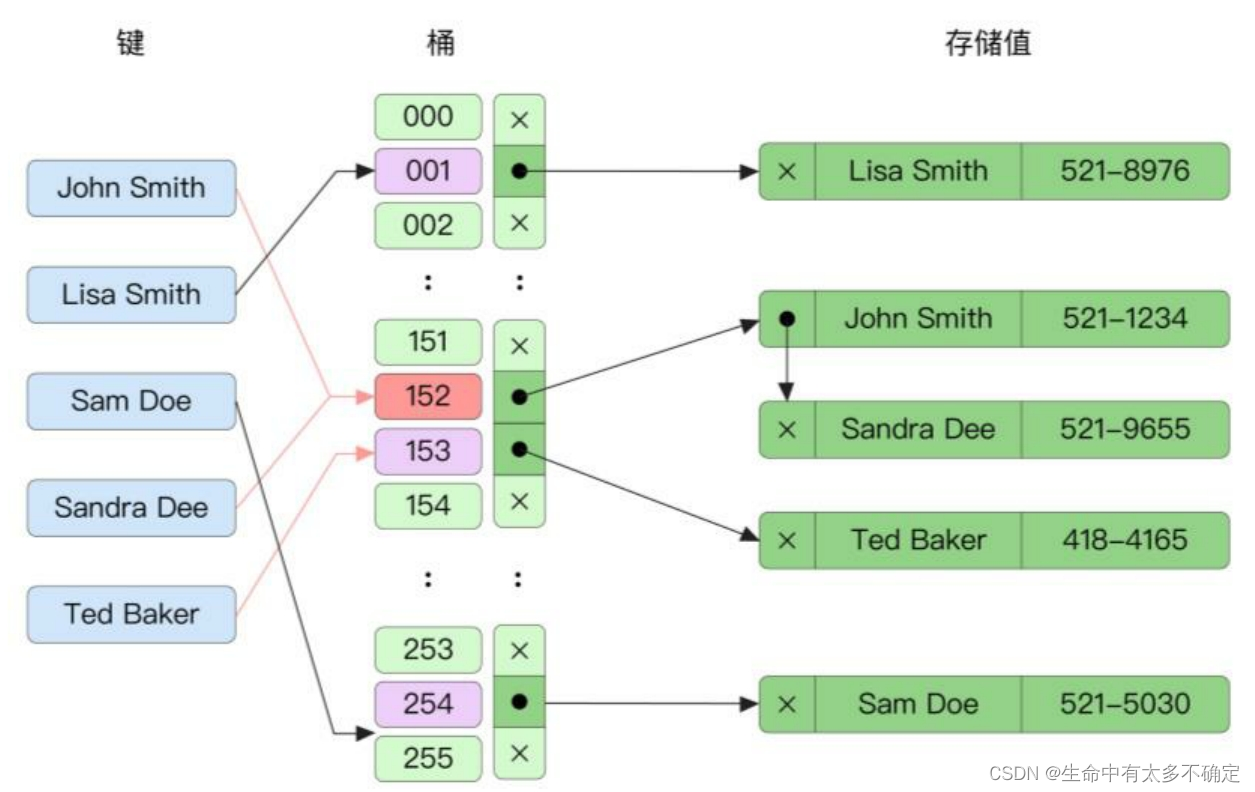
If multiple elements are placed in one bucket in , Will treat them as Linked list In the form of , Find the corresponding bucket after , Just traverse it .
shortcoming : Because of the use of linked lists to organize data , So extra pointers are needed , And it cannot be used efficiently CPU Cache
2.2、 Open address method
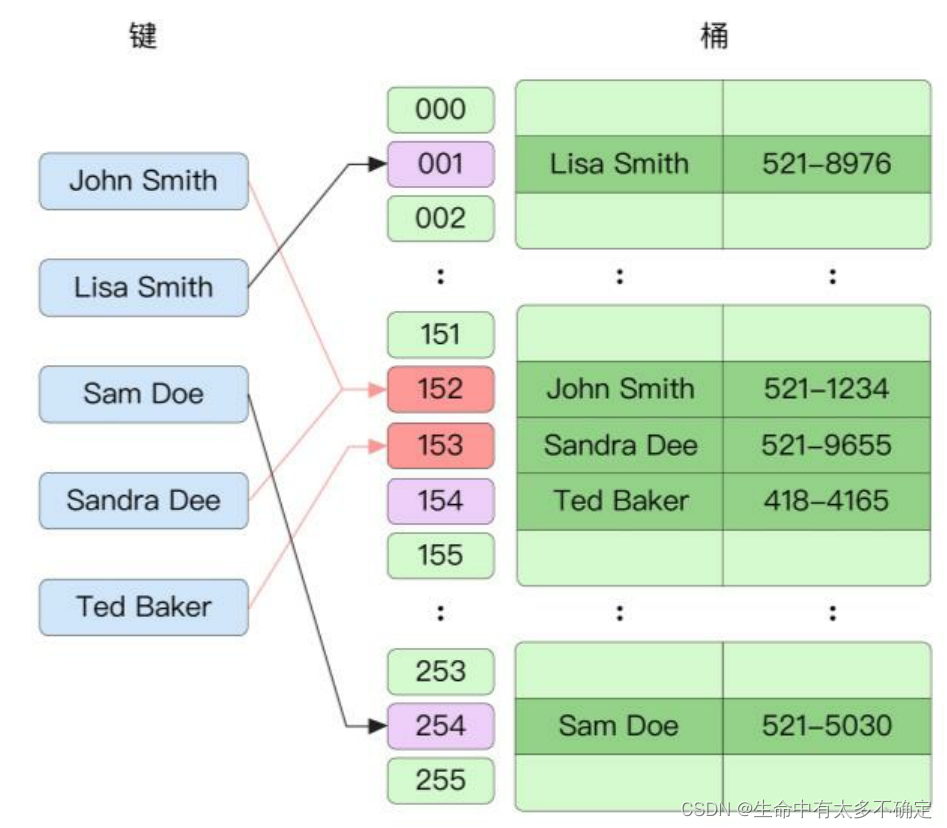
Unlike zipper hair , For the same bucket The elements in , It's using Array In the form of ,Go The language uses this formal way to resolve hash conflicts , When looking for elements, it traverses in sequence , This method can make better use of CPU The cache of .
3、 Common operations
3.1、 Declaration and creation
var m1 map[int]string // m1 by nil, Unable to operate
var m2 = make(map[int]int) // m2 Not for nil, The default length is 0
3.2、 Get value
var m = make(map[int]int)
v1 := m[1]
fmt.Println(v1) // 0
v2, ok := m[2]
fmt.Println(v2, ok) // 0 false
From the above example, it is not difficult to see , If you get a non-existent element , You will get this type of ” Zero value “, therefore , It is more recommended to use the second method to start from map Get the element , Through the second parameter, we can judge whether there is an expected value
3.3、 Assignment operation
var m = make(map[int]int)
// assignment :map[key] = value
m[1] = 666
fmt.Println(m[1]) // 666
// Delete :delete(map,key)
delete(m, 1)
fmt.Println(m[1]) // 0
3.4、key Comparability of
stay Go In language ,map Of key Must be comparable . except section 、 function 、map, Not comparable , Almost all other types are comparable . It is worth mentioning that , Comparability of structures , Depends on all its properties , If all fields are comparable , Then the structure is comparable , On the contrary, it is not comparable .
3.5、 Concurrency issues
// Test concurrent read and write
// Concurrent reading and writing will report errors fatal error: concurrent map read and map write
func test1() {
m := make(map[int]int)
go func() {
for {
m[0] = 5
}
}()
go func() {
for {
_ = m[1]
}
}()
select {
}
}
// Test concurrent reads
func test2() {
m := make(map[int]int)
go func() {
for {
_ = m[0]
}
}()
go func() {
for {
_ = m[1]
}
}()
select {
}
}
// Test and write
// Report errors : fatal error: concurrent map writes
func test3() {
m := make(map[int]int)
go func() {
for {
m[0] = 5
}
}()
go func() {
for {
m[1] = 5
}
}()
select {
}
}
It is not difficult to see from the above case ,Go In language Map Only concurrent reads are supported , The reason for this design , Because in most scenarios Map They all read more and write less , If we make every method mutually exclusive for the sake of that little bit of security, it will be a little more than worth the loss , therefore , The former is selected in terms of performance and concurrency security .
4、 The underlying structure
4.1、 Hash table structure
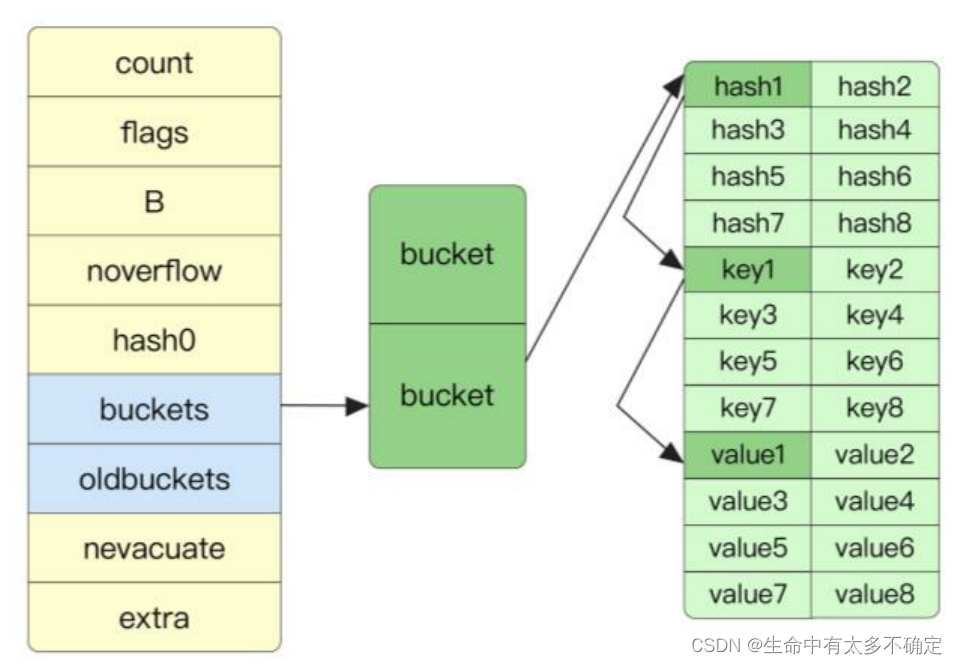
Map Structure
// A header for a Go map.
type hmap struct {
// Note: the format of the hmap is also encoded in cmd/compile/internal/reflectdata/reflect.go.
// Make sure this stays in sync with the compiler's definition.
count int // # live cells == size of map. Must be first (used by len() builtin)
flags uint8
B uint8 // log_2 of # of buckets (can hold up to loadFactor * 2^B items)
noverflow uint16 // approximate number of overflow buckets; see incrnoverflow for details
hash0 uint32 // hash seed
buckets unsafe.Pointer // array of 2^B Buckets. may be nil if count==0.
oldbuckets unsafe.Pointer // previous bucket array of half the size, non-nil only when growing
nevacuate uintptr // progress counter for evacuation (buckets less than this have been evacuated)
extra *mapextra // optional fields
}
With the help of translation software, we can know the function of most fields , I won't repeat the explanation here , Here is an introduction to those without English notes flag Field , The function of this field is to record the current map The state of , The concurrency problem mentioned above is judged with the help of this field
Bucket Structure
// A bucket for a Go map.
type bmap struct {
// tophash generally contains the top byte of the **hash** value
// for each key in this bucket. If tophash[0] < minTopHash,
// tophash[0] is a bucket evacuation state instead.
tophash [bucketCnt]uint8
// Followed by bucketCnt keys and then bucketCnt elems.
// NOTE: packing all the **keys** together and then all the **elems** together makes the
// code a bit more complicated than alternating key/elem/key/elem/... but it allows
// us to eliminate padding which would be needed for, e.g., map[int64]int8.
// Followed by an overflow pointer.
}
You can see... In the source code bucketCnt At run time 8, There is only one in this structure tophash attribute , It's a length of 8 Array of , You can know from the comments that it stores hash value , We can know from the following English explanation , It should be followed by key and value, When obtaining, it is obtained by calculating the offset . therefore , At runtime, the actual structure should look like the following
// A bucket for a Go map.
type bmap struct {
tophash [bucketCnt]uint8
key [bucketCnt]T
value [bucketCnt]T
......
}
The following English notes also explain , The reason for organizing data like this , It is to save the space filled by it
4.2、 Overflow bucket
Through the above analysis of the structure, we can know ,bucket The data in the structure is stored in the array , The length of the array is fixed 8, When to map When storing ,bucket The data in may exceed 8. In this case ,Go The approach of language is to create a new bucket, This new bucket be called Overflow bucket , primary bucket, And overflow barrels will form a chain , let me put it another way , primary bucket There will be a pointer to the overflow bucket .
4.3、map The reconstruction
In the use of key obtain value When , We will find the corresponding bucket, Then go back and traverse the elements inside , If so bucket If it is not found, it will check whether there is an overflow bucket , If there is, it will traverse the overflow bucket . We know that the efficiency of traversal is very poor , therefore , To improve performance , Need to add original bucket The number of , because map in bucket It is organized in an array , Therefore, you need to apply for a larger memory when expanding , And then put the old bucket Copy to the new array .
Capacity expansion condition
// If we hit the max load factor or we have too many overflow buckets,
// and we're not already in the middle of growing, start growing.
if !h.growing() && (overLoadFactor(h.count+1, h.B) || tooManyOverflowBuckets(h.noverflow, h.B)) {
hashGrow(t, h)
goto again // Growing the table invalidates everything, so try again
}
According to the English notes and the method name, it is not difficult to see , When the load factor reaches a certain threshold or there are too many overflowing barrels ( When the number of overflowing barrels is the same as that of normal barrels ), Will trigger map The reconstruction
Load factor
The following is the calculation formula of load factor :
negative load because Son = element plain Count The amount / b u c k e t Count The amount Load factor = Element quantity /bucket Number negative load because Son = element plain Count The amount /bucket Count The amount
The load factor can get the current general usage of space , If the current load factor is small , It indicates that the number of elements is much smaller than the applied capacity , for example : The load factor is 1, So, on average each bucket There's only one element , Because of every bucket Can be stored 8 Elements , From an average point of view , Only about 1/8 Space .
// Maximum average load of a bucket that triggers growth is 6.5.
// Represent as loadFactorNum/loadFactorDen, to allow integer math.
loadFactorNum = 13
loadFactorDen = 2
We can know from the above source code , At run time map The default maximum load factor for is 6.5, That is to say 13÷2 Result , in other words , When map The load factor reaches 6.5 Capacity expansion will be carried out when
Expansion strategy
func hashGrow(t *maptype, h *hmap) {
// If we've hit the load factor, get bigger.
// Otherwise, there are too many overflow buckets,
// so keep the same number of buckets and "grow" laterally.
bigger := uint8(1)
if !overLoadFactor(h.count+1, h.B) {
bigger = 0
h.flags |= sameSizeGrow
}
oldbuckets := h.buckets
newbuckets, nextOverflow := makeBucketArray(t, h.B+bigger, nil)
//......
}
map Structural weight B Fields and bucket The relationship between quantity is : 2 B = b u c k e t s 2^B = buckets 2B=buckets, in other words B Every increase 1,bucket It will double
In the above source code , It's not hard to see. , If the capacity expansion is caused by load factor ,bigger by 1, that B Will increase 1, That is to say buckets The number of will double , If the capacity expansion is caused by too many overflowing barrels ,bigger by 0, The number of barrels will remain the same , Horizontal “ growth ”.
4.4、 Delete principle
In the use of delete(map,key) Delete map When it comes to the elements in , Will bucket The value at the corresponding position in is set to emptyOne, If there is no value after this value , Will be set to emptyRest, The advantage of this is , encounter emptyRest Will not continue to traverse backwards . As shown in the figure below
边栏推荐
- How to quickly understand complex businesses and systematically think about problems?
- TOPSIS code part of good and bad solution distance method
- Roman numeral to integer
- Realize reverse proxy client IP transparent transmission
- 3 find the greatest common divisor and the least common multiple
- [speech processing] speech signal denoising and denoising based on Matlab GUI low-pass filter [including Matlab source code 1708]
- Sum of two numbers, sum of three numbers (sort + double pointer)
- Getting started stm32--gpio (running lantern) (nanny level)
- d3dx9_ How to repair 31.dll_ d3dx9_ 31. Solution to missing DLL
- Metasploit(msf)利用ms17_010(永恒之蓝)出现Encoding::UndefinedConversionError问题
猜你喜欢

30 optimization skills about mysql, super practical
LabVIEW打开PNG 图像正常而 Photoshop打开得到全黑的图像
openresty ngx_ Lua request response
2022 G3 boiler water treatment simulation examination and G3 boiler water treatment simulation examination question bank

LeetCode102. Sequence traversal of binary tree (output by layer and unified output)

How to quickly understand complex businesses and systematically think about problems?

Registration and skills of hoisting machinery command examination in 2022

【Note17】PECI(Platform Environment Control Interface)
MoCo: Momentum Contrast for Unsupervised Visual Representation Learning

Nangou Gili hard Kai font TTF Download with installation tutorial
随机推荐
Southeast Asia e-commerce guide, how do sellers layout the Southeast Asia market?
TOPSIS code part of good and bad solution distance method
Leetcode weekly The 280 game of the week is still difficult for the special game of the week's beauty team ~ simple simulation + hash parity count + sorting simulation traversal
Composition of interface
[digital signal denoising] improved wavelet modulus maxima digital signal denoising based on MATLAB [including Matlab source code 1710]
Hainan Nuanshen tea recruits warmhearted people: recruitment of the product experience recommender of Nuanshen multi bubble honey orchid single cluster
判断二叉树是否为完全二叉树
视频标准二三事
6-axis and 9-axis IMU attitude estimation
3D point cloud slam
Selenium+pytest automated test framework practice
Go语言实现原理——Map实现原理
Leetcode daily question 1189 The maximum number of "balloons" simple simulation questions~
【原创】程序员团队管理的核心是什么?
派对的最大快乐值
Three.JS VR看房
Starting from 1.5, build a micro Service Framework -- log tracking traceid
Spectrum analysis of ADC sampling sequence based on stm32
Masked Autoencoders Are Scalable Vision Learners (MAE)
LeetCode145. Post order traversal of binary tree (three methods of recursion and iteration)