当前位置:网站首页>Li Mu hands-on learning deep learning V2-bert and code implementation
Li Mu hands-on learning deep learning V2-bert and code implementation
2022-08-02 23:33:00 【cv_lhp】
一. BERT(来自Transformers的双向编码器表示)
1. 介绍
BERT通过使用预训练的Transformer编码器,能够基于其双向上下文表示任何词元,在下游任务的监督学习过程中,BERT在两个方面与GPT相似.首先BERT表示将被输入到一个添加的输出层中,根据任务的性质对模型架构进行最小的更改,例如预测每个词元与预测整个序列.The second is pre-trainingTransformer编码器的所有参数进行微调,而额外的输出层将从头开始训练.
2. 输入表示
在自然语言处理中,有些任务(如情感分析)以单个文本作为输入,而有些任务(如自然语言推断)以一对文本序列作为输入.BERT输入序列明确地表示单个文本和文本对.当输入为单个文本时,BERT输入序列是特殊类别词元“”、文本序列的标记、以及特殊分隔词元“”的连结.当输入为文本对时,BERT输入序列是“”、第一个文本序列的标记、“”、第二个文本序列标记、以及“”的连结.我们将始终如一地将术语“BERT输入序列”与其他类型的“序列”区分开来.例如,一个BERT输入序列可以包括一个文本序列或两个文本序列.To distinguish text pairs,Fragment embeddings learned from the input sequence e A \mathbf{e}_A eA和 e B \mathbf{e}_B eBare added to the token embeddings of the first and second sequences, respectively.For single text input,仅使用 e A \mathbf{e}_A eA.
下面的get_tokens_and_segments将一个句子或两个句子作为输入,然后返回BERTFragment indices of the input sequences and their corresponding sequence pairs.
import torch
import d2l.torch
from torch import nn
def get_tokens_segments(tokens_a,tokens_b=None):
"""获取输入序列的词元及其片段索引"""
tokens = ['<cls>']+tokens_a+['<sep>']
# 0和1分别标记片段A和B
segments = [0]*(len(tokens_a)+2)
if tokens_b is not None:
tokens += tokens_b+['<sep>']
segments += [1]*(len(tokens_b)+1)
return tokens,segments
BERT选择Transformer编码器作为其双向架构.在TransformerA positional embedding in the encoder is added to each position of the input sequence,However, with the originalTransformer编码器不同,BERT使用可学习的位置嵌入.总之,bert-input是BERTThe token embeddings of the input sequence、片段嵌入和位置嵌入的和.如下图所示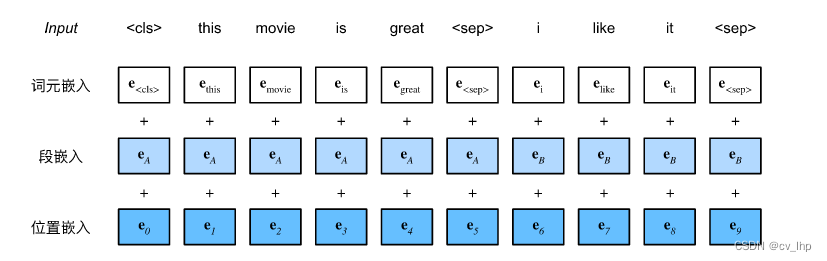
下面的BERTEncoder类与transformer的TransformerEncoder类一样.不同的是,BERTEncoder使用片段嵌入和可学习的位置嵌入.
class BERTEncoder(nn.Module):
"""BERT编码器"""
def __init__(self,vocab_size,num_hiddens,norm_shape,ffn_num_input,ffn_num_hiddens,num_heads,num_layers,dropout,max_len=1000,
key_size=768,query_size=768,value_size=768,use_bias=True):
super(BERTEncoder,self).__init__()
self.token_embedding = nn.Embedding(vocab_size,num_hiddens)
self.segment_embedding = nn.Embedding(2,num_hiddens)
# 在BERT中,位置嵌入是可学习的,因此我们创建一个足够长的位置嵌入参数
self.pos_embedding = nn.Parameter(torch.randn(size=(1,max_len,num_hiddens)))
self.blks = nn.Sequential()
for i in range(num_layers):
self.blks.add_module(f'{i}',d2l.torch.EncoderBlock(key_size,query_size,value_size,num_hiddens,norm_shape,ffn_num_input,ffn_num_hiddens,num_heads,dropout,use_bias))
def forward(self,tokens,segments,valid_lens):
# 在以下代码段中,X的形状保持不变:(批量大小,最大序列长度,num_hiddens)
X = self.token_embedding(tokens)+self.segment_embedding(segments)
X += self.pos_embedding.data[:,:X.shape[1],:]
for blk in self.blks:
X = blk(X,valid_lens)
return X
假设词表大小为10000,为了演示BERTEncoder的前向推断,Create an instance and initialize its parameters.
vocab_size,num_hiddens,ffn_num_input,ffn_num_hiddens,num_heads,num_layers = 1000,768,768,1024,4,2
norm_shape,dropout = [768],0.2
encoder = BERTEncoder(vocab_size,num_hiddens,norm_shape,ffn_num_input,ffn_num_hiddens,num_heads,num_layers,dropout)
将tokens定义为长度为8的2个输入序列,其中每个词元是词表的索引.使用输入tokens的BERTEncoder的前向推断返回编码结果,其中每个词元由向量表示,其长度由超参数num_hiddens定义,此超参数通常称为Transformer编码器的隐藏大小(隐藏单元数).
tokens = torch.randint(0,vocab_size,(2,8))
segments = torch.tensor([[0,0,0,0,1,1,1,1],[0,0,0,1,1,1,1,1]])
enc_outputs = encoder(tokens,segments,None)
enc_outputs.shape
输出结果如下:
torch.Size([2, 8, 768])
3.预训练任务
BERTEncoderThe forward inference of is given each token of the input text and the special token inserted“”及“”的BERT表示.These representations will be used next to compute pretrainingBERT的损失函数.预训练包括以下两个任务:Masked language model and next sentence prediction.
3.1 掩蔽语言模型(Masked Language Modeling)
为了双向编码上下文以表示每个词元,BERT随机掩蔽词元并使用来自双向上下文的词元以自监督的方式预测掩蔽词元,此任务称为掩蔽语言模型(完形填空).
在这个预训练任务中,将随机选择15%的词元作为预测的掩蔽词元.要预测一个掩蔽词元而不使用标签作弊,一个简单的方法是总是用一个特殊的“<mask>”替换输入序列中的词元.然而,人造特殊词元“<mask>”不会出现在微调中.为了避免预训练和微调之间的这种不匹配,如果为预测而屏蔽词元(例如,在“this movie is great”中选择掩蔽和预测“great”),则在输入中将其替换为:
- 80%时间为特殊的“<mask>“词元(例如,“this movie is great”变为“this movie is<mask>”;
- 10%时间为随机词元(例如,“this movie is great”变为“this movie is drink”);
- 10%时间内为不变的标签词元(例如,“this movie is great”变为“this movie is great”).
注意,在20%的时间中,有10%的时间插入了随机词元.这种偶然的噪声鼓励BERT在其双向上下文编码中不那么偏向于掩蔽词元(尤其是当标签词元保持不变时).
实现下面的MaskLM类来预测BERT预训练的掩蔽语言模型任务中的掩蔽标记.预测使用单隐藏层的多层感知机(self.mlp).在前向推断中,它需要两个输入:BERTEncoder的编码结果和用于预测的词元位置,输出是这些位置的预测结果.
class MaskLM(nn.Module):
"""BERT的掩蔽语言模型任务"""
def __init__(self,vocab_size,num_hiddens,num_inputs=768,**kwargs):
super(MaskLM,self).__init__()
self.mlp = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(num_inputs,num_hiddens),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.LayerNorm(num_hiddens),
nn.Linear(num_hiddens,vocab_size))
def forward(self,X,pred_positions):
num_pred_positions = pred_positions.shape[1]
pred_positions_id = pred_positions.reshape(-1)
batch_size = X.shape[0]
batch_id = torch.arange(0,batch_size)
batch_idx = torch.repeat_interleave(batch_id,num_pred_positions)
# 假设batch_size=2,num_pred_positions=3
# 那么batch_idx是np.array([0,0,0,1,1,1])
masked_X = X[batch_idx,pred_positions_id]
masked_X = masked_X.reshape((batch_size,num_pred_positions,-1))
mlm_Y_hat = self.mlp(masked_X)
return mlm_Y_hat
为了演示MaskLM的前向推断,created its instancemlm并对其进行了初始化.将mlm_positions定义为在encoded_X的任一输入序列中预测的3个指示.mlm的前向推断返回encoded_X的所有掩蔽位置mlm_positions处的预测结果mlm_Y_hat.对于每个预测,结果的大小等于词表的大小.
mlm = MaskLM(vocab_size,num_hiddens)
pred_positions = torch.tensor([[1,5,2],[6,1,5]])
mlm_Y_hat = mlm(enc_outputs,pred_positions)
mlm_Y_hat.shape
输出结果如下:
torch.Size([2, 3, 1000])
通过掩码下的预测词元mlm_Y的真实标签mlm_Y_hat,可以计算在BERT预训练中的遮蔽语言模型任务的交叉熵损失.
mlm_Y = torch.tensor([[7,8,9],[10,11,12]])
loss = nn.CrossEntropyLoss(reduction='none')
mlm_loss = loss(mlm_Y_hat.reshape((-1,vocab_size)),mlm_Y.reshape(-1))
print('mlm_loss:',mlm_loss,'\n shape:',mlm_loss.shape)
输出结果如下:
mlm_loss: tensor([7.0592, 6.6084, 6.6682, 6.9848, 8.1962, 6.7052],
grad_fn=<NllLossBackward0>)
shape: torch.Size([6])
3.2 下一句预测(Next Sentence Prediction)
尽管掩蔽语言建模能够编码双向上下文来表示单词,但它不能显式地建模文本对之间的逻辑关系.为了帮助理解两个文本序列之间的关系,BERT在预训练中考虑了一个二元分类任务——下一句预测.在为预训练生成句子对时,Half the time they are labeled“真”的连续句子;在另一半的时间里,第二个句子是从语料库中随机抽取的,标记为“假”.
下面的NextSentencePred类使用单隐藏层的多层感知机来预测第二个句子是否是BERT输入序列中第一个句子的下一个句子.由于Transformer编码器中的自注意力,特殊词元“”的BERT表示已经对输入的两个句子进行了编码.因此,多层感知机分类器的输出层(self.output)以X作为输入,其中X是多层感知机隐藏层的输出,而MLP隐藏层的输入是编码后的“”词元.
class NextSentencePred(nn.Module):
"""BERT的下一句预测任务"""
def __init__(self,num_inputs):
super(NextSentencePred,self).__init__()
self.output = nn.Linear(num_inputs,2)
def forward(self,X):
# X的形状:(batchsize,num_hiddens)
return self.output(X)
可以看到,NextSentencePred实例的前向推断返回每个BERT输入序列的二分类预测.
# NSP的输入形状:(batchsize,num_hiddens)
nsp = NextSentencePred(enc_outputs.shape[-1])
nsp_Y_hat = nsp(enc_outputs[:,0,:]) #只把<cls>(The feature dimension of the first token of each sequence)The feature dimension input of nsp中就行
print('nsp_Y_hat:',nsp_Y_hat,'\nnsp_Y_hat_shape:',nsp_Y_hat.shape)
输出结果如下:
nsp_Y_hat: tensor([[0.4534, 0.2836],
[0.5663, 0.1450]], grad_fn=<AddmmBackward0>)
nsp_Y_hat_shape: torch.Size([2, 2])
计算两个二元分类的交叉熵损失.
nsp_Y = torch.tensor([0,1])
nsp_loss = loss(nsp_Y_hat,nsp_Y)
print('nsp_loss:',nsp_loss,'\nnsp_loss_shape:',nsp_loss.shape)
输出结果如下:
nsp_loss: tensor([0.6119, 0.9258], grad_fn=<NllLossBackward0>)
nsp_loss_shape: torch.Size([2])
4. 整合代码
在预训练BERT时,最终的损失函数是掩蔽语言模型损失函数和下一句预测损失函数的线性组合.Now by instantiating three classesBERTEncoder、MaskLM和NextSentencePred来定义BERTModel类.前向推断返回编码后的BERT表示encoded_X、掩蔽语言模型预测mlm_Y_hat和下一句预测nsp_Y_hat.
class BERTModel(nn.Module):
"""BERT模型"""
def __init__(self,vocab_size,num_hiddens,norm_shape,ffn_num_input,ffn_num_hiddens,num_heads,num_layers,dropout,max_len=1000,key_size=768,query_size=768,value_size=768,use_bias=True,hid_in_features=768,mlm_in_features=768,nsp_in_features=768):
super(BERTModel,self).__init__()
self.encoder = BERTEncoder(vocab_size,num_hiddens,norm_shape,ffn_num_input,ffn_num_hiddens,num_heads,num_layers,dropout,max_len,key_size,query_size,value_size,use_bias)
self.mlm = MaskLM(vocab_size,num_hiddens,mlm_in_features)
self.hidden = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(hid_in_features,num_hiddens),
nn.Tanh())
self.nsp = NextSentencePred(nsp_in_features)
def forward(self,tokens,segments,valid_lens=None,pred_positions=None):
encoder_X = self.encoder(tokens,segments,valid_lens)
if pred_positions is not None:
mlm_Y_hat = self.mlm(encoder_X,pred_positions)
else:
mlm_Y_hat = None
# 用于下一句预测的多层感知机分类器的隐藏层,0是“<cls>”标记的索引
nsp_Y_hat = self.nsp(self.hidden(encoder_X[:,0,:]))
return encoder_X,mlm_Y_hat,nsp_Y_hat
5. 小结
- word2vec和GloVeEqual word embedding models are context-agnostic.They assign the same pretrained vector to the same word,而不考虑词的上下文(如果有的话).They have difficulty handling polysemy or complex semantics in natural language.
- For context-sensitive word representations,如ELMo和GPT,The representation of words depends on their context.
- ELMo对上下文进行双向编码,但使用特定于任务的架构(然而,Designing a specific architecture for each NLP task is actually not easy);而GPT是任务无关的,但是从左到右编码上下文.
- BERTCombines the best of both worlds:它对上下文进行双向编码,And requires minimal architectural changes for a large number of natural language processing tasks.
- BERT输入序列的嵌入是词元嵌入、片段嵌入和位置嵌入的和.
- 预训练包括两个任务:Masked language model and next sentence prediction.前者能够编码双向上下文来表示单词,而后者则显式地建模文本对之间的逻辑关系.
6. 全部代码
import torch
import d2l.torch
from torch import nn
def get_tokens_segments(tokens_a, tokens_b=None):
"""获取输入序列的词元及其片段索引"""
tokens = ['<cls>'] + tokens_a + ['<sep>']
# 0和1分别标记片段A和B
segments = [0] * (len(tokens_a) + 2)
if tokens_b is not None:
tokens += tokens_b + ['<sep>']
segments += [1] * (len(tokens_b) + 1)
return tokens, segments
class BERTEncoder(nn.Module):
"""BERT编码器"""
def __init__(self, vocab_size, num_hiddens, norm_shape, ffn_num_input, ffn_num_hiddens, num_heads, num_layers,
dropout, max_len=1000,
key_size=768, query_size=768, value_size=768, use_bias=True):
super(BERTEncoder, self).__init__()
self.token_embedding = nn.Embedding(vocab_size, num_hiddens)
self.segment_embedding = nn.Embedding(2, num_hiddens)
# 在BERT中,位置嵌入是可学习的,因此我们创建一个足够长的位置嵌入参数
self.pos_embedding = nn.Parameter(torch.randn(size=(1, max_len, num_hiddens)))
self.blks = nn.Sequential()
for i in range(num_layers):
self.blks.add_module(f'{i}',
d2l.torch.EncoderBlock(key_size, query_size, value_size, num_hiddens, norm_shape,
ffn_num_input, ffn_num_hiddens, num_heads, dropout, use_bias))
def forward(self, tokens, segments, valid_lens):
# 在以下代码段中,X的形状保持不变:(批量大小,最大序列长度,num_hiddens)
X = self.token_embedding(tokens) + self.segment_embedding(segments)
X += self.pos_embedding.data[:, :X.shape[1], :]
for blk in self.blks:
X = blk(X, valid_lens)
return X
vocab_size, num_hiddens, ffn_num_input, ffn_num_hiddens, num_heads, num_layers = 1000, 768, 768, 1024, 4, 2
norm_shape, dropout = [768], 0.2
encoder = BERTEncoder(vocab_size, num_hiddens, norm_shape, ffn_num_input, ffn_num_hiddens, num_heads, num_layers,
dropout)
tokens = torch.randint(0, vocab_size, (2, 8))
segments = torch.tensor([[0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1], [0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1]])
enc_outputs = encoder(tokens, segments, None)
enc_outputs.shape
class MaskLM(nn.Module):
"""BERT的掩蔽语言模型任务"""
def __init__(self, vocab_size, num_hiddens, num_inputs=768, **kwargs):
super(MaskLM, self).__init__()
self.mlp = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(num_inputs, num_hiddens),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.LayerNorm(num_hiddens),
nn.Linear(num_hiddens, vocab_size))
def forward(self, X, pred_positions):
num_pred_positions = pred_positions.shape[1]
pred_positions_id = pred_positions.reshape(-1)
batch_size = X.shape[0]
batch_id = torch.arange(0, batch_size)
batch_idx = torch.repeat_interleave(batch_id, num_pred_positions)
# 假设batch_size=2,num_pred_positions=3
# 那么batch_idx是np.array([0,0,0,1,1,1])
masked_X = X[batch_idx, pred_positions_id]
masked_X = masked_X.reshape((batch_size, num_pred_positions, -1))
mlm_Y_hat = self.mlp(masked_X)
return mlm_Y_hat
mlm = MaskLM(vocab_size, num_hiddens)
pred_positions = torch.tensor([[1, 5, 2], [6, 1, 5]])
mlm_Y_hat = mlm(enc_outputs, pred_positions)
mlm_Y_hat.shape
mlm_Y = torch.tensor([[7, 8, 9], [10, 11, 12]])
loss = nn.CrossEntropyLoss(reduction='none')
mlm_loss = loss(mlm_Y_hat.reshape((-1, vocab_size)), mlm_Y.reshape(-1))
print('mlm_loss:', mlm_loss, '\n shape:', mlm_loss.shape)
class NextSentencePred(nn.Module):
"""BERT的下一句预测任务"""
def __init__(self, num_inputs):
super(NextSentencePred, self).__init__()
self.output = nn.Linear(num_inputs, 2)
def forward(self, X):
# X的形状:(batchsize,num_hiddens)
return self.output(X)
# NSP的输入形状:(batchsize,num_hiddens)
nsp = NextSentencePred(enc_outputs.shape[-1])
nsp_Y_hat = nsp(enc_outputs[:, 0, :]) #只把<cls>(The feature dimension of the first token of each sequence)The feature dimension input of nsp中就行
print('nsp_Y_hat:', nsp_Y_hat, '\nnsp_Y_hat_shape:', nsp_Y_hat.shape)
nsp_Y = torch.tensor([0, 1])
nsp_loss = loss(nsp_Y_hat, nsp_Y)
print('nsp_loss:', nsp_loss, '\nnsp_loss_shape:', nsp_loss.shape)
class BERTModel(nn.Module):
"""BERT模型"""
def __init__(self, vocab_size, num_hiddens, norm_shape, ffn_num_input, ffn_num_hiddens, num_heads, num_layers,
dropout, max_len=1000, key_size=768, query_size=768, value_size=768, use_bias=True,
hid_in_features=768, mlm_in_features=768, nsp_in_features=768):
super(BERTModel, self).__init__()
self.encoder = BERTEncoder(vocab_size, num_hiddens, norm_shape, ffn_num_input, ffn_num_hiddens, num_heads,
num_layers, dropout, max_len, key_size, query_size, value_size, use_bias)
self.mlm = MaskLM(vocab_size, num_hiddens, mlm_in_features)
self.hidden = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(hid_in_features, num_hiddens),
nn.Tanh())
self.nsp = NextSentencePred(nsp_in_features)
def forward(self, tokens, segments, valid_lens=None, pred_positions=None):
encoder_X = self.encoder(tokens, segments, valid_lens)
if pred_positions is not None:
mlm_Y_hat = self.mlm(encoder_X, pred_positions)
else:
mlm_Y_hat = None
# 用于下一句预测的多层感知机分类器的隐藏层,0是“<cls>”标记的索引
nsp_Y_hat = self.nsp(self.hidden(encoder_X[:, 0, :]))
return encoder_X, mlm_Y_hat, nsp_Y_hat
7. 相关链接
BERT预训练第一篇:李沐动手学深度学习V2-bert和代码实现
BERT预训练第二篇:李沐动手学深度学习V2-bert预训练数据集和代码实现
BERT预训练第三篇:李沐动手学深度学习V2-BERT预训练和代码实现
边栏推荐
- 姑姑:给小学生出点口算题
- Golang source code analysis: juju/ratelimit
- 开关、电机、断路器、电热偶、电表接线图大全
- 云平台简介
- php 单引号 双引号 -> => return echo
- C# Barrier类
- Triacetin是什么化学材料
- J9 digital theory: the Internet across chain bridge has what effect?
- 2170. 使数组变成交替数组的最少操作数
- 特拉维夫大学 | Efficient Long-Text Understanding with Short-Text Models(使用短文本模型进行高效的长文本理解)
猜你喜欢
Parse the commonly used methods in the List interface that are overridden by subclasses

Translate My Wonderful | July Moli Translation Program Winners Announced
信息系统项目管理师必背核心考点(五十八)变更管理的主要角色

callback prototype __proto__

基于 outline 实现头像剪裁以及预览
Parse common methods in the Collection interface that are overridden by subclasses
KDD 2022 | 深度图神经网络中的特征过相关:一个新视角

程序员也许都缺一个“二舅”精神
GNN教程:图神经网络基础知识!
如何解决图像分类中的类别不均衡问题?不妨试试分开学习表征和分类器
随机推荐
unittest自动化测试框架总结
9,共模抑制比一-不受输入信号中共模波动的影响。【如何分析共模CM抑制比。】
PyTorch分布式backends
软件测试分类
Lvm逻辑卷
信息学奥赛一本通(1260:【例9.4】拦截导弹(Noip1999))
golang源码分析:time/rate
Thread线程类基本使用(上)
特拉维夫大学 | Efficient Long-Text Understanding with Short-Text Models(使用短文本模型进行高效的长文本理解)
.NET如何快速比较两个byte数组是否相等
软件成分分析:华为云重磅发布开源软件治理服务
ACE JET NPOI
golang 源码分析:juju/ratelimit
【手撕AHB-APB Bridge】~ AMBA总线 之 APB
Informatics Olympiad All-in-One (1260: [Example 9.4] Intercepting Missiles (Noip1999))
OpenCV开发中的内存管理问题
Solve the docker mysql can't write Chinese
Common tools and test methods for interface testing (Introduction)
ssdp协议搜索GB28181设备
交 叉 数 组