当前位置:网站首页>Pytorch study notes 7 - processing input of multi-dimensional features
Pytorch study notes 7 - processing input of multi-dimensional features
2022-07-31 06:32:00 【qq_50749521】
Pytorch学习笔记7——处理多维特征的输入
This is a dataset for diabetes classification.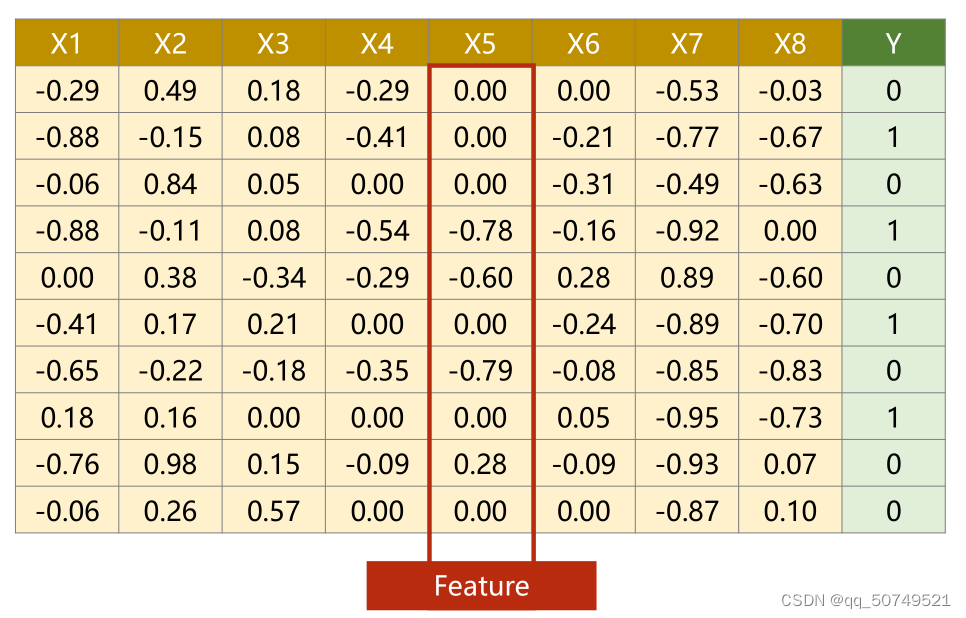
每一行代表一个样本Sample,Each column is called a featurefeature.shared here10个样本,每个样本有8个特征.Y为对应标签.
Dataset preparation is just that:取出前8列得到X矩阵作为input,最后1列得到Ymatrix as labels.
i表示样本索引,nRepresents the feature index.Each eigenvalue is multiplied by a weight.
The result must be a scalar.
对于N样本处理,在torch里继承的moduleFunctions are all vectorized functions,比如sigmoidIt is calculated by vector,The same operation is performed on each element in the matrix.
The weights and biases are the same here.z1 z2 … zn都是标量,组成一个向量.
这样,Matrix operations can be further combined.X矩阵变为N * 8的,w矩阵变成8 * 1的,b矩阵变成N * 1的,Through this vectorized calculation, we can have the ability of parallel computing,提高了运行速度.
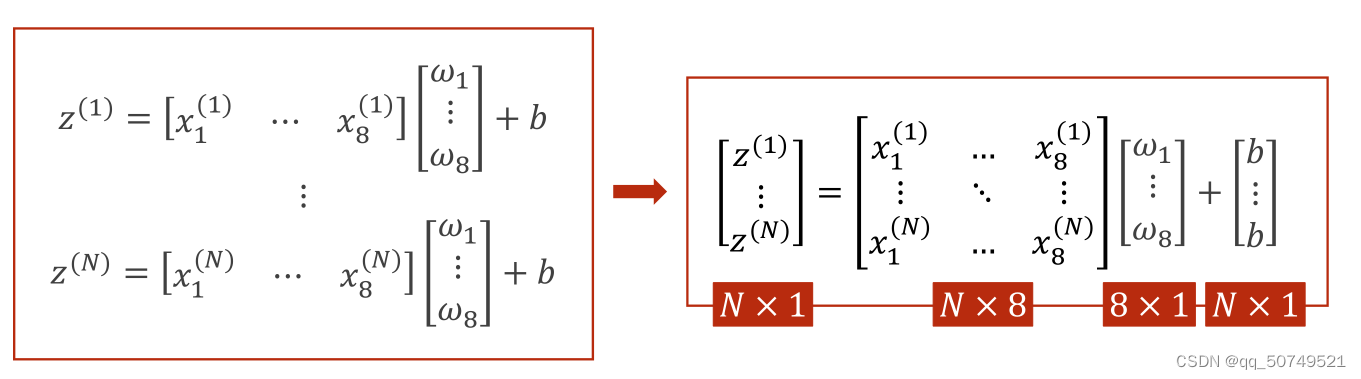
这样,在LinearThe linear layer we have to do is putInput(N, 8)转为output(N, 1).
torch.nn.Linear(input_dim, output_dim), 其中input_dim表示输入数据的特征维度, output_dim表示输出数据的特征维度,这里分别为8,1:
self.linear1 = torch.nn.Linear(8, 1)

损失计算: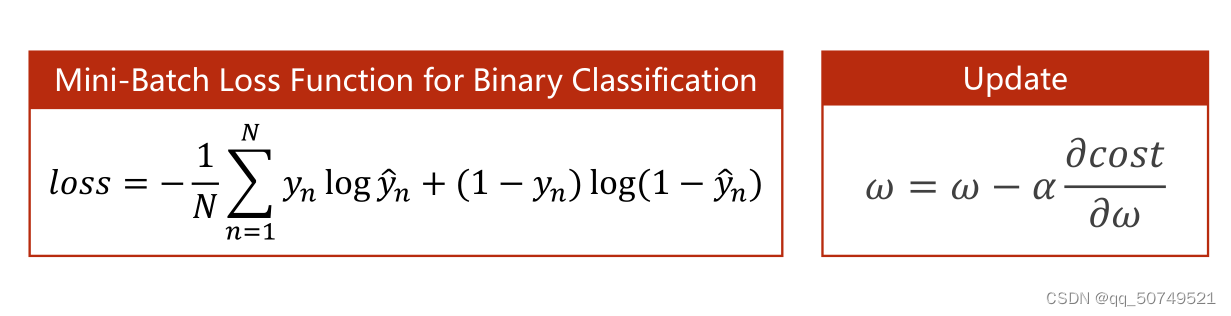
四步走:
- Prepare Dataset
- Design model using class
- construct loss and optimizer
- Training cycle(forward, backward, update)
#Preapre Dataset
import numpy as np
xy = np.loadtxt('F:\ASR-source\Dataset\diabetes.csv.gz', delimiter = ',', dtype = np.float32)
x_data = torch.from_numpy(xy[:,:-1])#Take out all but the last columnyoutside the front8列
y_data = torch.from_numpy(xy[:,[-1]])#取出最后一列
print(x_data.shape)
print(y_data.shape)
输出:
torch.Size([759, 8])
torch.Size([759, 1])
#Design model using class
import torch
class Model(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Model, self).__init__()
self.linear1 = torch.nn.Linear(8, 6)
self.linear2 = torch.nn.Linear(6, 4)
self.linear3 = torch.nn.Linear(4, 1)
self.relu = torch.nn.ReLU()
self.sigmoid = torch.nn.Sigmoid()
def forward(self, x):
x = self.relu(self.linear1(x))
x = self.relu(self.linear2(x))
x = self.sigmoid(self.linear3(x))
return x
#construc loss and optimizer
criterion = torch.nn.BCELoss(reduction='mean')
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(mymodel.parameters(), lr = 0.01)
#training cycle
epoch_list = []
loss_list = []
for epoch in range(500):
y_pred = mymodel(x_data) #得到预测值
loss = criterion(y_pred, y_data) #计算损失
optimizer.zero_grad() #梯度归0
loss.backward() #反向传播更新梯度
optimizer.step()#更新权重、偏置
print('='*10, 'Epoch = ', epoch+1, '='*10)
print(loss.item())
epoch_list.append(epoch)
loss_list.append(loss.item())
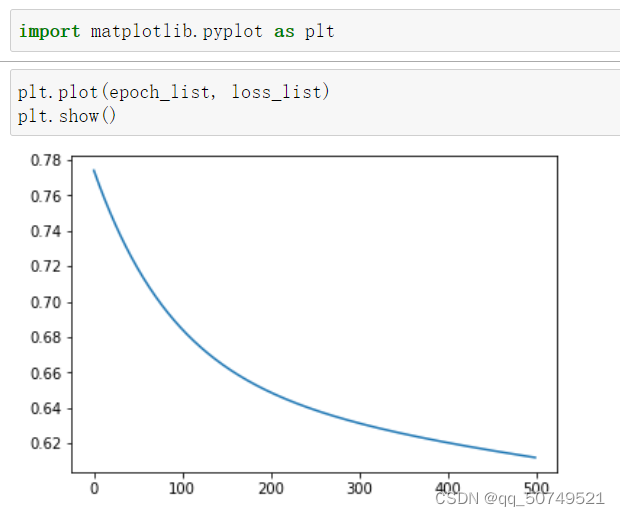
The spatial transformation of the actual species is non-linear.We often use multiple layers of linear transformations,通过找到最优的权重,把他们组合起来,to simulate nonlinear transformations,So the essence of neural network is to find nonlinear spatial transformation.
所以,LinearHere we can go first8D->6D, 6D->4D, 4D->1D,Step by step to reduce the dimensionality.
当然,You can also go up in dimension, 8DChange to higher dimensions24D,further lower.This determines the complexity of the network,As for how to get it,That's the problem with hyperparameter search,See who performs better on the dataset.
中间层数越多,神经元越多,模型的学习能力越强.但并不是越多越好,Too much learning ability will result in learning noisy values of the data,出现过拟合现象,Such models do not generalize well.
class Model(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Model, self).__init__()
self.linear1 = torch.nn.Linear(8, 6)
self.linear2 = torch.nn.Linear(6, 4)
self.linear3 = torch.nn.Linear(4, 1)
self.sigmoid = torch.nn.Sigmoid()
def forward(self, x):
x = self.sigmoid(self.linear1(x))
x = self.sigmoid(self.linear2(x))
x = self.sigmoid(self.linear3(x))
return x

We generally still use itReLU激活,但需要注意的是,ReLUThe input value is less than0都会输出0,This makes it impossible to compute gradients,So activation in the last layer must not be usedReLU,可以改成Sigmoid.如下:
class Model(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Model, self).__init__()
self.linear1 = torch.nn.Linear(8, 6)
self.linear2 = torch.nn.Linear(6, 4)
self.linear3 = torch.nn.Linear(4, 1)
self.relu = torch.nn.ReLU()
self.sigmoid = torch.nn.Sigmoid()
def forward(self, x):
x = self.relu(self.linear1(x))
x = self.relu(self.linear2(x))
x = self.sigmoid(self.linear3(x))#Note that the last step cannot be usedrelu,Avoid failing to compute gradients
return x

End
边栏推荐
- 自然语言处理相关list
- 钉钉H5微应用免登鉴权
- VTK环境配置
- IDEA控制台不能输入信息的解决方法
- cocos2d-x-3.2 create project method
- 多元线性回归方程原理及其推导
- jenkins +miniprogram-ci upload WeChat applet with one click
- After unicloud is released, the applet prompts that the connection to the local debugging service failed. Please check whether the client and the host are under the same local area network.
- 2021-09-30
- DSPE-PEG-COOH CAS: 1403744-37-5 Phospholipid-polyethylene glycol-carboxy lipid PEG conjugate
猜你喜欢

Pytorch学习笔记7——处理多维特征的输入
朴素贝叶斯文本分类(代码实现)

DSPE-PEG-Biotin,CAS:385437-57-0,磷脂-聚乙二醇-生物素可延长循环半衰期
MySQL 入门:Case 语句很好用
MySQL 主从切换步骤

Cholesterol-PEG-NHS NHS-PEG-CLS cholesterol-polyethylene glycol-active ester can modify small molecular materials

CNN的一点理解

MySQL master-slave switching steps
会话和饼干,令牌
Multi-Modal Face Anti-Spoofing Based on Central Difference Networks学习笔记
随机推荐
DSPE-PEG-COOH CAS: 1403744-37-5 Phospholipid-polyethylene glycol-carboxy lipid PEG conjugate
日志jar包冲突,及其解决方法
Jupyter内核正忙、内核挂掉
CNN的一点理解
多元线性回归方程原理及其推导
Cholesterol-PEG-NHS NHS-PEG-CLS cholesterol-polyethylene glycol-active ester can modify small molecular materials
二进制转换成十六进制、位运算、结构体
DingTalk Enterprise Internal-H5 Micro Application Development
ERROR Error: No module factory availabl at Object.PROJECT_CONFIG_JSON_NOT_VALID_OR_NOT_EXIST ‘Error
VS connects to MYSQL through ODBC (1)
Chemical Reagent Phospholipid-Polyethylene Glycol-Amino, DSPE-PEG-amine, CAS: 474922-26-4
钉钉H5微应用免登鉴权
mPEG-DSPE 178744-28-0 甲氧基-聚乙二醇-磷脂酰乙醇胺线性PEG磷脂
MW: 3400 4-Arm PEG-DSPE four-arm-polyethylene glycol-phospholipid a saturated 18-carbon phospholipid
Cholesterol-PEG-Azide CLS-PEG-N3 胆固醇-聚乙二醇-叠氮 MW:3400
pyspark.ml feature transformation module
ROS 之订阅多个topic时间同步问题
Research reagents Cholesterol-PEG-Maleimide, CLS-PEG-MAL, Cholesterol-PEG-Maleimide
VS2017 connects to MYSQL
MySQL 入门:Case 语句很好用