当前位置:网站首页>Golang Chapter 2: Program Structure
Golang Chapter 2: Program Structure
2022-08-03 22:11:00 【I don't know enough to learn~】
名称
规则:开头是字母或下划线,后面跟任意字符、数字和下划线,并区分大小写
书本P20:有25keywords are reserved,There are also three dozen built-in pre-declared constants、类型和函数
如果一个实体在函数声明,它只在函数局部有效.如果声明在函数外,则将Visible to all source files in the package.
The size of the first letter of an entity determines its visibility across packages.如果名称以大写字母开头,它是导出的,means it's rightOutside the package is visible and accessible的,可以被自己包之外的其他程序所引用,如fmt包中的Printf,
The package name itself always consists of lowercase letters
作用域越大,The longer the name used
Use camel case instead of underscore
Acronyms such as HTML,Usually the same case is used.
声明
A declaration names a program entity,并且设定其部分或全部属性.
There are four main declarations:
- 变量 var
- 常量 const
- 类型 type
- 函数 func
This chapter focuses on variables and types,Constants are in Chapter 3,Functions are in Chapter 5
A function declaration contains a name、一个参数列表、An optional list of return values,以及函数体.
变量
格式:var name type = expression
Type and expression can omit one,But it can't be ignored
如果类型省略,Its type is determined by the initializer expression;
如果表达式省略,Its initial value corresponds to the zero value of the type——数字是0,布尔值是false,字符串是"",接口和引用类型(slice、指针、map、通道、函数)是nil.For composite types such as arrays or structures,零值是其所有元素或成员的零值
Go不存在未初始化的变量
A list of variables can be declared,Choose to initialize with the corresponding expression list.Ignoring the type allows to declare multiple variables of different types
var i, j, k int //int int int
var b, f, s = true, 2.3, "four" //bool float64 string
It can also be initialized by calling a function that returns multiple values
var f, err = os.Open(name) //Returns a file and an error
短变量声明
格式:name := expression name的类型由expresssion决定
因其短小、灵活,故而在局部变量的声明和初始化The main use of short declarations.
varDeclarations are usually reserved for local variables whose type is inconsistent with the initializer expression,Or it is used when the variable assignment and variable initial value are not important until later
i := 100
var boiling float64 = 100 //一个float64类型的变量
var name []string
var err error
var p Point
Only accommodate variable declarations with multiple initializers when it helps readability
:=表示声明,而=表示赋值
i,j = j, i //交换i 和 j的值
注意:短变量声明不需要声明所有在左边的变量;If a variable has already been declared in the same syntax block,A short declaration of the variable would then be equivalent to an assignment.
A short variable declaration declares at least one new variable
指针
指针的值是一个变量的地址,You can use pointers without knowing the name of the variable,间接读取或更新变量的值
零值是nil
指针是可比较的,Two pointers if and only if they point to the same variable or bothniltime is equal
函数返回局部变量的地址是非常安全的
var p = f()
func f() *int{
v := 1
return &v
}
返回后v仍然存在,p指向v的地址
new函数
Another way to create variables
格式:new(T),创建一个未命名的T类型变量,初始化为T类型的零值,并返回其地址(地址类型为 *T)
每一次调用newboth return a different variable with a unique address
p := new(int)
q := new(int)
fmt.Println(p == q) //"false"
There is an exception to this rule:两个变量的类型不携带任何信息且是零值,如struct{}或[0]int,in the current implementation,They have the same address
new是一个预声明的函数,不是一个关键字,So it can be redefined to other types,例如:
func delta(old, new int) int{
return new - old
}
自然,在delta函数内,内置的new函数不可用
变量的生命周期
Refers to the time period during which the variable exists during program execution.
包级别变量的生命周期是整个程序的执行时间
局部变量有一个动态的生命周期:每次执行声明语句时创建一个新的实体,A variable lives until it becomes不可访问,这时它占用的存储空间被回收.
函数的参数和返回值也是局部变量,They are created when their closure function is called
The garbage collector determines whether a variable should be collected or not根可达算法,At the same time, local variables will also escape,跟java的差不多
赋值
多重赋值
Allows several variables to be assigned at once
在实际更新变量前,右边所有的表达式被推演,This form is especially useful when variables appear on both sides of an assignment operator,例如,当交换两个变量的值时:
x, y = y, x
a[i], a[j] = a[j], a[i]
It is also possible to make an ordinary assignment sequence compact
i, j, k = 2, 3, 5
如果表达式比较复杂,Avoid using the multiple assignment form,A series of independent statements is easier to read
可赋值性
An assignment statement is an explicit form of assignment,But assignments in many places in the program are implicit:A function call implicitly assigns the value of the parameter to the variable corresponding to the parameter:一个returnstatement implicitly willreturn操作数赋值给结果变量.
复合类型的字面量表达式,如slice:
medals := []string{
"gold", "sliver", "bronze"}
Implicitly assigns a value to each element,等同于:
medals[0] = "gold"
medals[1] = "sliver"
medals[2] = "bronze"
两个值使用 == 和 != 进行比较与可赋值性相关:任何比较中,第一个操作数对于第二个操作数的类型必须是可赋值的,或者可以反过来赋值
类型声明
typeA declaration defines a new named type,It uses the same underlying type as an existing type
格式:type name underlying-type,
type Celsius float64
type Fahrenheit float64
虽然Celsius类型和FahrenheitType bottom layer isfloat64,But they cannot be compared and merged,You can only do it again after forced rotation
详情看P29
包和文件
与java类似
详情看P30
作用域
与java类似
详情看P34
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
1 秒完成授权,Authing 全新上线一键登录功能
21天打卡挑战学习MySQL——《MySQL工具的使用》第一周 第二篇
HCIP第十三天
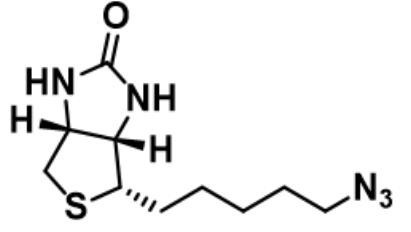
CAS:908007-17-0_Biotin-azide _生物素叠氮化物
七夕快乐!
2022年全国职业院校技能大赛网络安全 B模块 B-1任务一:主机发现与信息收集 国赛原题
shell编程基础
网络基础学习系列四(网络层,数据链路层和一些其他重要协议或技术)
易基因:植物宏病毒组研究:植物病毒的进化与生态 | 顶刊综述
LitJson报错记录
Codeup brushing notes - simple simulation
encapsulation, package, access modifier, static variable
九种方式,教你读取 resources 目录下的文件路径
CAS:122567-66-2_DSPE-Biotin_DSPE-Biotin
L2-041 插松枝
测试2年6.5K,每天“911”,我的心酸经历只有我自己知道···
Kubernetes入门到精通-Operator 模式
noip preliminary round
距LiveVideoStackCon 2022 上海站开幕还有2天!
CAS:1620523-64-9_Azide-SS-biotin_生物素-二硫-叠氮