当前位置:网站首页>【点云处理之论文狂读前沿版12】—— Adaptive Graph Convolution for Point Cloud Analysis
【点云处理之论文狂读前沿版12】—— Adaptive Graph Convolution for Point Cloud Analysis
2022-07-03 08:53:00 【LingbinBu】
Adaptive Graph Convolution for Point Cloud Analysis
摘要
- 问题: 标准的卷积操作无法在3D点间有区分地表示特征对应关系
- 方法: 本文提出Adaptive Graph Convolution(AdaptConv),根据3D点动态学习的特征生成自适应的kernel
- 与使用固定/等向的kernel相比,AdaptConv提高了point cloud卷积的灵活性,有效并精确地得到不同语义部分点间的多种关系
- 与使用注意力权重的方法不同,AdaptConv使得卷积操作更加具有自适应性,而不是简单的为neighboring points分配不同的权重
- 代码:PyTorch版本
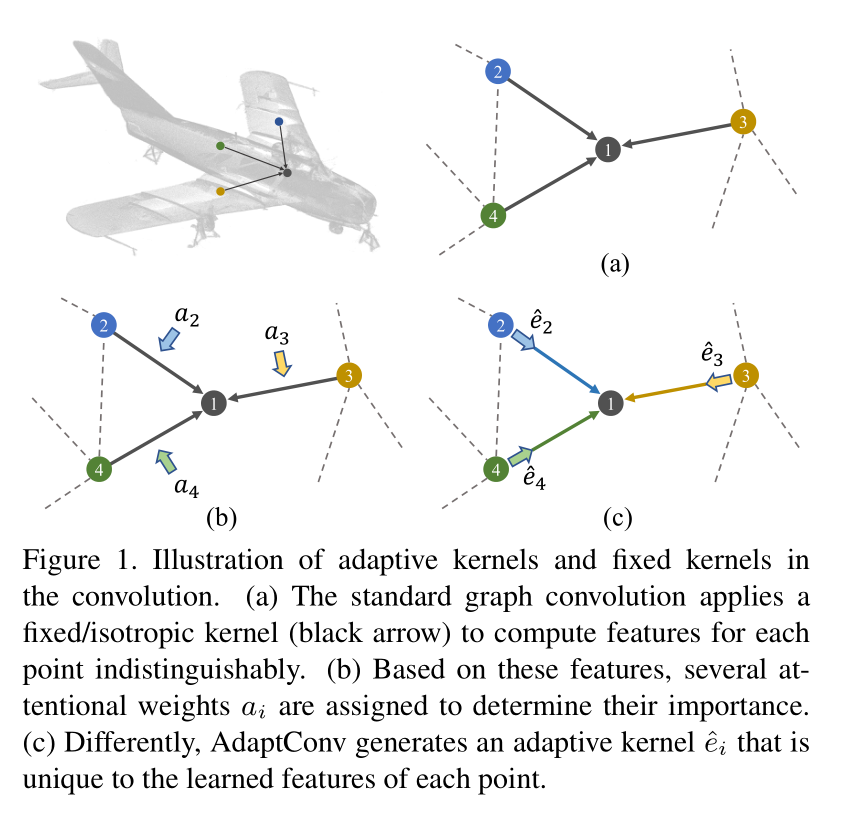
引言
Graph CNNs根据点间的空间/特征相似性将point cloud表示为graph数据,并将images上的2D卷积推广到3D点上。
标准的Graph CNNs通常会在每对点上使用共享权重函数抽取这对点的对应边特征,这会导致得到一个固定/同向的卷积kernel,当作用在所有点对上后,会忽略掉不同特征的对应关系。
该项工作的关键贡献在于AdaptConv能够在graph卷积内使用,而不是基于结果特征的权重函数。
此外,还开发了一些特征卷积设计,能够更加灵活地进行适应性卷积。
方法
Adaptive graph convolution
记 X = { x i ∣ i = \mathcal{X}=\left\{x_{i} \mid i=\right. X={ xi∣i= 1 , 2 , … , N } ∈ R N × 3 1,2, \ldots, N\} \in \mathbb{R}^{N \times 3} 1,2,…,N}∈RN×3为输入点云, F = { f i ∣ i = 1 , 2 , … , N } ∈ R N × D \mathcal{F}=\left\{f_{i} \mid i=1,2, \ldots, N\right\} \in \mathbb{R}^{N \times D} F={ fi∣i=1,2,…,N}∈RN×D为对应的特征,其中 x i x_{i} xi表示第第 i i i个点的 ( x , y , z ) (\mathbf{x}, \mathbf{y}, \mathbf{z}) (x,y,z)坐标,在其他情况下,还可以和其他特征进行结合。
然后根据给定的点云计算有向图 G ( V , E ) \mathcal{G}(\mathcal{V}, \mathcal{E}) G(V,E),其中 V = { 1 , … , N } \mathcal{V}=\{1, \ldots, N\} V={ 1,…,N}和 E ⊆ V × V \mathcal{E} \subseteq \mathcal{V} \times \mathcal{V} E⊆V×V 表示顶点和边的集合。通过包含self-loop的 k k k-nearest neighbors (KNN)构造graph。
在给定输入的 D D D维特征后,AdaptConv layer会产生一组新的 M M M维特征,点的数量和输入相同。与之前的graph convolution层相比,更能精确地反应局部结构特性。
记 x i x_{i} xi是graph convolution的中心点, N ( i ) = { j : ( i , j ) ∈ E } \mathcal{N}(i)=\{j:(i, j) \in \mathcal{E}\} N(i)={ j:(i,j)∈E}是相邻点的索引。由于点云的不规则性,之前的方法通常会在 x i x_{i} xi的所有neighbored points上应用固定的kernel函数,用于捕获patch的几何信息。但是,不同的neighbored points可能会得到对应 x i x_{i} xi不同的特征,特别是当 x i x_{i} xi位于显著区域,比如角或者边处。 在这种情况下,固定的kernel可能无法从graph convolution得到用于分类或分割的几何表示信息。
在本文的方法中,设计了一种自适应性kernel,用于计算每对点之间的显著关系。对于 M M M维输出特征的每一个通道,AdaptConv会动态地生成一个kernel,使用的是应用在points特征 ( f i , f j ) \left(f_{i}, f_{j}\right) (fi,fj) 上的函数:
e ^ i j m = g m ( Δ f i j ) , j ∈ N ( i ) . \hat{e}_{i j m}=g_{m}\left(\Delta f_{i j}\right), j \in \mathcal{N}(i) . e^ijm=gm(Δfij),j∈N(i).
其中 m = 1 , 2 , … , M m=1,2, \ldots, M m=1,2,…,M表示 M M M个输出维度的一个,对应于一个单独的filter。 Δ f i j = [ f i , f j − f i ] \Delta f_{i j}=\left[f_{i}, f_{j}-f_{i}\right] Δfij=[fi,fj−fi]用于捕获全局结构和局部领域特征, [ ⋅ , ⋅ ] [\cdot, \cdot] [⋅,⋅]是拼接操作, g ( ⋅ ) g(\cdot) g(⋅)是特征映射函数,即 M L P MLP MLP。
与2D卷积中的计算一样,将 D D D维输入和对应的filter权重进行卷积得到 M M M维输出中的一维,本文将adaptive kernel和对应的点 ( x i , x j ) \left(x_{i}, x_{j}\right) (xi,xj)进行卷积:
h i j m = σ * e ^ i j m , Δ x i j * , h_{i j m}=\sigma\left\langle\hat{e}_{i j m}, \Delta x_{i j}\right\rangle, hijm=σ*e^ijm,Δxij*,
其中 Δ x i j \Delta x_{i j} Δxij被定义为 [ x i , x j − x i ] \left[x_{i}, x_{j}-x_{i}\right] [xi,xj−xi]相似性, * ⋅ , ⋅ * \langle\cdot, \cdot\rangle *⋅,⋅*表示两个向量的内积,输出为 h i j m ∈ R h_{i j m} \in \mathbb{R} hijm∈R, σ \sigma σ是非线性激活函数。
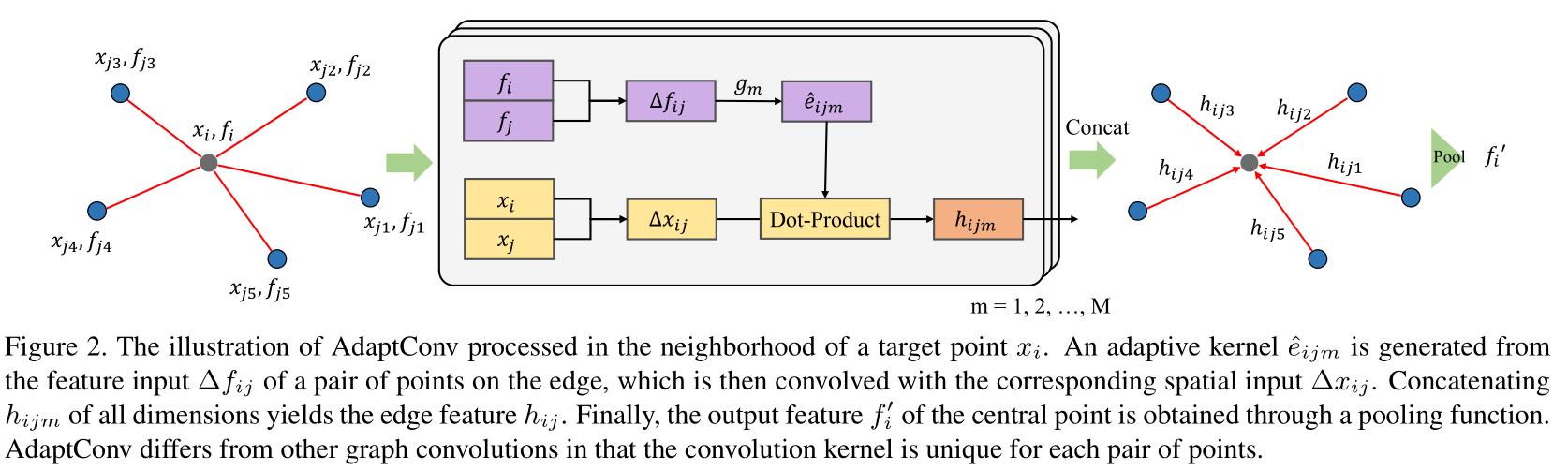
如图2所示,第 m m m个adaptive kernel e ^ i j m \hat{e}_{i j m} e^ijm与对应点 x j ∈ R 3 x_{j} \in \mathbb{R}^{3} xj∈R3的spatial relations Δ x i j \Delta x_{i j} Δxij结合,表示kernel的大小应当与内积相匹配,即特征映射 g m : R 2 D → R 6 g_{m}: \mathbb{R}^{2 D} \rightarrow \mathbb{R}^{6} gm:R2D→R6。存储每个通道的 h i j m h_{i j m} hijm,得到连接点 ( x i , x j ) \left(x_{i}, x_{j}\right) (xi,xj)间的边特征 h i j = h_{i j}= hij= [ h i j 1 , h i j 2 , … , h i j M ] ∈ R M \left[h_{i j 1}, h_{i j 2}, \ldots, h_{i j M}\right] \in \mathbb{R}^{M} [hij1,hij2,…,hijM]∈RM。
最后,通过利用邻域内所有边特征的聚合函数得到central point x i x_{i} xi的输出特征:
f i ′ = max j ∈ N ( i ) h i j , f_{i}^{\prime}=\max _{j \in \mathcal{N}(i)} h_{i j}, fi′=j∈N(i)maxhij,
其中max是以通道为单位的max-pooling函数。总之,AdaptConv的convolution weights被定义为defined as Θ = ( g 1 , g 2 , … , g M ) \Theta=\left(g_{1}, g_{2}, \ldots, g_{M}\right) Θ=(g1,g2,…,gM)。
Feature decisions
就是利用特征去寻找空间关系。
如果输入 x i ∈ R E x_i \in \mathbb{R}^E xi∈RE包含了更多的信息,那就是另外的选项,在实验中会考虑到。
将空间信息 Δ x i j \Delta x_{i j} Δxij替换为特征信息 Δ f i j \Delta f_{i j} Δfij,会得到不同的 e ^ i j m \hat{e}_{i j m} e^ijm,这个也是可以考虑的选项。
本文选择使用 Δ x i j \Delta x_{i j} Δxij作为变换域有着如下的考虑:
- 点特征已经被用于生成adaptive kernel了,在使用特征进行卷积会导致特征信息的冗余
- 特征的维度高,MLP在高维空间中学习起来很困难
- 消耗内存大,计算复杂度高
Network architecture

graph的结构在每一层都是动态更新的
实验
Classifcation

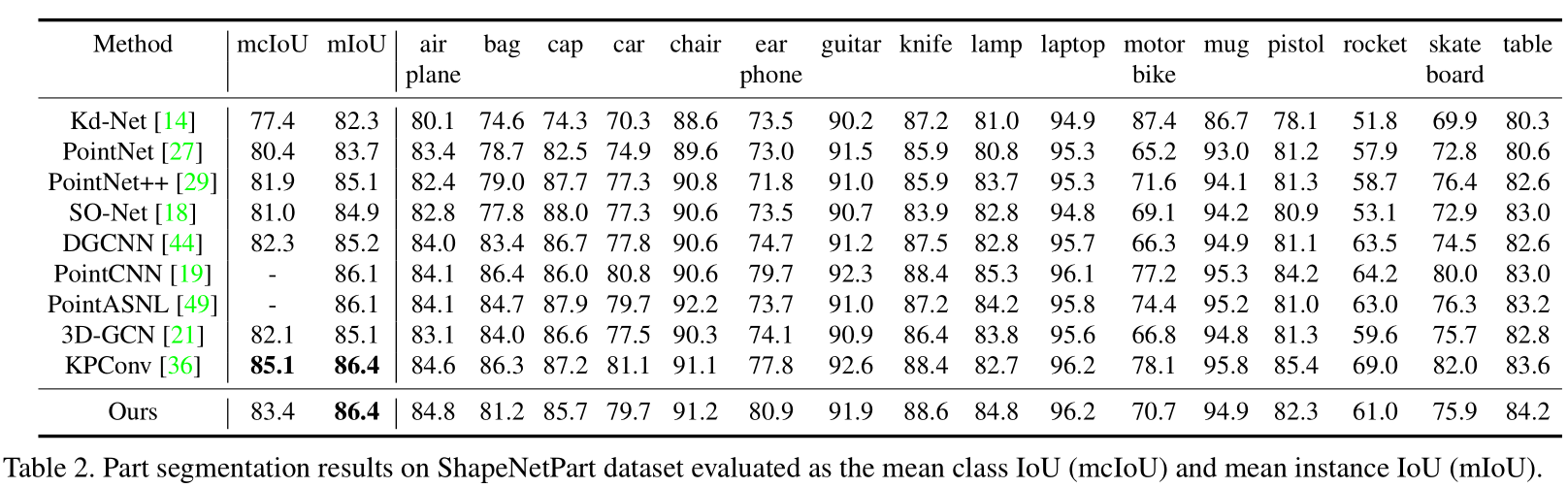
Part segmentation
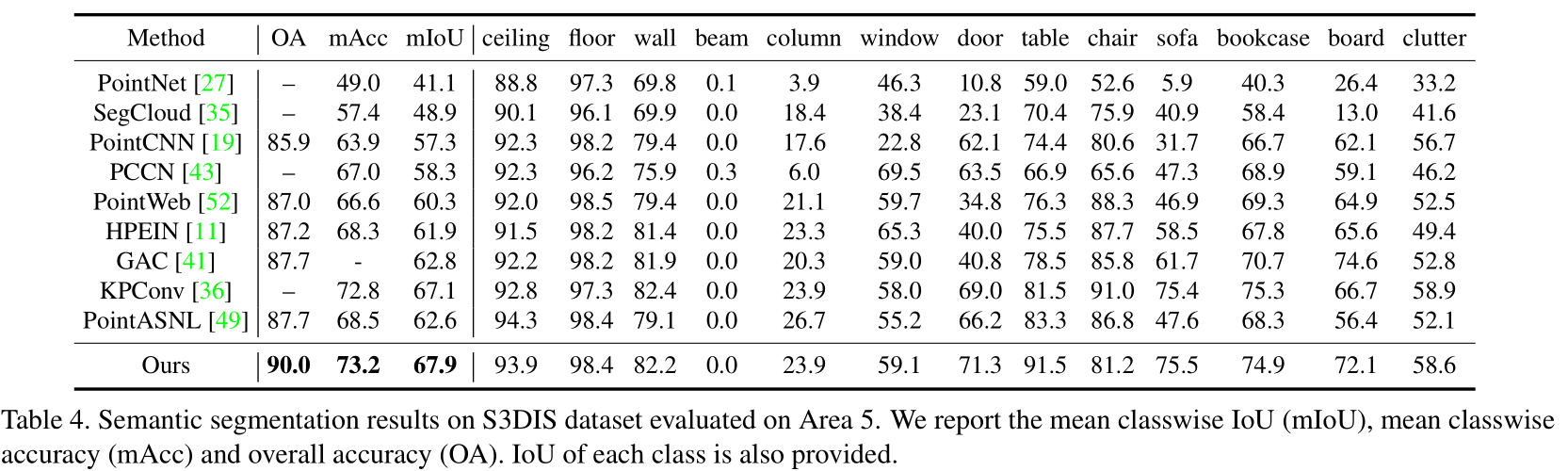
Indoor scene segmentation

Ablation studies
Adaptive convolution vs Fixed kernels & Feature decisions

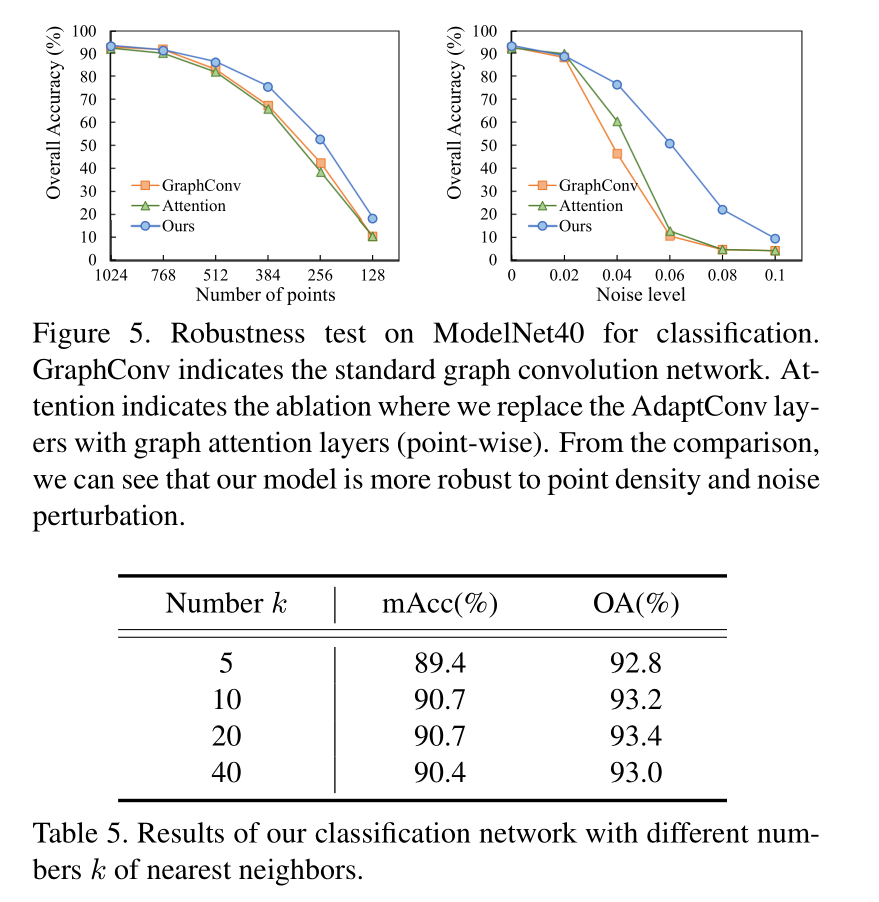
Robustness test
Efficiency

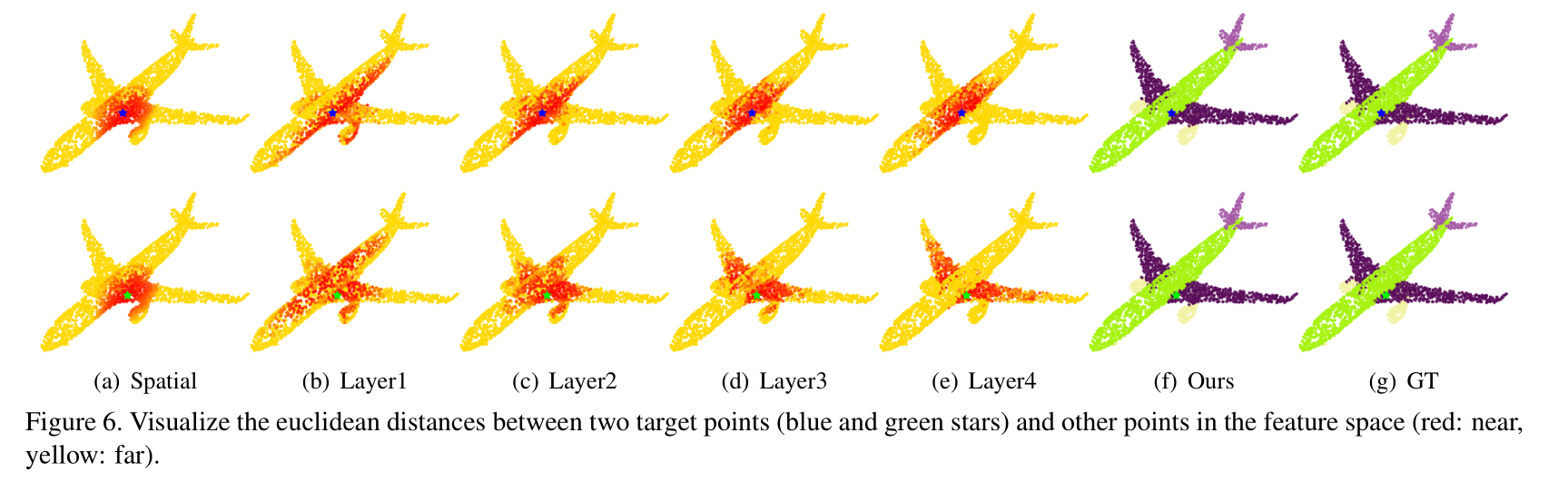
Visualization and learned features
边栏推荐
- What is an excellent fast development framework like?
- LeetCode 324. Swing sort II
- 20220630学习打卡
- LeetCode 515. Find the maximum value in each tree row
- 推荐一个 yyds 的低代码开源项目
- LeetCode 241. Design priorities for operational expressions
- 20220630 learning clock in
- Notes and bugs generated during the use of h:i:s and y-m-d
- Debug debugging - Visual Studio 2022
- Format - C language project sub file
猜你喜欢
How to use Jupiter notebook
Common penetration test range

LeetCode 30. Concatenate substrings of all words

LeetCode 241. Design priorities for operational expressions

How to place the parameters of the controller in the view after encountering the input textarea tag in the TP framework

Binary tree sorting (C language, int type)
Concurrent programming (III) detailed explanation of synchronized keyword

Tree DP acwing 285 A dance without a boss

Find the combination number acwing 886 Find the combination number II

Education informatization has stepped into 2.0. How can jnpf help teachers reduce their burden and improve efficiency?
随机推荐
樹形DP AcWing 285. 沒有上司的舞會
Character pyramid
Vscode connect to remote server
Apache startup failed phpstudy Apache startup failed
In the digital transformation, what problems will occur in enterprise equipment management? Jnpf may be the "optimal solution"
网络安全必会的基础知识
What is the difference between sudo apt install and sudo apt -get install?
PIC16F648A-E/SS PIC16 8位 微控制器,7KB(4Kx14)
AcWing 788. Number of pairs in reverse order
The "booster" of traditional office mode, Building OA office system, was so simple!
22-05-26 Xi'an interview question (01) preparation
【点云处理之论文狂读经典版8】—— O-CNN: Octree-based Convolutional Neural Networks for 3D Shape Analysis
LeetCode 715. Range module
DOM 渲染系统(render mount patch)响应式系统
【点云处理之论文狂读前沿版10】—— MVTN: Multi-View Transformation Network for 3D Shape Recognition
我们有个共同的名字,XX工
JS ternary operator - learning notes (with cases)
LeetCode 30. 串联所有单词的子串
TP5 order multi condition sort
Facial expression recognition based on pytorch convolution -- graduation project