当前位置:网站首页>Learning records of new keywords, references & pointers
Learning records of new keywords, references & pointers
2022-06-12 15:01:00 【From spring to winter】
List of articles
One 、New Keyword learning
1.C++ adopt new Keyword to dynamically allocate memory .
2.new The opened space is stored on the heap , The variables we define are stored on the stack .
3.new Allocated space usage delete Release ,new[] Use delete[] Release .
Int* pi = new int(5); // Indicates the dynamic allocation of a int, Initialize to 5
Int* pa = new int[5]; // Indicates dynamic allocation of an array , The array size is 5
If you define a class A, Class members are int i;
Constructor is :A::A(int _i):i(_i*_i);
A* pa = new A(3);
Three things have been done :
1. Get a piece of memory space , The space size is sizeof(A);
2. Call constructor ;
3. Return pointer pa
Two 、& Learning from
//1. Address fetch ,int Type pointer b The value of is a The address of
int a = 1; int* b = &a;
//2. quote ,b yes a Another name for
int a = 1;int &b = a;
3、 ... and 、 Pointer learning
1. What is the pointer ?
Pointer is “ Point to ” Another type of compound type . A composite type is a type defined based on other types .
Understanding pointers starts with memory , Memory is a big , Linear array of bytes . Each byte is a fixed size , from 8 Binary bits make up . The key is , Each byte has a unique number , Number from 0 Start , Until the last byte . After the program is loaded into memory , Variables used in programs 、 Constant 、 Functions and other data have their own unique number , This number is the address of the data .
The value of a pointer is essentially a memory unit ( The byte ) The number of , So the pointer looks at the value alone , It's also an integer , They usually use 16 Hexadecimal said . The value of the pointer is stored in the size of a machine word , in other words , For a machine, the word is w For a bit of computer , Its virtual address space is 0~2(w The next power )-1, The program can access at most 2 Of w Power bytes , That's why xp such 32 Bit system maximum support 4GB Memory reasons .
So it can be understood as : A pointer is the address of program data in memory , And pointer variables are variables that hold these addresses .
2. The storage of variables in a program
Let's take the simplest example int a = 1, Suppose the computer uses big end storage :
There are several rules for memory data :
① All data in the computer is stored in binary
② The data type determines the amount of memory used
③ The address occupying memory is the address of the byte with the smallest address value .
Now it's understandable a Why is the memory occupied 4 Bytes , And the first address is 0028FF40 了 .
3. Pointer object ( Variable )
The object used to hold the pointer , Is the pointer object .
If the pointer variable p1 Saved variables a The address of , Which means :p1 Points to the variable a, It can also be said that p1 Yes a The memory block where it is , This kind of pointing relationship , In the figure, it is generally indicated by an arrow :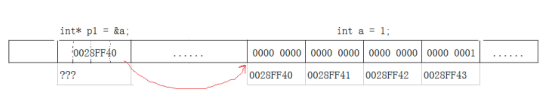
Pointer object p1 Also has its own memory space ,32 Bit machine occupation 4 Bytes ,64 Bit machine occupied 8 Bytes .
3.1 Define a pointer object
When defining pointer variables , Write a... Before the variable name * Number , This variable becomes a pointer variable of the corresponding variable type .
Add... If necessary () To avoid priority issues :
Int* p_int ; // Point to int Variable pointer of type
double* p_double; // Point to double Pointer to type
Student* p_stuct; // Pointer to a class or struct type
Int** p_pointer; // A pointer to a pointer to an integer variable
Int(*p_aar)[3]; // Point to containing 3 individual int Pointer to the array of elements
Int(*p_func)(int,int); // The return type is int, Yes 2 individual int Pointer to the function of the formal parameter
among , Several basic data types are briefly introduced
① Boolean type , namely bool, Its value can only be true perhaps false, Represents non-zero and zero respectively . The assignment of Booleans can be done directly with true perhaps false Assign a value .
② Character , namely char, It is a basic character type , One char The space should ensure that the numeric value corresponding to any character can be stored .
③ integer 
④ floating-point , namely float data type , It is considered to be single precision ,double The data type is usually float Twice the size of , So it is considered as double precision . seeing the name of a thing one thinks of its function ,long double Data types are better than double Be big . The exact size of these data types depends on the computer currently in use . The only guarantee is :
Double At least with float The same big as that
Long double At least with double The same big as that
about float The significant number is about 7 position , So the more bits the integer part occupies , The lower the precision of the decimal part , When the integer part exceeds 9999999 The last decimal part is completely out of precision .
And we sometimes use float64, It takes up... In a single memory 8 Bytes , It can effectively improve the accuracy .
3.2 Get object address
Pointer is used to store the address of an object , To get the address , You need to use the address character (&), as follows :
int add(int a,int b)
{
return a+b;
}
int main(void)
{
int num = 97;
float score = 10.00F;
int arr[3] = {
1,2,3};
int* p_num = #
int* p_arr1 = arr; //p_arr1 It means to point to the first element of the array
float* p_score = &score;
int (*p_arr)[3] = &arr;
int (*fp_add)(int, int) = add;
const char* p_msg = "Hi";
return 0;
}
You can see through it & Use , But there are a few examples that are not used &, Because this is a special case :
① The value of the array name is the address of the first element of the array
② The value of the function name is the address of the function
③ When the string literal constant is used as the right value , This is the name of the character array corresponding to this string , This is the address of the string in memory .
3.3 Resolve address objects
If the pointer points to an object , The dereference character... Is allowed (*) To access the object , as follows :
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
int age = 19;
int* p_age = &age;
*p_age = 20; // Modify the memory data pointed to by pointer
std::cout<<"age = "<<*p_age<<"\n"; // Read the memory data pointed to by the pointer
std::cout<<"age = "<<age<<std::endl;
return 0;
}
For structs and classes , The difference between the two is very small , So it can almost be equated with , Then use -> Symbol access internal members :
struct Student
{
char name[31];
int age;
float score;
};
int main()
{
Student stu = {
"Bob", 19, 98.0};
Student* p_stu = &stu;
p_stu->age = 20;
p_stu->score = 99.0;
std::cout<<"name"<<p_stu->name<<"age"<<p_stu->age<<"score"<<p_stu->score
<<std::endl;
return 0;
}
3.4 The state of the pointer value
Pointer value ( The address ) There will always be one of the following four states :
① Point to the address of an object
② Point to the next location in the space occupied by the next object
③ Null pointer , It means that the pointer doesn't point to any object
④ Invalid pointer , Values other than the above
3.5 Assignment between pointers
Pointer assignment and int Variable assignment is the same , Is to copy the value of the address to another . The assignment between pointers is a shallow copy , It is an efficient way to share memory data among multiple programming units .
Int* p1 = &a;
Int* p2 = p1;
4. The pointer contains information
Through the introduction above , We can see that the pointer contains two parts of information : The value and type information pointed to .
5. Functions and pointers
5.1 Arguments and pointers to functions
Arguments passed to parameters , It's delivered by value , in other words , A formal parameter in a function is a copy of an actual parameter , Formal and actual parameters are just the same on the value , Instead of the same memory data object .
That means : This data transfer is one-way , That is, from the caller to the called function , The transferred function cannot modify the parameters to achieve the effect of return .
#include <iostream>
void change(int a)
{
a++; // Only the local variables of the function are changed in the function a, And with the end of the function execution ,a Be destroyed .
}
int main()
{
int age = 19;
change(age);
std::cout<<"age = "<<age; //age = 19
return 0;
}
The output is age = 19, This indicates that the called function cannot modify the passed parameters to achieve the effect of returning
Sometimes we can use the return value of a function to return data , It can be done in simple cases , But if the return value has other uses ( For example, return the execution status of a function ), Or the returned data is more than one , The return value can't be solved .
Passing a pointer to a variable can easily solve the above problem
#include <iostream>
void change(int* a)
{
(*a)++; // Because the message is age The address of , therefore a Point to memory data age
// When you set a pointer in a function a When solving the address , It will go directly to the memory to find age This data , Then add it 1
}
int main()
{
int age = 19;
change(&age);
std::cout<<"age = "<<age; //age = 20
return 0;
}
So the return value is age = 20
In addition to the above methods , You can also choose to use references :
void change(int &a)
{
a++; //a Namely age Another name for , Or you can say nickname , So for a add 1 The same is true age
// Add 1
}
int main()
{
int age = 19;
change(age);
std::cout<<"age = "<<age; //age = 20
return 0;
}
5.2 Pointer to function
Each function itself is also a kind of program data , A function contains multiple execution statements , After it is compiled , It is essentially a collection of multiple machine instructions . After the program is loaded into memory , The machine instructions of functions are stored in a specific logical area : Code section . Since it is stored in memory , So the function also has its own pointer .
In fact, the function list is the pointer of this function when used alone .
#include <iostream>
int add(int a, int b) // Definition of function
{
return a+b;
}
int main()
{
int (*p_add)(int, int); // Declaration of function pointer
p_add = add; // Assign a value to a function pointer
p_add = &add; // It's the same as above
int c = p_add(1,2); // Use the same as the function name
int d = (*p_add)(1,2); // It is the same as the above call
std::cout<<"The value of c"<<c<<std::endl;
std::cout<<"The value of d"<<d<<std::endl;
return 0;
}
5.3 Return value and pointer
The only thing to note here is not to return the address of a non static local variable . We know that local variables are in the stack , Created and destroyed by the system , The returned address may be invalid , This will cause bug.
You can return global variables 、 Static local variables 、 Address return of dynamic memory, etc .
6.const With the pointer
Here are mainly pointer constants and constant pointers , The main difference between the two is that const Who are you decorating .
6.1 Constant pointer
It's actually a pointer , The pointer itself is a constant .
Int a = 97;
Int b = 98;
Int* const p = &a;
*p = 98; // correct
P = &b; // error
Constant pointers must be initialized , And once initialization is complete , Then its value cannot be changed .
6.2 pointer to const
Int a = 97;
Int b = 98;
Const int* p = &a;
Int const *p = &a; // Both have the same meaning
*p = 98; // Compilation error
P = &b; // correct
The so-called pointer to a constant only requires that the value of the object cannot be changed through the pointer , But the value of an object can be changed in other ways .
Summary
Today is another fishing day … Happy Monday [ love ]!
边栏推荐
- [SPARK][CORE] 面试问题之什么是 external shuffle service?
- Structure example
- Ankai microelectronics rushes to the scientific innovation board: the annual revenue of 500million Xiaomi industry fund is the shareholder
- Yiwei lithium energy plans to raise 9billion yuan: liujincheng and luojinhong jointly subscribe for 6billion yuan of layout Optical Valley
- 模块八
- 基于TensorRT的深度学习模型部署实战教程!
- Xshell 7 official website free download
- Browser fingerprint interpretation
- Element positioning of selenium
- Industrial end: a new battlefield of 618
猜你喜欢
![[writeup]buu SQL course1[entry level]](/img/eb/1b2541b04ca231cb07f1f3706f51c7.png)
[writeup]buu SQL course1[entry level]
![[wechat applet] 5 Applet structure directory](/img/d6/4796c8b8fe482b261c5a1fbf79ba2b.jpg)
[wechat applet] 5 Applet structure directory

Qiming cloud sharing | demonstrate the switch through an example of the matter protocol to control the light on and off through the matter protocol

【LDA】EM变分推理 粗略版笔记【待完善
![[LDA] rough version notes of EM variational reasoning [to be improved](/img/de/4b028e77694297db05a2d6b6589276.png)
[LDA] rough version notes of EM variational reasoning [to be improved

PTA:自测-2 素数对猜想 (20分)

Xshell 7 official website free download

odom坐标系的理解

Function recursion example

Jetpack architecture component learning (3) -- activity results API usage
随机推荐
Leader education was forced to be delisted: Softbank CMC suffered heavy losses only one year after listing
Assertion of selenium webdriver
Producers (send syncask requests) and consumers (with xxxask monitoring and Implementation)
基于TensorRT的深度学习模型部署实战教程!
C main函数
[lambda operation jcf]
Tensorrt based in-depth learning model deployment practice tutorial!
Serialization and deserialization mechanism in terms of games
[wechat applet] 6.1 applet configuration file
3D reconstruction system | L3 dual view motion recovery structure (SFM binocular SFM)
三维重建系统 | L3增量运动恢复结构(增量SFM)
JUnit test suite method sorting (method 2 is not easy to use)
分布式并发重复提交问题
PTA:自测-1 打印沙漏 (20分)
Shardingsphere practice (6) - elastic scaling
C operator
Apprendre est une chose contre la nature humaine
#include使用“文件名“和<文件名>引入头文件的区别及简述
Pta: self TEST-1 print Hourglass (20 points)
掌门教育被强制退市:上市仅一年时间 软银CMC损失惨重