当前位置:网站首页>Multimix: small amount of supervision from medical images, interpretable multi task learning
Multimix: small amount of supervision from medical images, interpretable multi task learning
2022-06-12 16:13:00 【deephub】
In this paper , I will discuss a new kind of semi supervision , Multi task medical imaging methods , be called Multimix,Ayana Haque(ME),Abdullah-Al-Zubaer Imran,Adam Wang、Demetri Terzopoulos. The paper was ISBI 2021 Included , And in 4 At the meeting in October .
MultiMix The joint semi supervised classification and segmentation are implemented by using a confidence based enhancement strategy and a new bridge module , The module also provides interpretability for multitasking . The model of deep learning under complete supervision can effectively perform complex image analysis tasks , But its performance depends heavily on the availability of large labeled datasets . Especially in the field of medical imaging , Manual tagging is not only expensive , And it takes time . Therefore, semi supervised learning from a limited number of labeled data is allowed , It is considered as a solution to the annotation task .
Learning multiple tasks in the same model can further improve the generality of the model . Multitasking allows learning of shared representations between tasks , At the same time, fewer parameters and calculations are required , So as to make the model more effective , More difficult to over fit .
Extensive experiments have been carried out on different amounts of labeled data and multi-source data , The paper proves the effectiveness of the method . It also provides cross task intra domain and cross domain assessments , To demonstrate the potential of the model to adapt to challenging generalization scenarios , This is a challenging but important task for medical imaging methods .
Background knowledge
In recent years , Because of the development of deep learning , Medical imaging technology based on deep learning has been developed . However, the fundamental problem of deep learning has always existed , That is, they need a lot of tag data to be effective . But this is a bigger problem in the field of medical imaging , Because it is very difficult to collect large data sets and annotations , Because they require domain expertise , expensive 、 Time consuming , And it's hard to organize in a centralized data set . In addition, in the field of medical imaging , Generalization is also a key issue , Because images from different sources are quite different qualitatively and quantitatively , Therefore, it is difficult to use one model in multiple fields to achieve strong performance , These problems prompted the research of this paper : We hope to solve these basic problems through some key methods centered on semi supervised and multi task learning .
What is semi supervised learning ?
In order to solve the problem of limited label data , Semi-supervised learning (SSL) As a promising alternative method, it has received extensive attention . In semi supervised learning , Use the unmarked example in conjunction with the marked example , Maximize the benefits of information . There have been a lot of studies on semi supervised learning , Including general and medical fields . I will not discuss these methods in detail , But if you're interested , Here is a list of outstanding methods for your reference [1,2,3,4].
Another solution to limited sample learning is to use data from multiple sources , Because this increases the number of samples in the data and the diversity of the data . But doing so is challenging , Because you need specific training methods , But if you do it right , It can be very effective .
What is multi task learning ?
Multi task learning (multitask Learning, MTL) It has been proved that the generalization ability of many models can be improved . Multitasking learning is defined as optimizing multiple losses in a single model , Learning to complete multiple related tasks through sharing . Training multiple tasks in one model can improve the generalization of the model , Because every task affects each other ( To select tasks that are relevant ). Suppose the training data come from different distributions , This can be used for a limited number of different tasks , Multitasking is useful in such scenarios for learning with little supervision . Combining multitasking with semi supervised learning can improve performance , And succeed in these two tasks . It is very useful to accomplish these two tasks at the same time , Because a single deep learning model can accomplish these two tasks very accurately .
Related work in the medical field , The specific method is as follows :[1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10]. However , The main limitation of these findings is that they do not use data from multiple sources , It limits their generalization , And most methods are single task methods .
therefore , This paper puts forward a new 、 A more general multitasking model MultiMix, The model combines the bridge block based on confidence , Joint learning of diagnostic classification and anatomical structure segmentation from multi-source data . Saliency maps can be used to analyze model predictions by visualizing meaningful visual features . There are several ways to generate saliency maps , The most obvious method is to calculate the gradient of class score from the input image . Although any deep learning model can be better explained through the significance map , But as far as we know , The significant bridge between two shared tasks in a single model has not been explored .
Algorithm

Let's first define our problem . Use two data sets for training , One for segmentation , One for classification . For split data , We can use symbols XS and Y, They are image and segmentation mask . For classified data , We can use symbols XC and C, Images and class labels .
The model architecture uses baselines U-NET framework , This structure is a common segmentation model . The function of the encoder is similar to the standard CNN. To use U-NET Perform multitasking , We will branch from the encoder , And use pooled and fully connected layer branches to get the final classification output .

classification
For the classification method , Use data enhancement and pseudo tagging . suffer [1] Inspired by the , An unlabeled image is used and two separate enhancements are performed .
First , Unlabeled images are weakly enhanced , And from the weakly enhanced version of the image , Set the prediction of the current state of the model as a pseudo label . This is why the method is semi supervised , But we'll talk about pseudo tag tags later .
secondly , Strong enhancement of the same unlabeled image , The loss is calculated by using the pseudo tags of the weakly enhanced image and the strongly enhanced image itself .
The theoretical basis of such operation is , It is hoped that the model can map the weakly enhanced image to the strongly enhanced image , In this way, the model can be forced to learn the basic features required for diagnostic classification . Enhancing the image twice can also maximize the potential knowledge gain of the unique image . It also helps to improve the generalization ability of the model , It's like the model is forced to learn the most important part of the image , It will be able to overcome the differences in images due to different domains .
In this paper, the conventional enhancement methods are used to weakly enhance the image , Such as horizontal flip and slight rotation . The strong reinforcement strategy is much more interesting : Create an unconventional , Powerful enhanced pool , A random amount of enhancement is applied to any given image . These enhancements are very “ metamorphosis ”, For example, cutting 、 Self contrast 、 brightness 、 Contrast 、 equilibrium 、 Uniformity 、 rotate 、 Sharpness 、 Cutting, etc . By applying any number of these elements , We can create a very wide range of images , This is particularly important when dealing with low sample data sets . We finally found out , This enhancement strategy is important for strong performance .
Now let's go back to the process of pseudo tagging . If the confidence level of the pseudo label generated by the model exceeds a tuning threshold , The image tag can prevent the model from learning from wrong and bad tags . Because when the forecast is uncertain at the beginning , The model mainly learns from the marked data . gradual , The model becomes more confident in label generation of unlabeled images , So the model becomes more efficient . In terms of improving performance , It's also a very important feature .
Now let's look at the loss function . The classification loss can be modeled by the following formula :

among L-sub-l To monitor losses ,c-hat-l Forecast for classification ,c-l Label ,lambda For unsupervised classification weights ,L-sub-u For unsupervised losses ,c-hat-s For the prediction of strongly enhanced images ,argmax(c-hat-w) Pseudo tags for weakly enhanced images ,t Is the false tag threshold .
This basically summarizes the classification methods , Now let's move on to the segmentation method .
Division

For segmentation , Via encoder with skip connection - Decoder architecture for prediction , It's very simple . The main contribution of this paper to segmentation is to combine a bridge module to connect two tasks , As shown in the figure above . Generate significant mappings based on the classes predicted by the model , Use a gradient that extends from the encoder to the classification branch . The whole process is shown above , But it essentially emphasizes which parts of the image the model is used to classify the pneumonia image .
Although we do not know whether the segmented image represents pneumonia , But the resulting map highlights the lungs . Therefore, when the saliency map is used to generate and visualize the class prediction of the image , It is similar to the lung facial mask to some extent . So we assume that these graphs can be used to guide the segmentation of the decoder stage , And it can improve the segmentation effect , At the same time, we can learn from the limited tag data .
stay MultiMix in , The generated saliency map is connected to the input image , Take the next sample , And added to the feature mapping input to the first decoder stage . The connection to the input image can enhance the connection between the two tasks , And improve the effectiveness of the bridge module ( Provides context ). Adding the input image and saliency mapping at the same time provides more context and information for the decoder , This is very important when dealing with low sample data .
Now let's talk about training and loss . For marking samples , We usually use the relation between the reference lung facial mask and the predicted segmentation dice Loss to calculate the split loss .
Since we do not have a segmentation mask for unlabeled segmentation samples , We cannot directly calculate their partition loss . Therefore, the difference between the segmentation predictions of the marked and unlabeled examples is calculated KL The divergence . This makes the model make predictions that are more and more different from the marked data , This makes the model more appropriate for unlabeled data . Although this is an indirect method of calculating losses , But it still allows the model to learn a lot from unmarked split data .
About loss , The division loss can be written as :
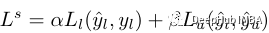
Compared with classification ,alpha It's split to reduce the weight ,y-hat-l Is the segmentation prediction of the tag ,y-l Is the corresponding mask ,beta Is an unsupervised split weight , and y-hat-u Is the unlabeled segment forecast .
The model uses the combination of classification and segmentation loss for training .
Data sets
The model is trained and tested for classification and segmentation tasks , The data for each task comes from two different sources : Pneumonia test data set , Let's call this Chex [11] Japanese Society of Radiology and technology or JSRT [12] [12] , Used for classification and segmentation respectively .
To validate the model , Two external datasets were used for Montgomery County chest X Ray or MCU [13], as well as NIH chest X A subset of the ray data set , Let's call this NIHX [14]. The diversity of sources poses a major challenge to the model , Because the image quality , size , The ratio of normal image to abnormal image and the difference of intensity distribution of the four data sets are very different . The following figure shows the difference in intensity distribution and an image example for each data set . all 4 All data sets use CC BY 4.0 license .

result
Many experiments have been carried out in this paper , Different amounts of tag data are used in multiple datasets and across domains .
Multiple baselines were used in the test , from Arale-net And standard classifiers (ENC) Start , The classifier is an encoder extractor with dense layers . then , We combine the two into a baseline multitasking model (UMTL). Semi supervised methods are also used (ENCSL),(UMTLS) And multi task model and semi supervised method (UMTLS-SSL) The multitasking model of .
In terms of training , Training is carried out on multiple labeled data sets . In order to classify , We used 100、1000 And all labels , For segmentation , We used 10、50 And all labels . For results , The symbol... Will be used : Model - label ( for example Multimix-10–100) The way to mark . In order to evaluate , Accuracy of use (ACC) and F1 fraction (F1-N and F1-P) To classify , Segmentation uses DS similarity (DS),JACCARD Similarity score (JS), Structural similarity index (SSIM) , Average Hausdorff distance (HD), precision (P) And recall (R).

This table shows how the performance of the model with each new component added improves . For classification tasks , Compared to the baseline model , Confidence based enhancement methods can significantly improve performance .Multimix-10–100 It is also superior to the fully supervised baseline encoder in terms of accuracy . For segmentation , Bridge module to baseline U-NET and UMTL The model has produced great improvements . Even with the lowest segment label , We can also see performance growth 30%, This proves the Multimix The validity of the model .
As shown in the table , Performance in multimode is as promising as in the inner domain . On all baseline models ,Multimix Score better in classified tasks . because NIHX and CHEX There are significant differences in data sets , As mentioned earlier , The score is not as good as that of the inner domain model . But it is better than other models .

The above figure shows the consistency of segmentation results for intra domain and cross domain evaluation . Each image in my dataset shows the model's dice fraction . From the picture , You can see , Compared to the baseline ,Multimix Is the strongest model .

The last figure is the visualization of the segmentation prediction of the model . The boundary of the prediction is shown to enable the truth value comparison of different labeled data to be added for each proposed segmentation task . The figure shows the relation with MultiMix Strong consistency of boundary predictions for real boundaries , Especially compared with the baseline . For cross domain MultiMix To a large extent, it is also the best , It shows a strong generalization ability .
summary
In this article , We explain a new sparse supervised multi task learning model for joint learning classification and segmentation tasks MultiMix. The paper uses four different breasts x Extensive experiments have been carried out on X-ray data sets , Proved MultiMix Effectiveness in intra domain and cross domain assessments .
The author also provides the source code , You can have a look if you are interested :
https://avoid.overfit.cn/post/a475b41b332845b7bb9e8cf09ec8c662
author :Ayaan Haque
边栏推荐
- Defer learning in golang
- Go Net Library (to be continued)
- When programming is included in the college entrance examination...
- Tensorflow function: tf nn. in_ top_ k()
- acwing 798二维差分(差分矩阵)
- Applet: how to get the user's mobile number in the plug-in
- Redis string type common commands
- Scanpy (VI) analysis and visualization of spatial transcriptome data
- 国产CPLD中AG1280Q48进行开发的实践之一:思路分析
- [practical case of light source] UV-LED curing innovation makes the production line more smooth
猜你喜欢

Multimix:从医学图像中进行的少量监督,可解释的多任务学习

IDEA中文棱形乱码错误解决方法--控制台中文输出棱形乱码

小程序:如何在插件中获取用户手机号

写代码也有本手俗手之分,而我们要善于发现妙手!

Project training of Software College of Shandong University rendering engine system point cloud processing (10)

acwing794 高精度除法
![In 2021, China's lottery sales generally maintained a rapid growth, and the monthly sales generally tended to be stable [figure]](/img/dd/1bf44d284c709b6bebd4b308ba2cee.jpg)
In 2021, China's lottery sales generally maintained a rapid growth, and the monthly sales generally tended to be stable [figure]

What is fintech? How fintech can help small businesses succeed

Why doesn't Alibaba recommend MySQL use the text type?

小飞页升级变智能修复Bug更快速了
随机推荐
批量--03---CmdUtil
从斐波那契数列求和想到的俗手、本手和妙手
acwing 797 差分
为什么阿里巴巴不建议MySQL使用Text类型?
[tool recommendation] personal local markdown knowledge map software
Golang collaboration scheduling (I): Collaboration Status
Project training of Software College of Shandong University rendering engine system radiation pre calculation (IX)
Reprise de Google net
What is fintech? How fintech can help small businesses succeed
acwing 803. 区间合并
Classic case of solidity - Smart games
PHP builds a high-performance API architecture based on sw-x framework (II)
Global and Chinese markets of bioreactors 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
ER diagram made by StarUML based on the last student achievement management system
Divide training set, test set and verification set
Job submission instructions upload jobs to network disk
5g new scheme! Upgrade the existing base station and UE simulator to 5g millimeter wave band
MYSQL---服务器配置相关问题
< 山东大学软件学院项目实训 > 渲染引擎系统——点云处理(十)
5-5配置Mysql复制 基于日志点的复制