当前位置:网站首页>Mysql database foundation: DQL data query language
Mysql database foundation: DQL data query language
2022-06-27 03:47:00 【Long lasting bangbangjun】
This chapter is pure notes
DQL Language
brief introduction
DQL(data query language) Data query language , Specifically used to query data .
1、 Basic query
1.1 grammar
Query the specified fields in the specified table 、 Constant etc.
SELECT Query list FROM Table name ;
Queries all fields in the specified table 、 Constant etc.
SELECT * FROM Table name ;
Display table structure
DESC Table name ;
1.2 Basic query features
1、 The query list can be fields in the table 、 Constant 、 expression 、 function
2、 The result of the query is a virtual table
3、 There can be multiple fields in the query list , Separated by commas
1.3 mark of emphasis ``( Double inverted quotation marks ) Use
Can be used to Distinguish between fields and keywords , Such as :
SELECT `NAME` FROM A table ;
1.4 Query constant value
SELECT 100;
SELECT 'John';
1.5 Query expression
SELECT 100%98;
1.6 Query function
SELECT VERSION(); #VERSION() Is the function , The function is to show mysql edition
1.7 Alias fields
# Mode one Use AS
SELECT 100%98 AS result ; # result :2
SELECT last_name AS surname , first_name AS name FROM Table name ;
# Mode two You can omit AS
SELECT last_name surname ,first_name name FROM Table name ;
The benefits and fallibility of aliasing
- Easy to understand
- If the query field has the same name , Use aliases to distinguish
- It's better not to take a space in the alias , If there is a space , Can be modified with double quotation marks
for example :
# Suppose you want to query salary salary, The result is out put, With space in the middle , Use double quotation marks out put Lead up
SELECT salary AS "out put" FROM Table name ;
1.8 duplicate removal —distinct
# Remove the redundant data that appears repeatedly in the field
SELECT DISTINCT Field FROM Table name ;
1.9 “+” Use of numbers
effect : There's only one function , Add as an operator
# Both operands are numeric , Then add directly
SELECT 100+100;
# One of them is character type , Trying to convert a character value to a numeric value , If the conversion is successful , Then add , If you fail , Then convert the character value to 0
SELECT '123' + 90;
# As long as one of them is null, The result must be null
SELECT null + 10; # The result is null
2、 Conditions of the query
2.1 grammar
where Keywords are used to give query conditions .
SELECT
Query list ;
FROM
Table name ;
WHERE
filter ;
2.2 classification
2.2.1 Filter by conditional expression
Conditional operator :>( Greater than )< ( Less than ) =( be equal to ) !=( It's not equal to ) <>( It's not equal to )
# Case study 1: Query salary >12000 Employee information
SELECT
*
FROM
employees
WHERE
salary>12000; # Conditions
# Case study 2: Query department number is not equal to 90 The employee name and department number of the
SELECT
last_name,
department_id
FROM
employees
WHERE
department_id <> 90; #<> Or you could write it as !=
2.2.2 Filter by logical expression
Logical operators :
| Logical operators | effect |
|---|---|
| && | And |
| || | or |
| ! | Not |
| and | Word form “ And ” |
| or | Word form “ or ” |
| not | Word form ” Not “ |
effect : Join conditional expressions
# Case study 1: Check salary at 10000 To 20000 Between the employee's name 、 Salary and bonus
SELECT
last_name,
salary,
commission_pct
FROM
employees
WHERE
salary >= 10000
AND
salary <= 20000;
# Case study 2: The inquiry department number is not in 90 To 110 Between , Or pay more than 15000 Employee information
SELECT
*
FROM
employees
WHERE
NOT(department_id >= 90 AND department_id <= 110) OR salary>15000;
# Or as follows
select
*
FROM
employees
WHERE
department_id NOT BETWEEN 90 AND 110
OR
salary>15000;
2.2.3 Fuzzy query
1、like
characteristic : Generally used with wildcards .
| wildcard | effect |
|---|---|
| % | Represents any number of characters |
| _ | Underline , Represents any single character |
| / | Escape character |
# Case study 1: Query employee hit contains characters a Employee information
SELECT
*
FROM
employees
WHERE
last_name LIKE '%a%';
# Case study 2: The third character in the query employee name is e, The fifth character is a Employee name of
SELECT
last_name
FROM
employees
WHERE
last_name LIKE '__e_a%';
# The second character in the employee name is _ Employee name of
SELECT
last_name
FROM
employees
WHERE
last_name LIKE '_\_%';
# Or it could be written as :last_name LIKE '_$_%' ESCAPE '$';
2、between…and…
meaning : The expression is in the middle of the two expressions , If you add not It means not in the middle .
characteristic :
- Use between and It can improve the conciseness of sentences
- Contains a critical value
SELECT
*
FROM
employees
WHERE
employee_id >= 100 AND employee_id <= 120;
# The above code is as useful as the following code
SELECT
*
FROM
employees
WHERE
emoloyees_id between 100 AND 120;
3、in
meaning : Determine whether the value of a field belongs to in An item in the list .
characteristic :
- It can improve the introduction of sentences
- in The value types of the list must be uniform or compatible
- I won't support it in The values in the list plus wildcards
# The job number of the employee is IT_PROT,AD_VP An employee's name and job number in the
SELECT
last_name,job_id
FROM
employees
WHERE
job_id IN('IT_PROT','AD_VP');
4、is null and is not null
Be careful :
= or != or <> Can not be used to judge null value , and adopt is null and is not null Can be judged null value
# Query the employee name and bonus rate without bonus
SELECT
last_name,commission_pct
FROM
employees
WHERE
commission_pct IS NULL;
5、 Safety is equal to <=>
SELECT
last_name,salary
FROM
employees
WHERE
salary <=> 12000;
is null and <=> difference :
IS NULL: Can be judged NULL value , High readability
<=>: You can judge NULL value , You can also judge the normal value , Poor readability .
3、 Sort query
3.1 grammar
SELECT
Query list
FROM
Table name
WHERE
filter
ORDER BY
Sort list (asc \ desc)
#asc Ascending 、desc Descending , Default ascending order
3.2 Examples demonstrate
# Case study 1: Query department number is greater than or equal to 90 Employee information , Sort according to the employment time 【 By filter criteria 】
SELECT
*
FROM
employees
WHERE
department_id>=90
ORDER BY
hiredate ASC;
# Case study 2: Display employee information and salary by annual salary Annual salary 【 Query by expression 】
SELECT
*,salary*12*(1 + IFNULL(commission_pct, 0)) Annual salary
FROM
employees
ORDER BY
salary*12*(1 + IFNULL(commission_pct, 0)) DESC;
# Case study 3: Display employee information and salary by annual salary Annual salary 【 Query by alias 】
SELECT
*,salary*12*(1 + IFNULL(commission_pct, 0)) Annual salary
FROM
employees
ORDER BY
Annual salary DESC;
# Case study 4: Display the employee's name and salary by the length of the name 【 Sort by function 】
SELECT
LENGTH(last_name) bytes , last_name, salary
FROM
employees
ORDER BY
LENGTH(last_name);
# Case study 5: Search for employee information , It is required that the salary be increased first , Then sort by employee number in descending order 【 Sort by multiple fields 】
SELECT
*
FROM
employees
ORDER BY
salary ASC, employees_id DESC;
4、 Common function
4.1 function
Be similar to Java The method in , Encapsulating a set of logical statements in a method body , Name of external exposure method .
4.2 benefits
1、 Hide implementation details ,
2、 Improve code reusability
4.3 Call syntax
SELECT Function name ( Argument list ) 【FROM surface 】;
4.4 classification :
1、 One line function
Such as :concat、length、isfull etc.
2、 Group function
For statistical use , It's also called statistical function , Aggregate functions , Group functions .
4.5 Introduction to single line functions
4.5.1 Character functions
#length Gets the number of bytes of the parameter value
#----------------------------------------------
SELECT LENGTH('john'); #4
SELECT LENGTH(' Zhang Sanfeng hahaha'); #15
#concat Concatenate characters
#----------------------------------------------
SELECT CONCAT(last_name,'_',first_name) FROM employees;
#upper\lower Convert letters to case
#----------------------------------------------
SELECT UPPER('john');
SELECT LOWER('joHN');
#substr\substring
#-----------------------------------------------
# Pay attention to the index from 1 Start , That is, the first index number is 1
# Intercept all characters after the specified index
SELECT SUBSTR(' Li Mochou fell in love with Lu Zhanyuan ',7) AS out_put; # Output : Lu Zhanyuan
# Intercepts the characters of the specified length at the specified index
SELECT SUBSTR(' Li Mochou fell in love with Lu Zhanyuan ',1,3) AS out_put; # Output : Li Mochou
#instr Returns the index of the first occurrence of the substring , Return if not found 0
#-----------------------------------------------
SELECT INSTR(' Don't try so hard , Use your brain ',' mind ') AS out_put; # result :12
#trim Remove the specified characters on both sides
#-----------------------------------------------
SELECT LENGTH(TRIM(' Zhang Cuishan ' )) AS out_put; # result : length 9, The blanks on both sides are removed , The Chinese character bytes are 3byte, So the length is 9
SELECT TRIM('a' FROM 'aaaaaa Zhang aaaaaaa Cuishan aaaaa') AS out_put; # result : Zhang aaaaaaa Cuishan ( Removed both sides a)
#lpad Fill the specified length with the specified characters
#-----------------------------------------------
SELECT LPAD(' YanSuSu ',10,'*') AS out_put; # result :******* YanSuSu
#rpad Fill the specified length with the specified characters
#-----------------------------------------------
SELECT RPAD(' YanSuSu ',10,'*') AS out_put; # result : YanSuSu *******
#replace Replace
#-----------------------------------------------
SELECT REPLACE(' Zhouzhiruo zhouzhiruo ',' Zhou Zhiruo ',' Zhao Min ') AS out_put; /* Zhaomin replaces zhouzhiruo */
# result : Zhaomin Zhaomin
4.5.2 Mathematical functions
#round rounding
#------------------------------------------------
SELECT ROUND(1.45); /* rounding */ # result :1
SELECT ROUND(1.567,2); /* Take two decimal places */ # result :1.57
#ceil Rounding up , Returns the smallest integer greater than or equal to the parameter
#------------------------------------------------
SELECT CEIL(-1.02); # result :-1
#floor Rounding down , Returns the maximum integer less than or equal to the parameter
#------------------------------------------------
SELECT FLOOR(-9.99); # result :-10
#truncate Truncate from decimal places , Do not round off
#------------------------------------------------
SELECT TRUNCATE(1.69999,1); # result :1.6
#mod Remainder
#------------------------------------------------
SELECT MOD(10,3); # 1
# Add : The method of finding the remainder : hypothesis MOD(a,b) = a-a/b*b;
4.5.3 Date function
# now Returns the current system date + Time
SELECT NOW();
# Or this
SELECT SYSDATE();
# curdate Returns the current system date , Not including time
SELECT CURDATE();
# curtime Return to current system time , Excluding date
SELECT CURTIME();
# Gets the specified part , year , month , Japan , Hours , minute , second
SELECT YEAR(NOW()) year ; # result :2022
SELECT YEAR('2022-1-1') year ; # result :2022
SELECT MONTH(NOW()) month ; # 4
SELECT MONTHNAME(NOW()) month ; # April
# last_day Get the last day of the current month
SELECT LAST_DAY(SYSDATE());
# str_to_date: Converts a character to a date in a specified format ( Generally, the returned characters are of character type , So this function is used to convert characters to standard dates
SELECT STR_TO_DATE('1994-3-3','%Y-%c-%d') AS out_put; # Output :1994-03-3
# Example
SELECT * FROM employees where hiredate = STR_TO_DATE('4-3 1994','%c-%d %Y');
# Will be 4-3 1994 convert to 1994-4-3 This form
# date_format: Convert date to character
SELECT DATE_FORMAT(NOW(),'%Y year %m month %d Japan ') AS out_put;
# Example Check the name and date of the employee with bonus (xx month xx Japan %y year )
SELECT last_name, DATE_FORMAT(hiredate, '%m month %d Japan %y year ') Date of entry ;
FROM employees
WHERE commission_pct IS NOT NULL;
4.5.4 Other functions
# Query the current version number
SELECT VERSION();
# Query the user
SELECT USER();
4.5.5 Process control functions
# if function :
# If the comparison result is true, select the left , Select the right side for the false
SELECT IF(10<5,' Big ',' Small '); # Small
# for example :
SELECT last_name,commission_pct,IF(commission_pct IS NULL,' No bonus , ha-ha ',' Bonus , Joy ') remarks FROM employees;
# case function
# Use 1: case Be similar to switch The effect of
/* case The field or expression to determine when Constant 1 then The value to display 1 Or words 1( There is no semicolon at the end ) when Constant 2 then The value to display 2 Or words 2 ... else The value to display n Or words n end AS name FROM Table name ; */
# for example :
/* Case study : Check the salary of employees , The requirements are as follows : Department number =30, The wage shown is 1.1 times Department number =30, The wage shown is 1.2 times Department number =40, The wage shown is 1.3 times Other departments , The wage shown is the original wage */
# Realization :
SELECT
salary The original wage ,department_id,
CASE
department_id
WHEN 30 THEN salary*1.1
WHEN 40 THEN salary*1.2
WHEN 50 THEN salary*1.3
ELSE
salary
END AS New pay
FROM
employees;
# The new salary is listed at the end of the queried table
# Use 2: Similar to multiple if
/* case when Conditions 1 then The value to display 1 Or words 1 when Conditions 2 then The value to display 2 Or words 2 ... else The value to display n Or words n end */
# for example :
/* Case study : Check the salary of employees If wages >20000, Show A Level If wages >15000, Show B Level If wages >10000, Show C Level Otherwise, it will show D Level */
# Realization
SELECT
salary Wages ,
CASE
WHEN salary>20000 THEN 'A'
WHEN salary>15000 THEN 'B'
WHEN salary>10000 THEN 'C'
ELSE
'D'
END AS Salary level
FROM
employees;
4.6 Group function
sum Sum up ,avg Average ,max Maximum ,min minimum value ,count Calculate the number of
#1、 Easy to use
SELECT SUM(salary) FROM employees;
SELECT AVG(salary) FROM employees;
SELECT MIN(salary) FROM employees;
SELECT MAX(salary) FROM employees;
SELECT COUNT(salary) FROM employees;
#2、 Which types of parameters are supported
#sum and avg Suitable for numeric types
#max,min,count Suitable for any type
#3、 Grouping functions ignore null value
#4、 and distinct Collocation de duplication
SELECT SUM(DISTINCT salary) FROM employees;
#5、count A separate introduction to functions
# In general use count(*) Used to count lines , perhaps count(1)
SELECT COUNT(*) FROM employees;
#6、 There are restrictions on the fields that can be queried with the grouping function , The requirement is group by Fields after
5、 Group query
5.1 grammar
select Group function , Column ( The requirement appears at the same time group by Behind )
from Table name
group by A list of groups
order by Clause ;
5.2 Easy to use
# Check the maximum salary for all jobs
SELECT
MAX(salary),job_id
FROM
employees
GROUP BY
job_id;
5.3 Add filter
# Case study 1
# There are... In the query message a Letter , The average salary of all departments
SELECT
AVG(salary), department_id
FROM
employees
WHERE
email LIKE "%a%" # Add filter
GROUP BY
department_id;
# Case study 2
# Query the number of employees in each department >2
SELECT
COUNT(*), department_id
FROM
employees
GROUP BY
department_id
HAVING
count(*)>2; # Add filter
5.4 characteristic :
1、 The screening criteria are divided into two categories
| Keywords used | Screening timing | data source | Location |
|---|---|---|---|
| where | Filter before grouping | Original table | group by Before clause |
| having | Filter after grouping | Grouped result set | group by After Clause |
2、 The condition of grouping function must be having clause , If you can use pre group filtering, you can use pre group filtering
3、where and having It is also used to filter conditions , What's the difference?
(1)where and having They all do conditional screening
(2)where The execution time is longer than having Early
(3)where Group functions cannot appear after
(4)having Group functions can appear later
(5)where The statement should be followed by from Back
(6)having The statement should be followed by group by Back
4、 Be careful :
(1)where The back must be 【 You can't 】 Group functions appear
(2) If select、having A group function appears after the statement , that select、having Columns that are not modified by group functions , Must appear in group by Back ( It's very important )
6、 Link query
6.1 meaning
It is also called multi table query , When the fields of a query come from multiple tables , You'll use join queries .
Cartesian product : surface 1 Yes m That's ok , surface 2 Yes n That's ok , result =m*n That's ok
Cause of occurrence : There are no valid connection conditions
How to avoid : Add valid connection conditions
6.2 classification
By age
- sql192 standard : Only internal connections are supported
- sql199 standard ( recommend ): Support internal connection , External connection ( Right outer connection and left outer connection ,mysql All external connections are not supported in , Cross connect )
By function
- Internal connection
- Equivalent connection
- Non equivalent connection
- External connection
- Right connection
- The left outer join
- Full outer join
- Cross connect
6.3 sql192 standard
6.3.1 Equivalent connection
# Case study 1
# Query the employee name and the corresponding department name
SELECT
last_name,department_name
FROM
employees,departments
WHERE
employees.`department_id`=departments.`department_id`;
# Note the back quotes
# Case study 2
# Name the table
/* 1、 Improve sentence conciseness 2、 Distinguish multiple fields with duplicate names Be careful : If you alias a table , The query field cannot use the original table name */
# Query employee name , official account , Name of work
SELECT
e.last_name,e.job_id,j.job_title
FROM
employees e, jobs j
WHERE
e.`job_id`=j.`job_id`;
# Case study 3
# Plus screening
# Query the name of the employee with bonus , Department name
SELECT
last_name, department_name,commission_pct
FROM
employees e, departments d
WHERE
e.`department_id`=d.`department_id`
AND
e.`commission_pct` IS NOT NULL;
# Case study 3
# Add groups
SELECT
count(*) Number ,city
FROM
departments d,locations l
WHERE
d.`location_id`=l.`location_id`
GROUP BY
city;
6.3.2 Non equivalent connection
Is to connect the “=” It was replaced by something else such as >,<,between …and… etc.
6.4 sql199 standard
6.4.1 grammar
select Query list
from surface 1 Alias 【 Connection type 】
join surface 2 Alias
on Connection condition
【where filter 】
【group by Grouping conditions 】
【having filter 】
【order by Sort list 】
6.4.2 classification
6.4.2.1 Internal connection : inner
1、 grammar (inner It can be omitted )
select Query list
from surface 1 Alias
inner join surface 2 Alias
on Connection condition
2、 classification
(1) Equivalent connection
# Case study 1: Query employee name , Department name
SELECT last_name, department_name
FROM employees e
INNER JOIN departments d
on e.`department_id` = d.`department_id`;
# Case study 2: The query name contains e Name of the employee and type of work
SELECT last_name,job_title
FROM employees e
INNER JOIN jobs j
ON e.`job_id` = j.`job_id`
WHERE e.`last_name` LIKE '%e%';
(2) Non equivalent connection
# Check the salary level of employees
SELECT salary,grade_level
FROM employees e
INNER JOIN job_grades g
ON e.`salary` BETWEEN g.`lowest_sal` AND g.`highest_sal`;
# Wages in lowest_sal and highest_sal Between
(3) Self join
# Check the name of the employee , The name of the superior
SELECT e.last_name,m.last_name
FROM employees e
JOIN employees m
ON e.`manager_id`=m.`employee_id`;
6.4.2.2 External connection outer
1、 Use scenario : Used to query a table with , The other table doesn't have records .
2、 characteristic :
The query result of the external connection is all the records in the main table , If there is a match from the table , The value of the match , If there is no match from the table , Is displayed null.

External connection query results = Internal connection result + Records that exist in the master table but not in the slave table
The test table
# Create two tables
CREATE TABLE test_1(
id INT,
`name` VARCHAR(20),
girl_id INT
);
CREATE TABLE test_2(
id INT,
`name` VARCHAR(20)
);
INSERT INTO test_1(id,name,girl_id)VALUE (1," Liu Ye ",4);
INSERT INTO test_1(id,name,girl_id)VALUE (2," Hu Jun ",9);
INSERT INTO test_1(id,name,girl_id)VALUE (3," Deng Chao ",7);
INSERT INTO test_1(id,name,girl_id)VALUE (4," Liu Yijun ",91);
INSERT INTO test_2(id,name) VALUE (6," Xiaohong ");
INSERT INTO test_2(id,name) VALUE (7," Sun Li ");
INSERT INTO test_2(id,name) VALUE (8," Little black ");
INSERT INTO test_2(id,name) VALUE (2," Little green ");
desc test_1;
desc test_2;
show tables;
SELECT * from test_1;
SELECT * from test_2;
3、 classification :
(1) Left lateral :left 【outer】join
left join On the left is the main watch .
# The left outer join
SELECT a.girl_id, b.*
FROM test_1 a
LEFT OUTER JOIN test_2 b
ON a.`girl_id` = b.`id`
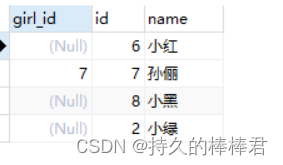
(2) Right outside :right 【outer】join
right join The one on the right is from the table .
# Right connection
SELECT a.girl_id, b.*
FROM test_1 a
RIGHT OUTER JOIN test_2 b
ON a.`girl_id` = b.`id`

(3) Total external :full 【outer】join
Table take Union
Left outer and right outer exchange the order of two tables , Can achieve the same effect
6.4.2.3 Cross connect cross
grammar :
SELECT b.*,bo.*
FROM beauty b
CROSS JOIN boys bo;
7、 Subquery
7.1 meaning
In other statements select sentence , Called subquery or inner query , The external query statement is called primary query or external query
7.2 characteristic
The idea of subquery is , Take the first one. sql Query result of statement , In the second sql Use in statement , At this time, the first one sql Result of statement , In the second sql Can act as a where A value in the condition , Or act as a virtual table .
(1) Subqueries in parentheses
(2) Subqueries are usually placed on the right side of the condition
(3) The execution of the subquery takes precedence over the execution of the main query
7.3 classification
- Where the subquery appears
(1)where or having Back *( Scalar subquery 、 Column query 、 Line sub query )
(2)select Back ( Only scalar subqueries are supported )
(3)from Back ( Support table subquery )
(4)exists Back ( Support table subquery )
where/having Back *
- Scalar subquery ( The result is only one row and one column )
# Example 1 : Inquire about job_id And 141 Same as employee No ,salary Than 143 The name of the employee with more employees ,job_id, And wages
# The first (1) Step : Inquire about 141 Of employee No job_id
SELECT job_id
FROM employees
WHERE employee_id = 141
# The first (2) Step : Inquire about 143 The no. salary
SELECT salary
FROM employees
WHERE employee_id=143
# The first (3) Step : Check the name of the employee ,job_id, And wages , requirement job_id=(1), also salary>(2)
SELECT last_name,job_id,salary
FROM employees
WHERE job_id=(
SELECT job_id
FROM employees
WHERE employee_id = 141
) AND salary>(
SELECT salary
FROM employees
WHERE employee_id=143
)
------------------------------------------------------
# Example 2 : The minimum wage is greater than 50 The Department of minimum wage id And its minimum wage
# The first (1) Step : Inquire about 50 The minimum wage of department No
SELECT
MIN(salary)
FROM
employees
WHERE
department_id=50
# The first (2) Step : Check the minimum wage of each department
SELECT
MIN(salary)
FROM
employees
GROUP BY
department_id
# The first (3) Step : stay (2) Filter based on ,min(slary)>(1)
SELECT MIN(salary),department_id
FROM employees
GROUP BY department_id
HAVING MIN(salary)>(
SELECT MIN(salary)
FROM employees
WHERE department_id=50
)
- Column query ( The result is only one column with multiple rows )
characteristic : Back to multiple lines
Use the multiline comparison operator , for example :IN,NOT IN,ANY,SOME,ALL
# return location_id yes 1400 or 1700 The names of all employees in the Department
# The first (1) Step : Inquire about location_id yes 1400 or 1700 Department number of
SELECT department_id
FROM departments
WHERE location_id in (1400,1700)
# The first (2) Step : The required department number is (1) One of the list
SELECT last_name
FROM employees
WHERE department_id in(
SELECT department_id
FROM departments
WHERE location_id in (1400,1700)
)
- Line sub query ( The result is one row with multiple columns or multiple rows with multiple columns )
# Query the employee information with the lowest employee number and the highest salary
# Search for the minimum employee number
SELECT MIN(employee_id)
FROM employees
# Query maximum wage
SELECT MAX(salary)
FROM employees
# final result
SELECT *
FROM employees
WHERE (employee_id,salary)=(
SELECT MIN(employee_id),MAX(salary)
FROM employees
)
select Back
# Query the number of employees in each department
SELECT d.*,(
SELECT count(*)
FROM employees
)
FROM departments d
from Back
# Query the average wage level of each department
# The first (1) Step : Query the average salary of each department
SELECT AVG(salary),department_id
FROM employees
GROUP BY department_id
# The first (2) Step : Connect (1) The result set and job_grades surface , Screening criteria average wage between lowest_sal and highest_sal
SELECT ag_dep.*, g.`grade_level`
FROM(
SELECT AVG(salary) ag,department_id
FROM employees
GROUP BY department_id
) ag_dep
INNER JOIN job_grades g
ON ag_dep.ag BETWEEN lowest_sal and highest_sal
exists Back ( Correlation subquery )
exists The only result is 0 and 1
# Check the Department name of the employee
SELECT department_name
FROM departments d
WHERE EXISTS(
SELECT *
FROM employees e
WHERE d.`department_id`=e.`department_id`
)
8、 Paging query
Application scenarios
When one page of data to be displayed is incomplete , Paging submission is required sql requestgrammar
select Query criteria
from surface 1
[join type join surface 2]
on Connection condition
where filter
group by Grouping field
having Filtering after grouping
order by Sorted fields
limit offset,size;
# offset, To display the starting index of an entry , Index from 0 Start
# size, Number of items to display
# Be careful limit Keywords must be at the end
- Example
# Check the first five employee information
# Check the first five employee information
SELECT *
FROM employees
LIMIT 0,5
The formula
hypothesis : Number of pages to display :page, Number of entries per page size
that :limit (page-1)*size,size
9、 The joint query
Definition
union union , Merge , Combine the results of multiple query statements into one result .
# Check department number >90 Or the mailbox contains a Employee information
# The first way :OR
SELECT *
FROM employees
WHERE email
LIKE '%a%'
OR
department_id>90;
# The second way UNION The joint query
SELECT *
FROM employees
WHERE email LIKE '%a%'
UNION
SELECT *
FROM employees
WHERE department_id>90;
Joint query features
- The number of query columns of multiple query statements is required to be consistent
- The type and order of each column of a query that requires multiple query statements should be the best
- UNION Keywords are de duplicated by default , have access to union all Can not go heavy
边栏推荐
- 乐得瑞LDR6035 USB-C接口设备支持可充电可OTG传输数据方案。
- 与STM32或GD32替换说明
- Knowledge of iPhone certificate structure
- 如何让 EF Core 6 支持 DateOnly 类型
- Pat grade a 1021 deep root
- Pat grade a 1019 general palindromic number
- 投资理财产品的钱有保障吗?会不会没有了?
- USB DRIVER
- Pat grade a 1025 pat ranking
- 2019LXMERT:Learning Cross-Modality Encoder Representations from Transformers
猜你喜欢

Ledrui ldr6035 usb-c interface device supports rechargeable OTG data transmission scheme.

There are two problems when Nacos calls microservices: 1 Load balancer does not contain an instance for the service 2. Connection refused

2021:Beyond Question-Based Biases:Assessing Multimodal Shortcut Learning in Visual Question Answeri

【promise一】promise的介绍与手撸的关键问题

文旅灯光秀打破时空限制,展现景区夜游魅力

发现一款 JSON 可视化工具神器,太爱了!

2021:Check it again:Progressive Visual Question Answering via Visual Entailment通过视觉暗示进行渐进式视觉问答

PAT甲级 1021 Deepest Root

promise源码-class版本【三、Promise源码】【代码详细注释/测试案例完整】
![Promise [II. Promise source code] [detailed code comments / complete test cases]](/img/ac/abf3181fa7b3345efcc9abc046cea5.png)
Promise [II. Promise source code] [detailed code comments / complete test cases]
随机推荐
fplan-布局
2021:adavqa: overlapping language priors with adapted margin cosine loss *
CVPR2021:Separating Skills and Concepts for Novel Visual Question Answering将技巧与概念分开的新视觉问答
A^2=E | 方程的解 | 这个方程究竟能告诉我们什么
Is the money invested in financial products guaranteed? Is there no more?
Anaconda3安装过程及安装后缺失大量文件,没有scripts等目录
通信中的机器学习最佳阅读资料列表
Anaconda3 is missing a large number of files during and after installation, and there are no scripts and other directories
Kotlin Compose 自定义 CompositionLocalProvider CompositionLocal
再探Handler(下)(Handler核心原理最全解析)
2022中式面点师(高级)复训题库及在线模拟考试
NestJS环境变量配置,解决如何在拦截器(interceptor)注入服务(service)的问题
Ledrui ldr6035 usb-c interface device supports rechargeable OTG data transmission scheme.
手机新领域用法知识
超级详细,2 万字详解,吃透 ES!
Topolvm: kubernetes local persistence scheme based on LVM, capacity aware, dynamically create PV, and easily use local disk
ERP demand and sales management Kingdee
办公室VR黄片,骚操作!微软HoloLens之父辞职!
基于MobileNet-Yolov4搭建轻量化目标检测
苹果手机证书构体知识