当前位置:网站首页>The UVM Primer——Chapter2: A Conventional Testbench for the TinyALU
The UVM Primer——Chapter2: A Conventional Testbench for the TinyALU
2022-07-02 12:51:00 【ICER Xiaoshi tablet】
In the building UVM Before validating the environment , Let's start with SystemVerilog Verify the platform , Then, step by step, transition to the complete UVM Verification platform .
TinyALU The requirements for the verification platform are as follows :
- Full test TinyALU The function of
- Simulation RTL Each line of code and the path through these lines of code
So we need to create the content that needs to be covered , Then create a verification platform to cover the code . And create a self checking verification platform , In this way, there is no need to check manually when running back .
TinyALU Functional coverage model
We use SystemVerilog Of covergroup To achieve ( For details, please refer to the green book SystemVerilog), Coverage targets are as follows :
- Test all instructions
- Full of all instructions ”0” Input simulation
- Full of all instructions ”1” Input simulation
- Run after reset of all instructions
- A single cycle instruction is followed by a multiplication instruction
- A single cycle instruction is run after the multiply instruction
- Simulation of two consecutive runs of instructions
After all the above conditions are verified and passed , We can confirm this TinyALU Is available . Whether to achieve 100% Code coverage also needs to be checked .
testbench file
Put the verification platform in the same simulation file , This file contains three parts : incentive 、 Self inspection and coverage . Instantiate in the file DUT, And for it Apply an incentive and Use self-test and Overlay acquisition Of always Module to monitor it .
testbench Variable definitions
Define motivation in a form that is easy to define TinyALU Instructions , The verification platform signal is defined as follows :
module top;
typedef enum bit[2:0] {no_op = 3'b000,
add_op = 3'b001,
and_op = 3'b010,
xor_op = 3'b011,
mul_op = 3'b100,
rst_op = 3'b111} operation_t;
byte unsigned A;
byte unsigned B;
bit clk;
bit reset_n;
wire [2:0] op;
bit start;
wire done;
wire [15:0] result;
operation_t op_set;
assign op = op_set;
tinyalu DUT (.A, .B, .clk, .op, .reset_n, .start, .done, .result);Use SystemVerilog The enumeration type of will TinyALU The instruction of is defined as enumerating variables . In order to facilitate the use of the verification platform , We will DUT Not found in rst_op Instruction adds instruction enumeration type .assign Statement is used to enter instructions into DUT On the command bus .
We use SystemVerilog Of byte and bit To define incentive variables . Last , We use the form of port sequence mapping ( So you don't have to write the signal name twice , It's a good feature ) To exemplify DUT.
covergroup modular
use covergroup To capture functional coverage . First define covergroup, Re instantiate and use it to collect
covergroup op_cov;
coverpoint op_set {
bins single_cycle[] = {[add_op : xor_op], rst_op,no_op};
bins multi_cycle = {mul_op};
bins opn_rst[] = ([add_op:mul_op] => rst_op);
bins rst_opn[] = (rst_op => [add_op:mul_op]);
bins sngl_mul[] = ([add_op:xor_op],no_op => mul_op);
bins mul_sngl[] = (mul_op => [add_op:xor_op], no_op);
bins twoops[] = ([add_op:mul_op] [* 2]);
bins manymult = (mul_op [* 3:5]);
}
endgroup
covergroup zeros_or_ones_on_ops;
all_ops : coverpoint op_set {
ignore_bins null_ops = {rst_op, no_op};}
a_leg: coverpoint A {
bins zeros = {'h00};
bins others= {['h01:'hFE]};
bins ones = {'hFF};
}
b_leg: coverpoint B {
bins zeros = {'h00};
bins others= {['h01:'hFE]};
bins ones = {'hFF};
}op_cov This covergroup To ensure that we cover all instructions and possible combinations between these instructions .zeros_or_ones_on_ops This covergroup Used to check whether we use all... On all instructions 0 And all 1 Operands are tested .
After defining these covergroup after , We need to Statement , Exemplification and collection :
initial begin : coverage
oc = new();
c_00_FF = new();
forever begin @(negedge clk);
oc.sample();
c_00_FF.sample();
end
end : coverageThis is a very simple coverage model . We check on the falling edge of each clock TinyALU Input and record instructions and data . To achieve complete coverage, we need to use constrained random excitation .
tester modular
You can write a direct test case for each coverage target to verify , For small DUT It is feasible. . A more efficient way is to use random incentives , And it is a random excitation with constraints . Use here get_op( ) and get_data( ) Two functions to realize random excitation with constraints :
initial begin : tester
reset_n = 1'b0;
@(negedge clk);
@(negedge clk);
reset_n = 1'b1;
start = 1'b0;
repeat (1000) begin
@(negedge clk);
op_set = get_op();
A = get_data();
B = get_data();
start = 1'b1;
case (op_set) // handle the start signal
no_op: begin
@(posedge clk);
start = 1'b0;
end
rst_op: begin
reset_n = 1'b0;
start = 1'b0;
@(negedge clk);
reset_n = 1'b1;
end
default: begin
wait(done);
start = 1'b0;
end
endcase // case (op_set)
end
$stop;
end : testerThis cycle is TinyALU Generated 1000 individual transaction. Each time we cycle from get_op() Get random instructions in , from get_data( ) Get random operands in , Then drive them to TinyALU, And executed start Signal protocol . These two functions ensure that we get legal instructions and valid data .
scoreboard Cycle self-test
Scoreboard Recycle the expected results to check TinyALU Result . The cycle will monitor done The signal , whenever done Signal up ,scoreboard according to TinyALU The input of predicts the result , And check whether it is correct .
always @(posedge done) begin : scoreboard
shortint predicted_result;
#1;
case (op_set)
add_op: predicted_result = A + B;
and_op: predicted_result = A & B;
xor_op: predicted_result = A ^ B;
mul_op: predicted_result = A * B;
endcase // case (op_set)
if ((op_set != no_op) && (op_set != rst_op))
if (predicted_result != result)
$error ("FAILED: A: %0h B: %0h op: %s result: %0h",
A, B, op_set.name(), result);
end : scoreboard
Simple verification platform
It has been finished by now TinyALU Verification platform , Delivery function coverage , Check whether all instructions work properly , Little work to generate incentives , With only one module and file .
But this verification platform is not a good example , All the behaviors are mixed together in one file . this
These make this verification platform difficult to reuse . How to improve the verification platform ? The first thing we noticed was scoreboard modular , coverage Module and tester Modules are defined on top of completely different functions , They don't have to be in the same file . After separating them , We can reuse the modules in this verification platform to other verification platforms , It is convenient to modify other Test Other modules in the module , Like motivation .
边栏推荐
- About the loading of layer web spring layer components, the position of the layer is centered
- Linear DP acwing 896 Longest ascending subsequence II
- About wechat enterprise payment to change x509certificate2 read certificate information, publish to the server can not access the solution
- std::vector批量导入快速去重方法
- JSON序列化 与 解析
- Execute any method of any class through reflection
- 线性DP AcWing 896. 最长上升子序列 II
- Does C language srand need to reseed? Should srand be placed in the loop? Pseudo random function Rand
- Linear DP acwing 897 Longest common subsequence
- 2.6 using recursion and stack - [tower of Hanoi problem]
猜你喜欢

js5day(事件监听,函数赋值给变量,回调函数,环境对象this,全选反选案例,tab栏案例)

spfa AcWing 852. SPFA judgement negative ring
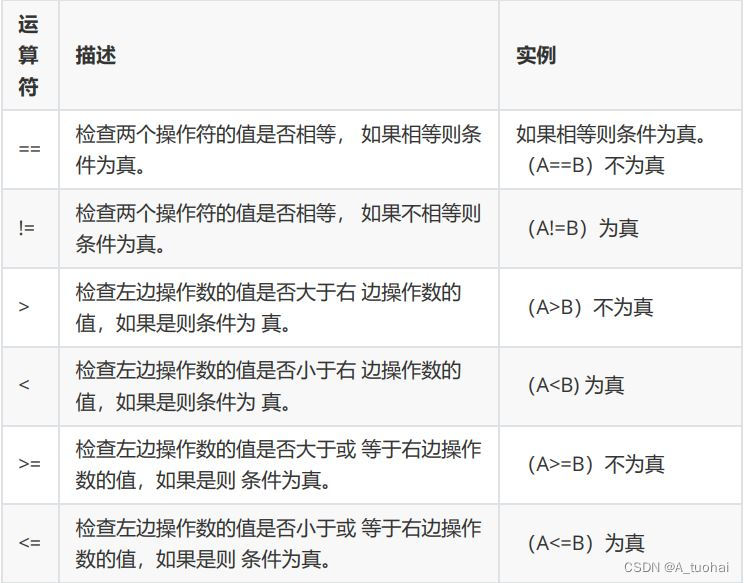
C operator

JS7day(事件对象,事件流,事件捕获和冒泡,阻止事件流动,事件委托,学生信息表案例)
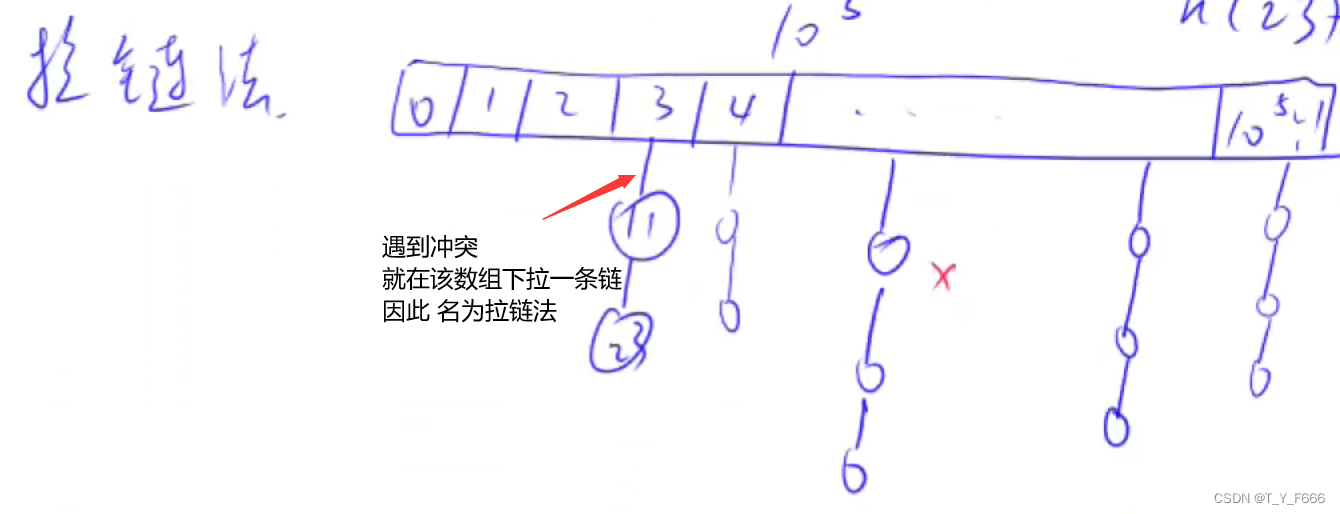
哈希表 AcWing 840. 模拟散列表

Js3day (array operation, JS bubble sort, function, debug window, scope and scope chain, anonymous function, object, Math object)
![[ybtoj advanced training guidance] cross the river [BFS]](/img/4e/83f14452ea6410768cdd01e725af2e.jpg)
[ybtoj advanced training guidance] cross the river [BFS]

Js7day (event object, event flow, event capture and bubble, prevent event flow, event delegation, student information table cases)
Get started REPORT | today, talk about the microservice architecture currently used by Tencent

How can attribute mapping of entity classes be without it?
随机推荐
Mongodb redis differences
ASP. Net MVC default configuration, if any, jumps to the corresponding program in the specified area
Interval DP acwing 282 Stone merging
JSON serialization and parsing
8A Synchronous Step-Down regulator tps568230rjer_ Specification information
Linear DP acwing 902 Shortest editing distance
C operator
Browser node event loop
Mui WebView down refresh pull-up load implementation
BOM DOM
哈希表 AcWing 840. 模拟散列表
Hundreds of web page special effects can be used. Don't you come and have a look?
BOM DOM
计数类DP AcWing 900. 整数划分
IPhone 6 plus is listed in Apple's "retro products" list
Redis avalanche, penetration, breakdown
线性DP AcWing 899. 编辑距离
C#运算符
Counter attack of flour dregs: MySQL 66 questions, 20000 words + 50 pictures in detail! A little six
Bom Dom